Vector-finite-element parallel solving simulation method based on LabVIEW and FPGA
A finite element and vector technology, applied in the field of vector finite element parallel solution simulation, can solve problems such as limited flexibility, high cost, and high energy consumption, and achieve the effect of improving speed and programming efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
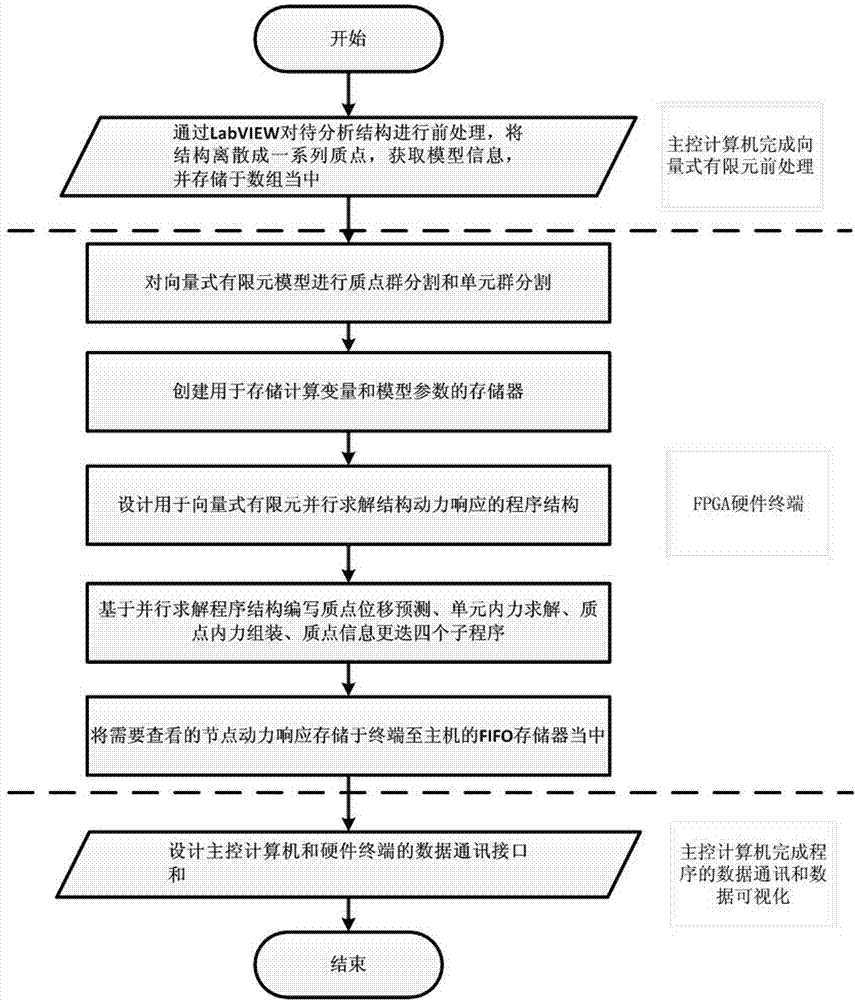
[0036]Describe the specific embodiment of the present invention in detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and example, wherein figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the implementation process of the embodiment of the present invention, and its implementation steps are as follows:
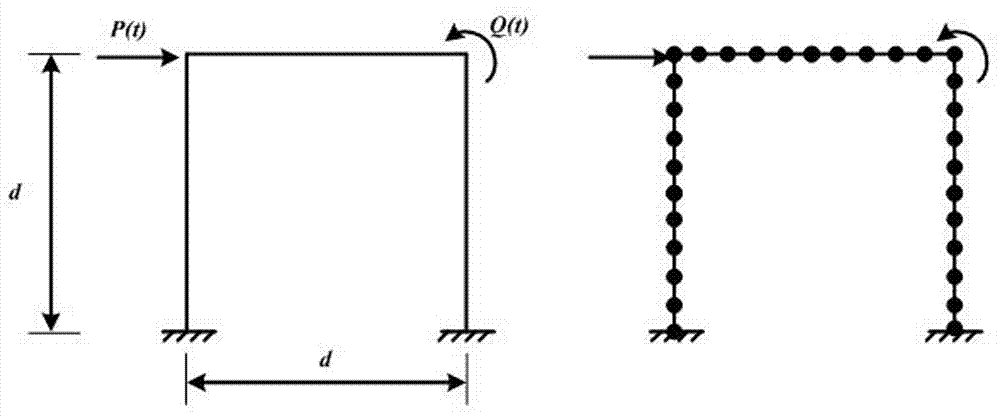
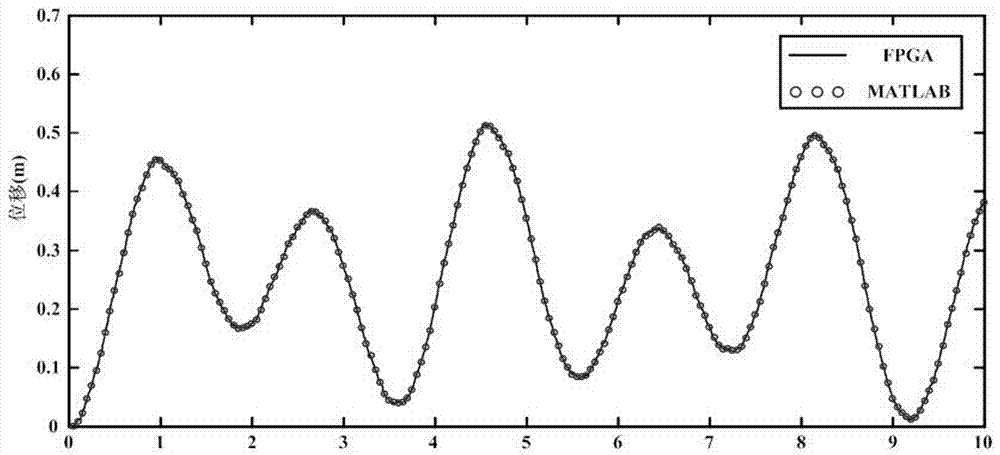
[0037] In this embodiment, the plane beam element in the vector finite element is used to calculate the rigid angle at the left end of the plane rigid frame under the concentrated load P(t)=200N horizontally to the right and the cosine periodic bending moment load Q(t) acting on the rigid angle at the right end. )=500cos(2t)N·m, the large deformation dynamic response. For detailed dimensions of the model, see figure 2 , where the cross-sectional area of the beam A=0.25m 2 , the second moment of section I=5.2×10 -3 m 4 , Young's modulus E=1×10 6 N / m 2 , mass density ρ v =50kg / m 3 , the beam length d=4m; the cross-sectional area of the column A=0.125m 2 , the second moment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com