Acceleration measurement method and device based on atomic interference in optical waveguide
A technology of acceleration measurement and optical waveguide, which is applied in the direction of acceleration measurement using inertial force, which can solve the problems of complex structure, large well depth, and large accumulated error for a long time, so as to improve the measurement sensitivity, the system structure is simple, and the measurement reduction is achieved. effect of error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
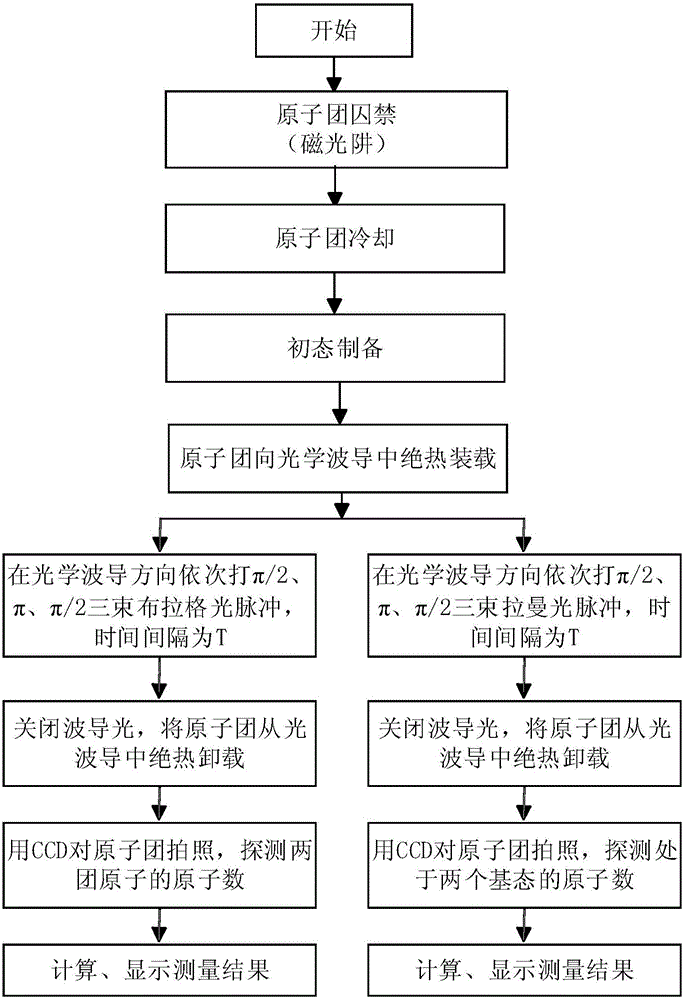
[0035] S1. Preparation of cold atomic groups.
[0036] Firstly, it is necessary to carry out pre-cooling (to obtain cold atomic groups with a temperature of about 20μk) through classical magneto-optic traps (MOT for short) and Polarization Gradient Cooling (PGC for short), and then the The temperature of the atomic group is further reduced (50nK-10μk) by means of evaporative cooling, optical lattice cooling or sideband cooling.
[0037] S2. Preparation of the initial state and loading of the optical waveguide.
[0038] Prepare the atomic group in a magnetically insensitive state|F=1,m F =0>, then open the optical waveguide, and pack the atomic groups into the optical waveguide. Wherein, preferably, the direction of the optical waveguide is horizontal, forming an included angle of 90 degrees with the direction of gravity.
[0039] S3, atomic interference.
[0040] Two beams of Raman light or Bragg light respectively apply three beams of light pulses of π / 2, π and π / 2 to the...
Embodiment 1
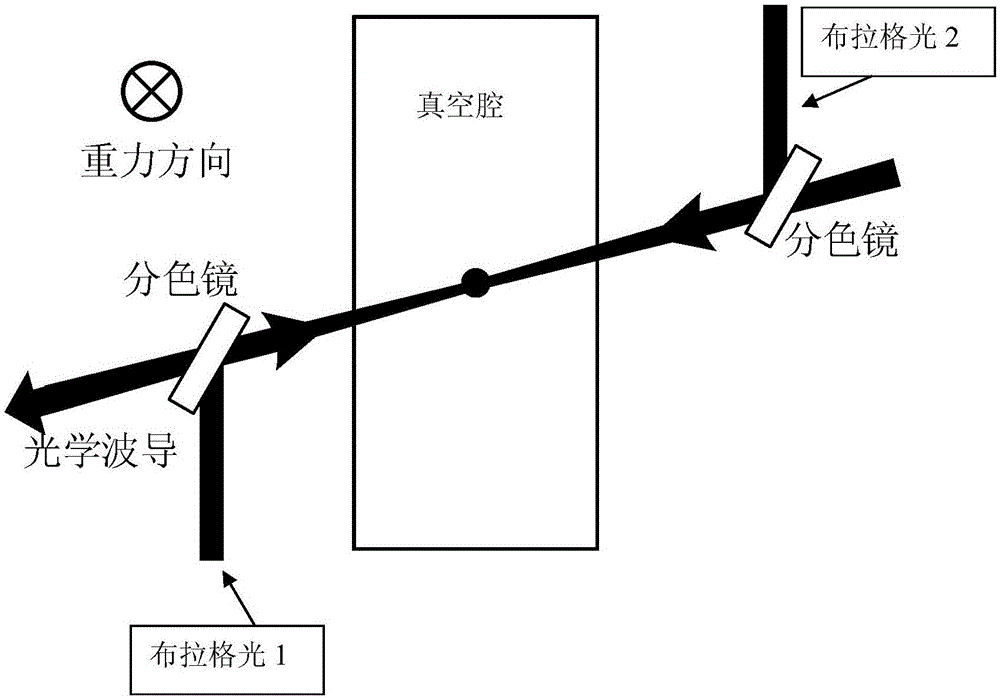
[0045] Embodiment 1: as figure 2 As shown, the acceleration measurement device based on atomic interference in the optical waveguide of the present invention includes:
[0046] Vacuum cavities for lasers that create optical waveguides;
[0047] Two phase-locked Bragg lights, the frequency difference of the two Bragg lights is several KHz;
[0048] Optical waveguide, the direction of the optical waveguide is any horizontal direction, and the optical waveguide is equipped with atomic groups; the atomic group is a group of cooled atomic groups (temperature is 50nK ~ 10μk), which is in a magnetically insensitive state after state preparation|F=1, m F =0>.
[0049] Preferably, in a preferred embodiment, the potential well depth of the optical waveguide should be greater than the temperature of the atomic groups, so that the atomic groups can exist in the optical waveguide for a longer time without escaping from the waveguide.
[0050] In a specific application example, three o...
Embodiment 2
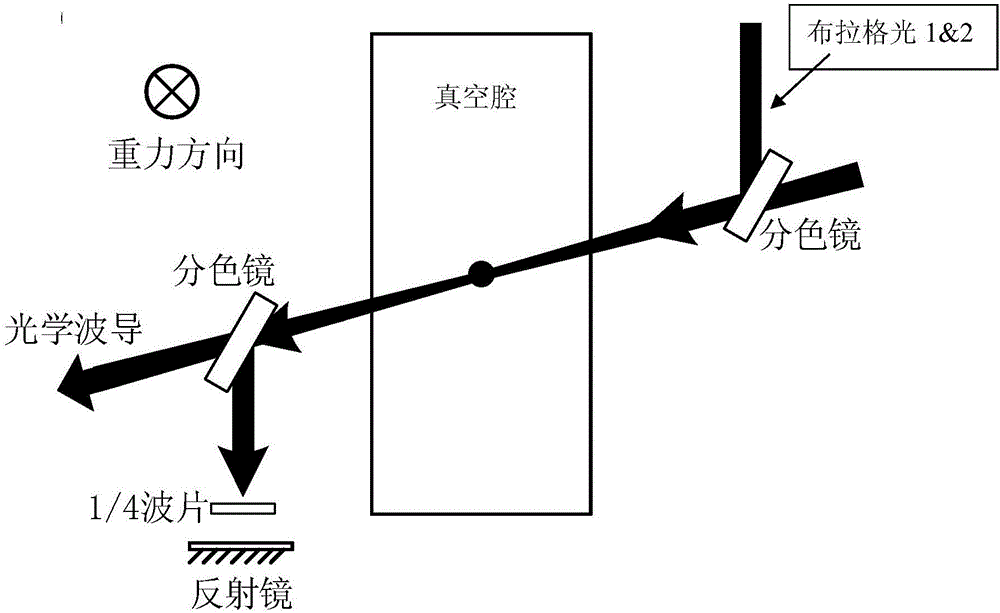
[0051] Embodiment 2: as image 3 As shown, the acceleration measurement device based on atomic interference in the optical waveguide of the present invention includes:
[0052] Vacuum cavities for lasers that create optical waveguides;
[0053] Two phase-locked Bragg lights, the frequency difference of the two Bragg lights is several KHz.
[0054] Optical waveguide, the direction of the optical waveguide is any horizontal direction, and the optical waveguide is equipped with atomic groups; the atomic group is a group of cooled atomic groups (temperature 50nK ~ 10μk), which is in a magnetically insensitive state after state preparation|F=1,m F =0>.
[0055] Preferably, in a preferred embodiment, the potential well depth of the optical waveguide should be greater than the temperature of the atomic groups, so that the atomic groups can exist in the optical waveguide for a longer time without escaping from the waveguide.
[0056] In a specific application example, three optical...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com