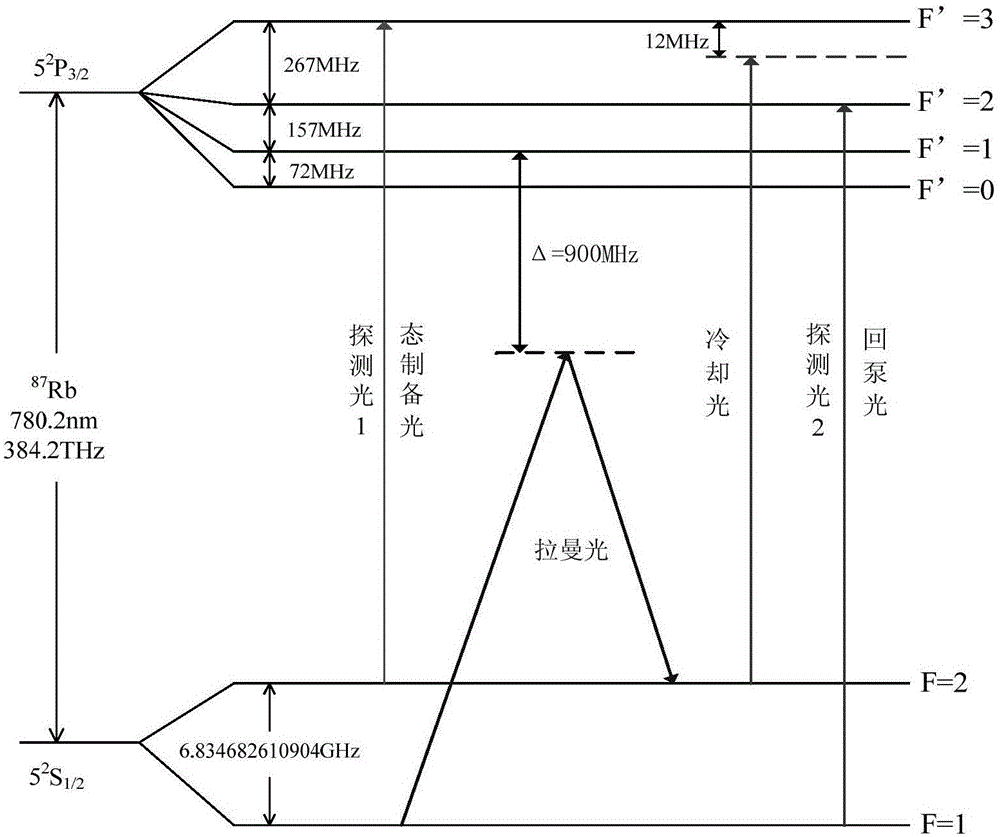
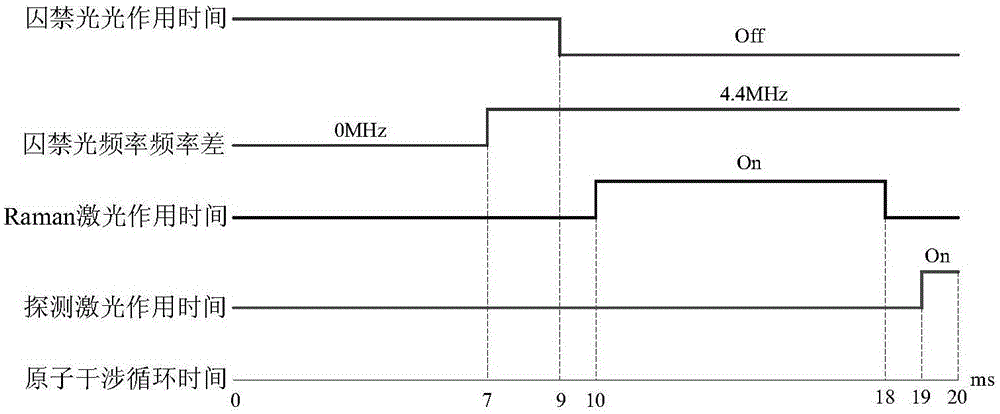
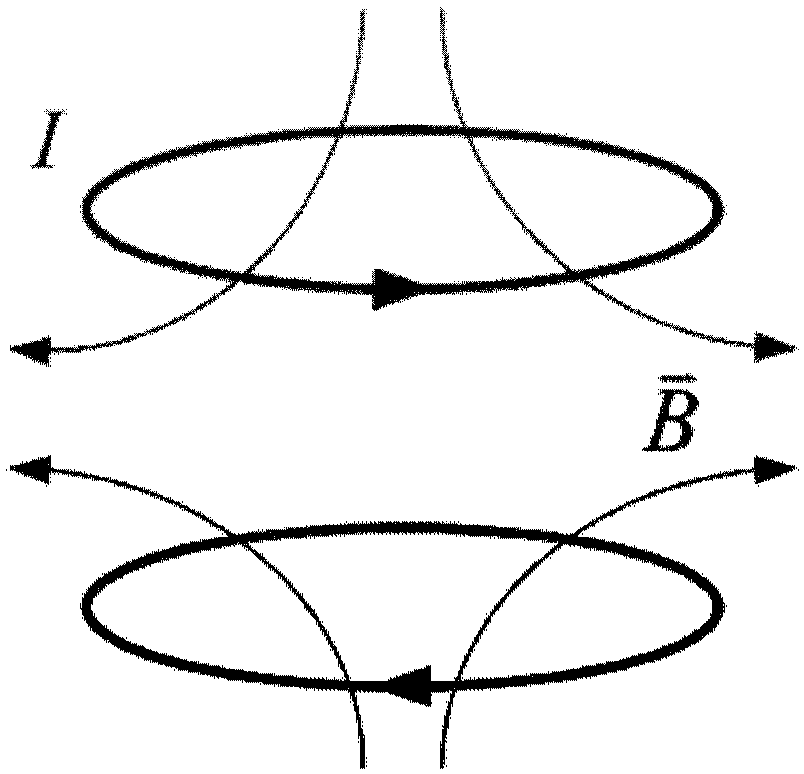
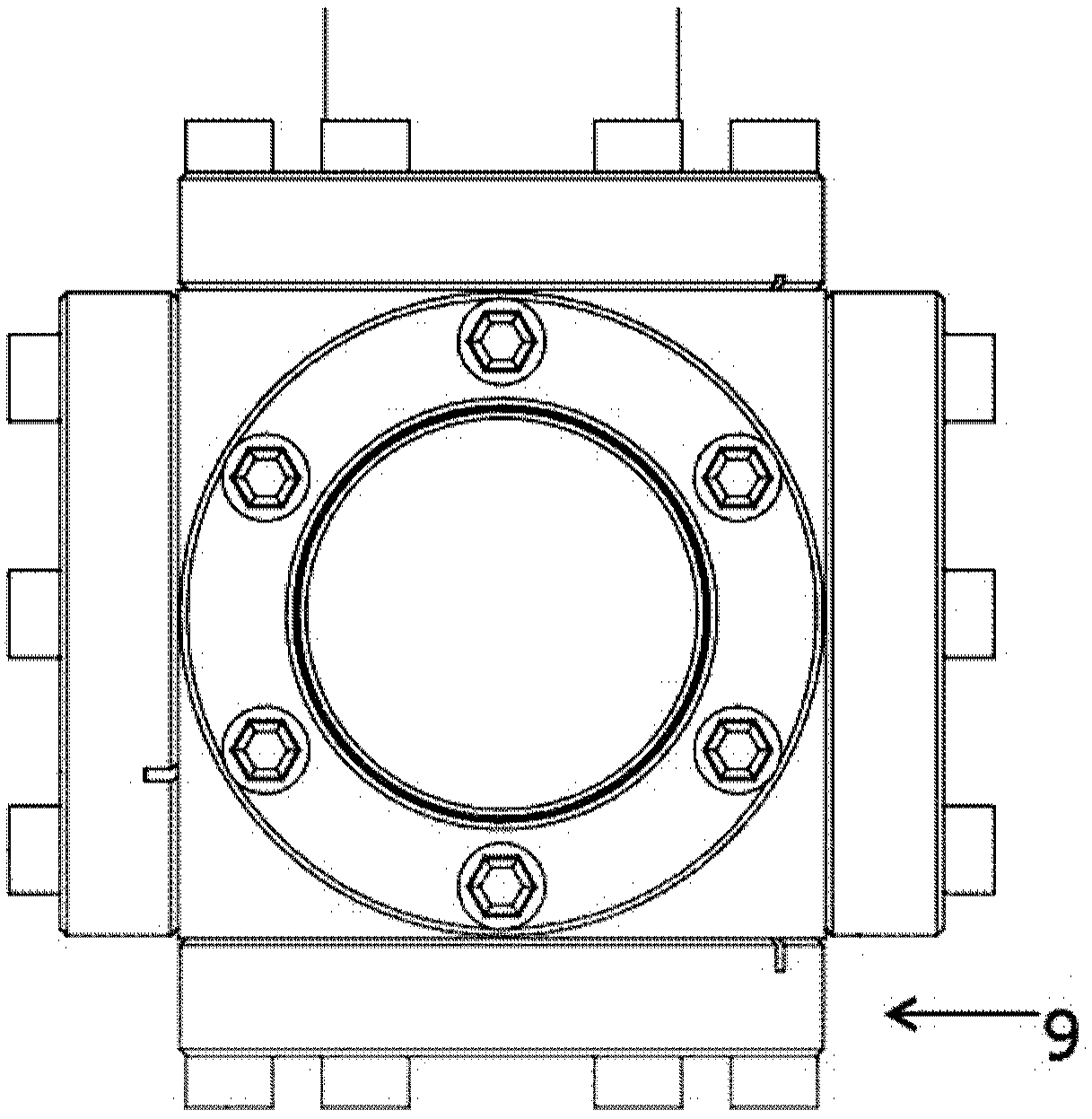
Patents
Literature
117 results about "Atom interferometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
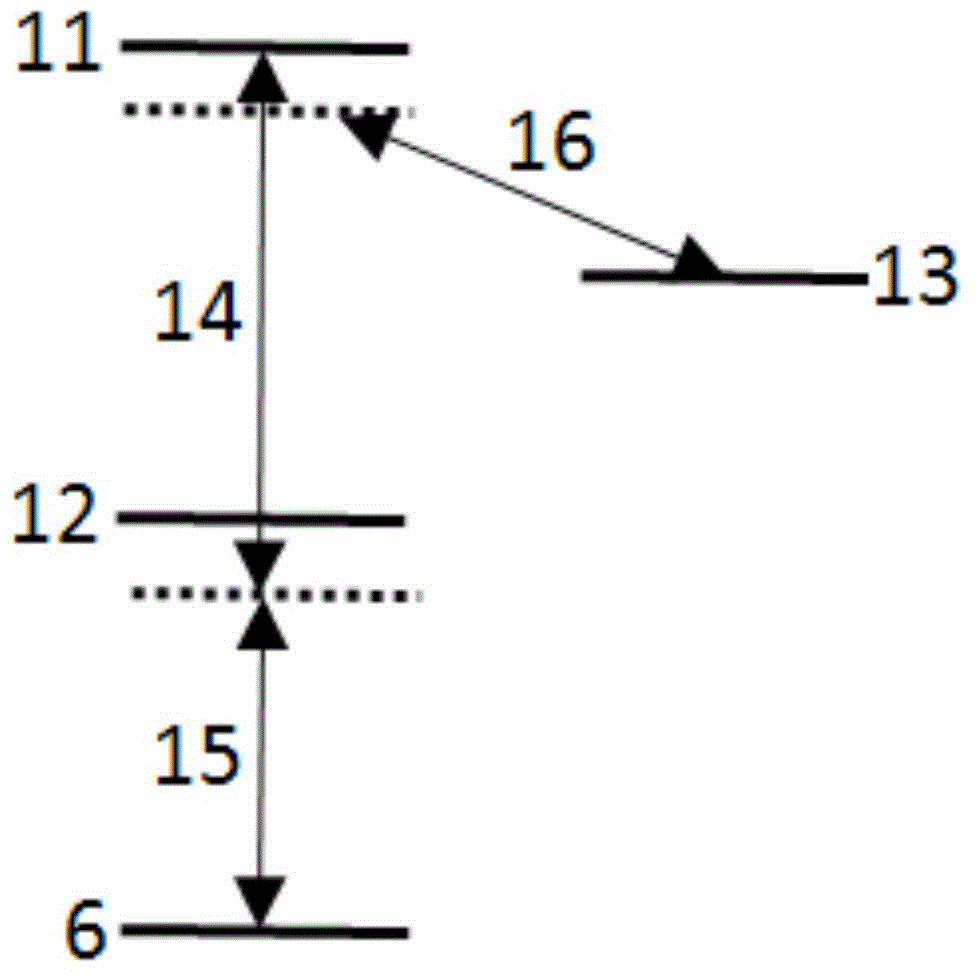
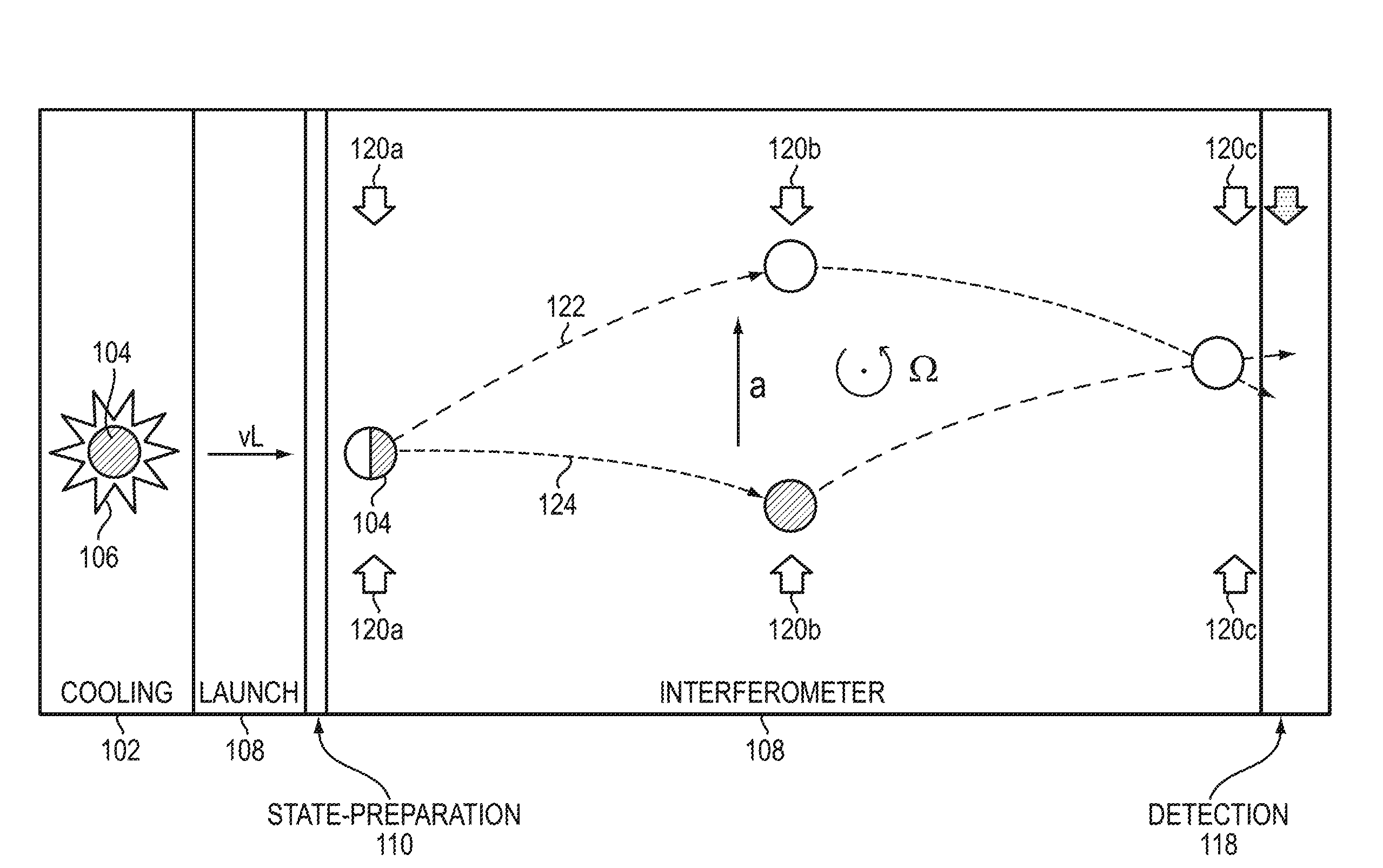
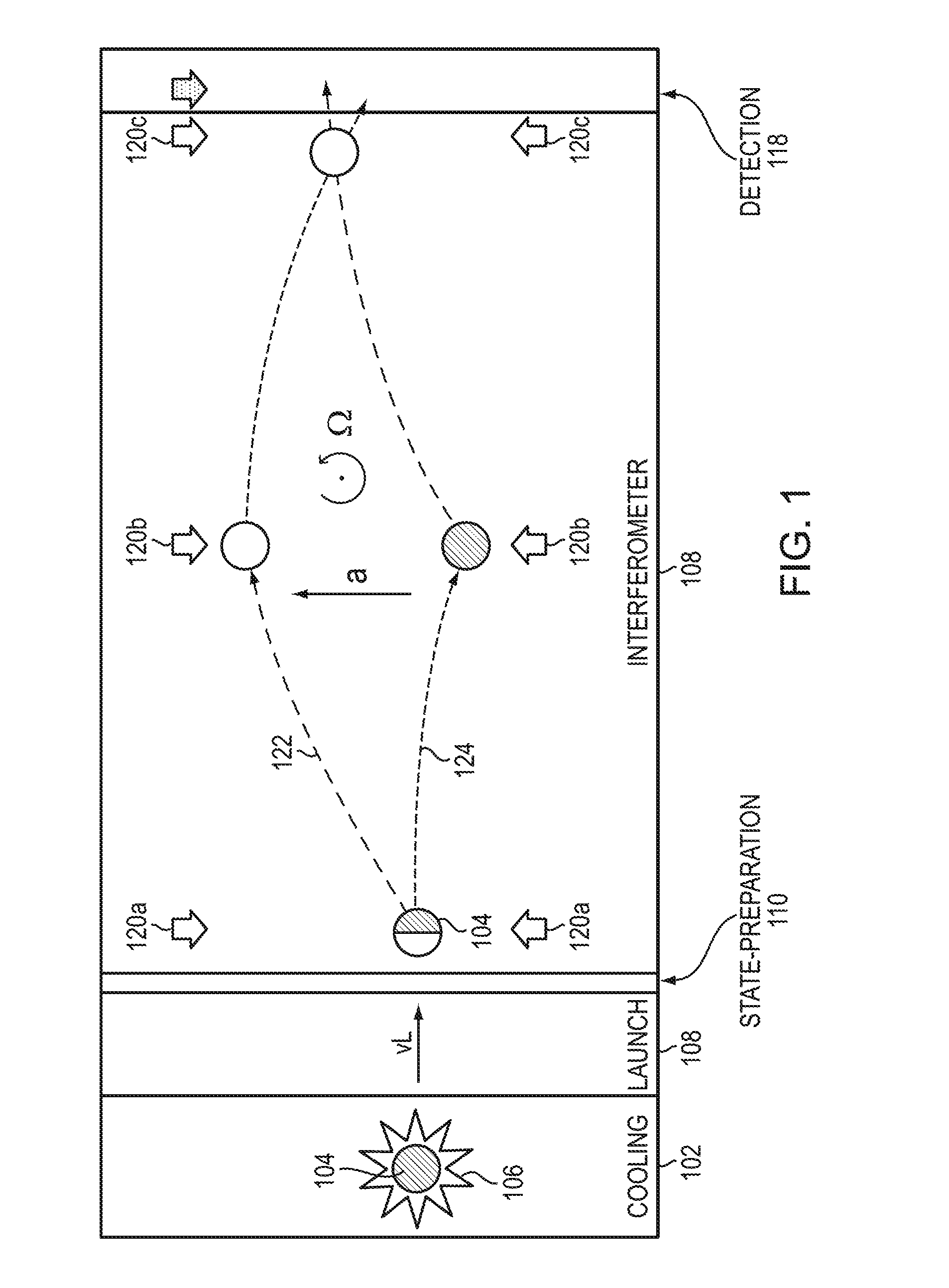
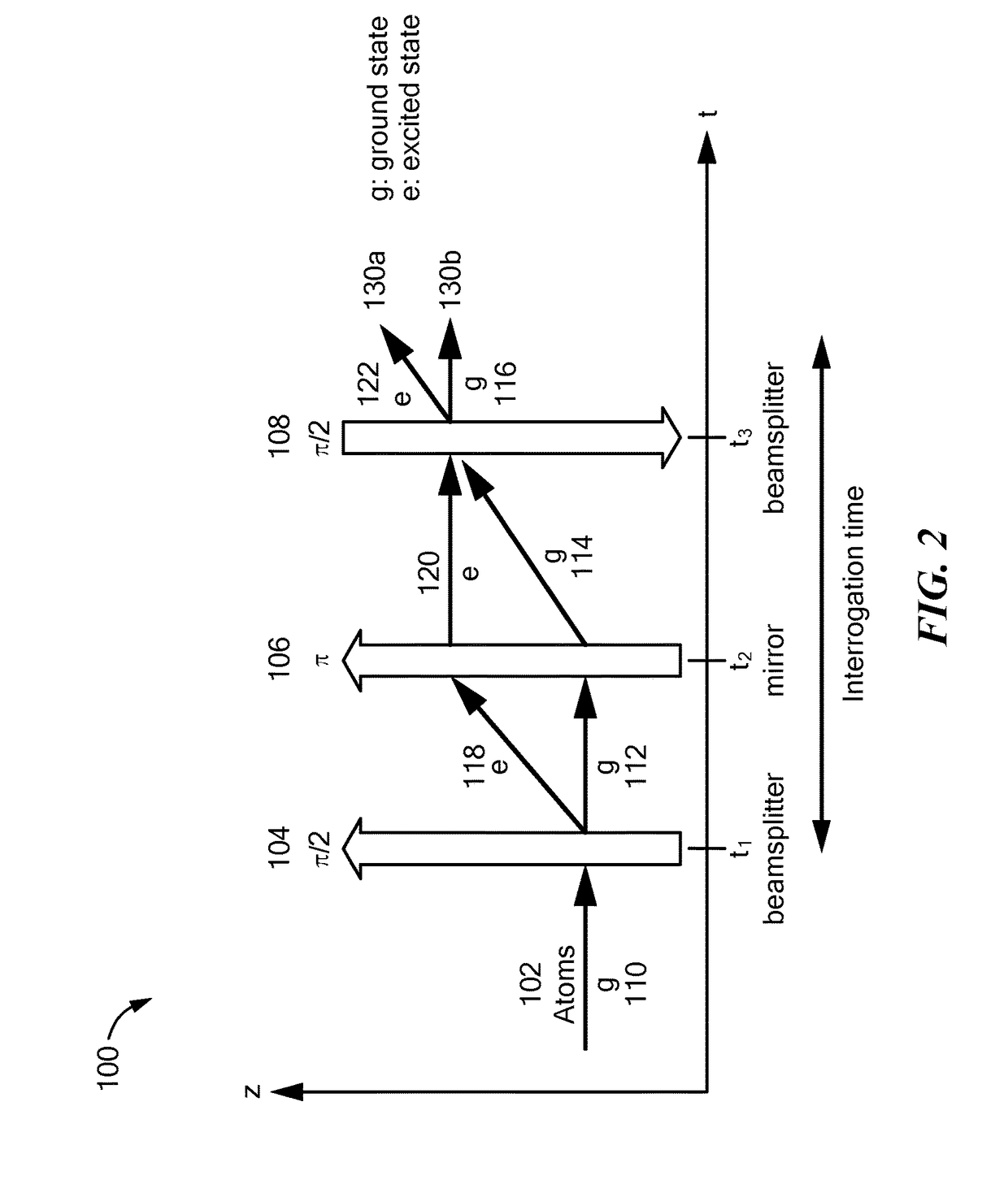
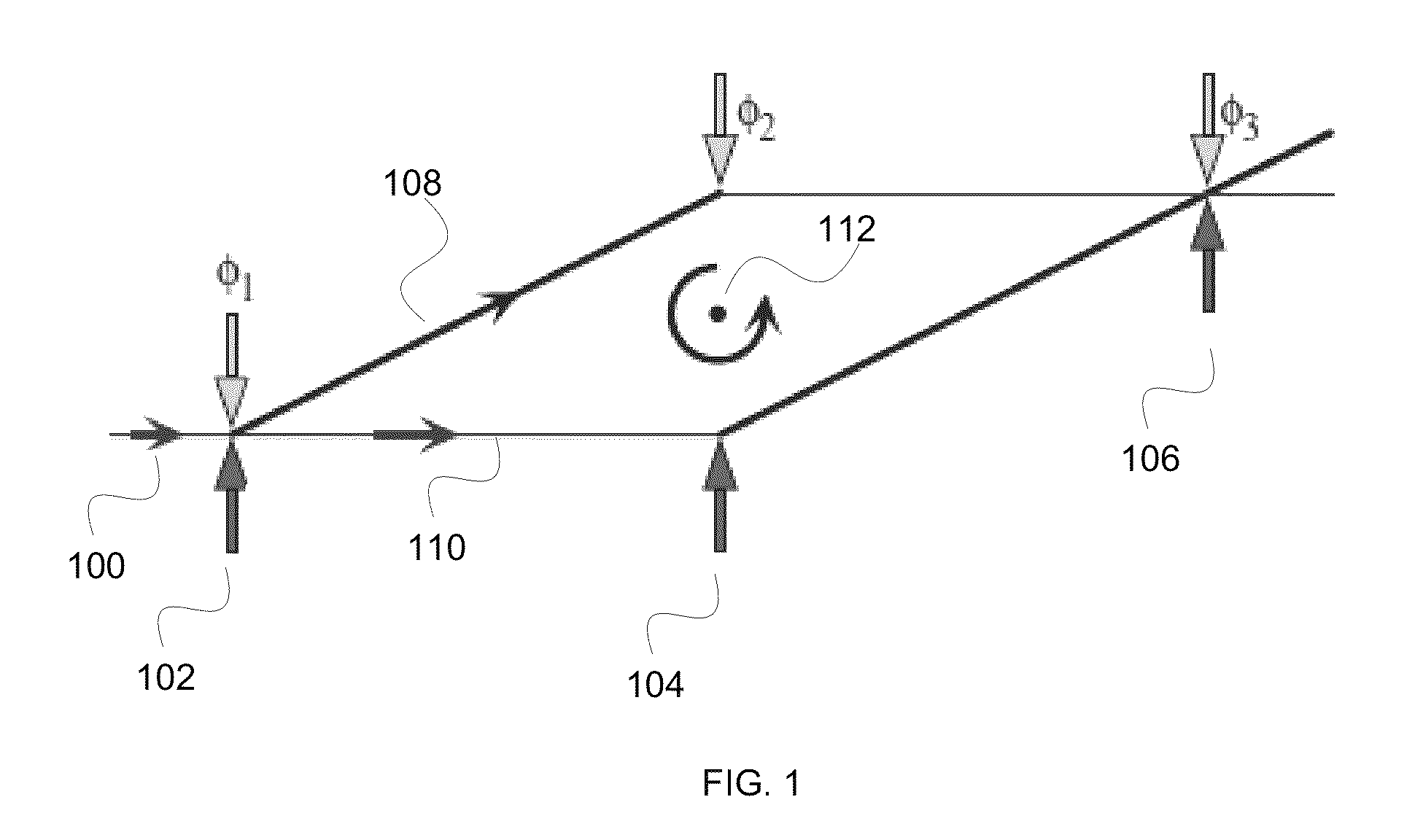
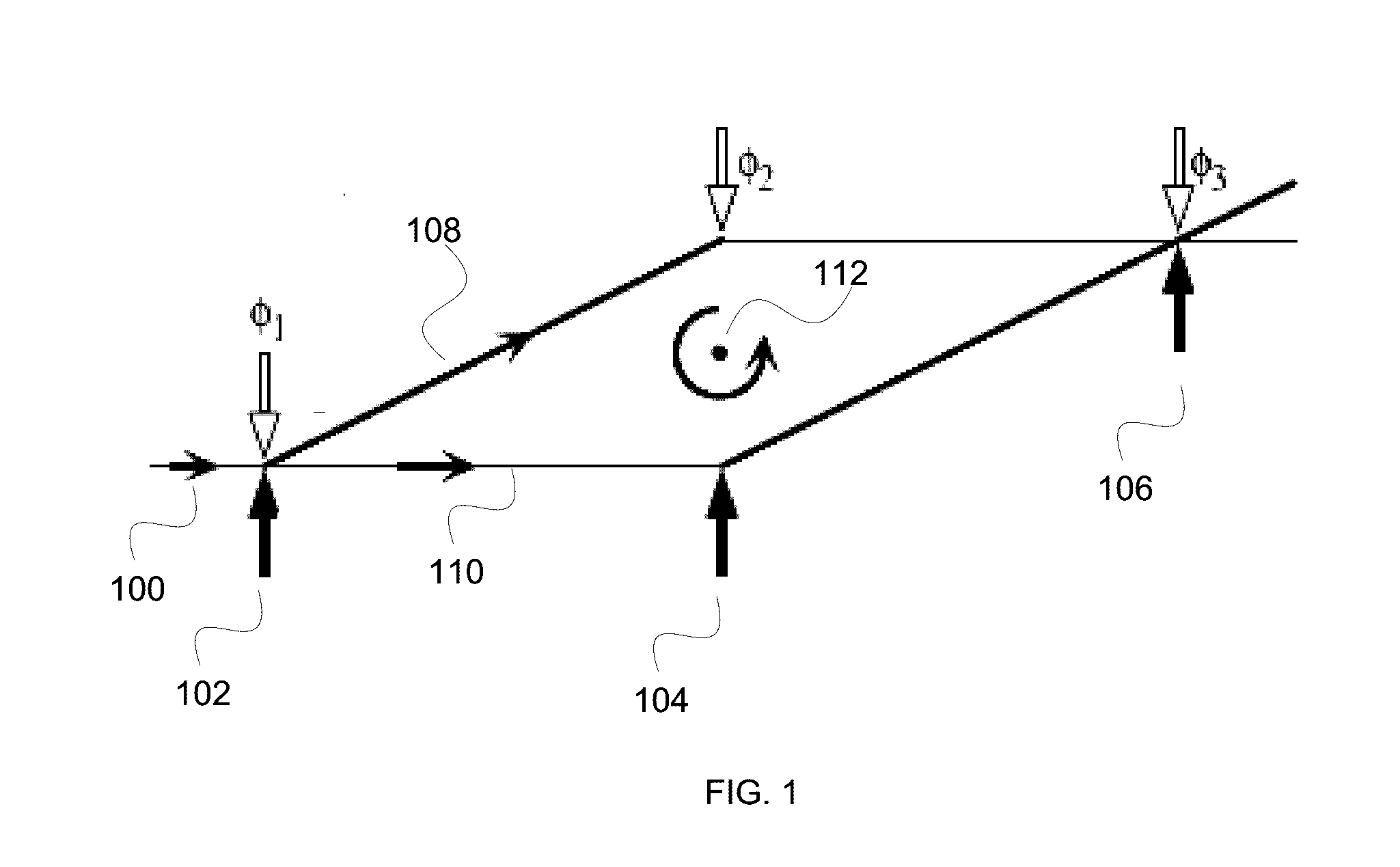
An atom interferometer is an interferometer which uses the wave character of atoms. Similar to optical interferometers, atom interferometers measure the difference in phase between atomic matter waves along different paths. Atom interferometers have many uses in fundamental physics including measurements of the gravitational constant, the fine-structure constant, the universality of free fall, and have been proposed as a method to detect gravitational waves. They also have applied uses as accelerometers, rotation sensors, and gravity gradiometers.
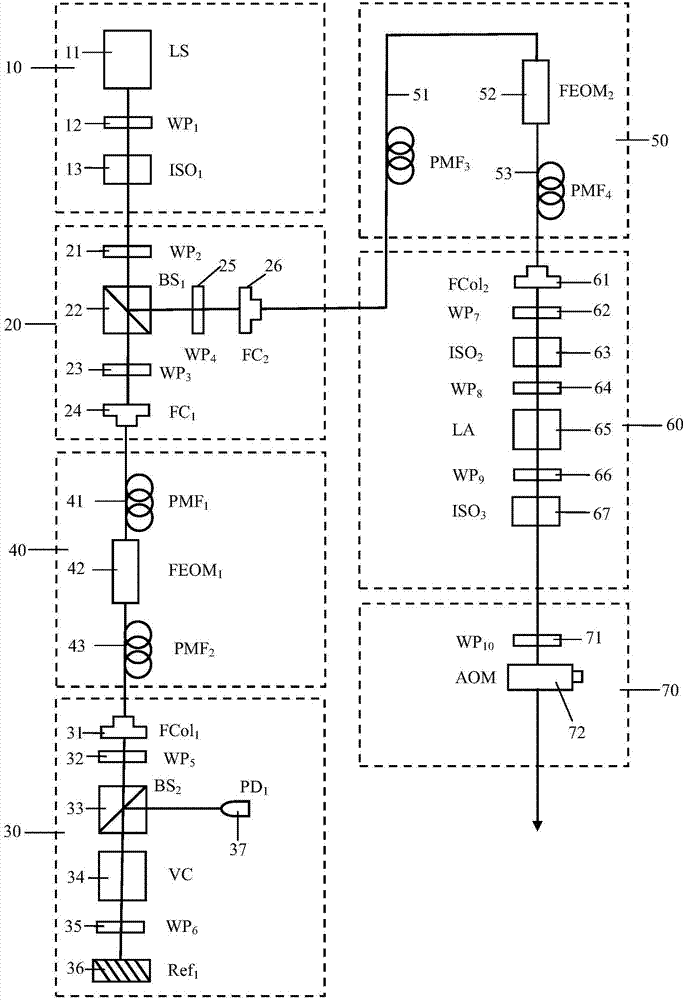
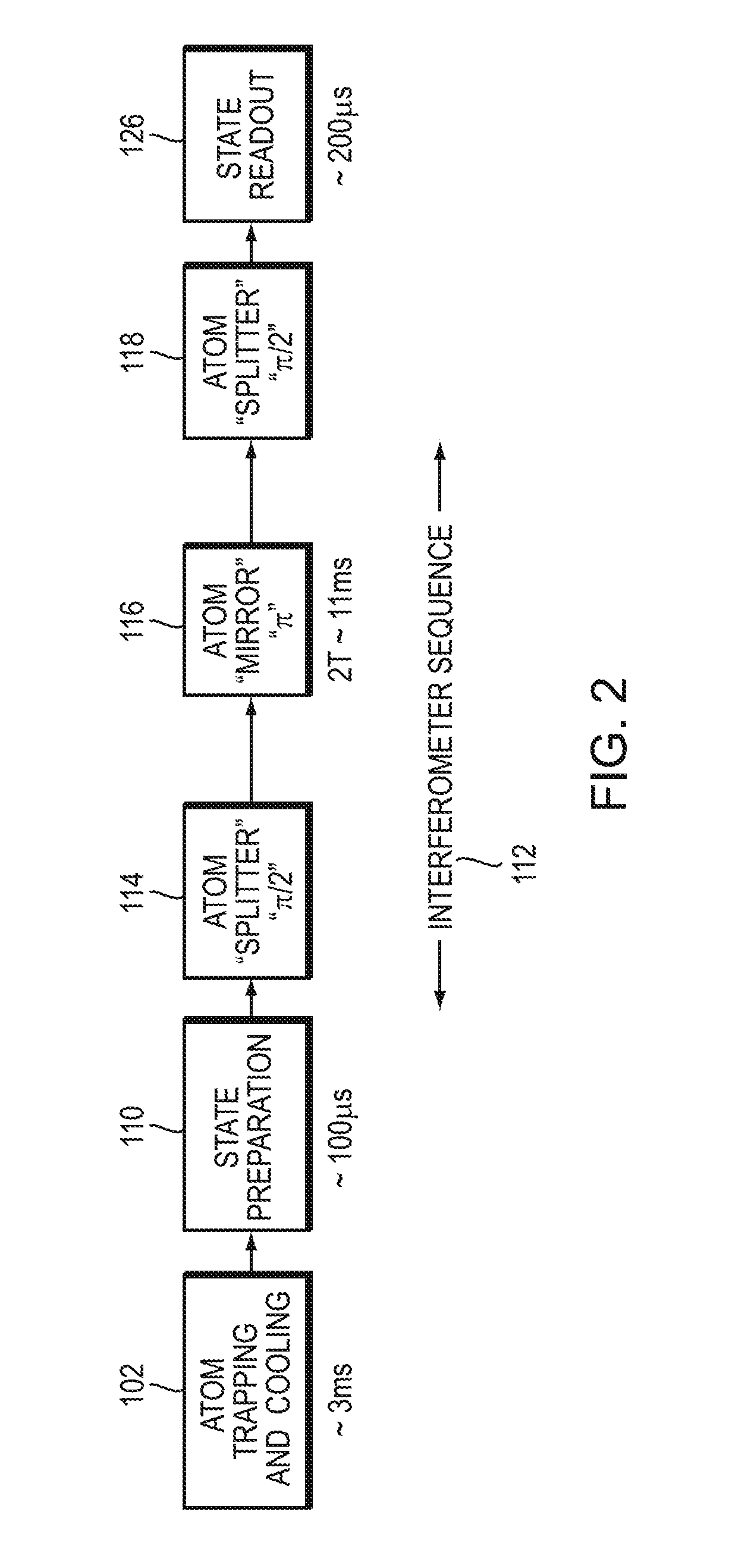
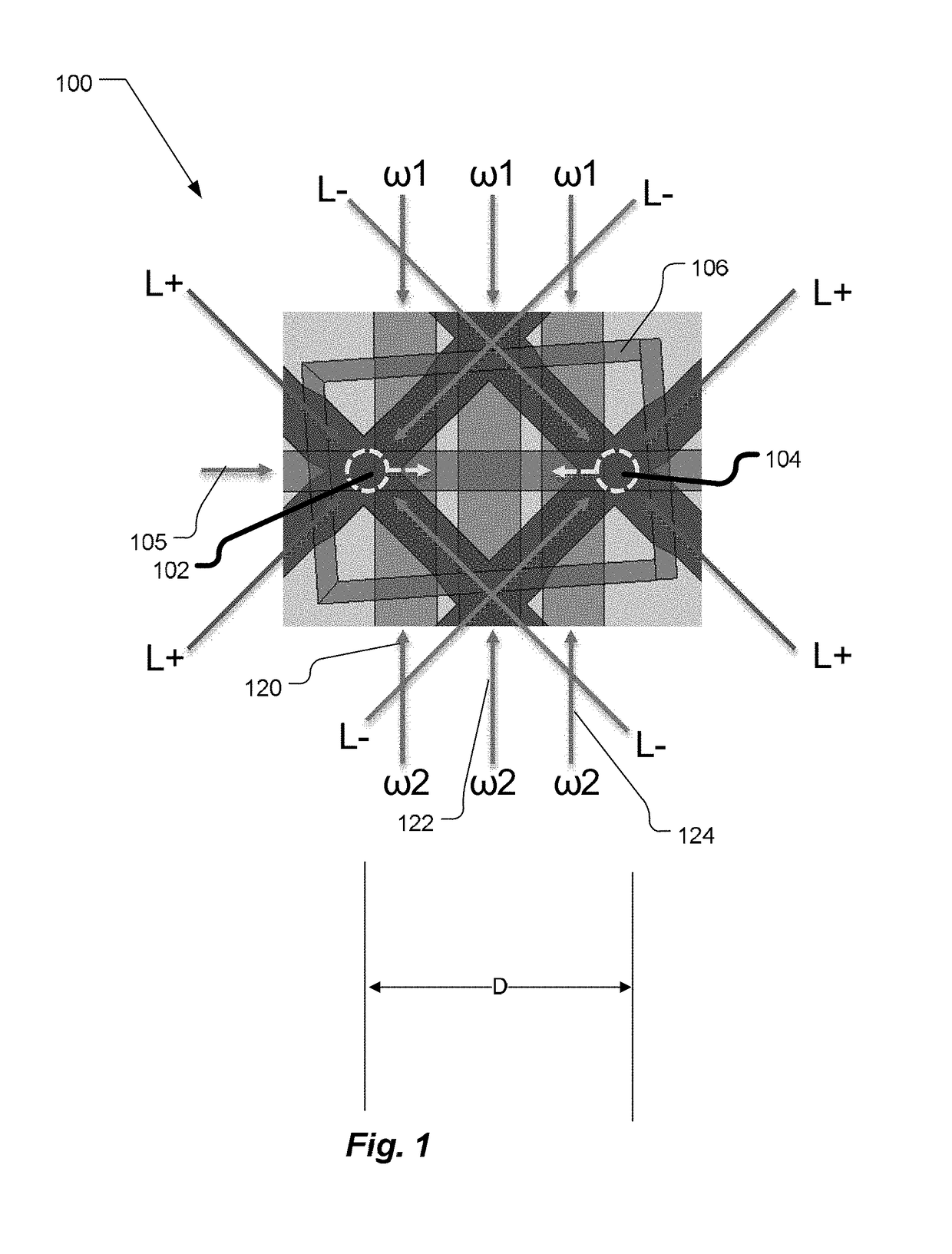
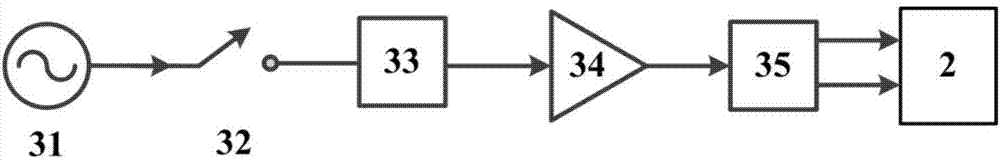
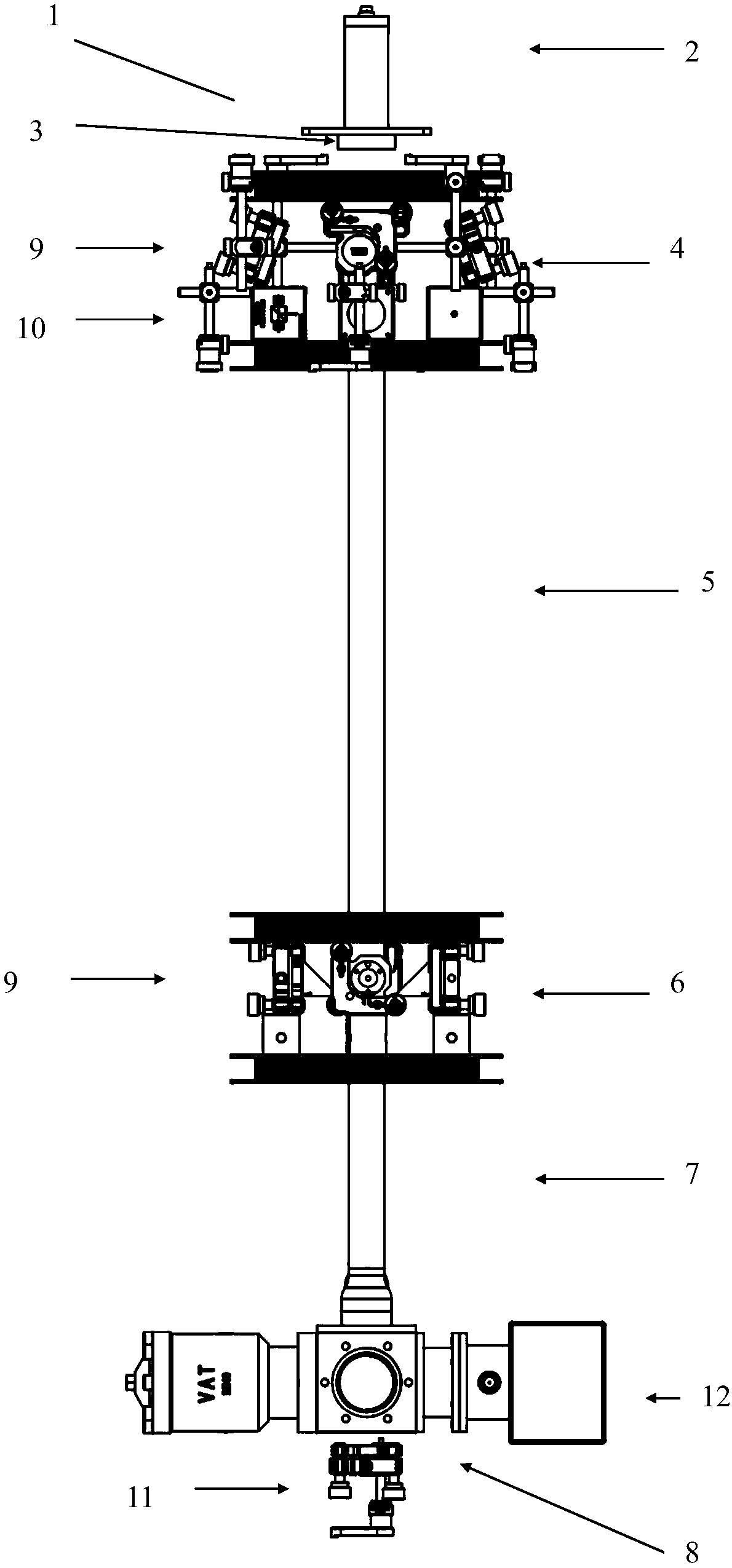
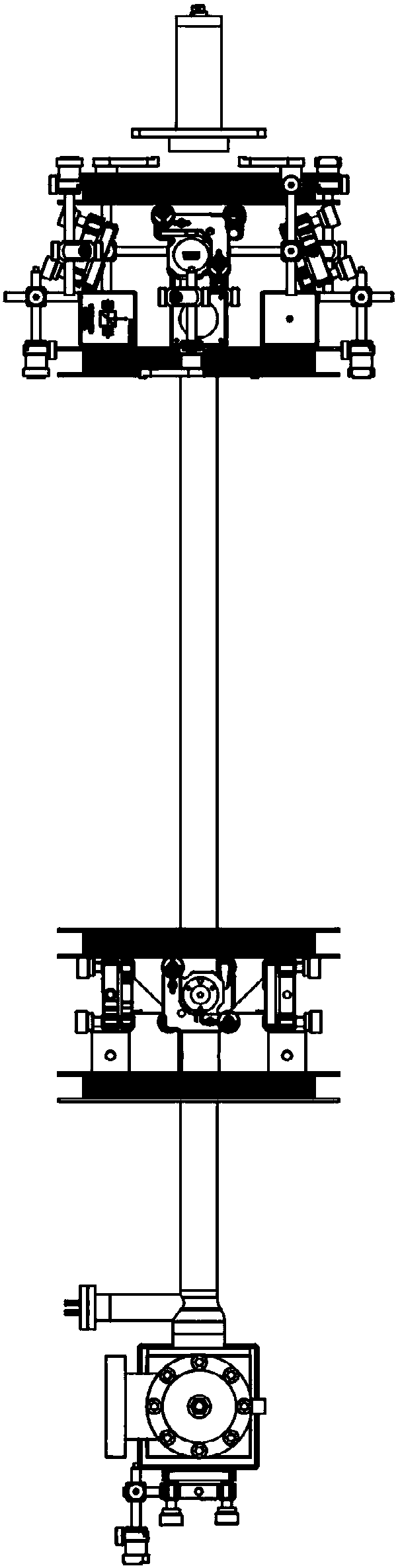
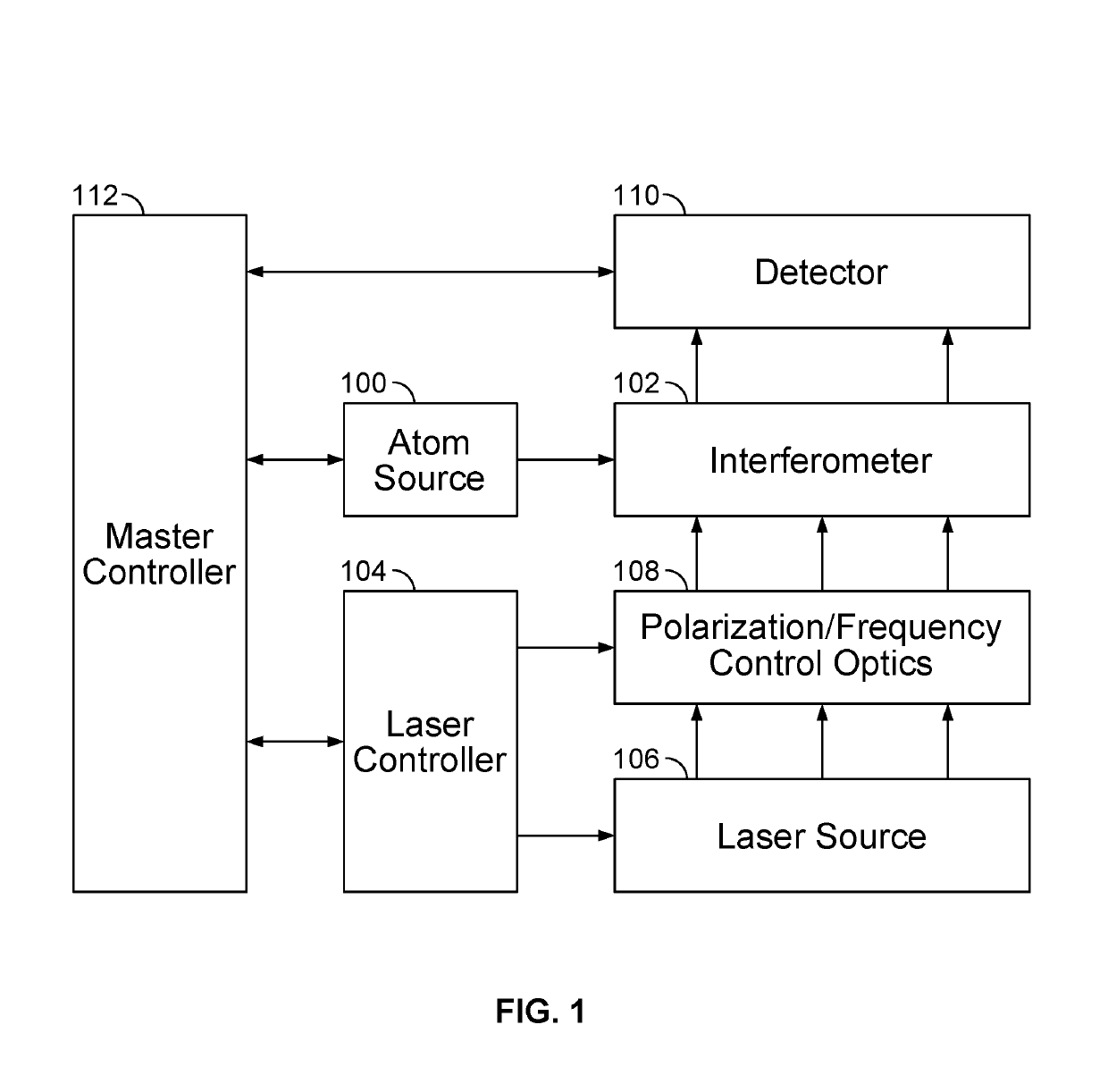
Light-pulse atom interferometric device
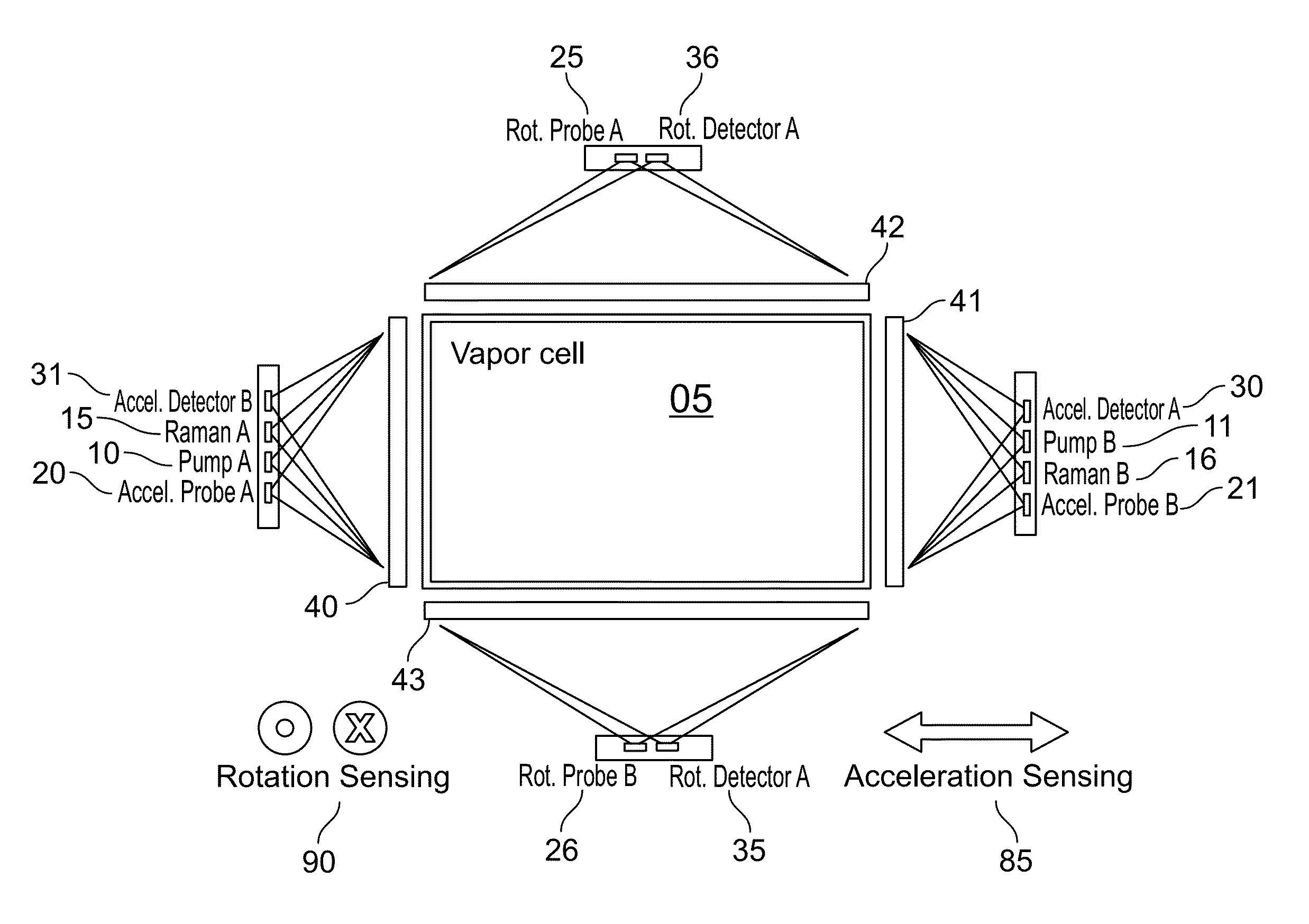
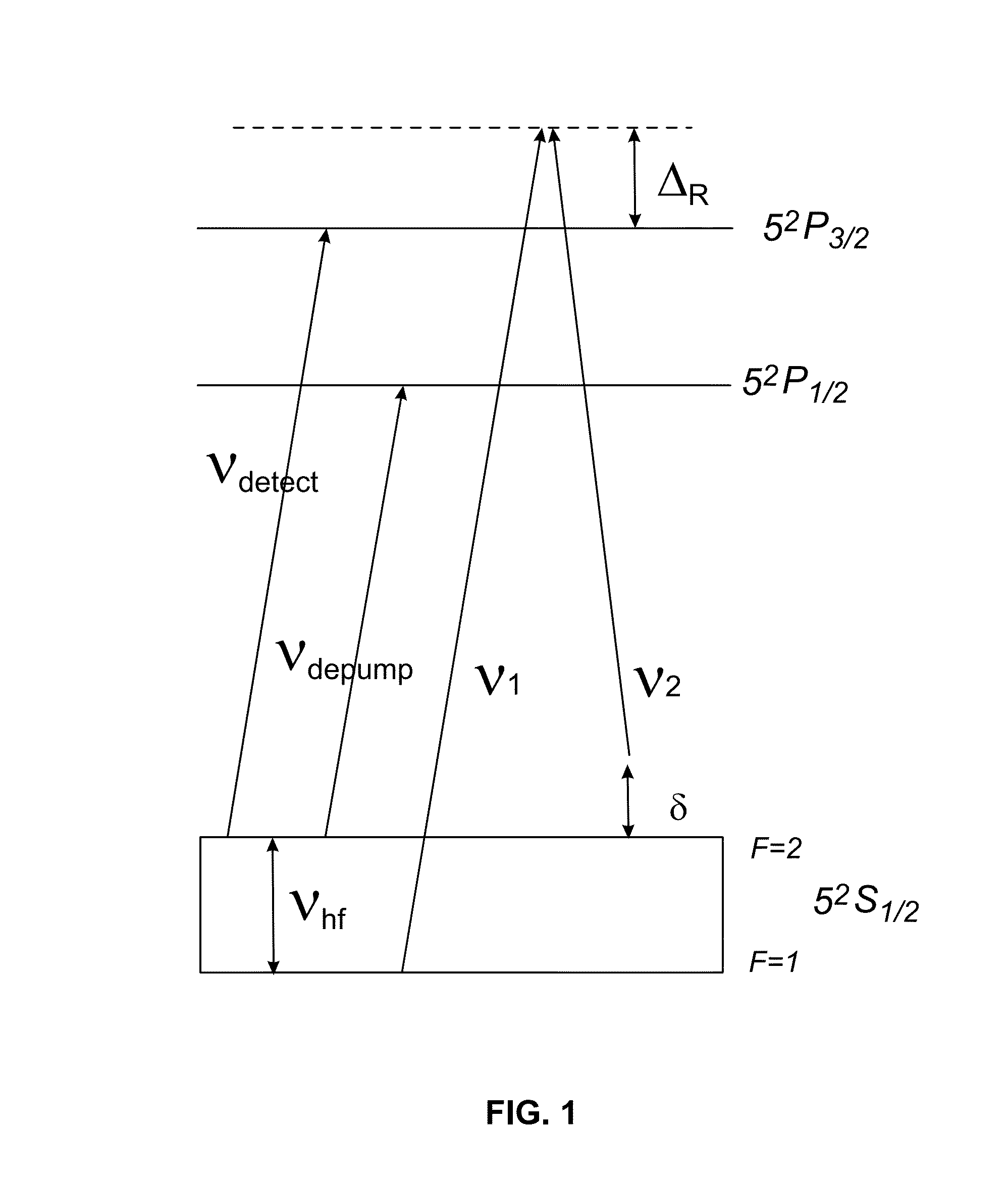
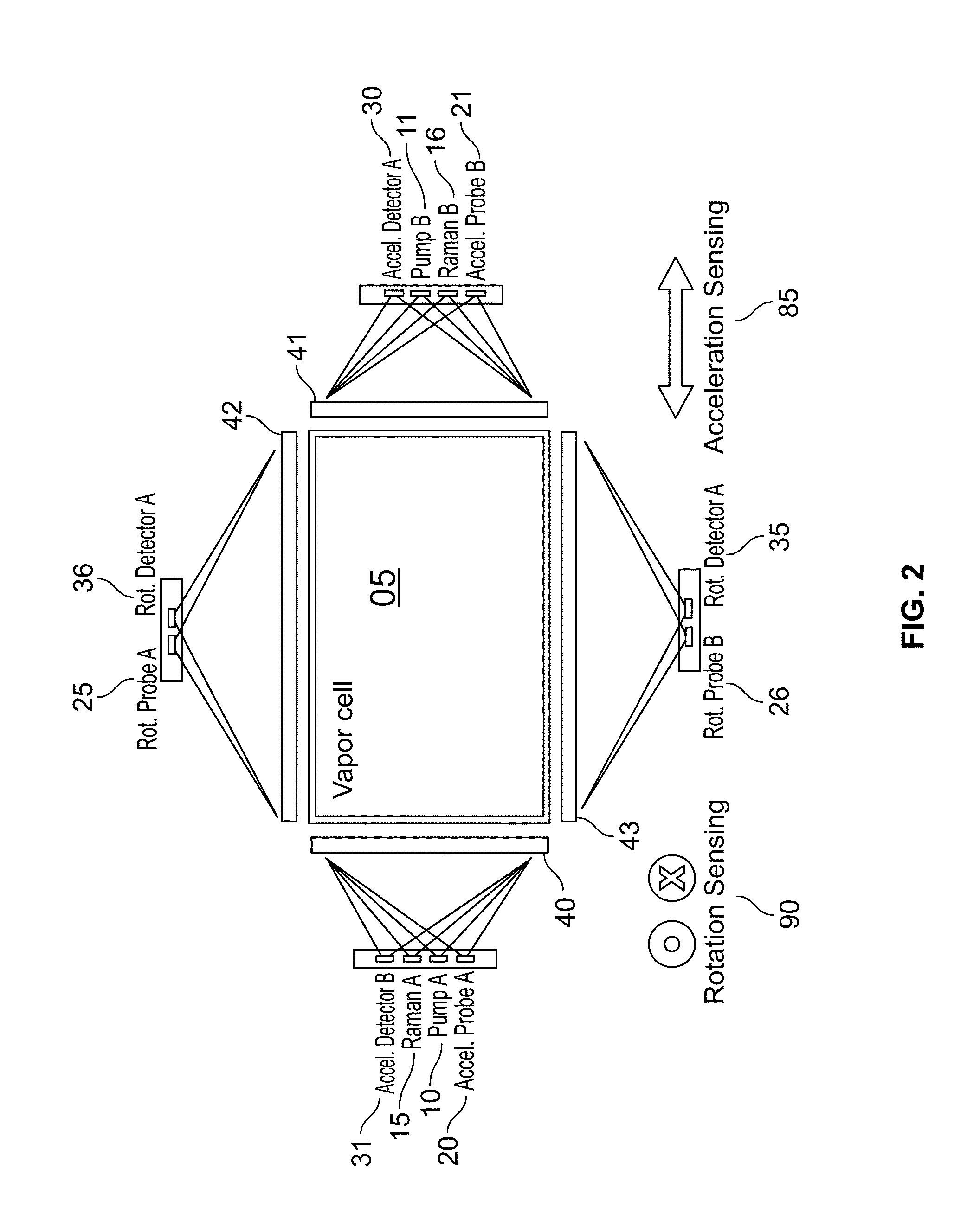
ActiveUS9291508B1Optical measurementsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesChemical speciesOptic system
An atomic interferometric device useful, e.g., for measuring acceleration or rotation is provided. The device comprises at least one vapor cell containing a Raman-active chemical species, an optical system, and at least one detector. The optical system is conformed to implement a Raman pulse interferometer in which Raman transitions are stimulated in a warm vapor of the Raman-active chemical species. The detector is conformed to detect changes in the populations of different internal states of atoms that have been irradiated by the optical system.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Combination inertial sensor based on multi-component atom interferometer and measurement method of combination inertial sensor
ActiveCN103837904ARealize synchronized measurementsHighly integratedAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEarthquake monitoringLaser light
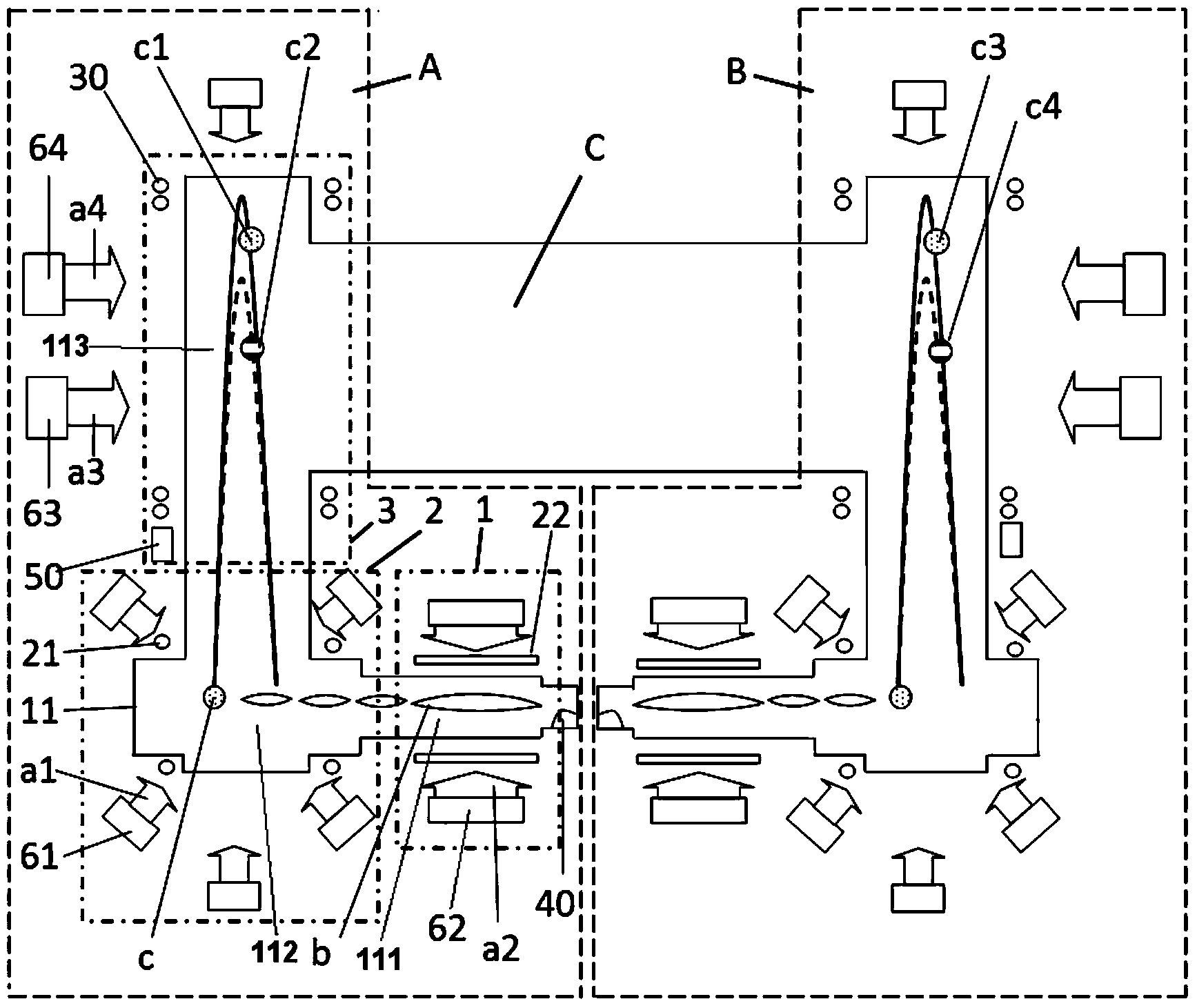
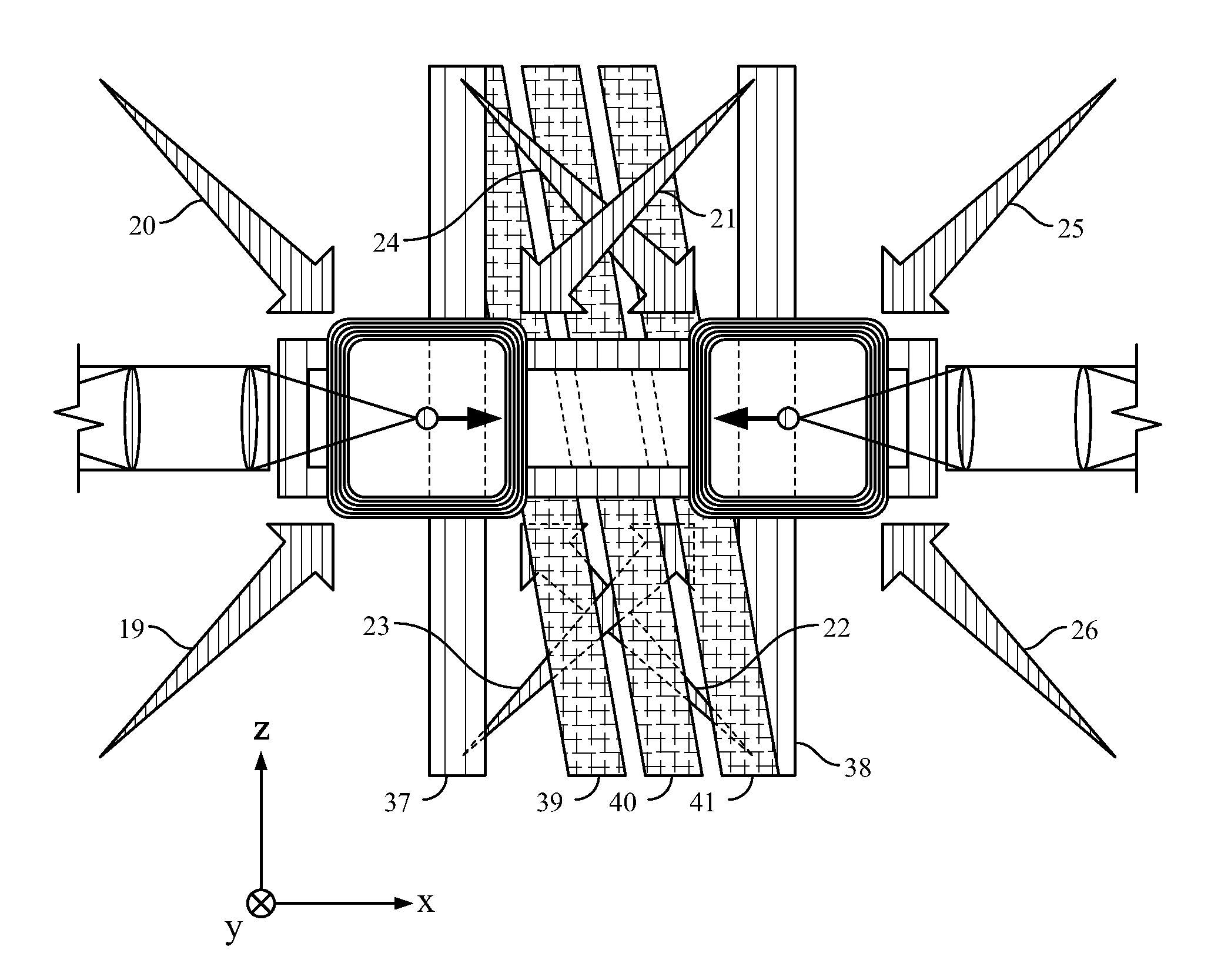
The invention discloses a combination inertial sensor based on a multi-component atom interferometer and a measurement method of the combination inertial sensor, and relates to the technical field of inertial measurement through atom interference. The combination inertial sensor comprises a first inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer, a second inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer and a vacuum communication cavity, wherein the first inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer and the second inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer are the same in structure. The vacuum communication cavity is communicated with an atom interference area of the first inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer and an atom interference area of the second inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer in the horizontal direction. According to the measurement method, multi-frequency laser light is used for simultaneously and independently manipulating two types of alkali metal atoms in the same physical unit, wherein the acceleration and the gravity gradient of one type of alkali metal atoms are measured through a three-pulse pi / 2-pi-pi / 2 Raman laser sequence, and the rotating speed of the other type of alkali metal atoms is measured through a four-pulse pi / 2-pi-pi-pi / 2 Raman laser sequence. Synchronous measurement of a plurality of inertial moments is realized through a simplex physical device at the same time, and the combination inertial sensor based on the multi-component atom interferometer and the measurement method of the combination inertial sensor can play an important role in inertial navigation, resource exploration, earthquake monitoring, physical geographical research and other fields.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Microwave electric field intensity meter based on cold Rydberg atom interferometer and measuring method thereof
ActiveCN104880614AHigh measurement accuracyMake up for the defect that only point frequency measurement can be realizedElectrostatic field measurementsRydberg atomBeam splitting
The invention discloses a microwave electric field intensity meter based on a cold Rydberg atom interferometer and a measuring method thereof. The microwave electric field intensity meter comprises: a vacuum system, which is used for cooling and trapping atom to generate a cold atom cloud for preparing a Rydberg state and generating an interference effect so as to generate a phase difference by coherent atomic states; a laser, which is used for generating coupling light and detection light and exciting the cold atom in the vacuum system from a ground state to the Rydberg state coherently; a photoelectric detector, which is used for detecting an interference fringe generated by two beams of cold atom clouds due to coherence; and a microwave source, which is used for generating a microwave electric field. According to the invention, when the microwave electric field intensity meter is applied to the evolution process of coherent beam splitting and combination, the atom cloud in the Rydberg state interacts with a to-be-measured microwave electric field, thereby generating an alternating-current stark effect; and the to-be-measured microwave electric field intensity is associated with a phase generated by the an alternating-current stark, thereby realizing precise measurement of the microwave electric field.
Owner:清远市天之衡量子科技有限公司
Phase extraction between coupled atom interferometers using ellipse-specific fitting
InactiveUS20050027489A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsPhase shiftedEllipse
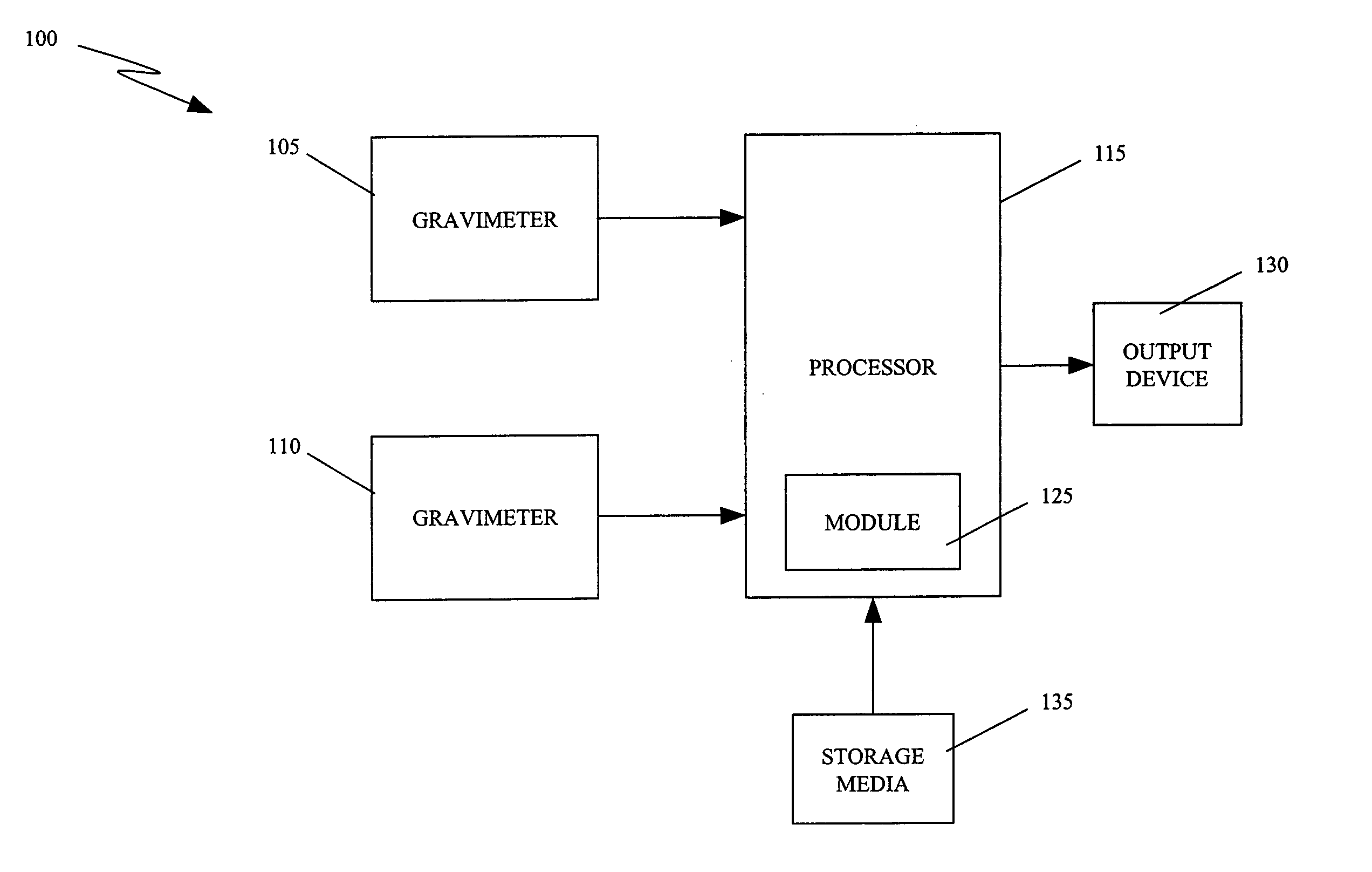
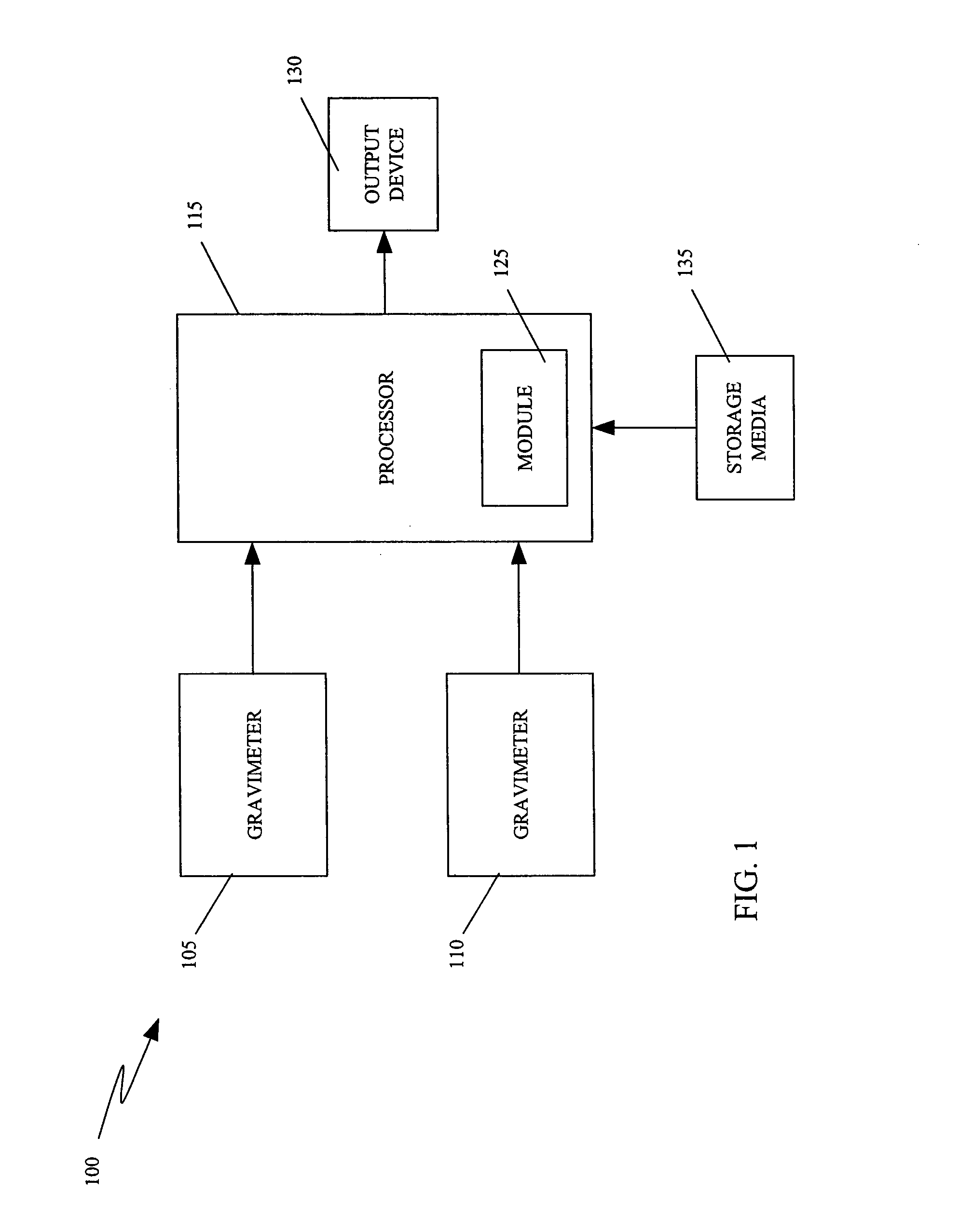
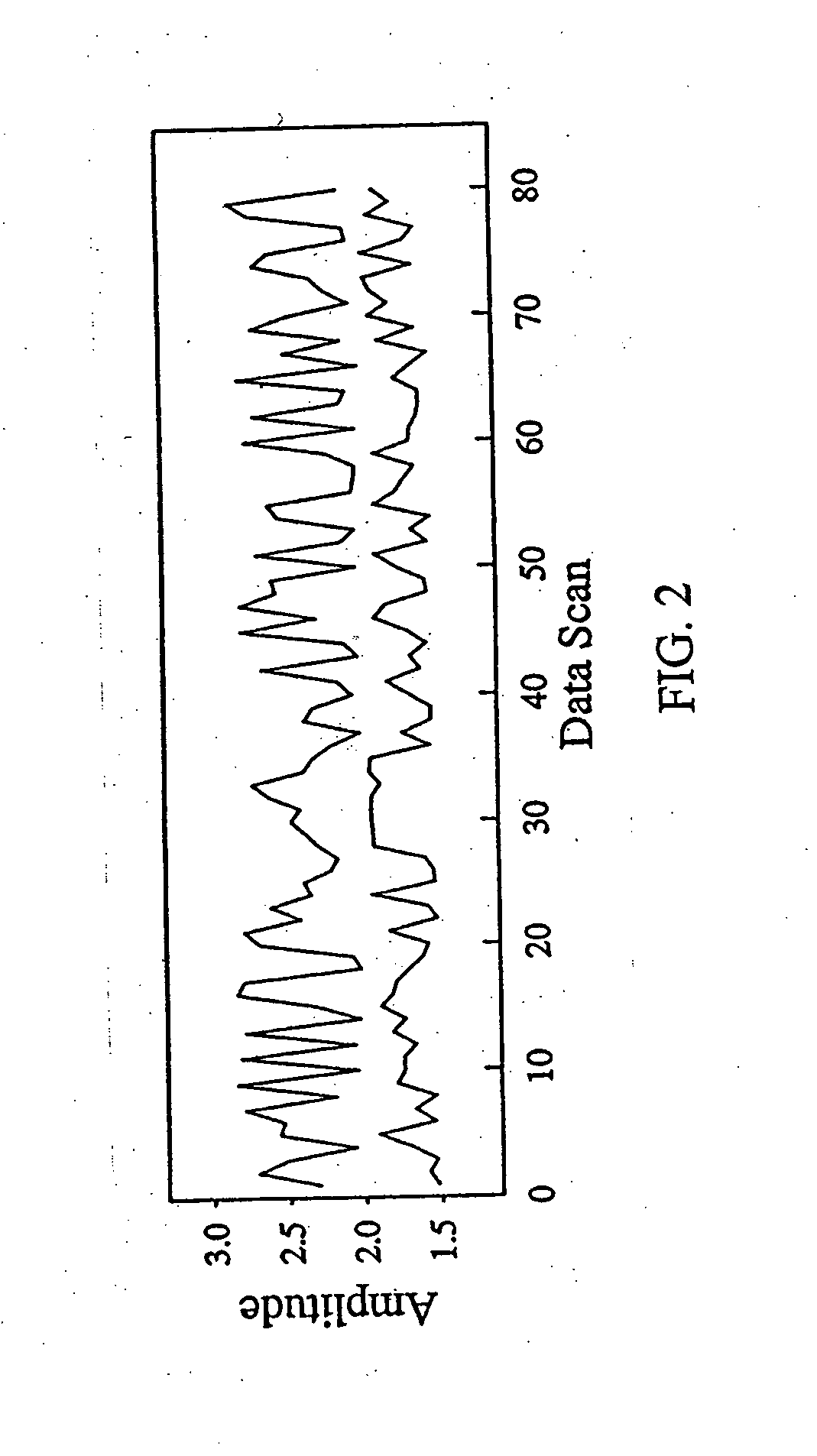
There is provided a method for phase extraction between coupled atom interferometers using ellipse-specific fitting. The method includes fitting an ellipse to data representing a first gravimeter measurement and a second gravimeter measurement, and determining a phase shift between the first gravimeter measurement and the second gravimeter measurement based on a spread of the data around the ellipse.
Owner:YALE UNIV
High data rate atom interferometric device
ActiveUS9086429B1High sensitivityHigh bias stabilityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMagnetic field gradientMagneto-optical trap
A light-pulse atomic interferometry (LPAI) apparatus is provided. The LPAI apparatus comprises a vessel, two sets of magnetic coils configured to magnetically confine an atomic vapor in two respective magneto-optical traps (MOTs) within the vessel when activated, and an optical system configured to irradiate the atomic vapor within the vessel with laser radiation that, when suitably tuned, can launch atoms previously confined in each of the MOTs toward the other MOT. In embodiments, the magnetic coils are configured to produce a magnetic field that is non-zero at the midpoint between the traps. In embodiments, the time-of-flight of the launched atoms from one MOT to the other is 12 ms or less. In embodiments, the MOTs are situated approximately 36 mm apart. In embodiments, the apparatus is configured to activate the magnetic coils according to a particular temporal magnetic field gradient profile.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Integrated optical system for cold atom interferometer
ActiveCN107328355AReduce complexityReduce volumeUsing optical meansICT adaptationControl powerBeam splitting
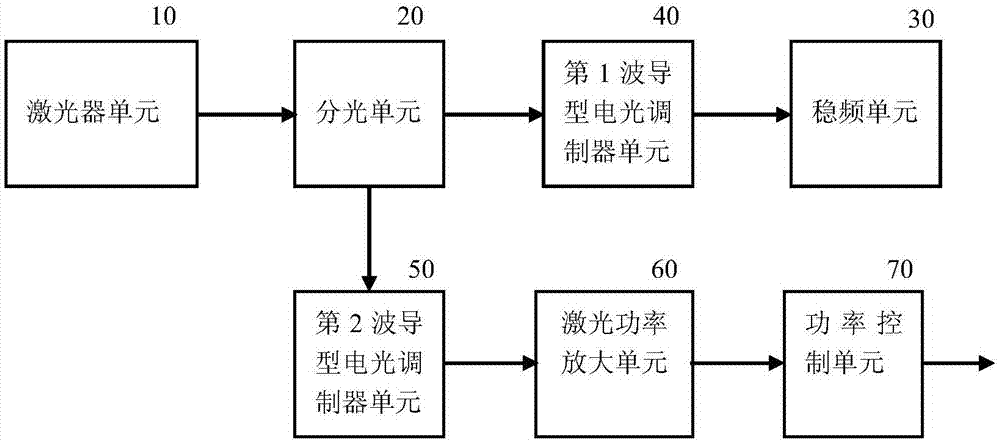
The invention discloses an integrated optical system for a cold atom interferometer, and belongs to the field of cold atom interferometry precise measurement. According to the structure of the integrated optical system, a laser device unit (10) generates single-frequency lasers which are split into two laser beams through a beam splitting unit (20), one output laser beam sequentially passes through a first waveguide type electrooptical modulator unit (40) and a frequency stabilizing unit (30) to obtain an electrical feedback signal, and the other output laser beam sequentially passes through a second waveguide type electrooptical modulator unit (50), a laser power amplifying unit (60) and a power control unit (70) and is then transmitted to a physical system of the atom interferometer. According to the system, full-optical-fiber modularization design can be used, the optical system is not sensitive to temperature fluctuation, mechanical pressure, vibration and the like, and then the stability of the system is improved.
Owner:中科酷原科技(武汉)有限公司
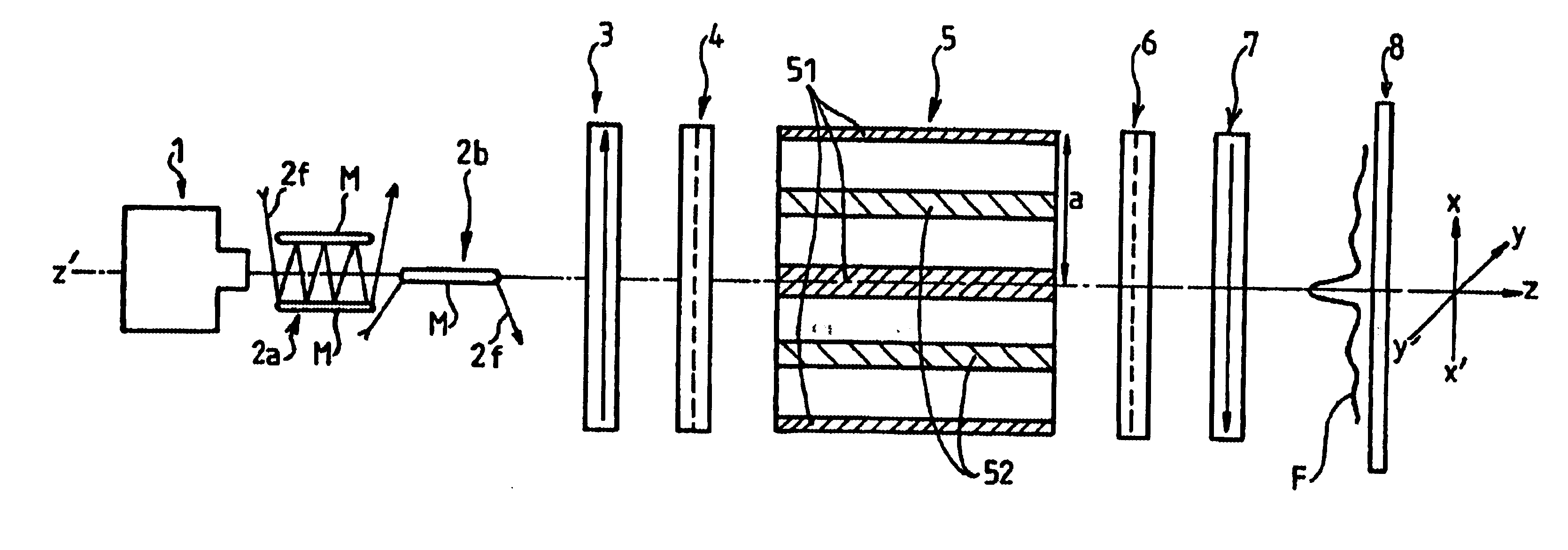
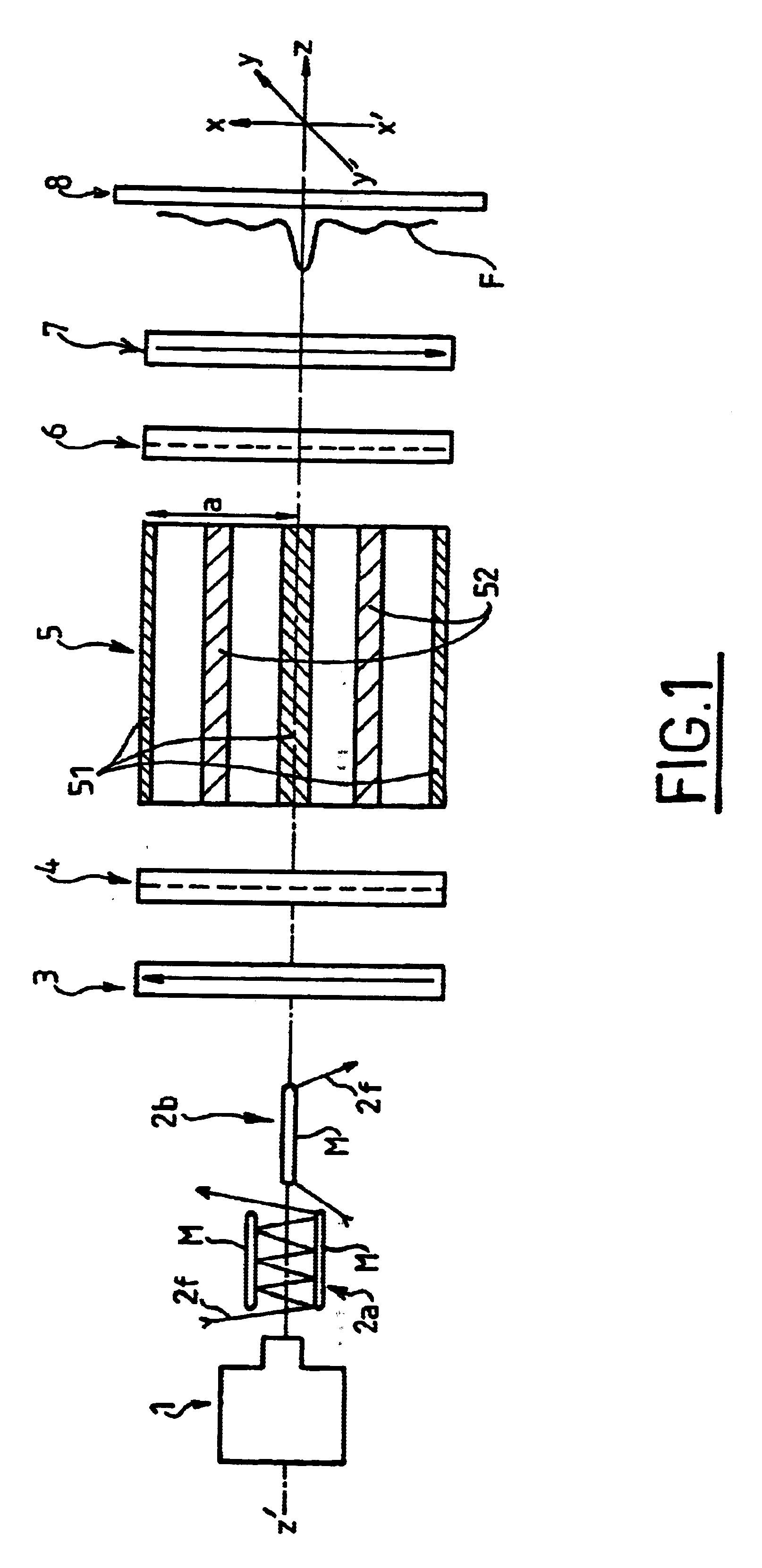
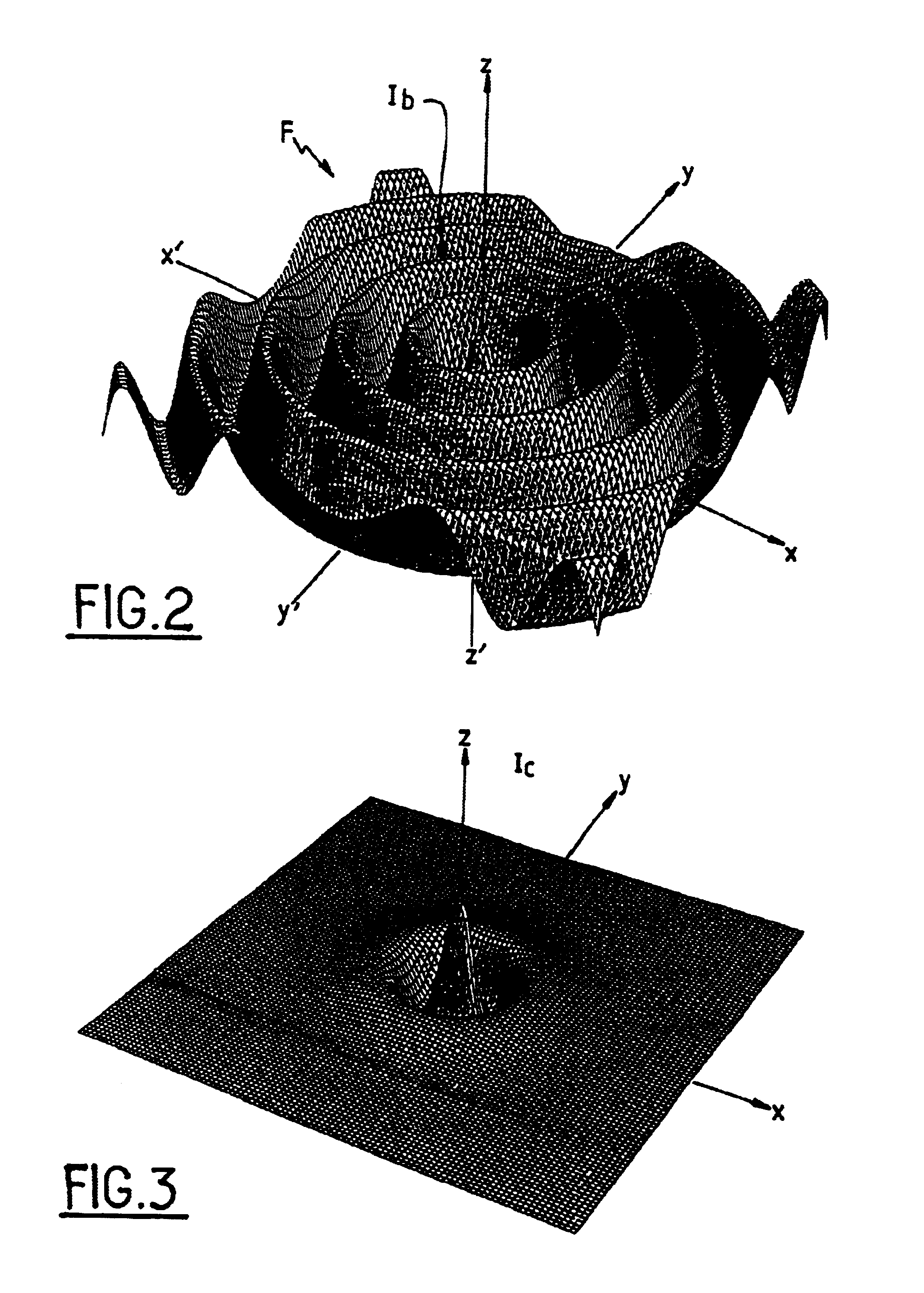
Method and device for atomic interferometry nanolithography
InactiveUS6891623B1Eliminate interference fringesReduce contrastElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsNanolithographyUniform field
The invention proposes a novel technique for implementing high performance atomic lithography, and in particular high resolution lithography. The technique makes use of Stern-Gerlach type atomic interferometry enabling disturbances to be implemented in the atomic phase of the beam. Such interaction then directly modulates the intensity of the associated wave in the plane extending transversely to the beam of atoms, and does so in controllable manner. The installation of the invention for nanolithography by atomic interferometry comprises a Stern-Gerlach type interferometer comprising, as its phase object, four-pole magnetic induction having a transverse gradient created by four parallel bars carrying alternating direct currents, bracketed between two separator plates, preceded and followed respectively by a spin polarizer and by an analyzer operating by laser pumping. An additional uniform field is being created by another four additional bars powered in paired manner by adjustable currents in order to create a uniform field of arbitrary intensity and orientation for the interference pattern by adjusting the two current parameters. The source of atoms is a source that continuously discharges metastable helium or argon with approximately Maxwell type speed dispersion of about 30% to 40% in order to obtain a central spot.
Owner:PARIS 13 UNIVERSITY
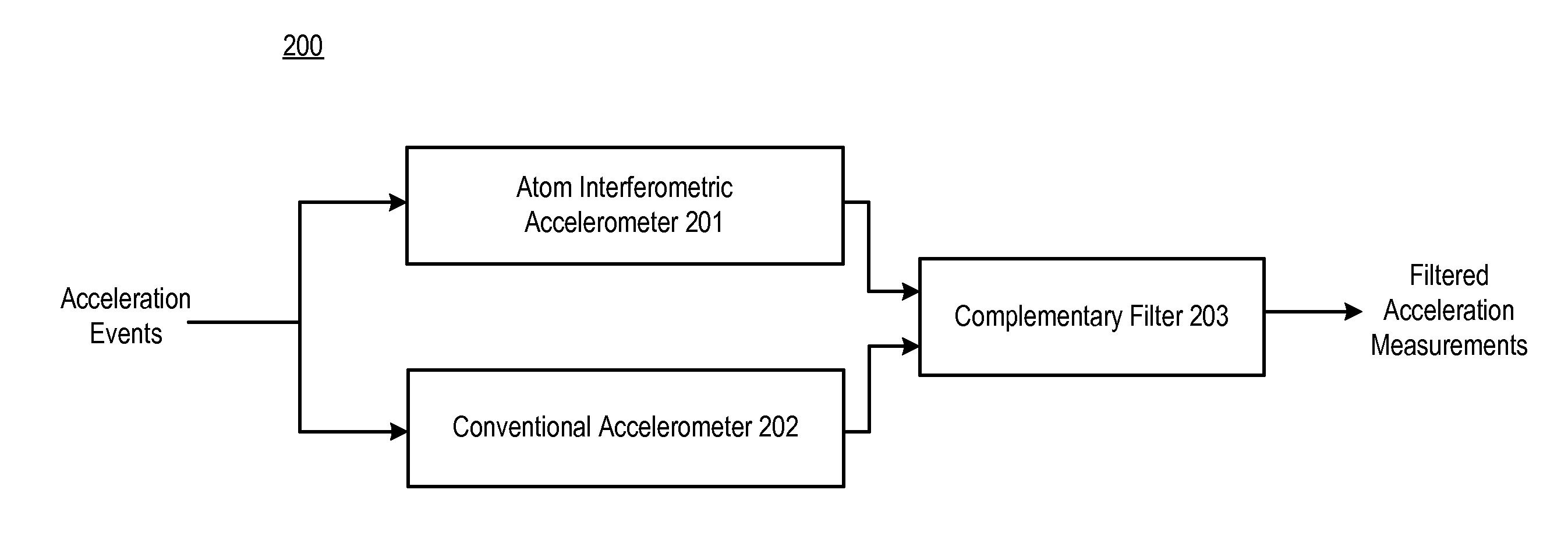
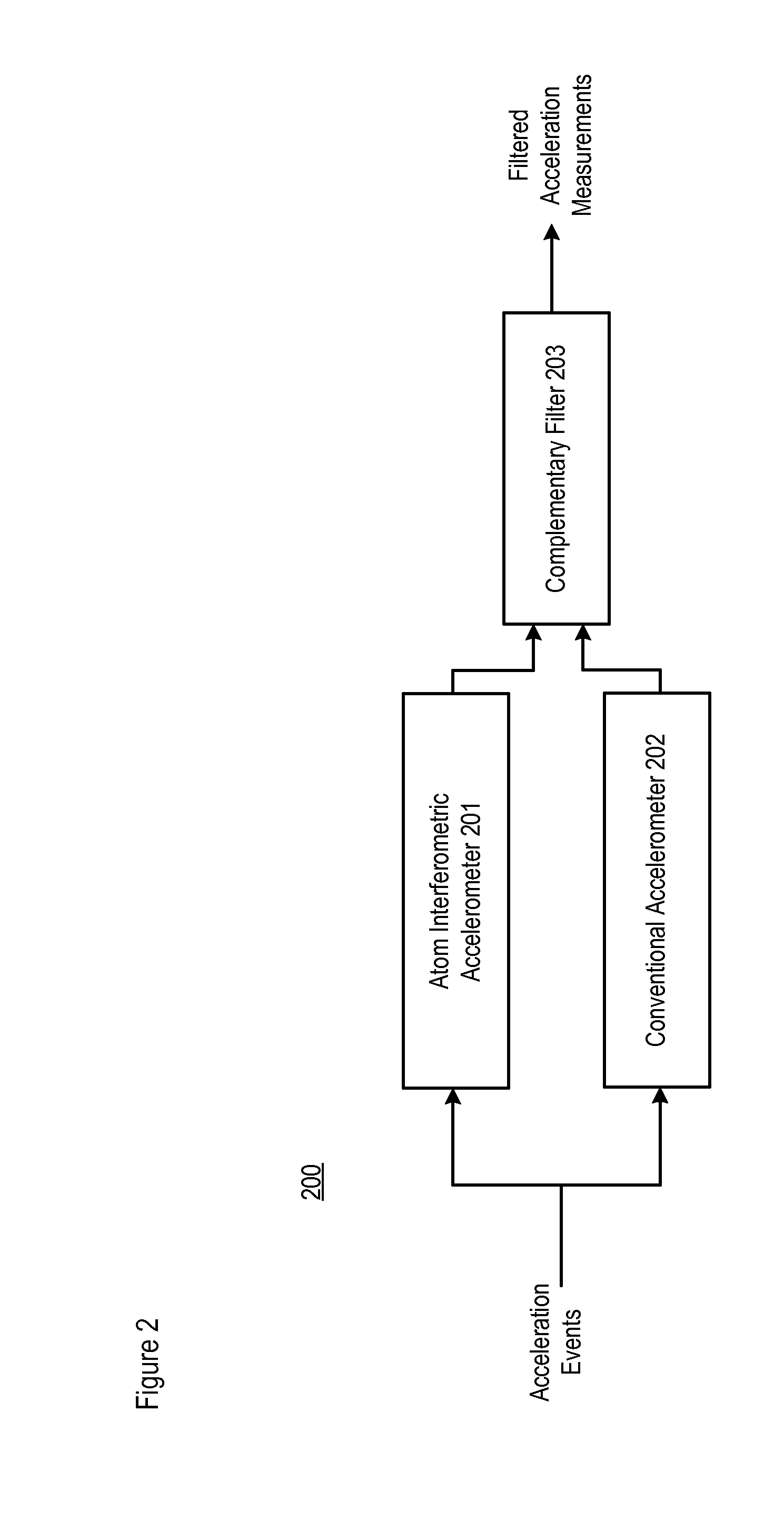
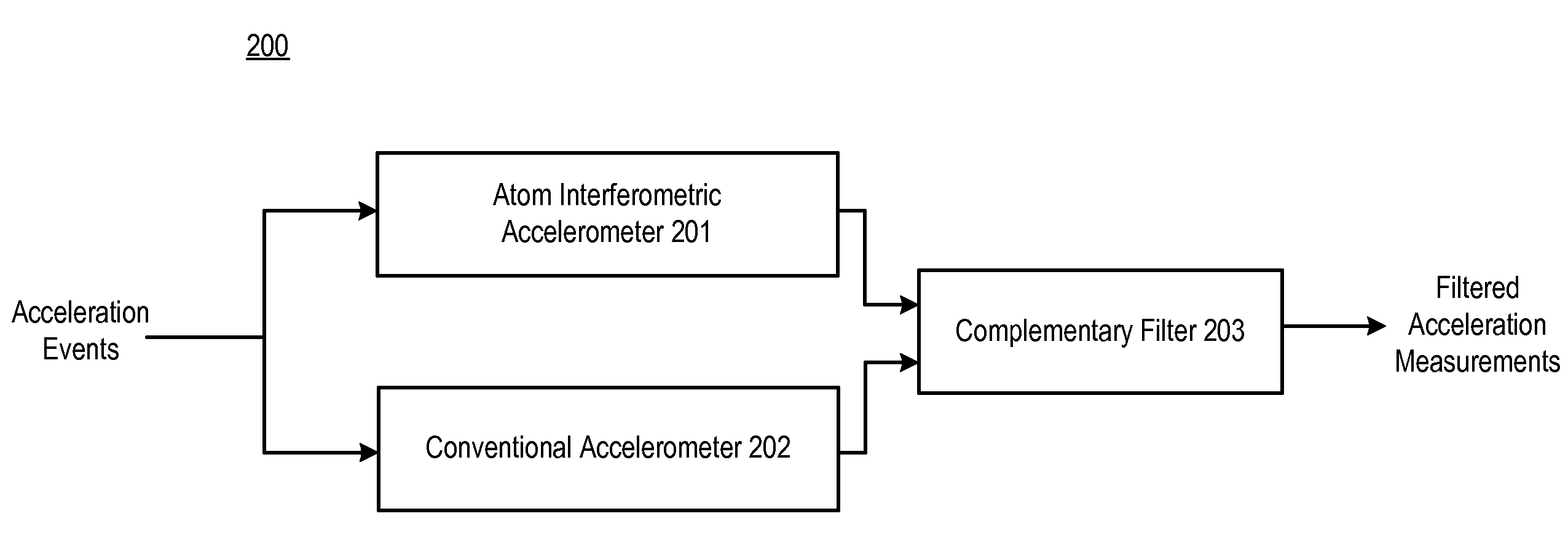
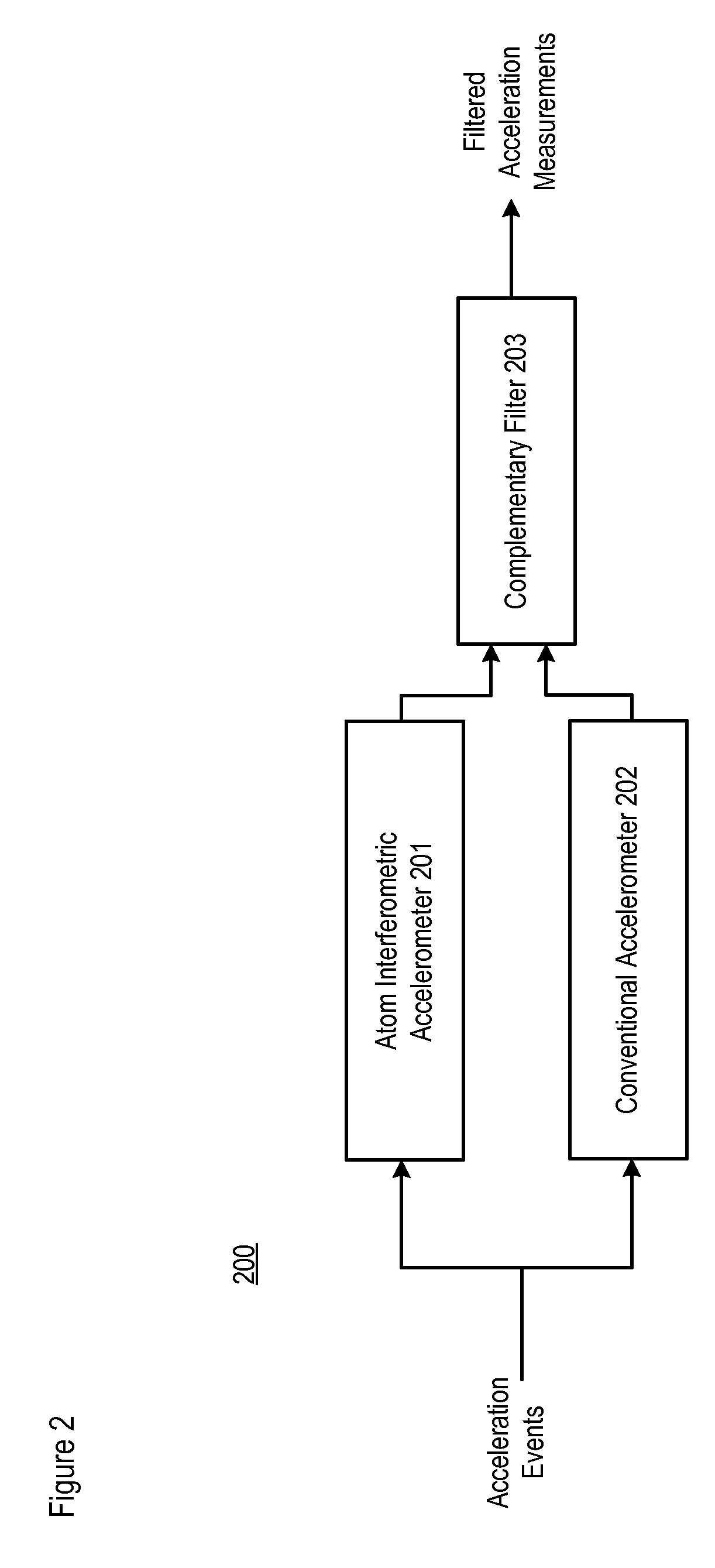
Performance of an Atom Interferometric Device through Complementary Filtering
InactiveUS20100149541A1Performance advantageLong output sample timeAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using accelerationGyroscopeAccelerometer
A technique is disclosed which offers an improvement in the performance of an atom interferometric (AI) sensor, such as one that is used in an accelerometer or a gyroscope. The improvement is based on the recognition that the AI-based device, which is associated with superior low-frequency performance, can be augmented with a conventional device having a superior high-frequency performance, as well as a wider frequency response, compared with that of the AI-based device. The disclosed technique combines acceleration measurements from the AI-based device, which is characterized by transfer function G(s), with acceleration measurements from the conventional device that have been adjusted by a complementary function, 1−Ĝ(s), where Ĝ(s) is an approximation of G(s). The conventional device has a considerably wider bandwidth than that of the AI-based device, and the quasi-unity transfer function of the conventional device makes possible the 1−Ĝ(s) adjustment of the measurements provided by the conventional device.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Cold atom interferometry principle-based inertia measuring device
ActiveCN105066991ASynchronization work statusNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsBeam splitterRubidium
The invention discloses a cold atom interferometry principle-based inertia measuring device. The cold atom interferometry principle-based inertia measuring device comprises three inertia measuring units, a Raman laser, and a light dividing device with adjustable splitting ratio; each inertia measuring unit comprises a single-mode narrow linewidth laser, an interferometic cavity, a optical fiber beam splitter, four acoustic optical modulators (AOM), and one electrooptical modulator (EOM); the interferometic cavities are filled with rubidium atomic vapor; Raman laser light send by the Raman laser can be divided into three beams of Raman laser light via the light dividing device with adjustable splitting ratio, and the three beams of Raman laser light are send to the three inertia measuring units; wherein the incidence directions of the three beams of Raman laser light are orthogonal to each other. According to the cold atom interferometry principle-based inertia measuring device, a reasonable structure scheme is adopted; three atom interferometers are arranged in a pyramid mode, so that sensitive acceleration directions of the atom interferometers are orthogonal to each other, and sensitive angular velocity directions are orthogonal to each other. One set of laser system is shared by the three atom interferometers, so that synchronization of atom interference process is realized, and the atom interferometer-based inertia measuring units are sensitive to inertial parameters with six degrees of freedom simultaneously.
Owner:NO 717 INST CHINA MARINE HEAVY IND GRP
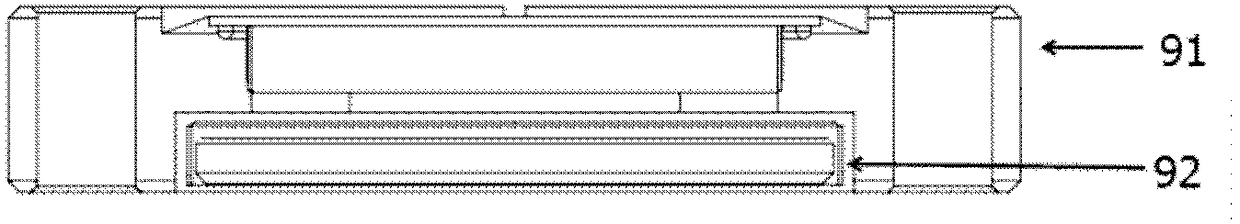
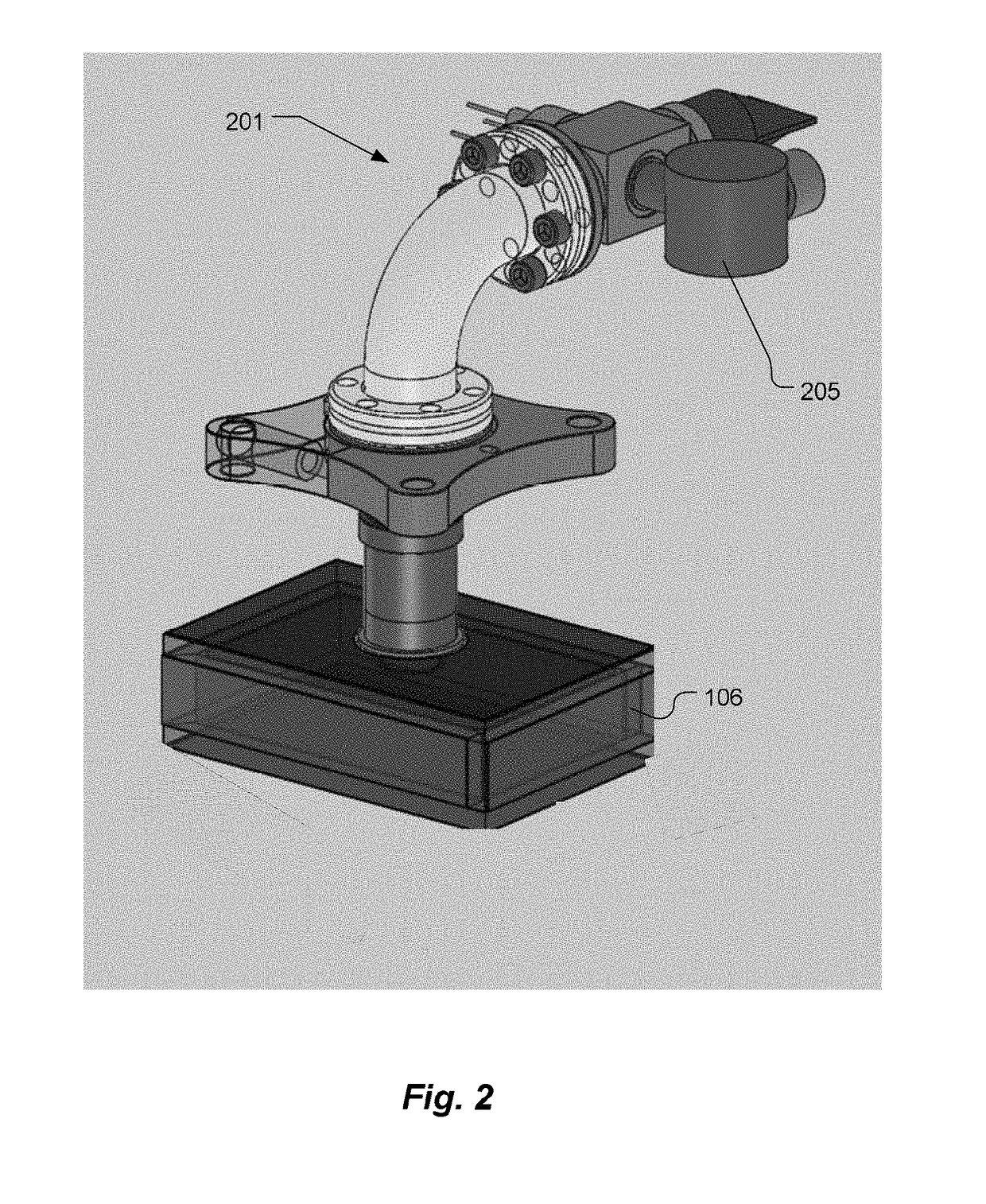
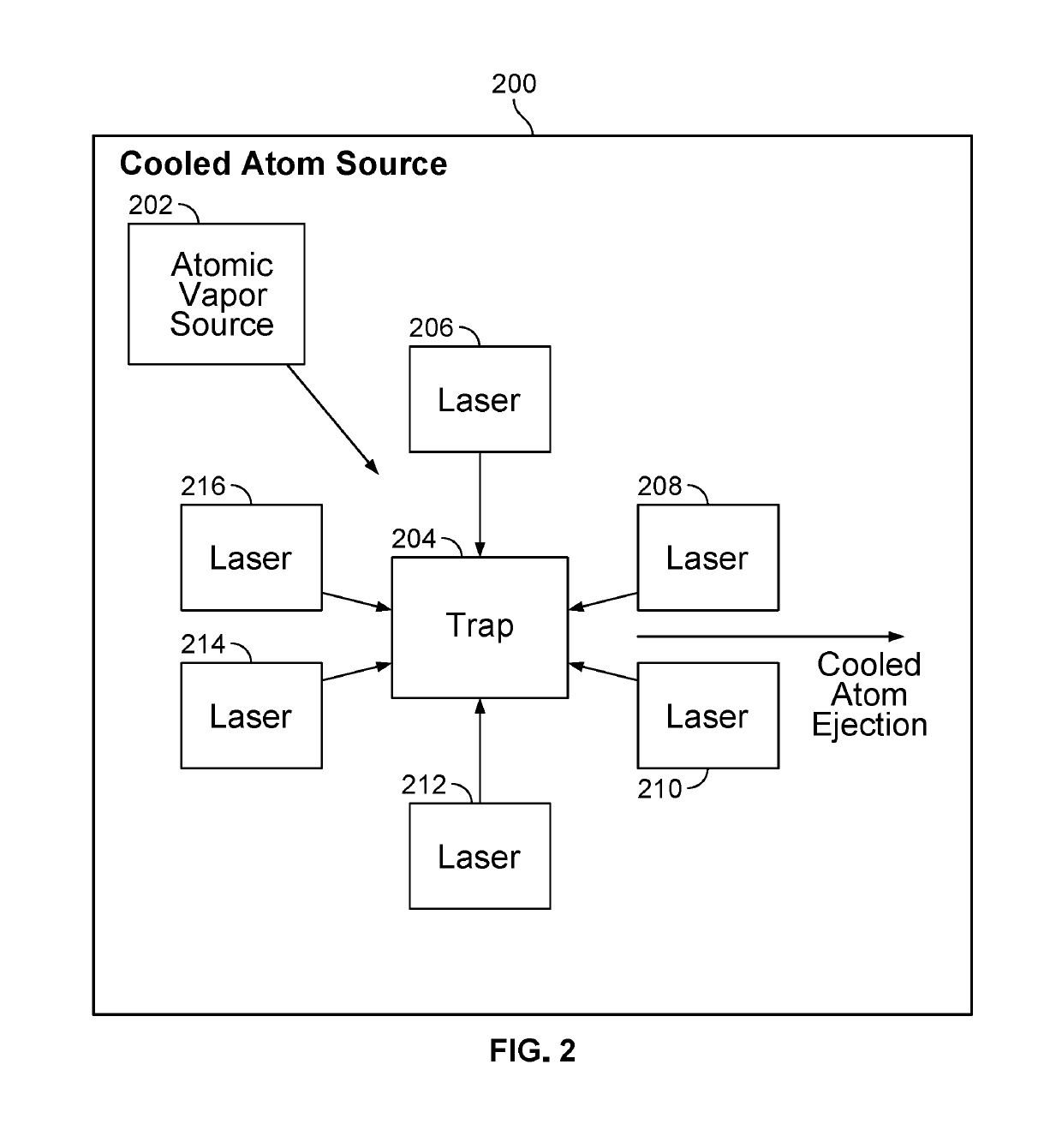
Vacuum structure for miniaturizing atomic interferometer
ActiveCN108279441AReduce weightSmall sizeGravitational wave measurementGyroscopeMagneto-optical trap
The present disclosure provides a vacuum apparatus for miniaturizing an atomic interferometer. The appratus includes an upper window, a lower window, a square cavity, a connecting member, an atomic source component, a three-dimensional magneto-optical trap component, an interference component, and a detecting component. Fasteners matched with the upper and lower windows are sealed with thick glasscoated with anti-reflection coating on both faces, and systematic errors caused by wavefront distortion effects can be greatly reduced. Optical windows beyond the upper and lower windows are reasonably designed and are directly embedded into a vacuum chamber in a welded manner, a reasonable atomic cooling interference solution is adopted, and the vacuum apparatus are greatly reduced in size and weight and is simple and reliable in structure. A vacuum structure is properly modified and is also suitable for applications such as cold atomic gyroscopes, gravity gradiometers and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Ring architecture for sequential operation of an atomic gyroscope
ActiveUS20160298967A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerGyroscope
Compact inertial measurement systems and methods based on atom interferometry. Certain examples provide a combination atomic accelerometer-gyroscope configured to recapture and cycle atom samples through atom interferometers arranged to allow the next measurement to use the atoms from the previous measurement. Examples of the apparatus provide inertial measurements indicative of rotation for different inertial axes by applying atom interferometry to a plurality of atom samples launched in opposite directions to allow for measurement of both acceleration and rotation rates. In some examples, the inertial measurement apparatus provide a combined atomic gyroscope and an atomic accelerometer in a compact six Degrees of Freedom (6 DOF) IMU.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Atom-Interferometric, Stepped Gravity Gradient Measuring System
InactiveUS20100064767A1Improve accuracyImprove signal-to-noise ratioAcceleration measurement using interia forcesUsing mechanical meansAccelerometerComputational physics
A full-tensor, gravity gradient measuring system is disclosed that is based on atom interferometry. Each axis in the three-axis measuring system is served by a different gravity gradiometer, where each gradiometer comprises three pairs of atom interferometric (AI) accelerometers. The accelerometers in each pair are mounted on opposite sides of the gradiometer's rotation axis from each other. The three AI accelerometer pairs are step-rotated, instead of being continuously rotated, thereby providing enhanced signal-to-noise performance. The three gradiometers in the overall measuring system are mounted orthogonally with respect to one another on a local-level platform, in order to achieve a full-tensor measuring system. The measuring system can be step-rotated as an overall unit around an axis perpendicular to a local level reference. The multiple levels of stepped rotation, as enabled by the atom interferometry being utilized, yields improved results with lower costs than what is achievable with some prior-art techniques.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Micro displacement measuring system with double light-source-adjustable Fabry-Perot interferometers
ActiveCN104266593AHigh measurement resolutionSolve measurement resolutionUsing optical meansClassical mechanicsLength wave
The invention relates to a micro displacement measuring system with double laser-source-adjustable Fabry-Perot interferometers, and belongs to the technical field of geometrical product measurement. According to the measuring system, two Fabry-Perot interferometers with wavelength-adjustable lasers as light sources are used for measuring the displacement of a measured target, the two adjustable light sources are used for alternately tracking the frequencies of different resonant modes of Fabry-Perot cavities, and the range of displacement measurement is broadened while it is guaranteed that the Fabry-Perot interferometers have the high measurement resolving ability. The micro displacement measuring system effectively solves the conflict between the improvement of the interferometer measurement resolving ability and the broadening of the measurement range, and can be applied to micro displacement measurement with nanometer-level accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING CHANGCHENG INST OF METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
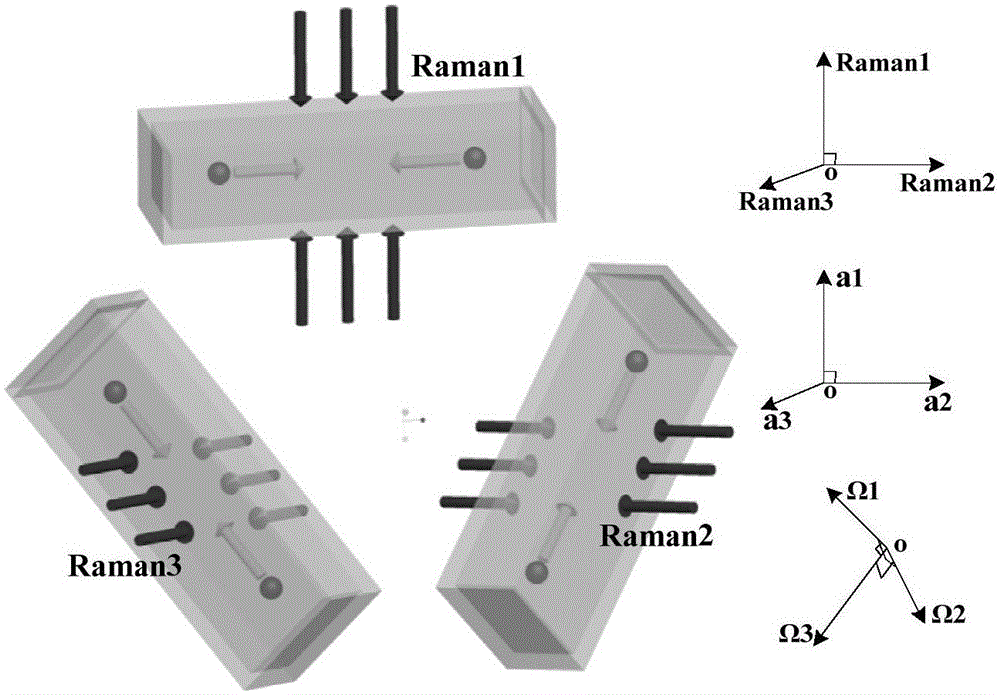
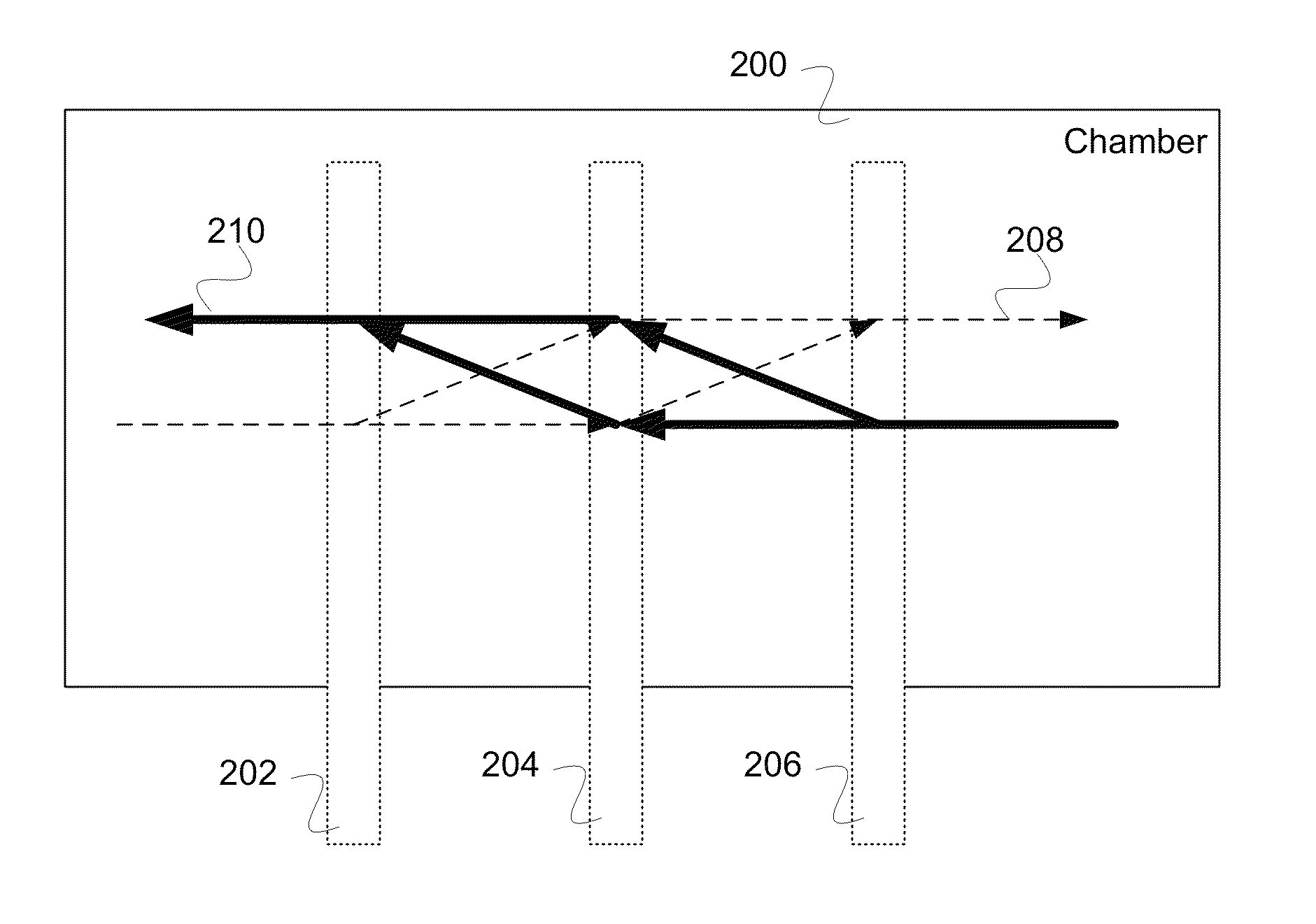
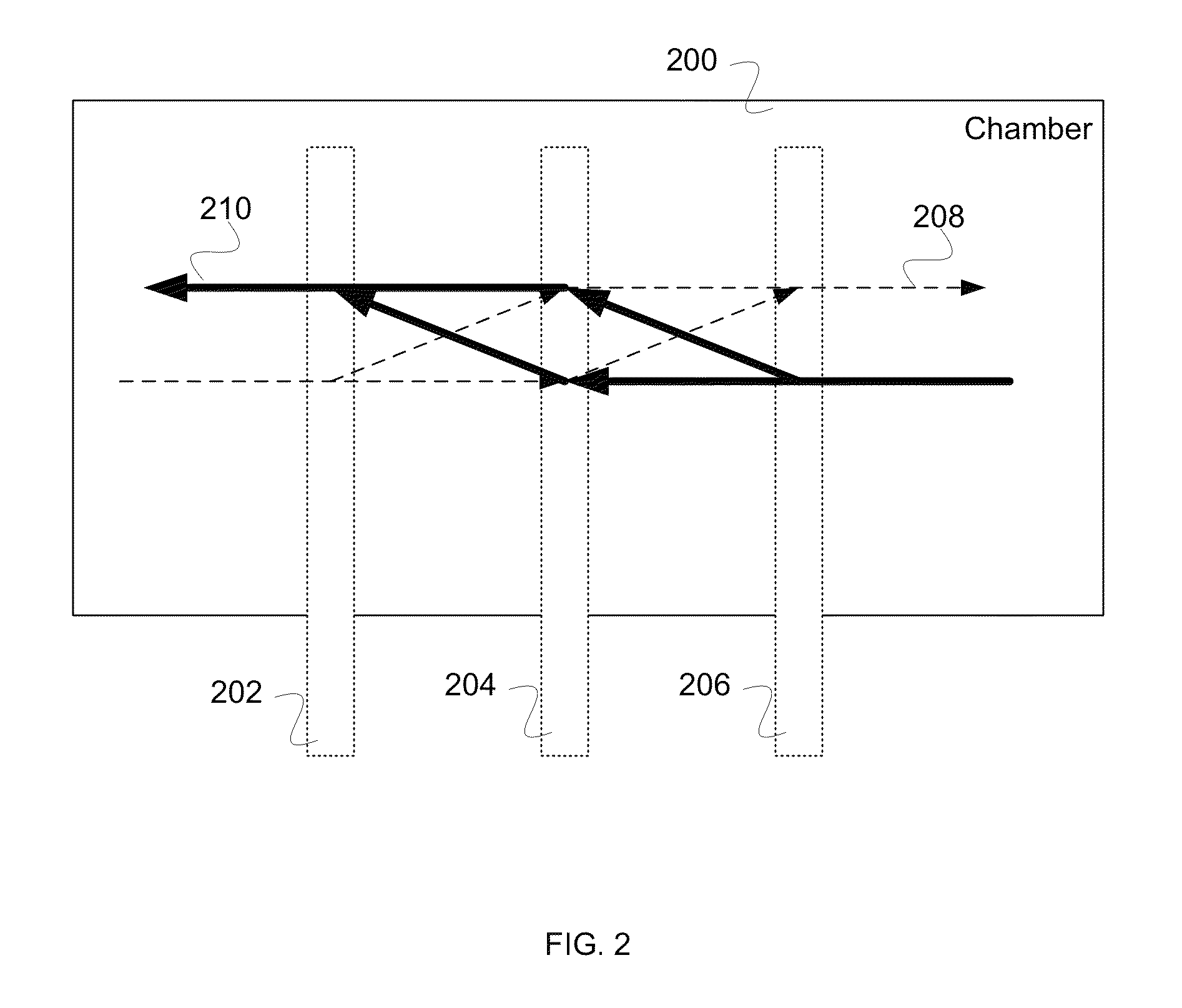
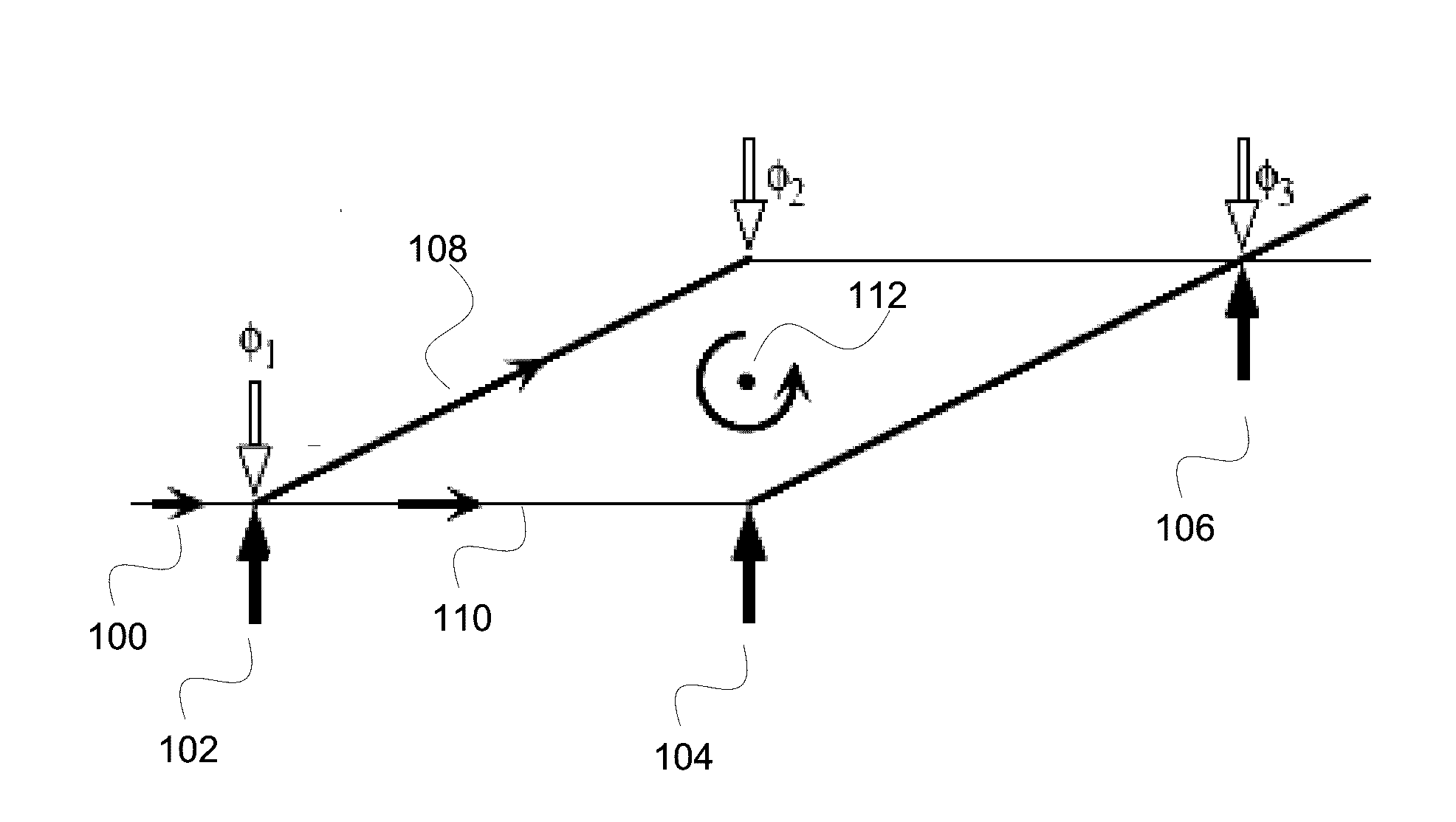
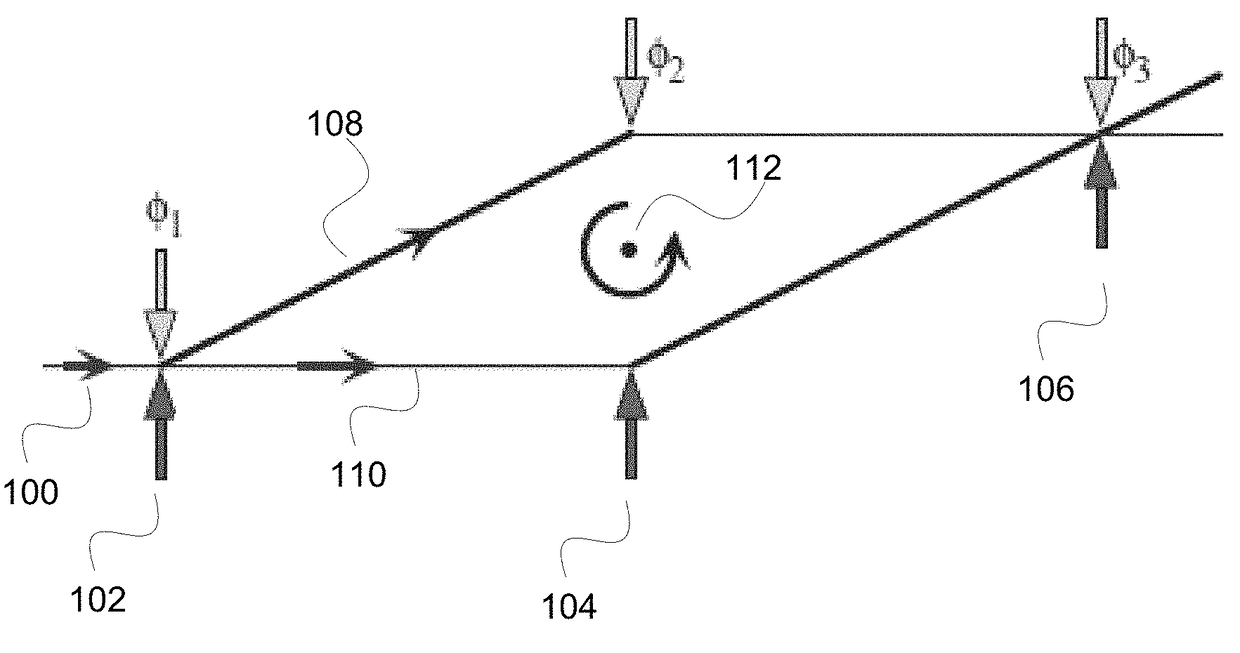
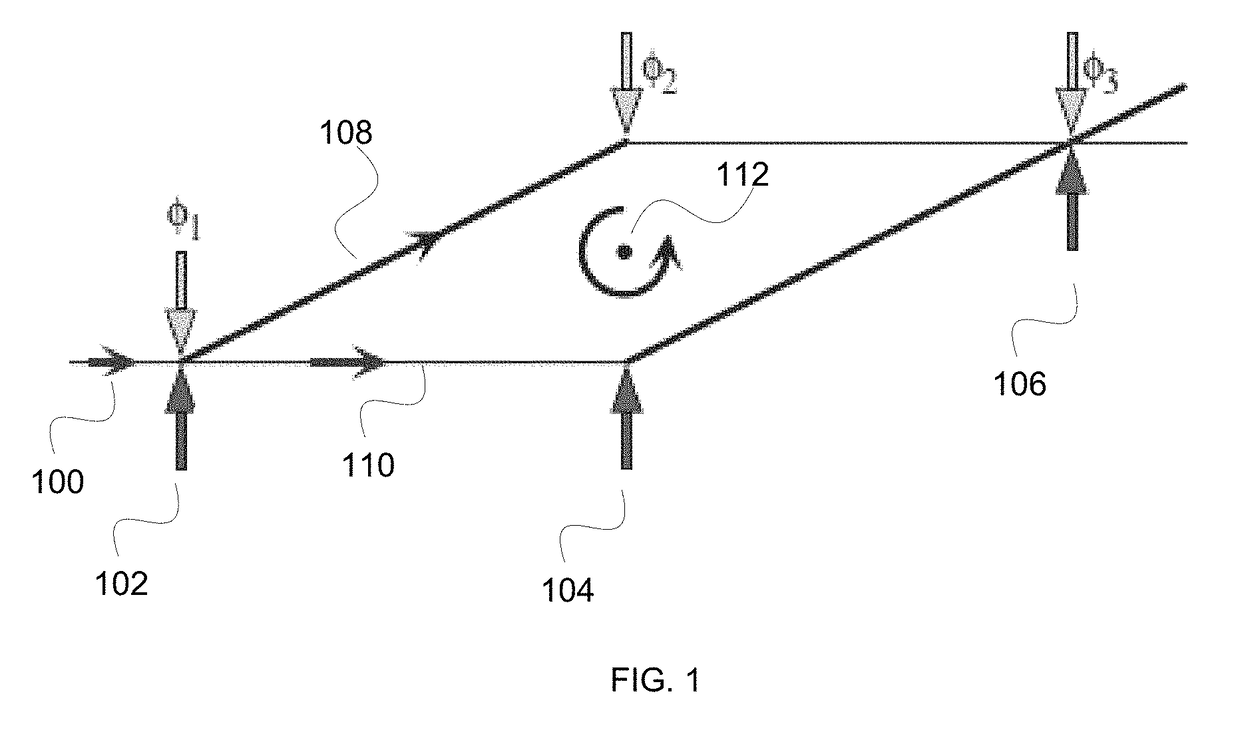
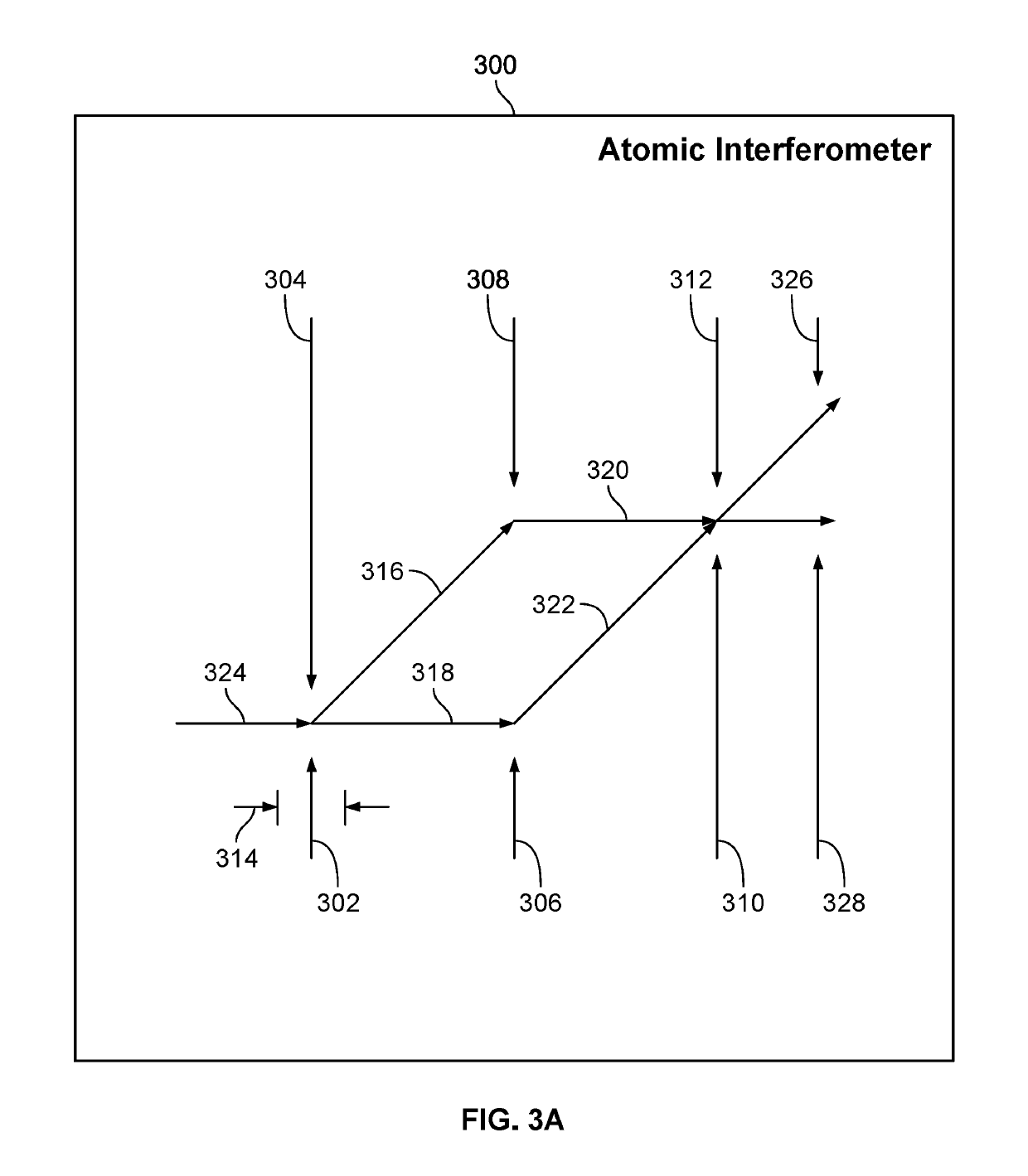
Separated Parallel Beam Generation for Atom Interferometry
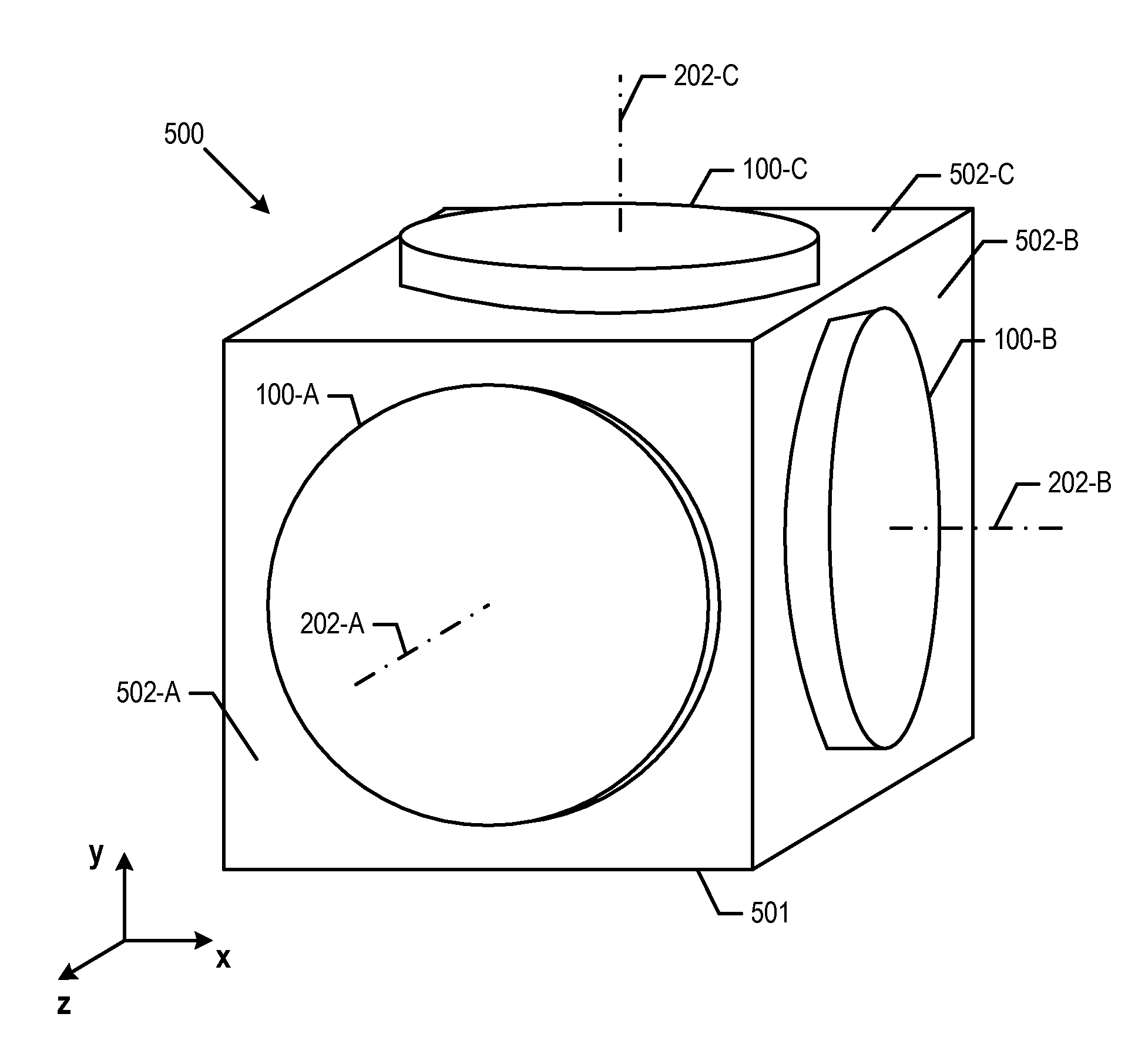
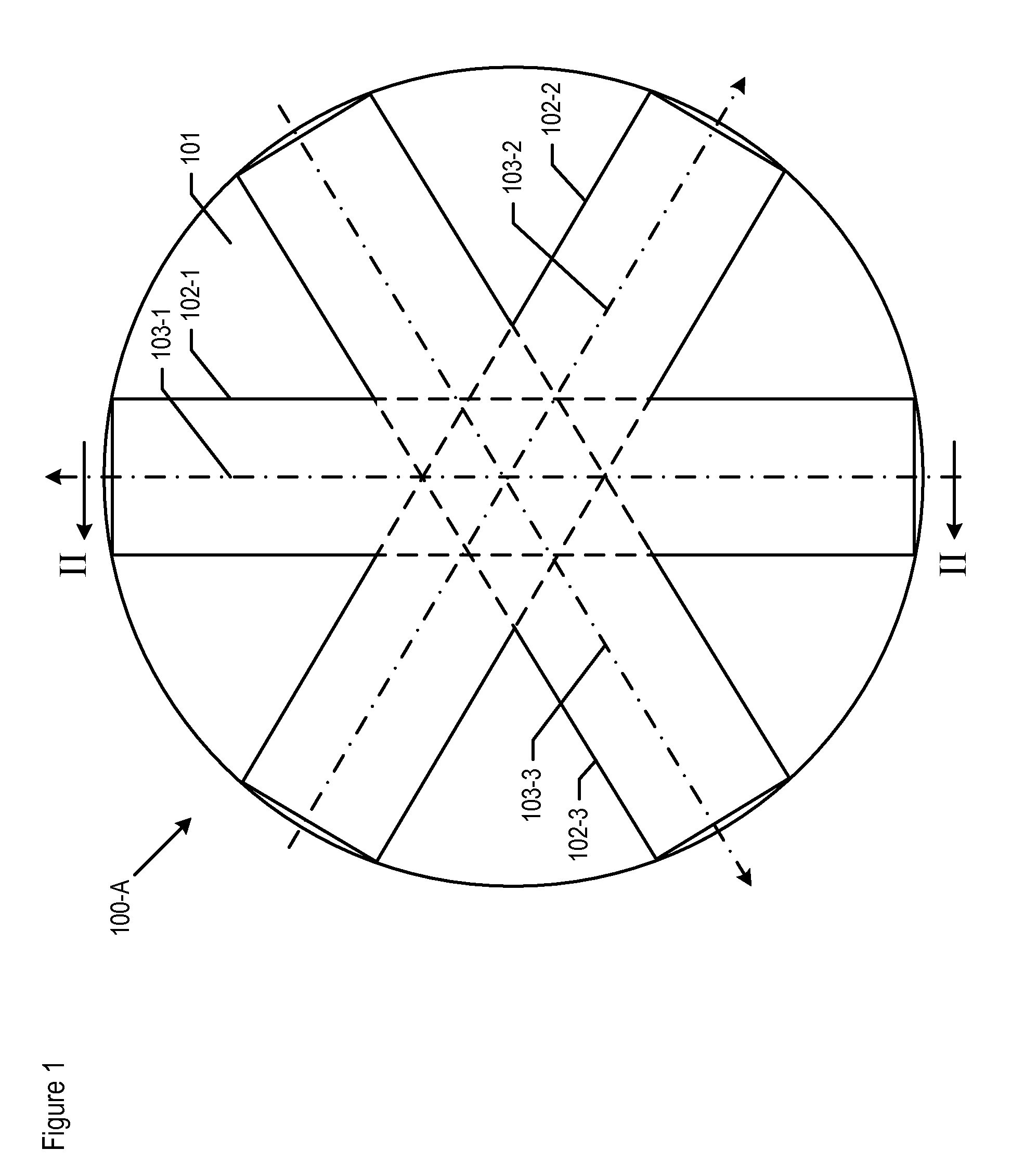
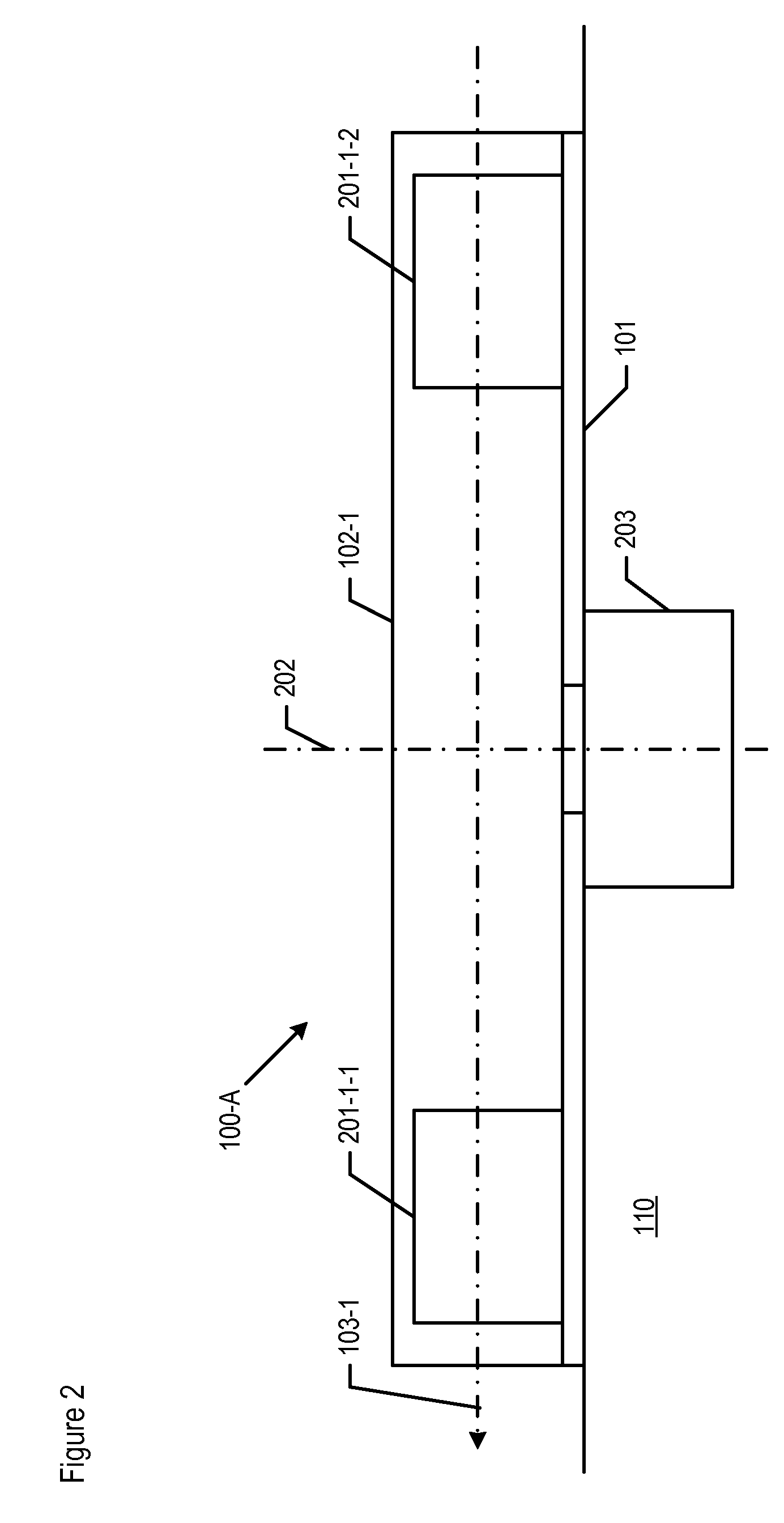
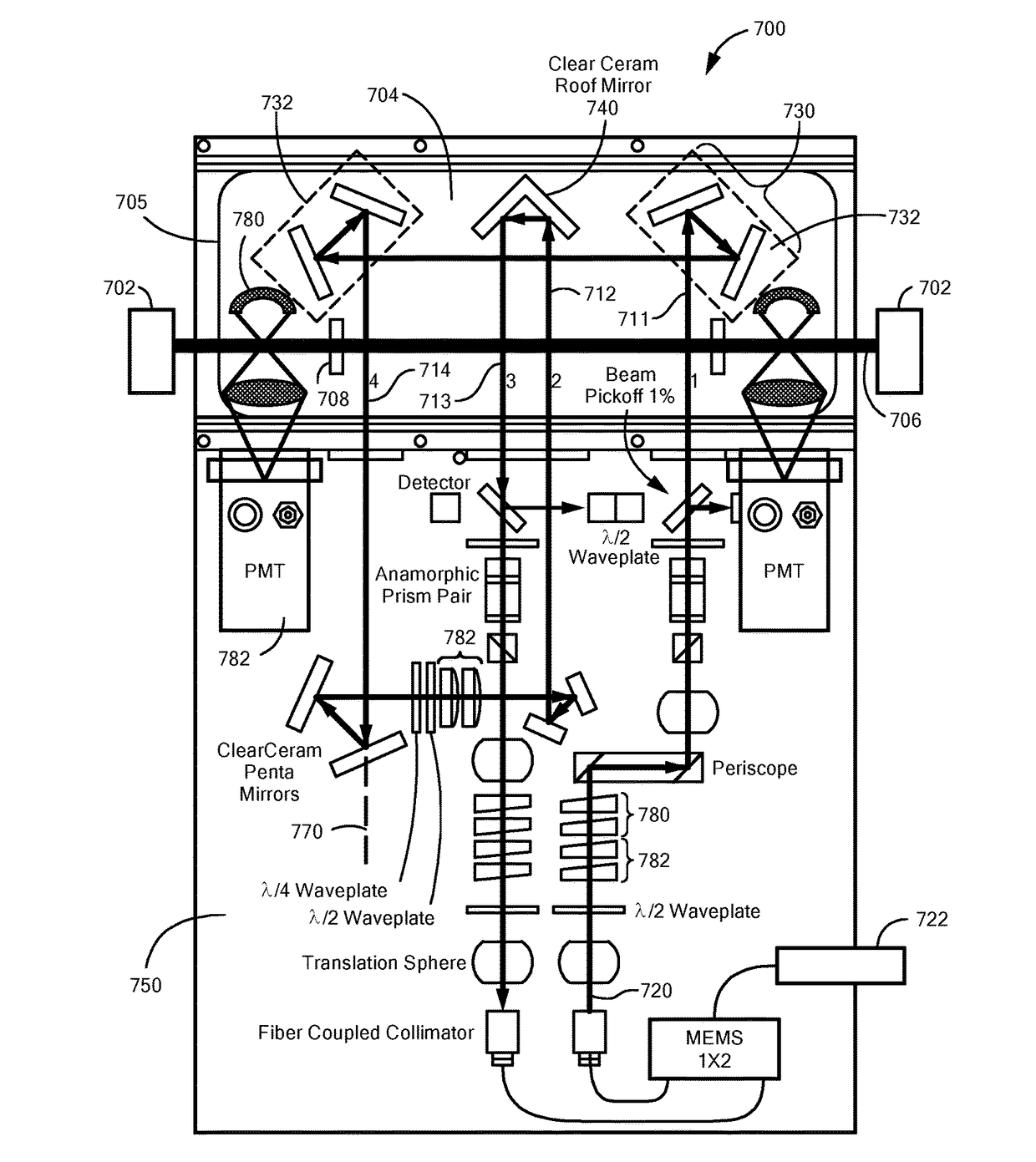
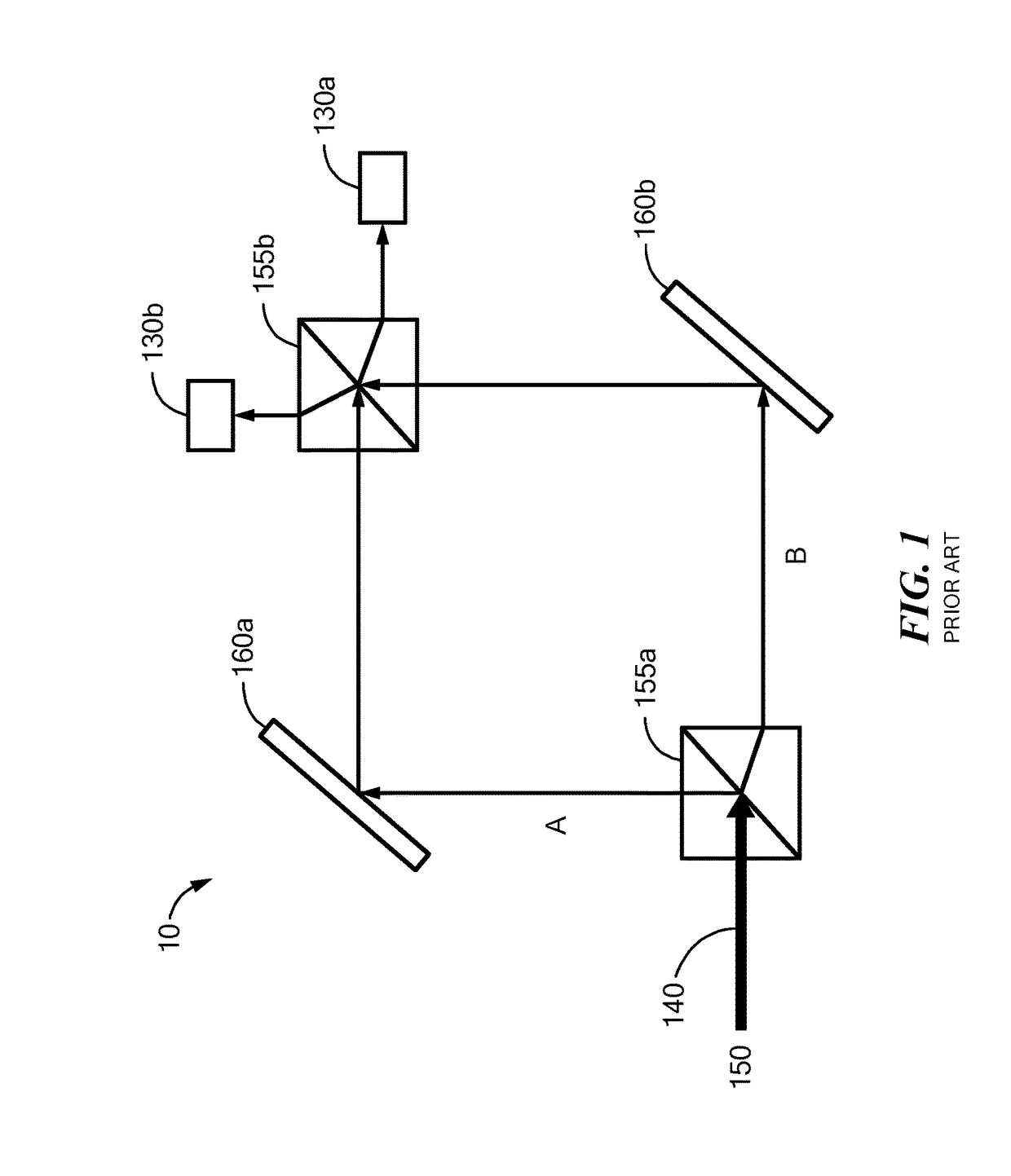
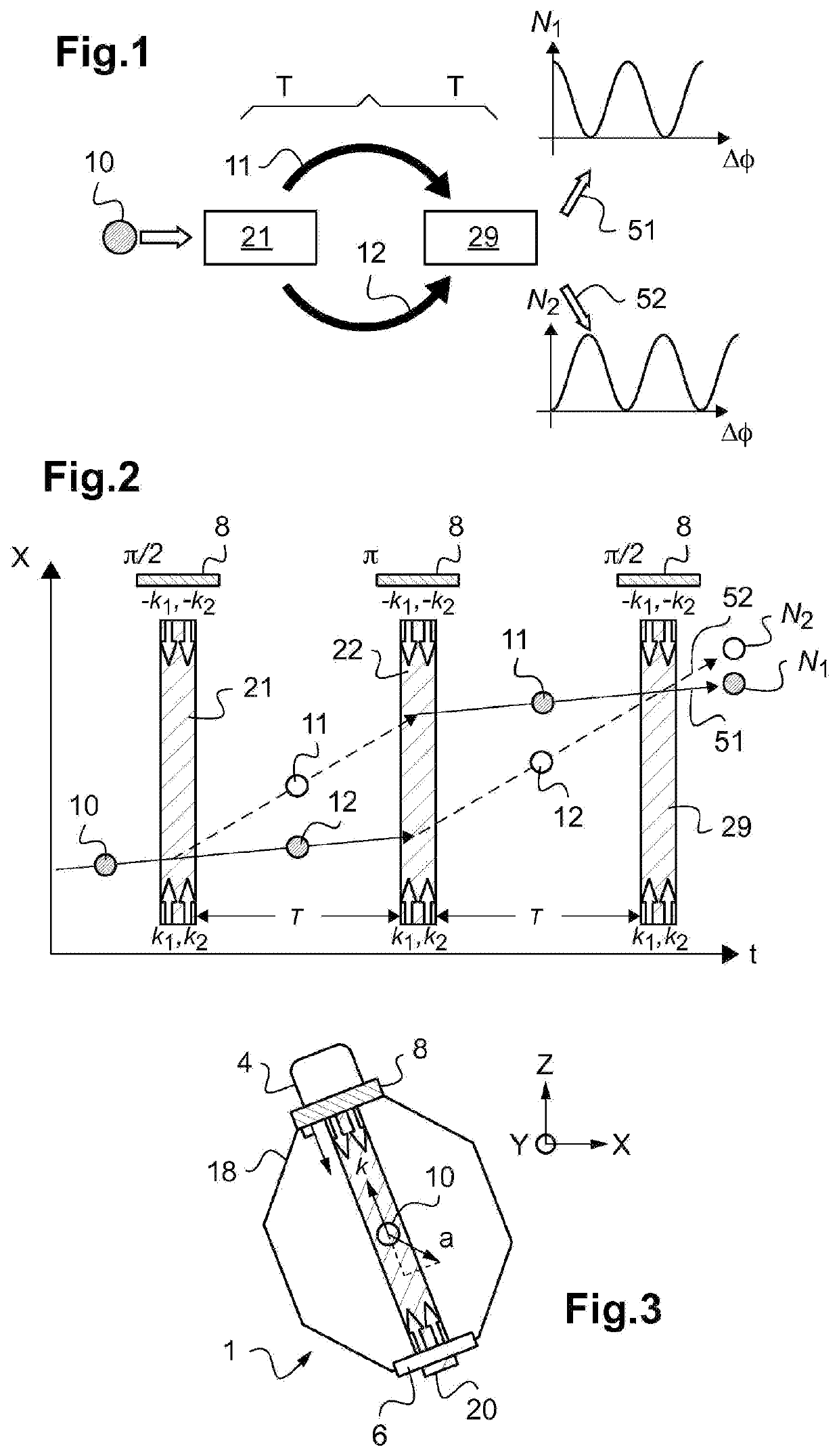
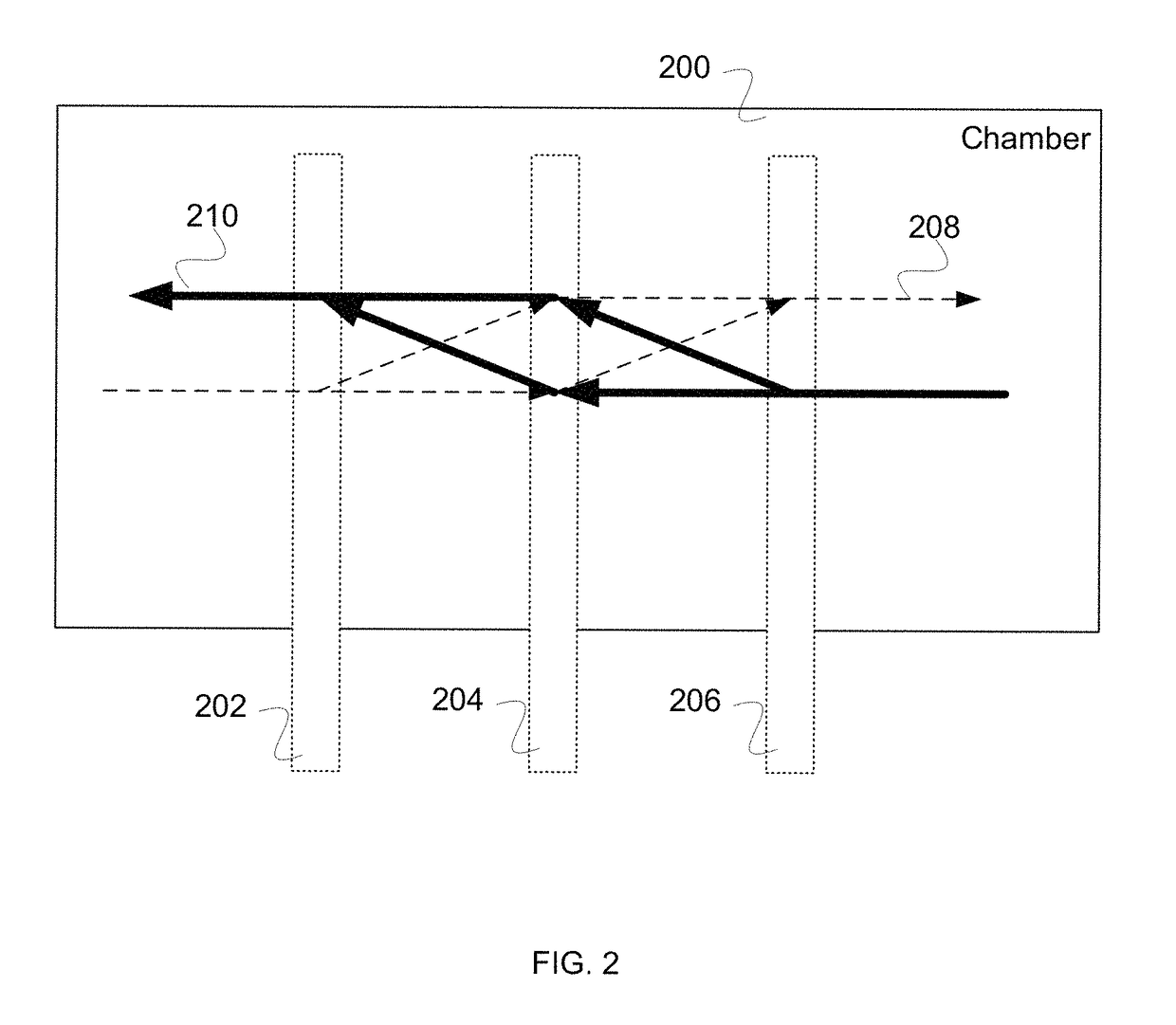
An atomic interferometer and methods for measuring phase shifts in interference fringes using the same. The atomic interferometer has a laser beam traversing an ensemble of atoms along a first path and an optical components train with at least one alignment-insensitive beam routing element configured to reflect the laser beam along a second path that is anti-parallel with respect to the first laser beam path. Any excursion from parallelism of the second beam path with respect to the first is rigorously independent of variation of the first laser beam path in yaw parallel to an underlying plane.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Cold Atom Interferometry
ActiveUS20170372808A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionFiberBeam splitting
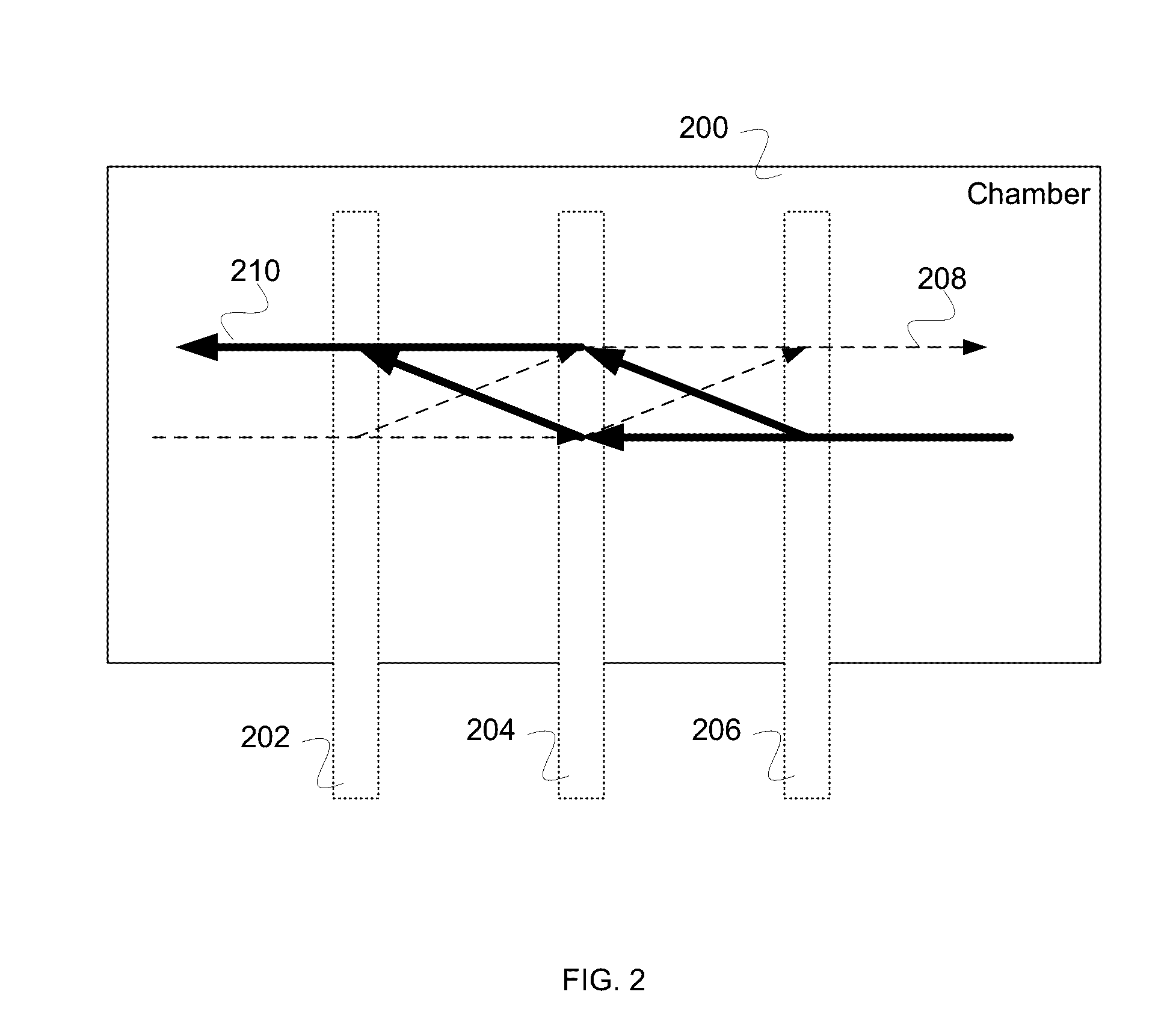
Improvements to atom interferometers. An improved atom interferometer has a single polarization-preserving fiber, coupled for propagation of beams of two Raman frequencies, and a parallel displacement beamsplitter for separating the laser beams into respective free-space-propagating parallel beams traversing at least one ensemble of atoms. A reflector generates one or more beams counterpropagating through the ensemble of atoms. Other improvements include interposing a beam-splitting surface common to a plurality of parallel pairs of beams counterpropagating through the ensemble of atoms, generating interference fringes between reflections of the beams to generate a detector signal; and processing the detector signal to derive at least one of relative phase and relative alignment between respective pairs of the counterpropagating beams.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Atomic interferometer light source based on sideband suppression
PendingCN107959222ARealize multiplexingHigh resolutionLaser detailsDual frequencyRadio frequency signal
The invention discloses an atomic interferometer light source based on sideband suppression, including a laser, an interferometric laser phase modulator and a control module. The input end of the interferometric laser phase modulator is connected to the output end of the laser, and the control end of the interferometric laser phase modulator is connected to the output end of the control module. Under the action of a radio frequency signal output by the control module, the interferometric laser phase modulator modulates the frequency of laser output by the laser, and suppresses a sideband or suppresses carriers at the same time, in order to realize dual frequency output or single sideband output. In the invention, the interferometric laser phase modulator suppresses excess sidebands which are produced when a general electro-optic modulator is used, and avoids the interference of excess sidebands on the whole experiment process. Therefore, the high resolution of an atomic interferometerunder the condition that an optical phase locked loop is used can be achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
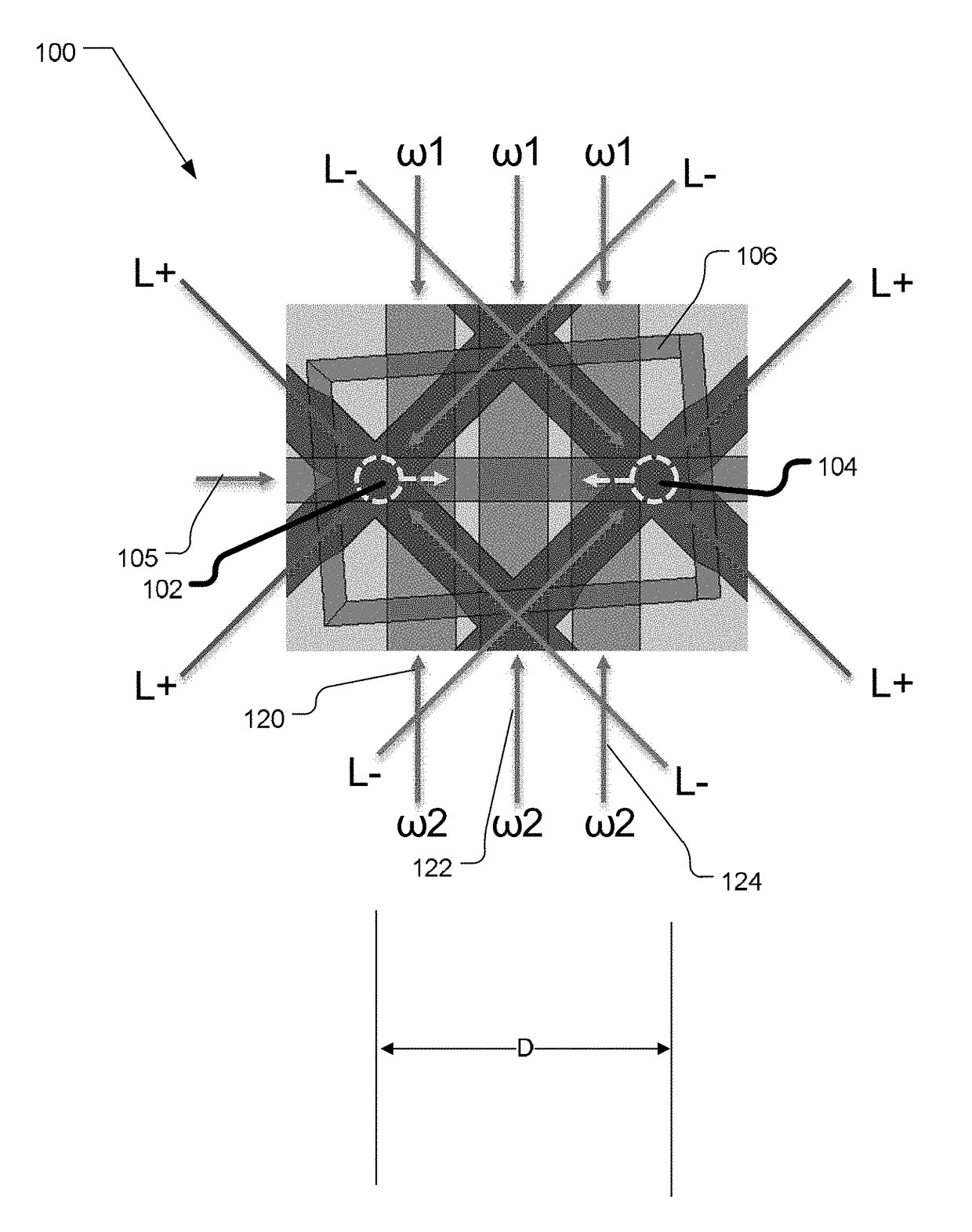
Phase control for dual atom interferometers
A system for controlling a phase measurement in an atom interferometer comprising one or more lasers, a processor, and a memory. The one or more lasers are for providing interrogating beams. A first group of atoms and a second group of atoms traverse an interrogating region of the atom interferometer in substantially opposite directions. The interrogating beams interact substantially simultaneously with both atoms in the first group and atoms in the second group. The first group of atoms and the second group of atoms interact with each of the interrogating beams in a different order. The processor is configured to determine a phase adjustment offset of at least one interrogating beam based at least in part on one or more past interactions of one or more interrogating beams with either the first group of atoms or the second group of atoms.
Owner:AOSENSE
High data-rate atom interferometers through high recapture efficiency
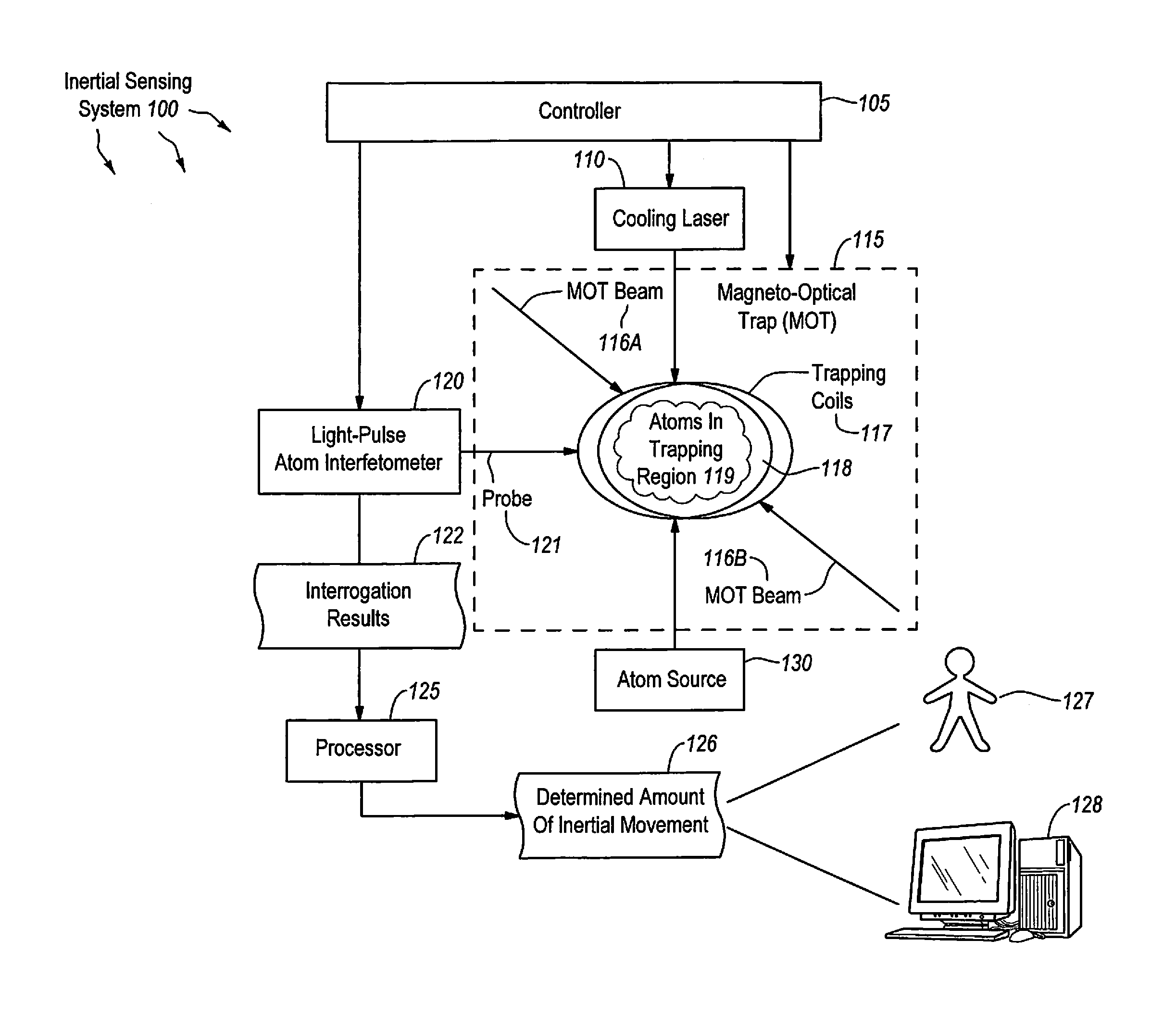
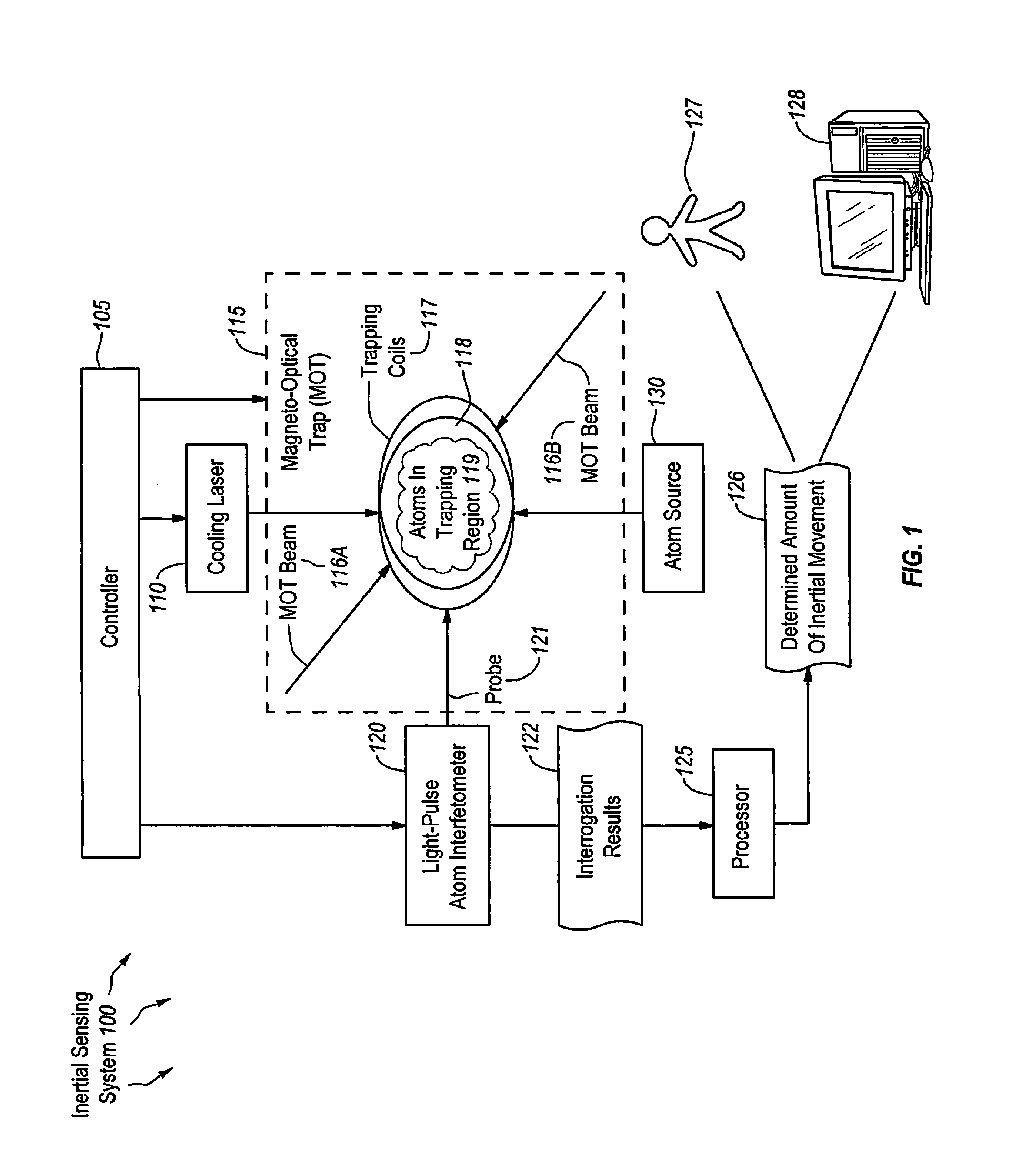
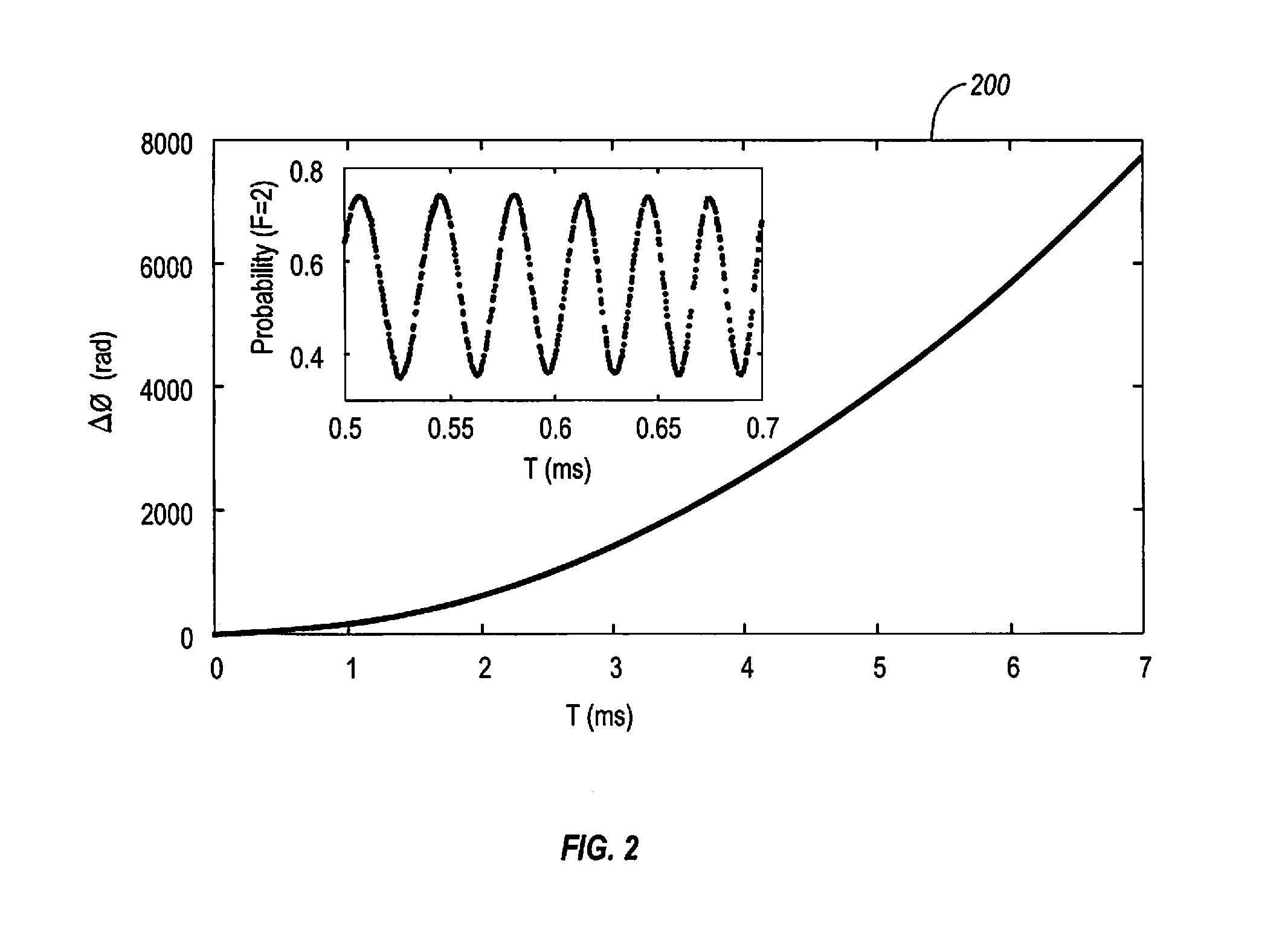
An inertial sensing system includes a magneto-optical trap (MOT) that traps atoms within a specified trapping region. The system also includes a cooling laser that cools the trapped atoms so that the atoms remain within the specified region for a specified amount of time. The system further includes a light-pulse atom interferometer (LPAI) that performs an interferometric interrogation of the atoms to determine phase changes in the atoms. The system includes a controller that controls the timing of MOT and cooling laser operations, and controls the timing of interferometric operations to substantially recapture the atoms in the specified trapping region. The system includes a processor that determines the amount inertial movement of the inertial sensing system based on the determined phase changes in the atoms. Also, a method of inertial sensing using this inertial sensing system includes recapture of atoms within the MOT following interferometric interrogation by the LPAI.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Hybrid inertial measurement system and method using a light pulse cold atom interferometer
ActiveUS20190376790A1Avoid loss of sensibilityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsElectronic systemsHybrid system
Disclosed is a hybrid inertial measurement system including a cold atom interferometric inertial sensor having a laser source generating a sequence of laser pulses towards a cold atom burst and a conventional inertial sensor attached to the inertial reference frame of the interferometric inertial sensor. The hybrid system includes a signal processing system suitable for receiving an inertial measurement signal from the conventional inertial sensor and for generating in real time a non-linear frequency modulation signal, the feedback loop electronic system being configured to modulate in real time the central optical frequency of the laser according to the modulation signal, such that the cold atom interferometric inertial sensor generates a first hybrid inertial measurement signal by atomic interferometry corrected for the relative movements of the inertial reference frame.
Owner:EXAIL +3
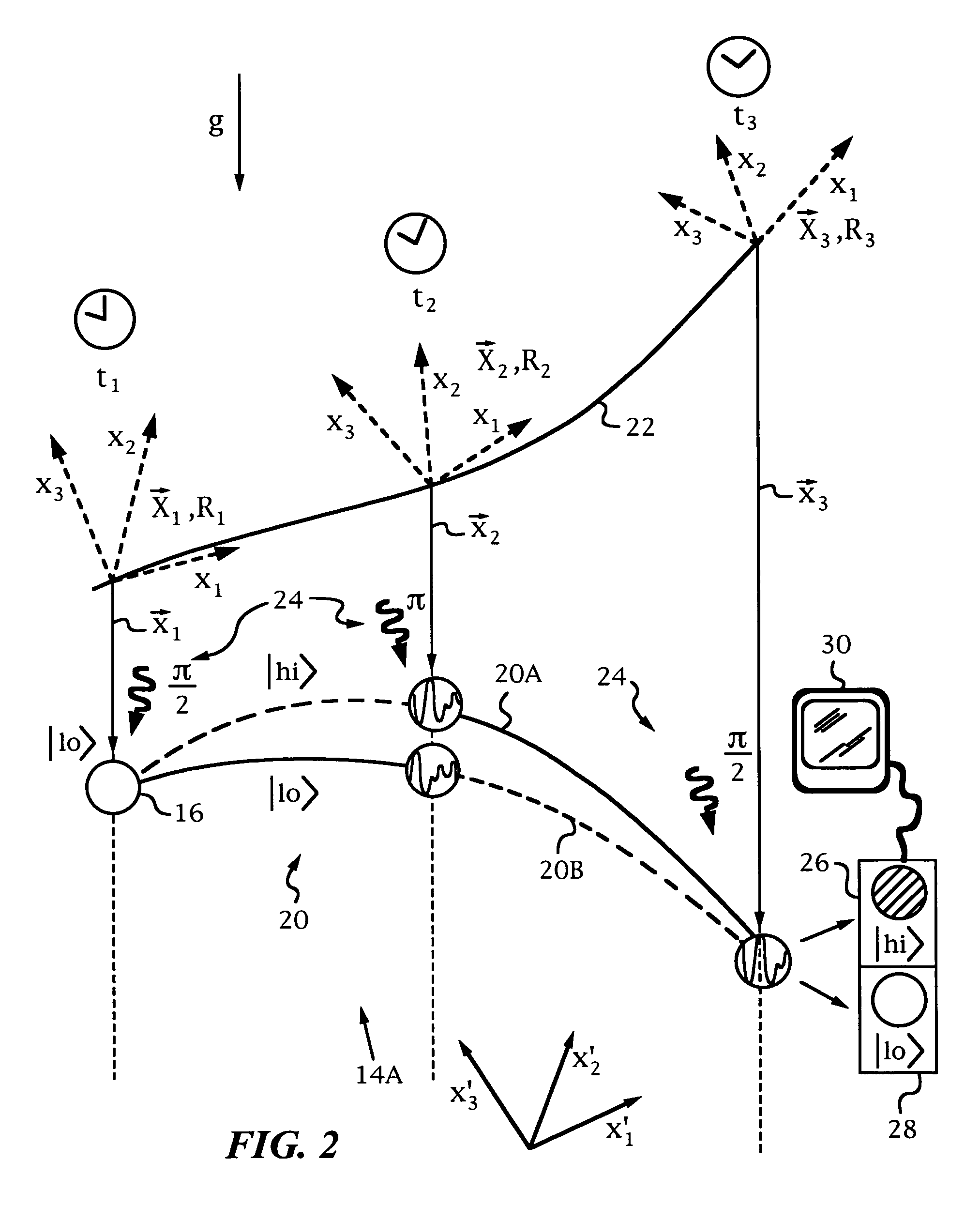
Kinematic sensors employing atom interferometer phases
An apparatus and method for determining the coordinates of a body, where the coordinates express the body's inertial or kinematic properties, including, for example, its trajectory. The apparatus and method employ atom interferometers provided in a body frame X of the body whose inertial or kinematic properties are to be studied. During operation, interfering entities used by the atom interferometers are released into a known frame X′, such as an inertial frame or the Earth frame Xe, that is decoupled from the body frame X and an optical pulse sequence is applied to the interfering entities to affect the quantum-mechanical matter-wave phases of the interfering entities as a function of the coordinates. Under these conditions, the coordinates of the body are determined from the phases of the atom interferometers and analytic expressions for the trajectories of the interfering entities under the simultaneous action of the gravity gradient, Coriolis and centrifugal forces.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
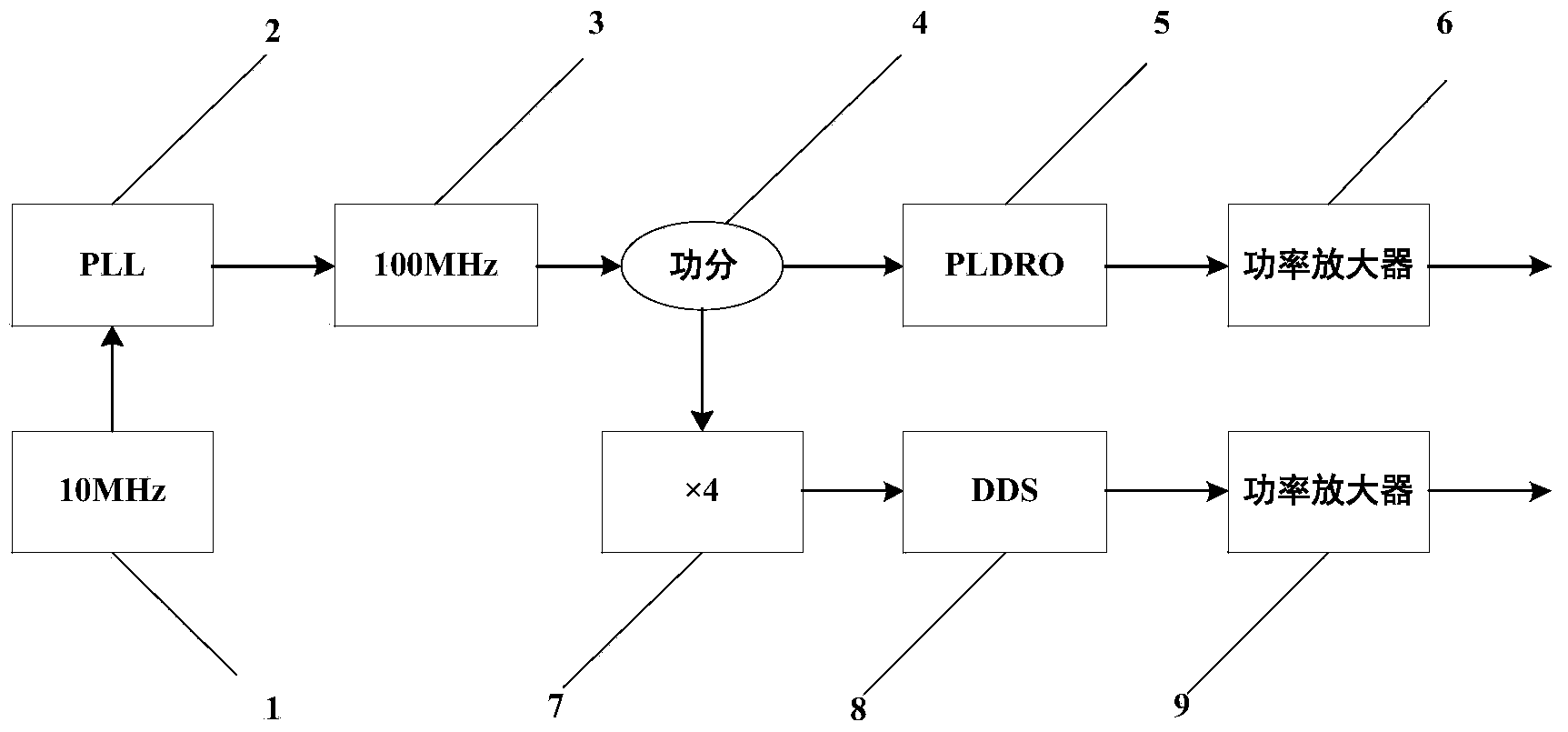
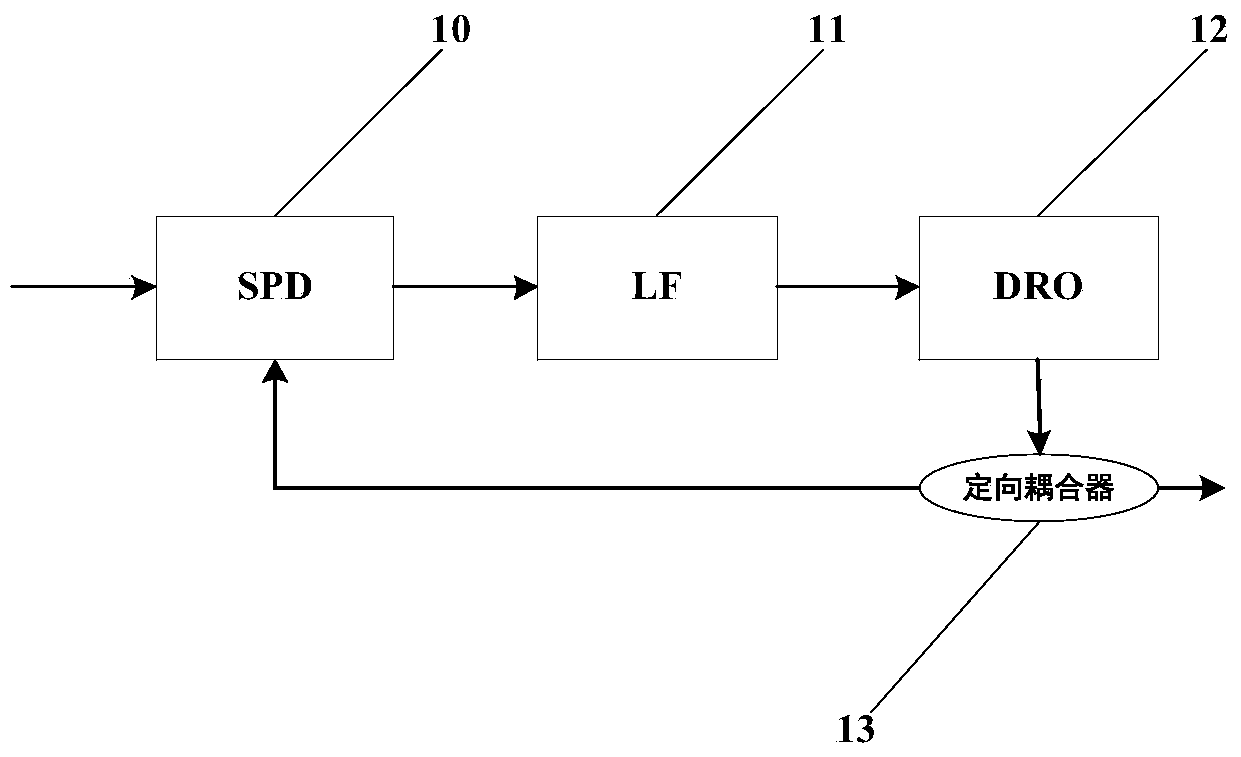
Microwave frequency source device for Raman laser system of atom interferometer
InactiveCN104378113AReduced Phase Noise DeteriorationReduce phase noisePulse automatic controlLow noisePhase noise
The invention discloses a microwave frequency source device for a Raman laser system of an atom interferometer. The microwave frequency source device comprises a constant-temperature crystal oscillator, a phase-locked loop (PLL), a voltage-controlled crystal oscillator, a power divider, a phase-locked medium oscillator, a first low-noise power amplifier, a quadrupler, a direct digital synthesizer (DDS) and a second low-noise power amplifier. The voltage-controlled crystal oscillator is locked to the ultralow-phase-noise constant-temperature crystal oscillator through the PLL and then divided into two paths through the power divider, one path undergoes frequency amplification through the phase-locked medium oscillator and power amplification through the first power amplifier, and the other path is processed by the quadrupler and then undergoes frequency conversion through the DDS and power amplification through the second power amplifier. By adopting the DDS and the sampling phase-locked medium oscillator, the phase noise of the Raman laser system is effectively lowered; by adopting the ultralow-phase-noise crystal oscillator to provide a reference signal, the size and the power consumption of a microwave frequency source are reduced, and the practicability and motility are improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Phase control for dual atom interferometers
A system for controlling a phase measurement in an atom interferometer comprising one or more lasers, a processor, and a memory. The one or more lasers are for providing interrogating beams. A first cloud of atoms and a second cloud of atoms traverse an interrogating region of the atom interferometer in substantially opposite directions. The interrogating beams interact substantially simultaneously with both atoms in the first cloud and atoms in the second cloud. The first cloud of atoms and the second cloud of atoms interact with each of the interrogating beams in a different order. The processor is configured to determine a phase adjustment offset of at least one interrogating beam based at least in part on one or more past interactions of one or more interrogating beams with either the first cloud of atoms or the second cloud of atoms.
Owner:AOSENSE
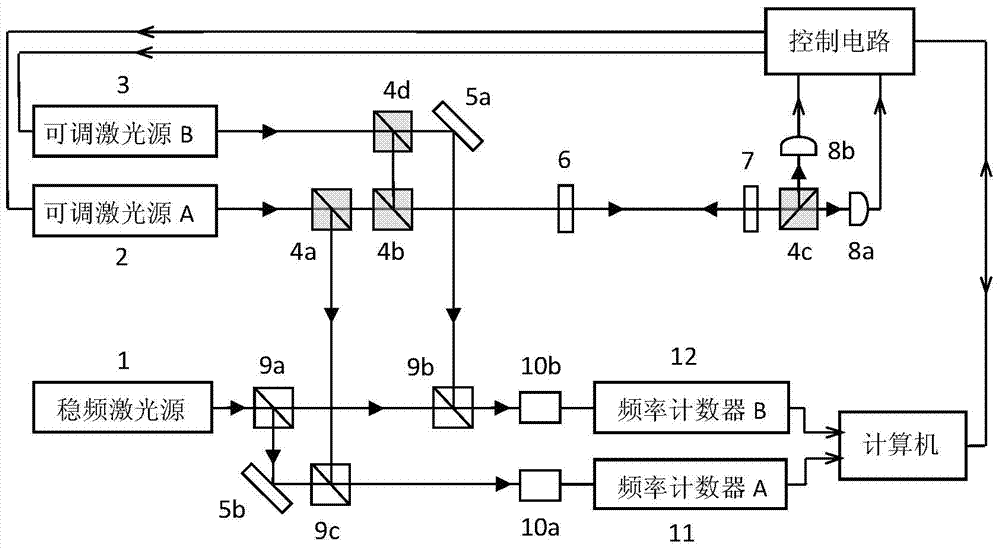
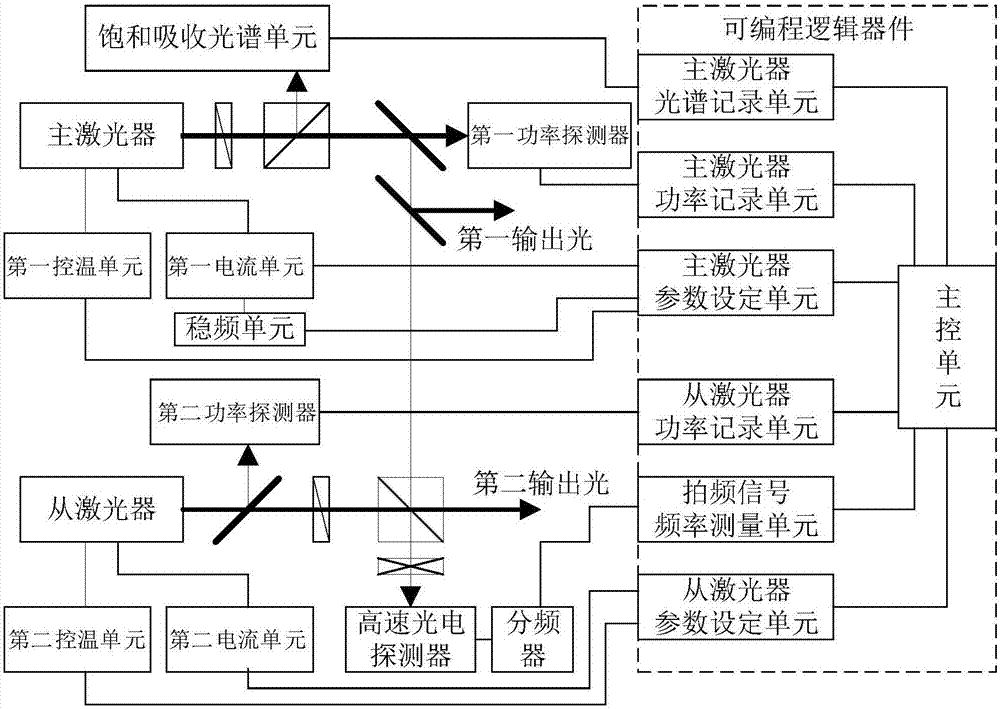
Control system and control method capable of automatically judging and setting laser frequency and power
The invention discloses a control system and a control method capable of automatically judging and setting a laser frequency and power. According to the invention, a double-laser structure is adopted; a main control unit can automatically search and automatically judge an output frequency of a main laser according to a spectrum signal, and automatically locks the frequency onto an atom or molecule spectral line after automatically optimizing an output power of the main laser to a target power; after outputs of a slave laser and the main laser are subjected to beam combination, a beat frequency signal is generated, and the main control unit can automatically judge a size relationship of the output frequencies of the main laser and the slave laser so as to accurately and automatically judge the output frequency of the slave laser, after the output power of the slave laser is automatically optimized to the target power, a frequency locking error signal is generated by utilizing the main control unit, and in a range of 80GHz, locking on the frequency of the slave laser is implemented; and the method disclosed by the invention can be widely applied to the technical fields of fundamental researches and precision measurement of laser cooling, atomic frequency standards, an atom interferometer, a laser wavelength meter and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
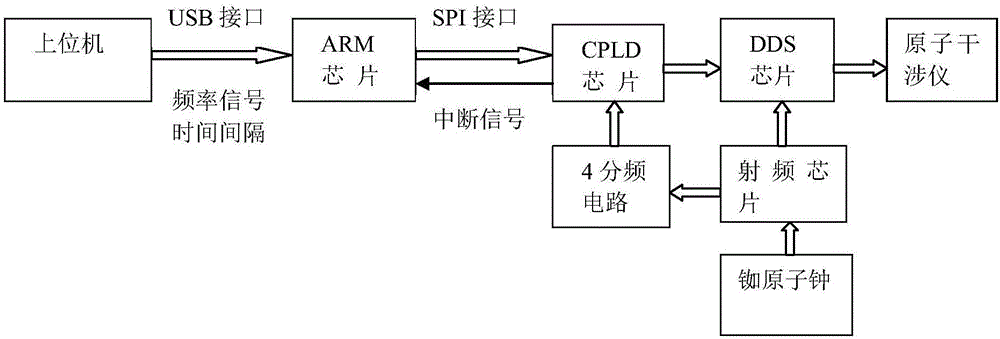
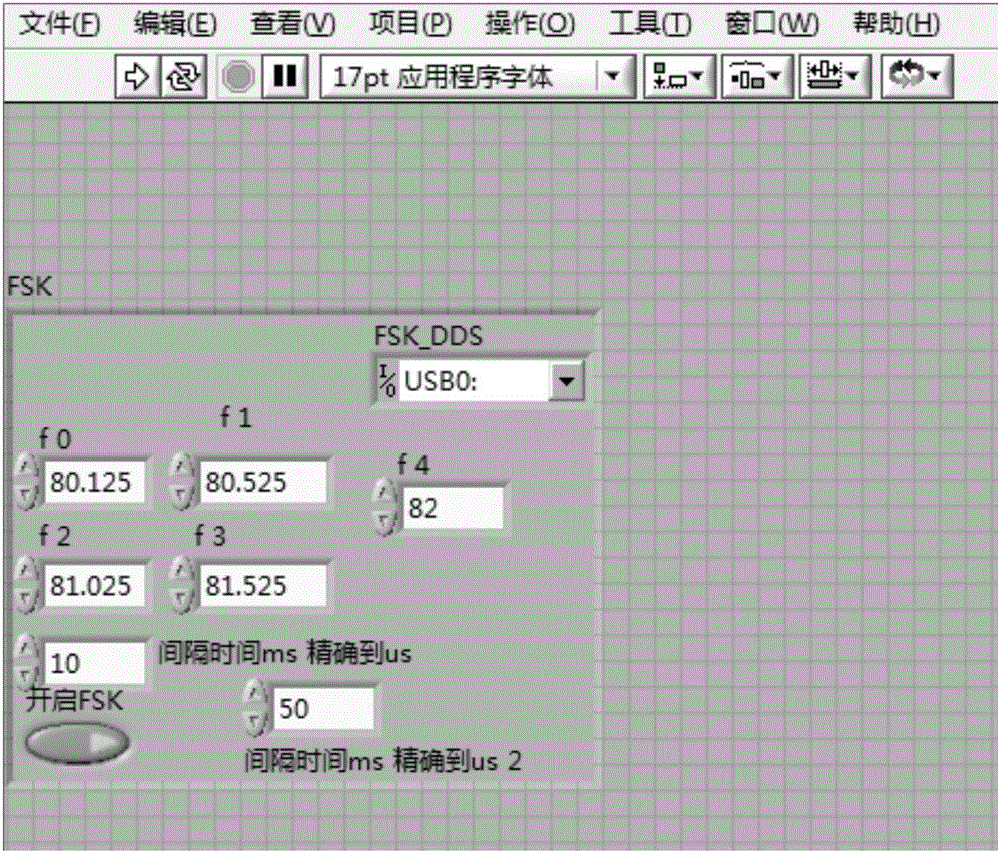
DDS (Direct Digital Frequency Synthesizer) frequency hopping device used for laser time sequence control of cold atom interferometer
ActiveCN106647926AIncrease phase noise levelAvoid the effects of timing controlDigital function generatorsPhase noiseRubidium
The invention relates to a DDS (Direct Digital Frequency Synthesizer) frequency hopping device used for the laser time sequence control of a cold atom interferometer. The device comprises an upper computer with a LABVIEW control program, an ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) chip, a CPLD (Complex Programmable Logic Device) chip, a rubydium atomic clock, a radio frequency chip and a DDS chip. The setting of frequencies required for the atomic velocity selection and the microwave frequency mixing of the cold atom interferometer as well as for an atomic wave packet to carry out beam splitting, inversion and beam combination under a function of a [Pi] / 2-[Pi]-[Pi] / 2 Raman pulse sequence can be realized. The device adopts the following methods that the rubidium atomic clock is used for replacing a common quartz crystal oscillator, and the reference crystal oscillator of the complex programmable logic device chip and the reference crystal oscillator of the DDS chip use the same radio frequency source. Compared with a traditional DDS frequency hopping device, the device disclosed by the invention is characterized in that the setting of the frequencies of different hopping frequencies and frequency time intervals can be realized, and the device exhibits a higher phase noise level and higher phase continuity on an aspect of output frequency switching.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
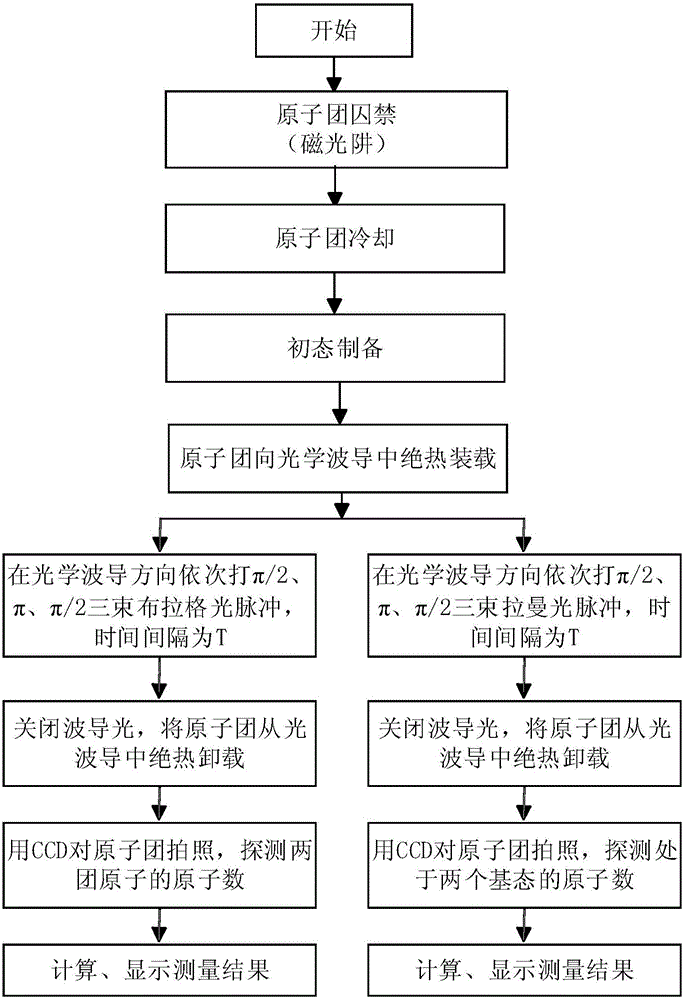
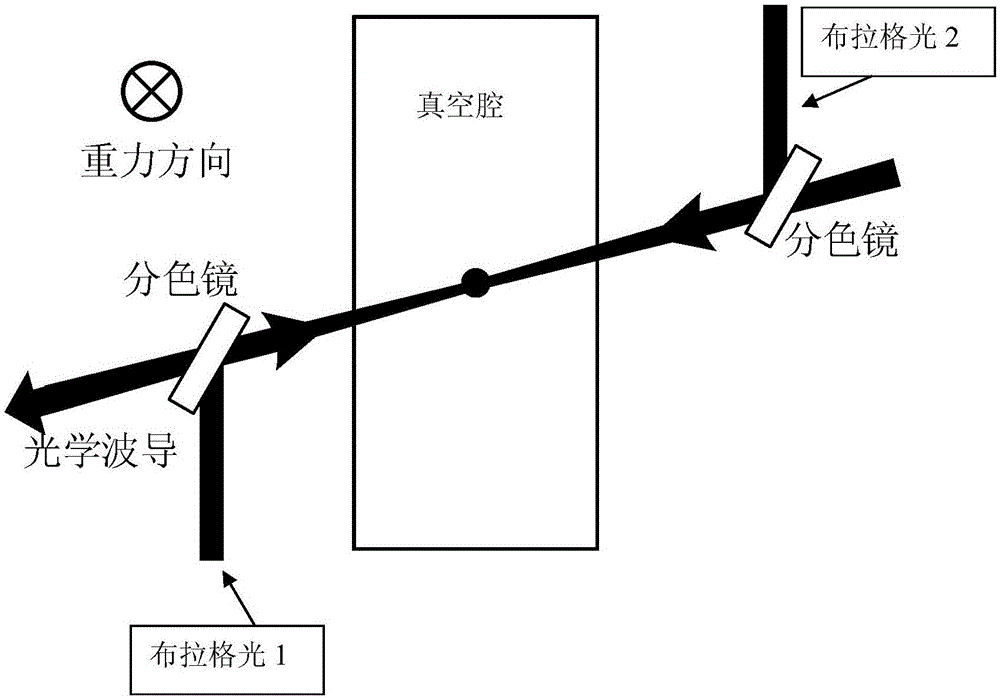
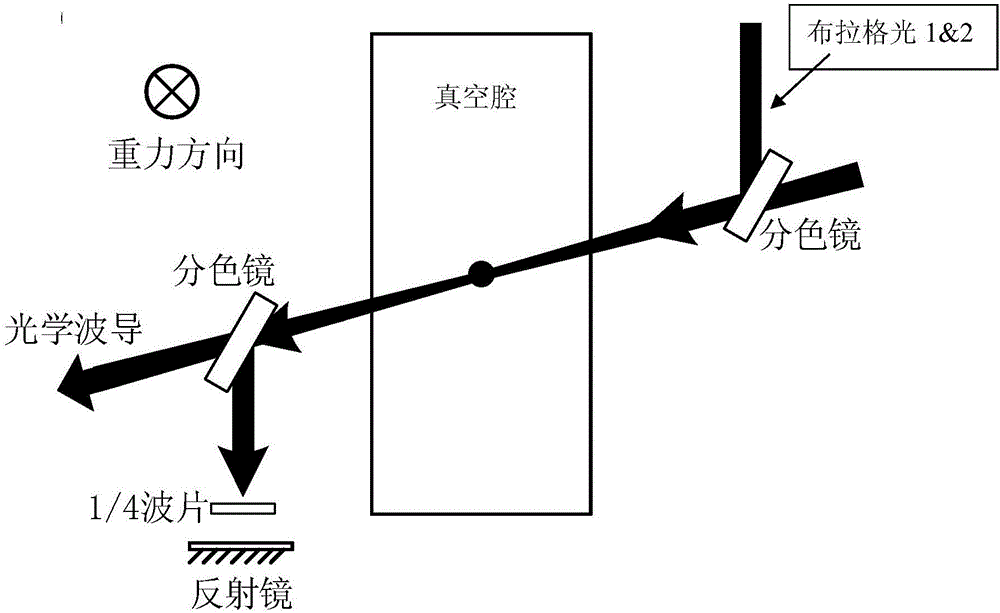
Acceleration measurement method and device based on atomic interference in optical waveguide
InactiveCN107525946AChange direction at willReduce measurement errorAcceleration measurement using interia forcesBeam splittingAtomic group
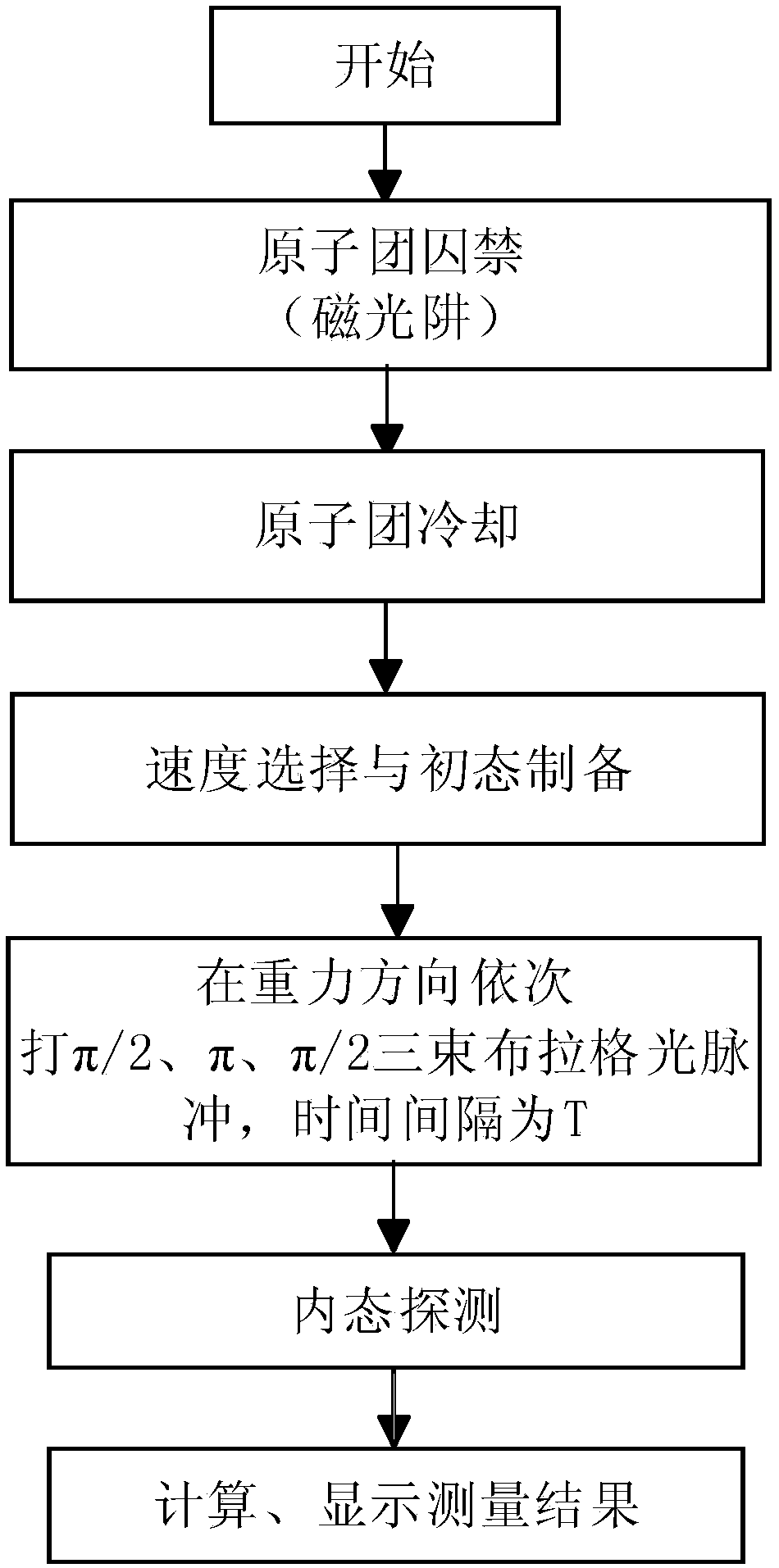
The invention discloses an acceleration measurement method based on atomic interference in an optical waveguide, which includes the following steps: S1, preparing a cold atomic group; S2, loading an optical waveguide: keeping the atomic group in a magnetic insensitive state, opening the optical waveguide, and putting the atomic group in the optical waveguide; S3, atomic interference: applying PI / 2, PI and PI / 2 light pulses to the atomic group through two beams of Raman light or Prague light to realize beam splitting and combining of the atomic group, and constructing an atom interferometer; and S4, imaging detection: after interference, letting the atomic group freely fall for a period of time, carrying out detection through CCD or PD, and calculating the axial acceleration of the optical waveguide according to the detection result. The method and the device have the advantages of simple principle, simple operation, high accuracy, and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Performance of an atom interferometric device through complementary filtering
InactiveUS7847924B2Wide bandwidthEliminate delaysAcceleration measurement using interia forcesUsing optical meansGyroscopeAccelerometer
A technique is disclosed which offers an improvement in the performance of an atom interferometric (AI) sensor, such as one that is used in an accelerometer or a gyroscope. The improvement is based on the recognition that the AI-based device, which is associated with superior low-frequency performance, can be augmented with a conventional device having a superior high-frequency performance, as well as a wider frequency response, compared with that of the AI-based device. The disclosed technique combines acceleration measurements from the AI-based device, which is characterized by transfer function G(s), with acceleration measurements from the conventional device that have been adjusted by a complementary function, 1−Ĝ(s), where Ĝ(s) is an approximation of G(s). The conventional device has a considerably wider bandwidth than that of the AI-based device, and the quasi-unity transfer function of the conventional device makes possible the 1−Ĝ(s) adjustment of the measurements provided by the conventional device.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method and device for measuring gravity gradient of pyramid-like atomic interference based on two-dimensional cross gratings
ActiveCN108169804AConsistency is easy to guaranteeHigh measurement sensitivityGravitational wave measurementGratingAtomic group
A method and a device for measuring the gravity gradient of pyramid-like atomic interference based on two-dimensional cross gratings are provided. The method comprises the following steps: S1, preparation of a cold atomic group: a cold atomic group is obtained through pre-stage cooling; S2, velocity selection and state preparation: the temperature of the atomic group further decreases through Raman velocity selection, and a state is prepared on a magnetically insensitive state |F=1, mF=0>; S3, atomic interference: PI / 2, PI and PI / 2 light pulses are applied to the atomic group through two beamsof Raman light to realize the splitting and combining of the atomic group, and an atomic interferometer is constructed; and S4, internal state detection: after interference, the atomic group falls freely for a period of time, the number of atomic populations at a hyperfine energy level in two ground states is measured through the effect of probe light, pump light and astigmatic light, and the transition probability and the gravity acceleration value are finally obtained. The device is used to implement the method. The method and the device have the advantages of small overall size, strong robustness, low cost, high measuring accuracy, and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Phase control for dual atom interferometers
A system for controlling a phase measurement in an atom interferometer comprising one or more lasers, a processor, and a memory. The one or more lasers are for providing interrogating beams. A first cloud of atoms and a second cloud of atoms traverse an interrogating region of the atom interferometer in substantially opposite directions. The interrogating beams interact substantially simultaneously with both atoms in the first cloud and atoms in the second cloud. The first cloud of atoms and the second cloud of atoms interact with each of the interrogating beams in a different order. The processor is configured to determine a phase adjustment offset of at least one interrogating beam based at least in part on one or more past interactions of one or more interrogating beams with either the first cloud of atoms or the second cloud of atoms.
Owner:AOSENSE
Integrated optical system for atom interferometers
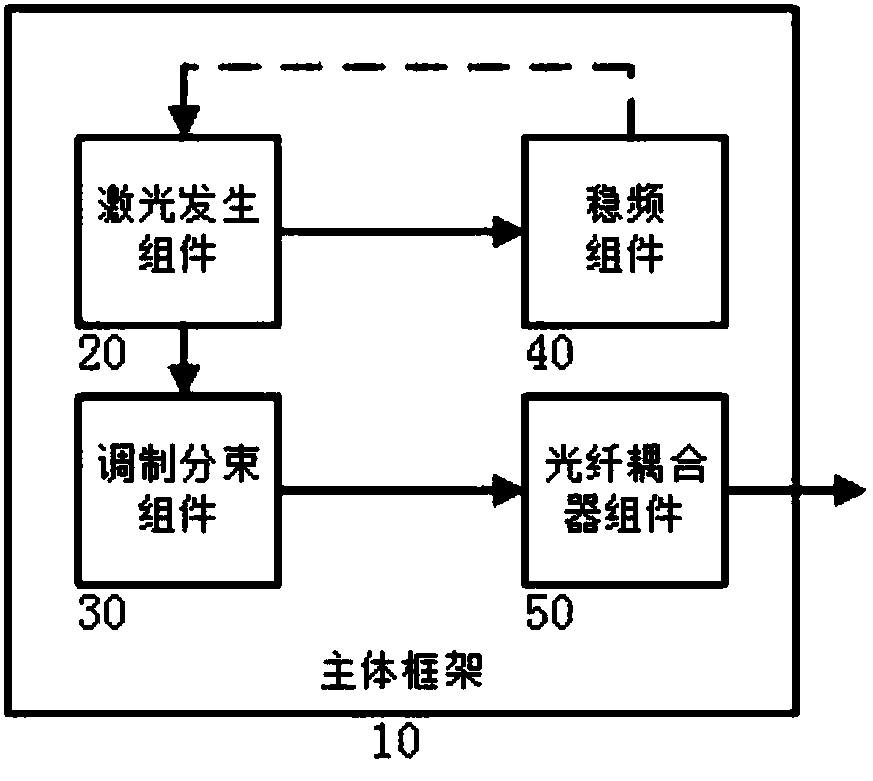
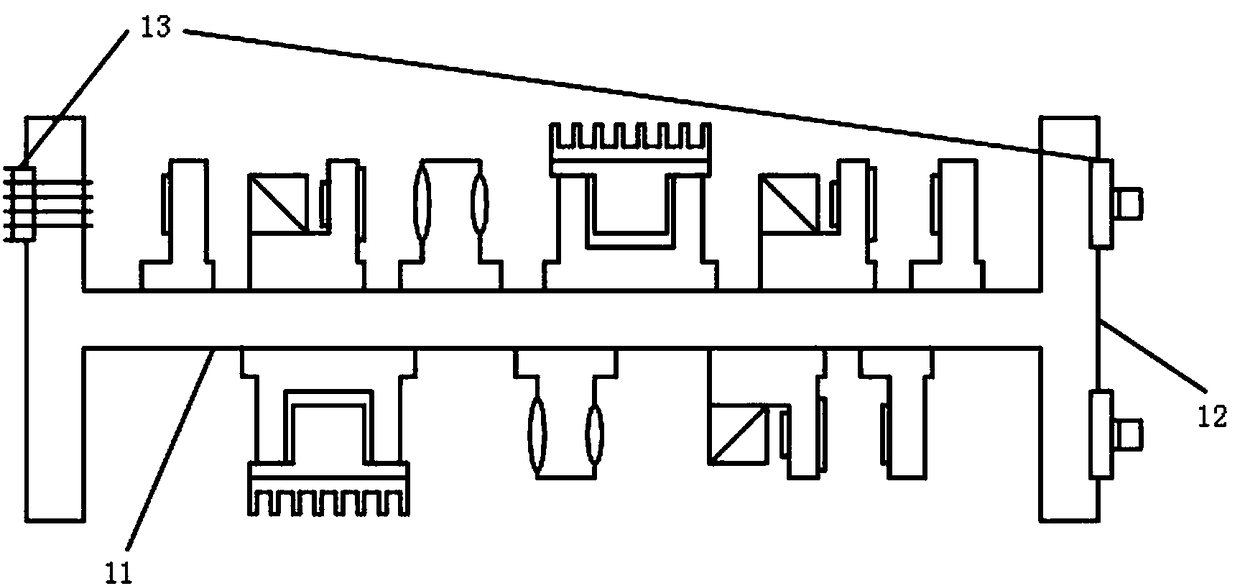
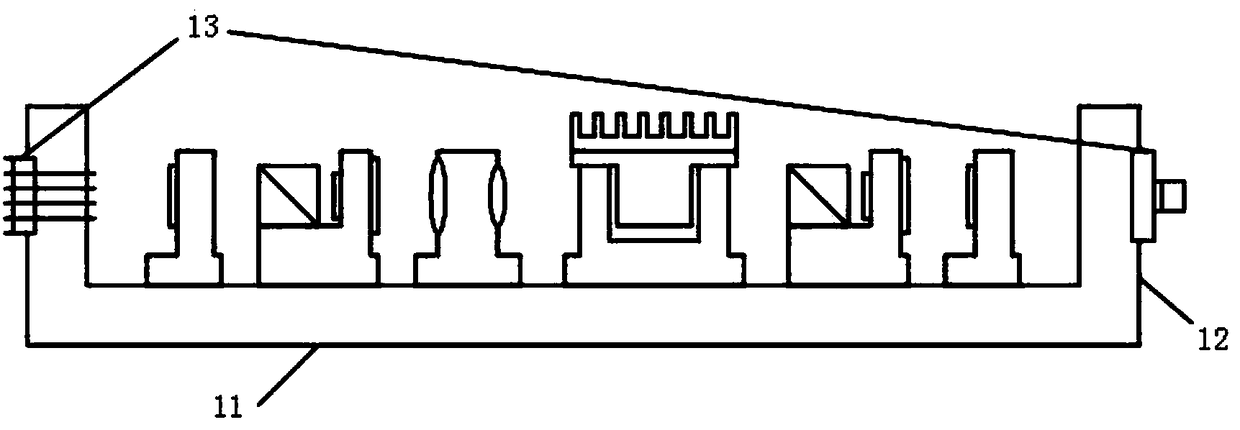
PendingCN108592783AReduce the temperatureImprove thermal stabilityUsing optical meansBeam splittingClosed loop
The invention discloses an integrated optical system for atom interferometers, and belongs to the technical field of precision measurement based on the atom interferometers. The system comprises a main body frame (10), a laser generation component (20), a modulating and beam splitting component (30), a frequency stabilizing component (40) and an optical fiber coupler component (50). The laser generation component (20), the modulating and beam splitting component (30), the frequency stabilizing component (40) and the optical fiber coupler component (50) are arranged on the main body frame (10).The laser generation component (20), the modulating and beam splitting component (30) and the optical fiber coupler component (50) interact with one another sequentially. The laser generation component (20) and the frequency stabilizing component (40) are in closed-loop interaction. The integrated optical system has the advantages that conflicts between functional needs and integration and between the functional needs and stability in existing atom interferometers are solved, and the problem of lack of measures to remotely adjust the light intensity proportion of double-frequency components,which form Raman light, in existing atom interferometer optical systems is also solved.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Light pulse atom interferometer velocity reference
ActiveUS10330459B1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesUsing optical meansLaser beamsAtomic physics
A light pulse interferometer includes a first atom source and a first laser. The first atom source is configured to direct a first group of atoms in a first direction. The first laser is configured to generate one or more interferometer laser beam pairs. The one or more interferometer laser beam pairs interact with the first group of atoms in an interferometer sequence of three or more pulses to produce atom interference. A first laser beam pair of the one or more interferometer laser beam pairs is disposed to interact with the first group of atoms to perform 1D-cooling and velocity control of the first group of atoms prior to the interferometer sequence.
Owner:AOSENSE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com