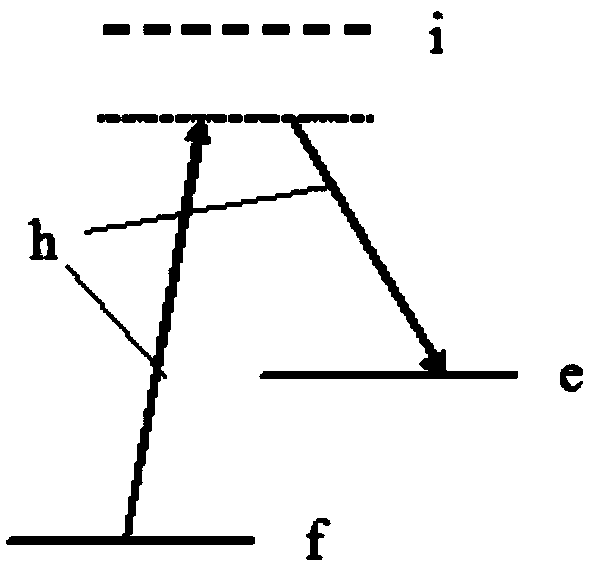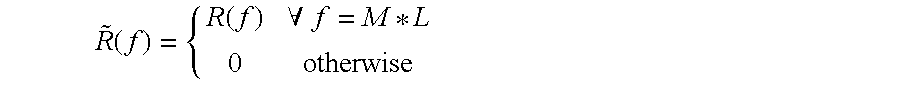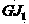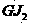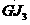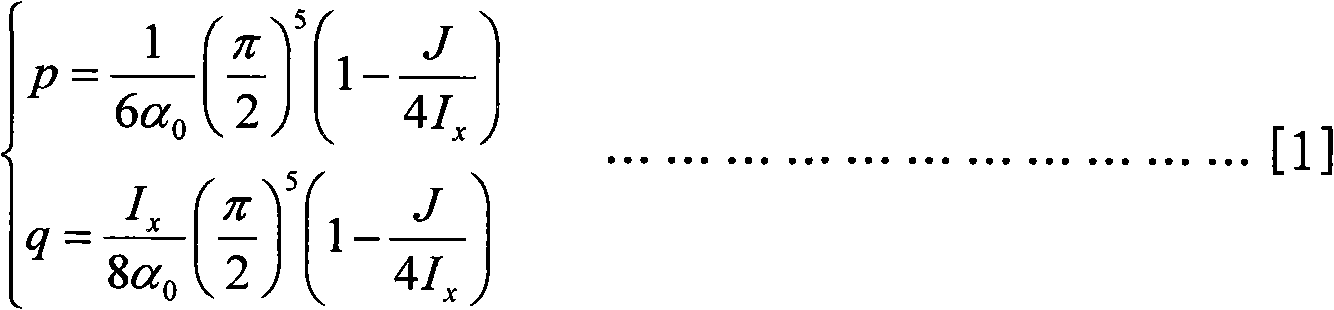Patents
Literature
240 results about "Inertial moment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
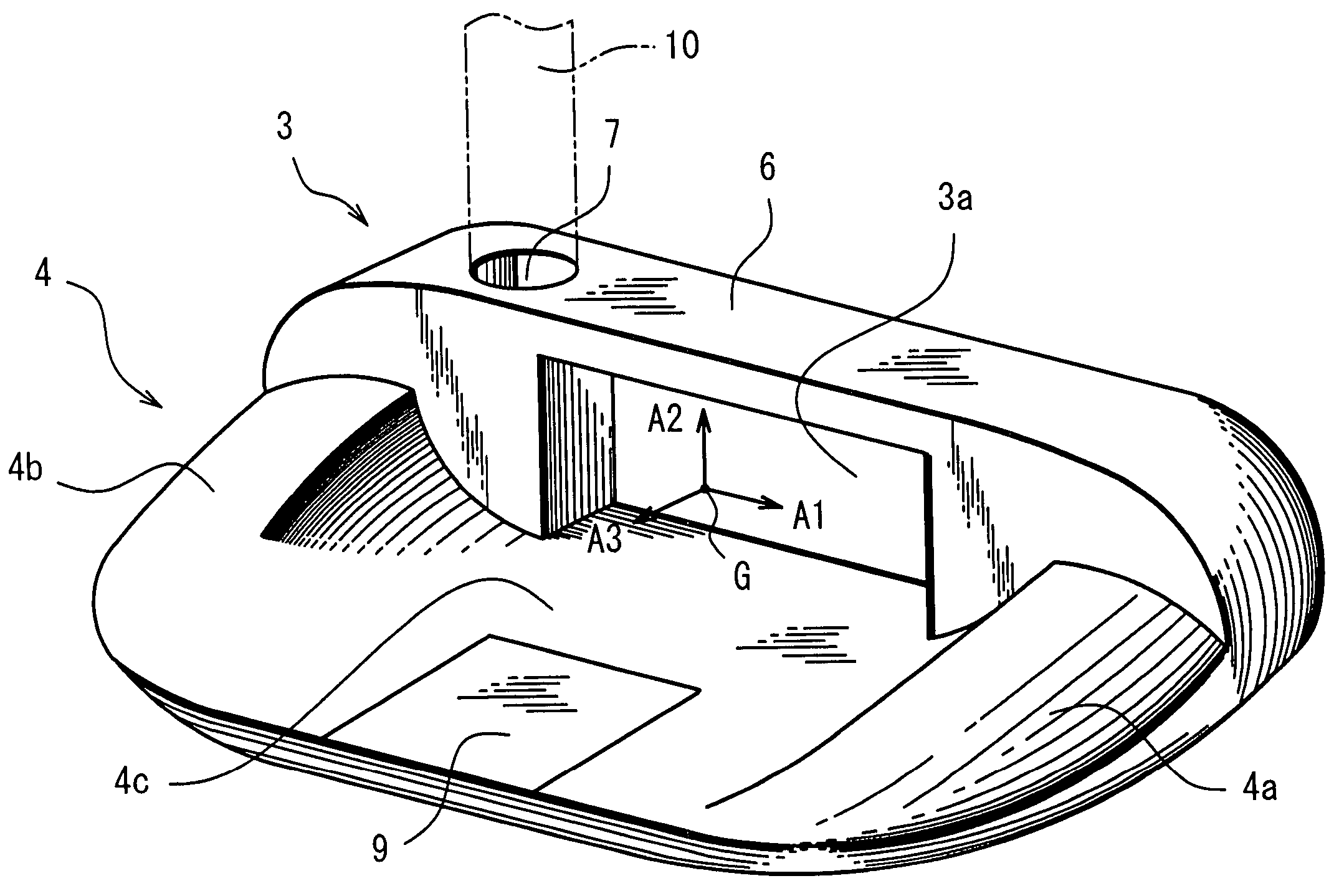
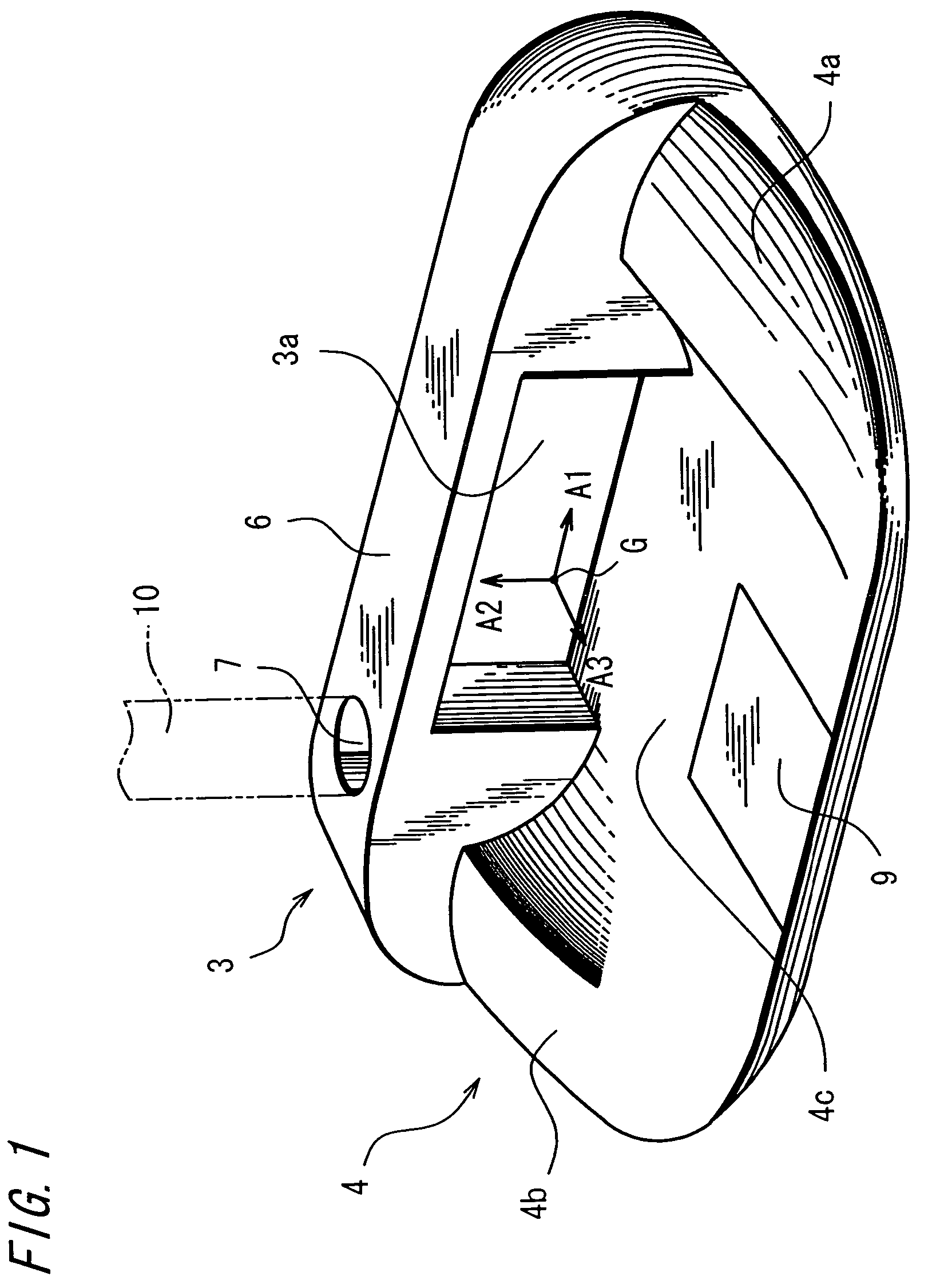
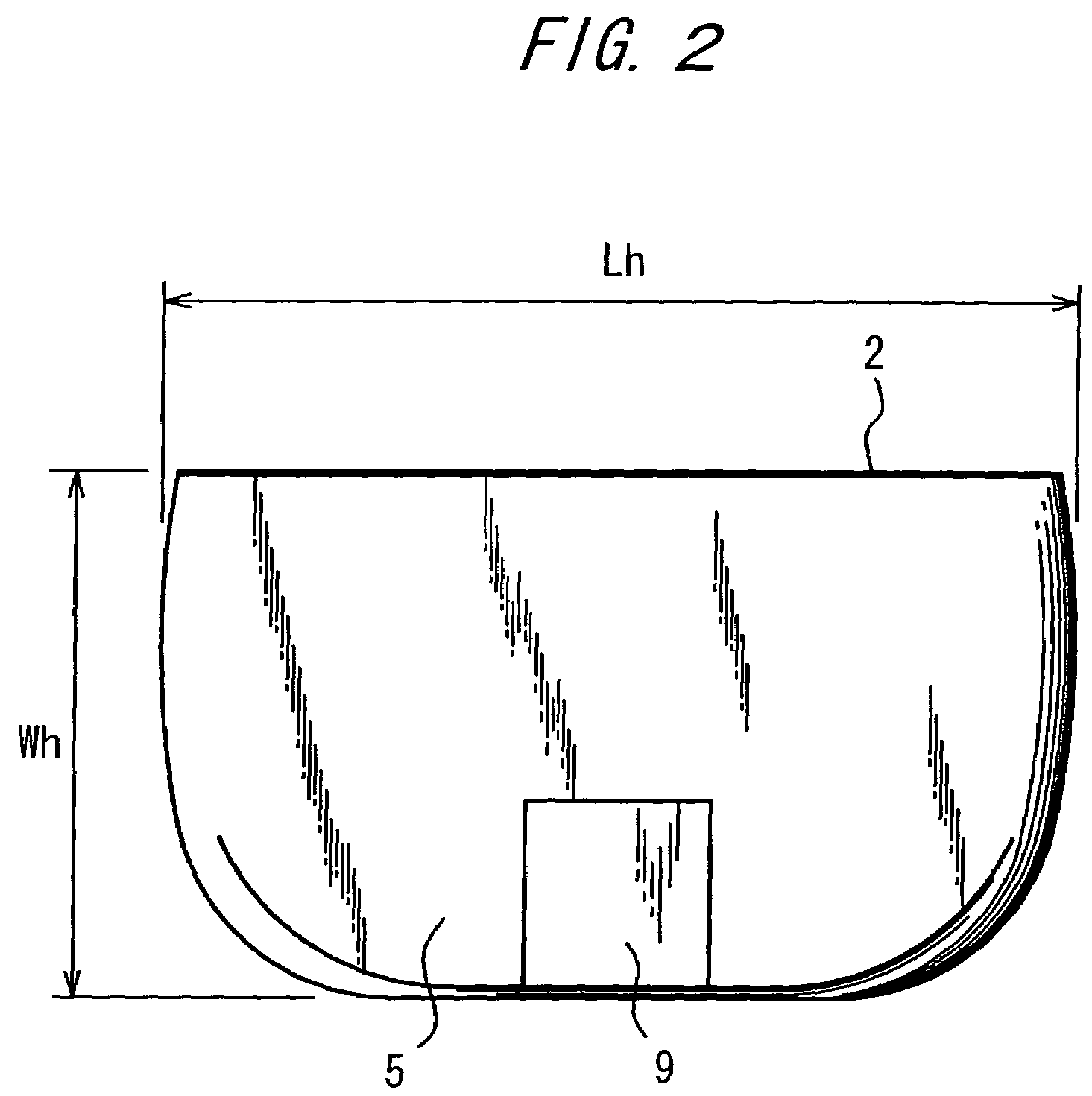
Moment of inertia is the name given to rotational inertia, the rotational analog of mass for linear motion. It appears in the relationships for the dynamics of rotational motion. The moment of inertia must be specified with respect to a chosen axis of rotation.
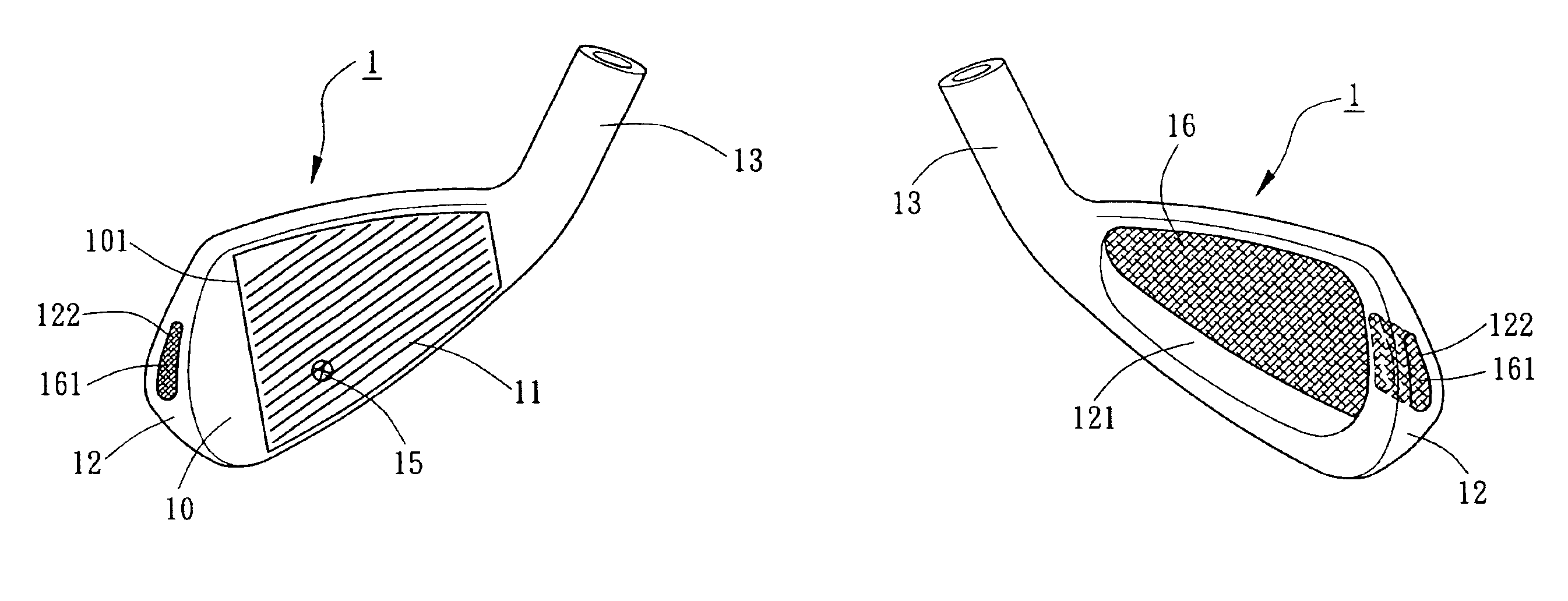
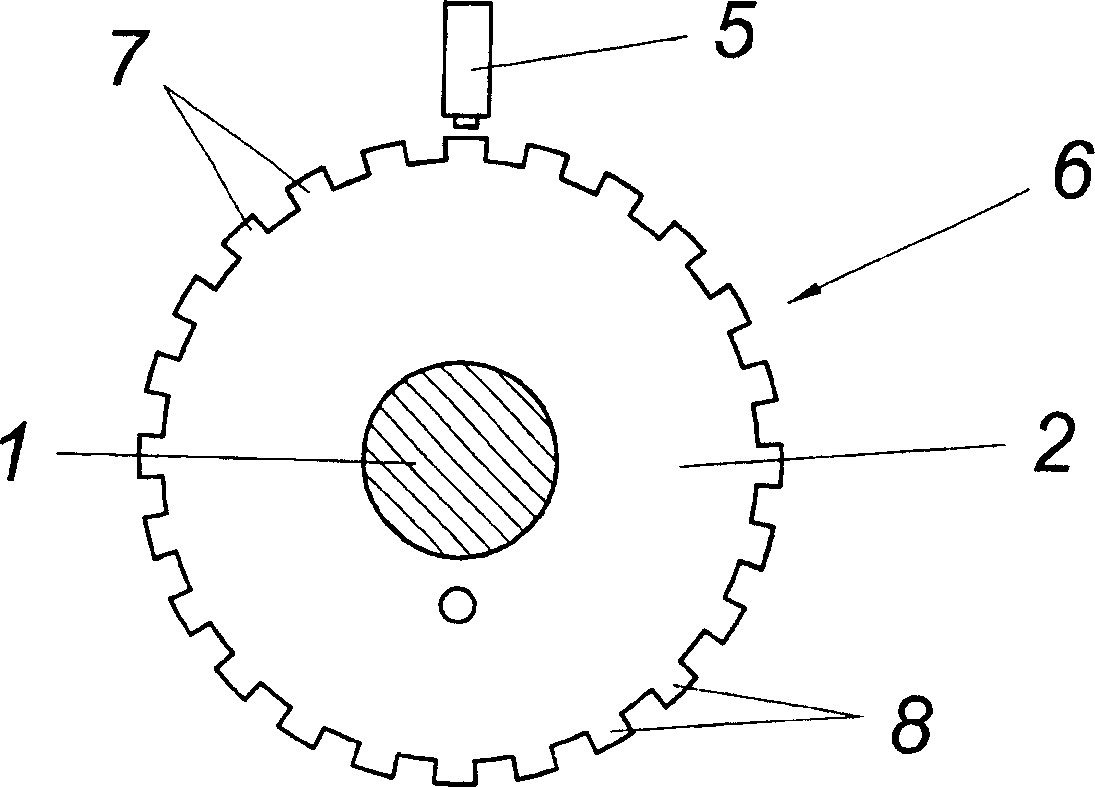
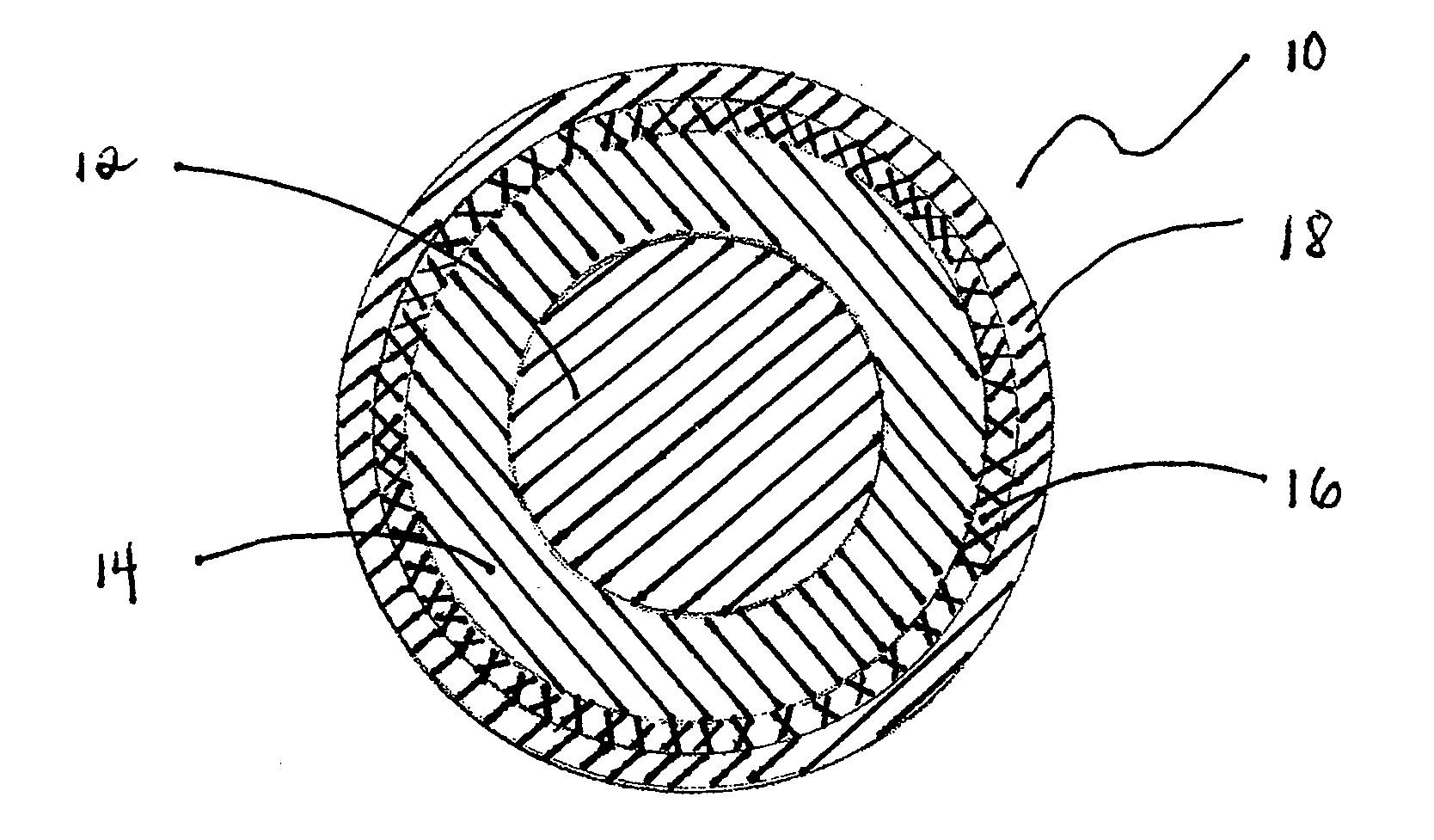
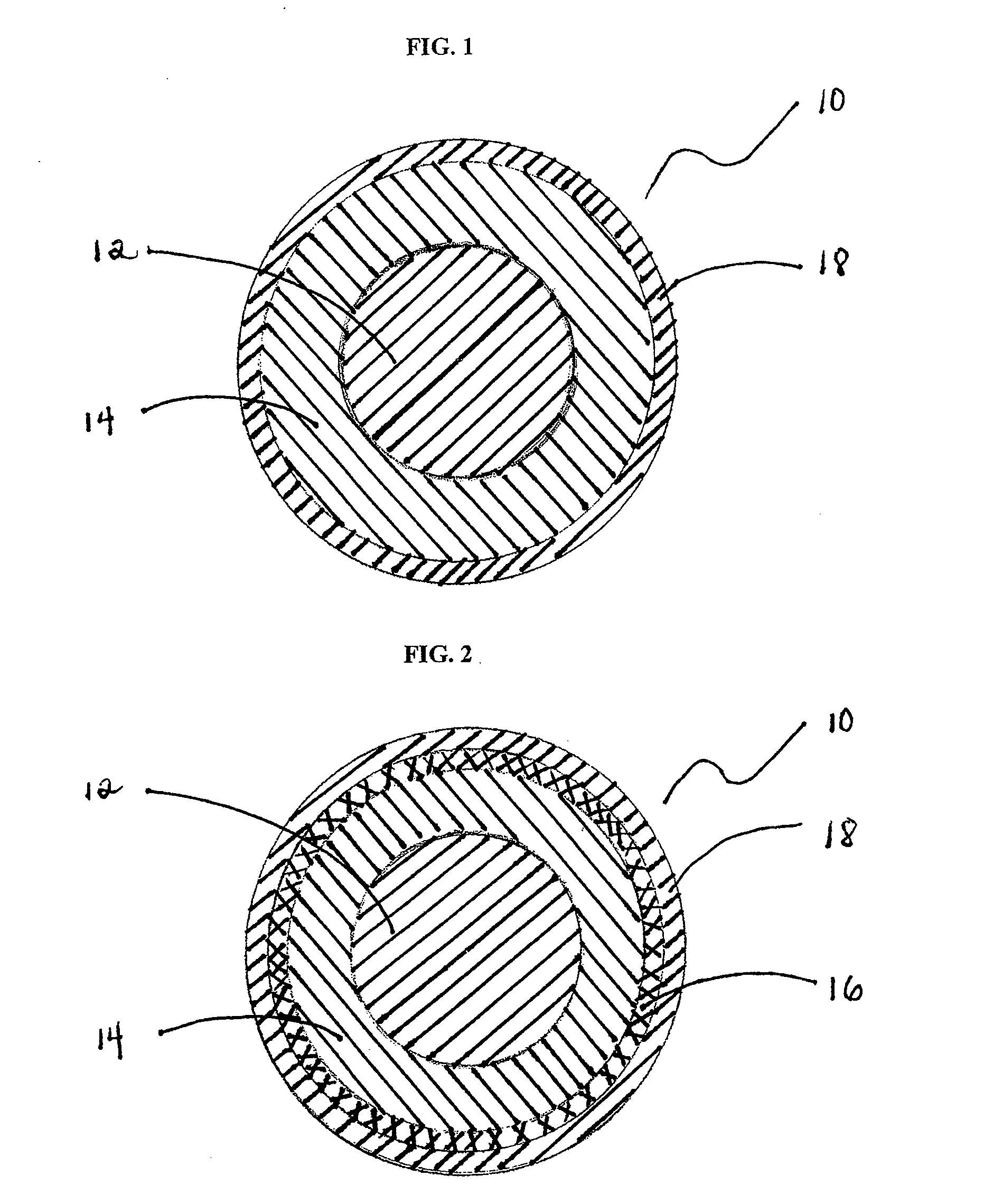
Golf club head with peripheral weighting
InactiveUS6890267B2Increase moment of inertiaVariable distributionOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWound drainsMoment of inertiaGolf Ball
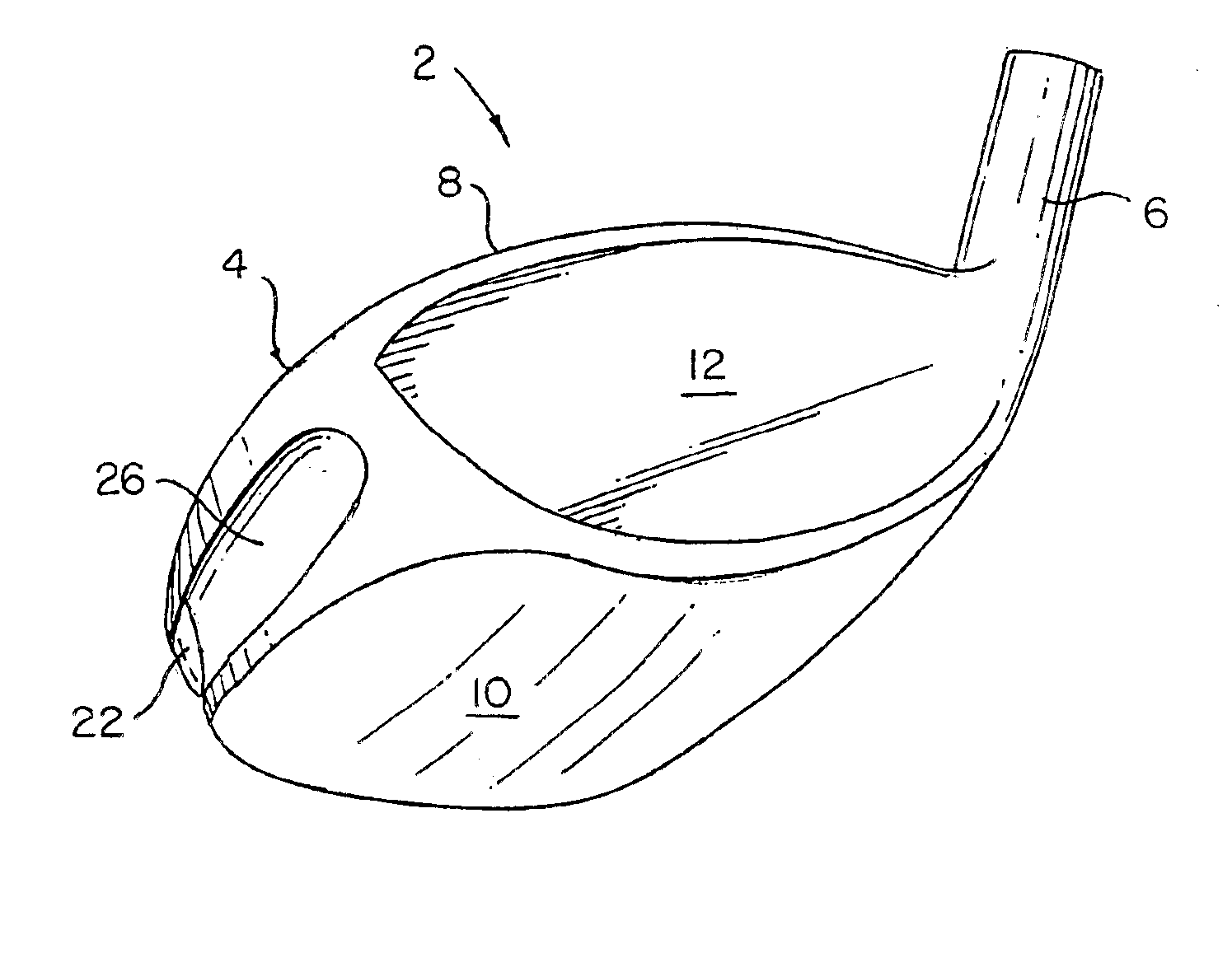
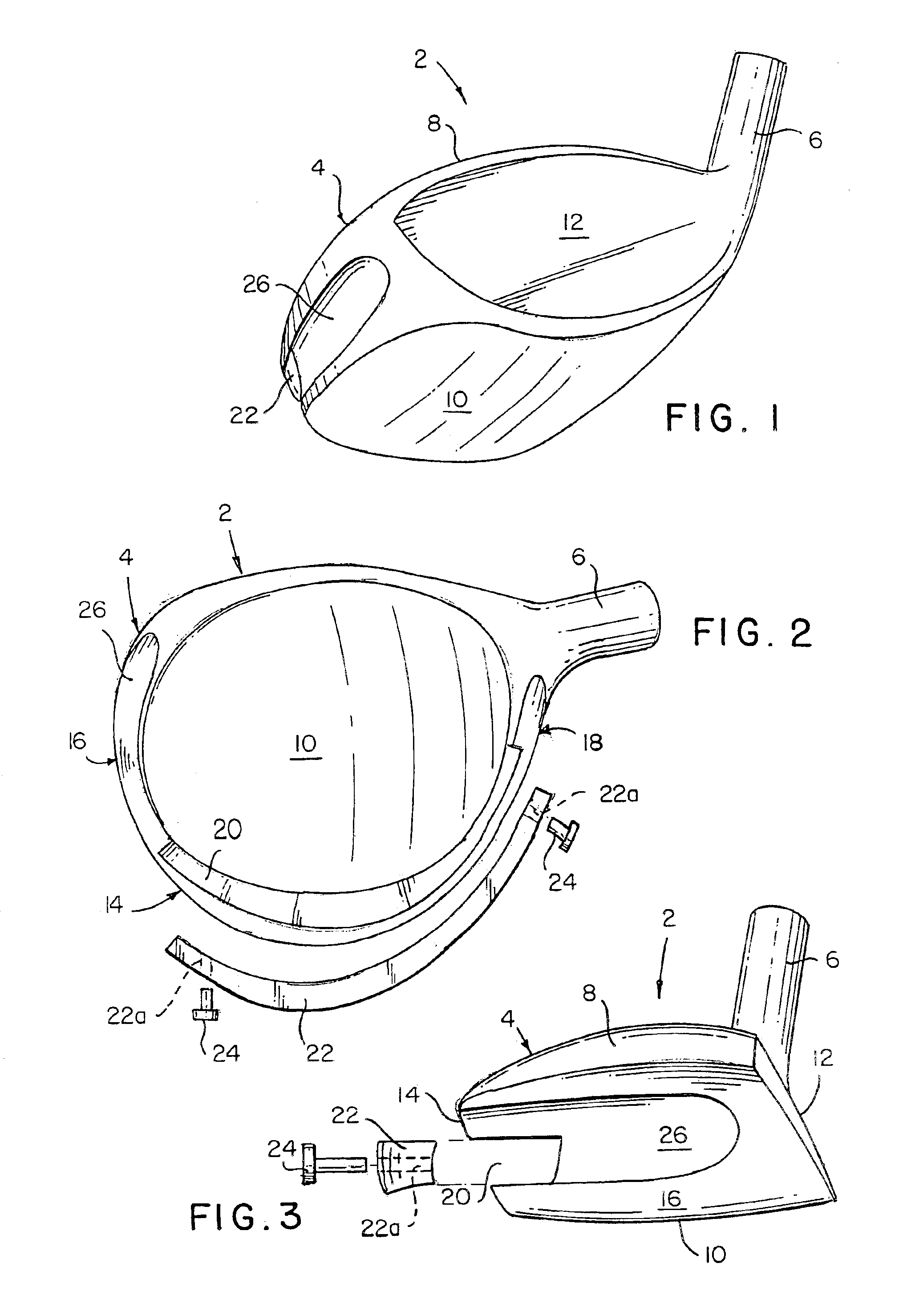
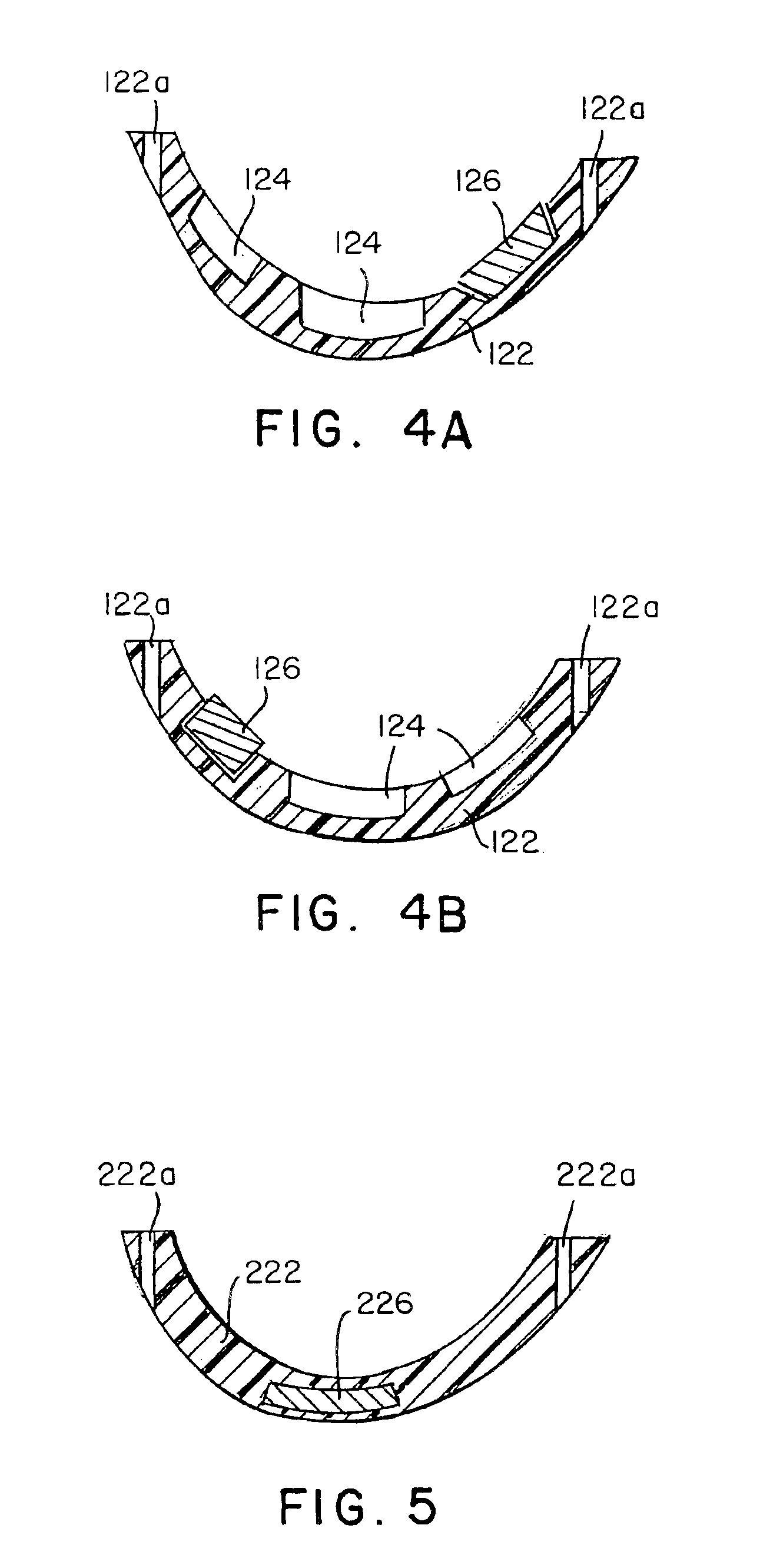
A golf club head with low peripheral and rearward weighting includes C-shaped and annular weights connected with at least one of the rear and bottom surfaces, respectively, of the head. The weighting within the peripheral weights is adjustable between the heel, rear, and toe portions of the head to customize the weight distribution of the head in accordance with a golfer's swing. The added weight and its orientation increases the moment of inertia of the head and reduces the rotation thereof.
Owner:THE TOP FLITE GOLF
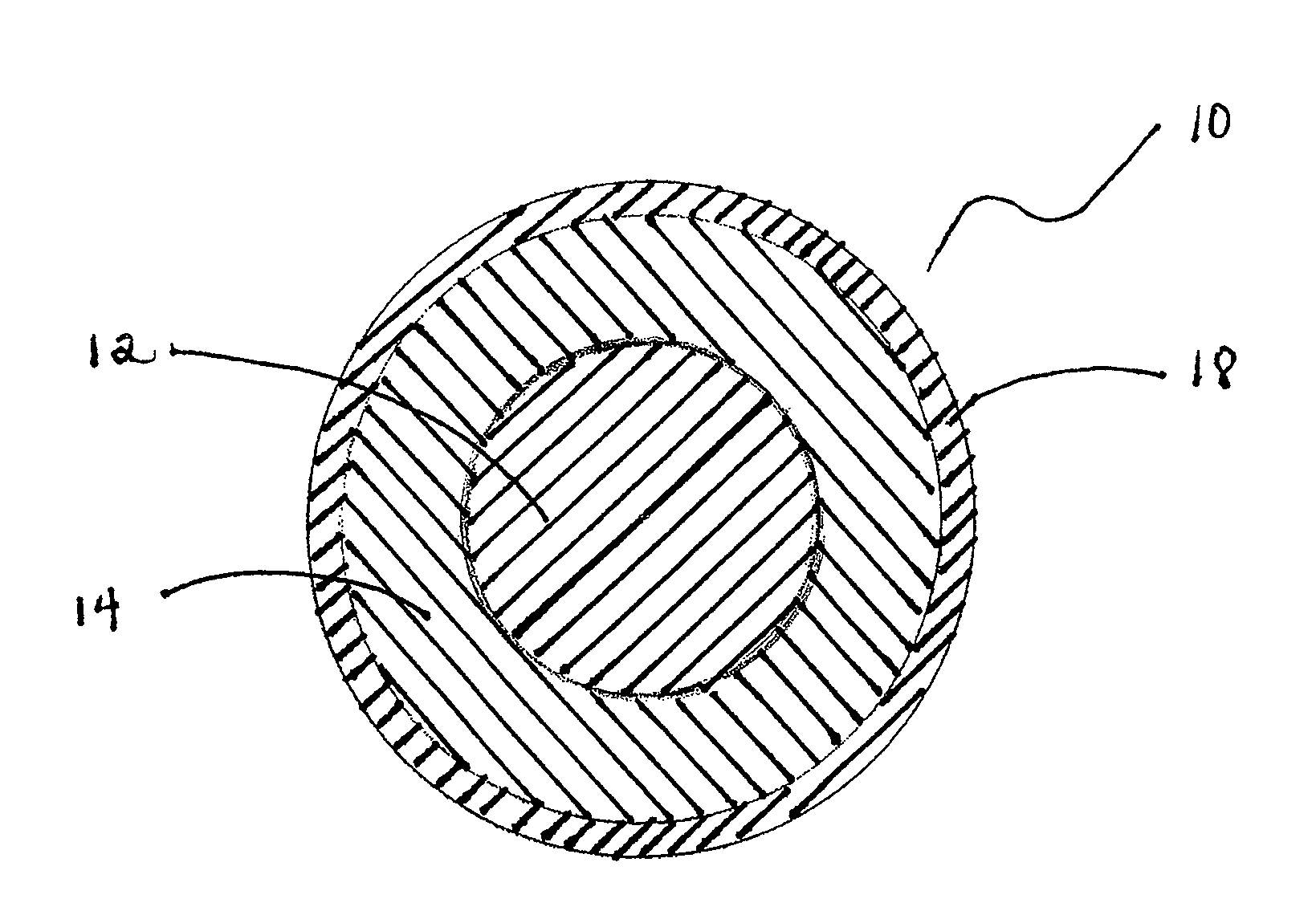
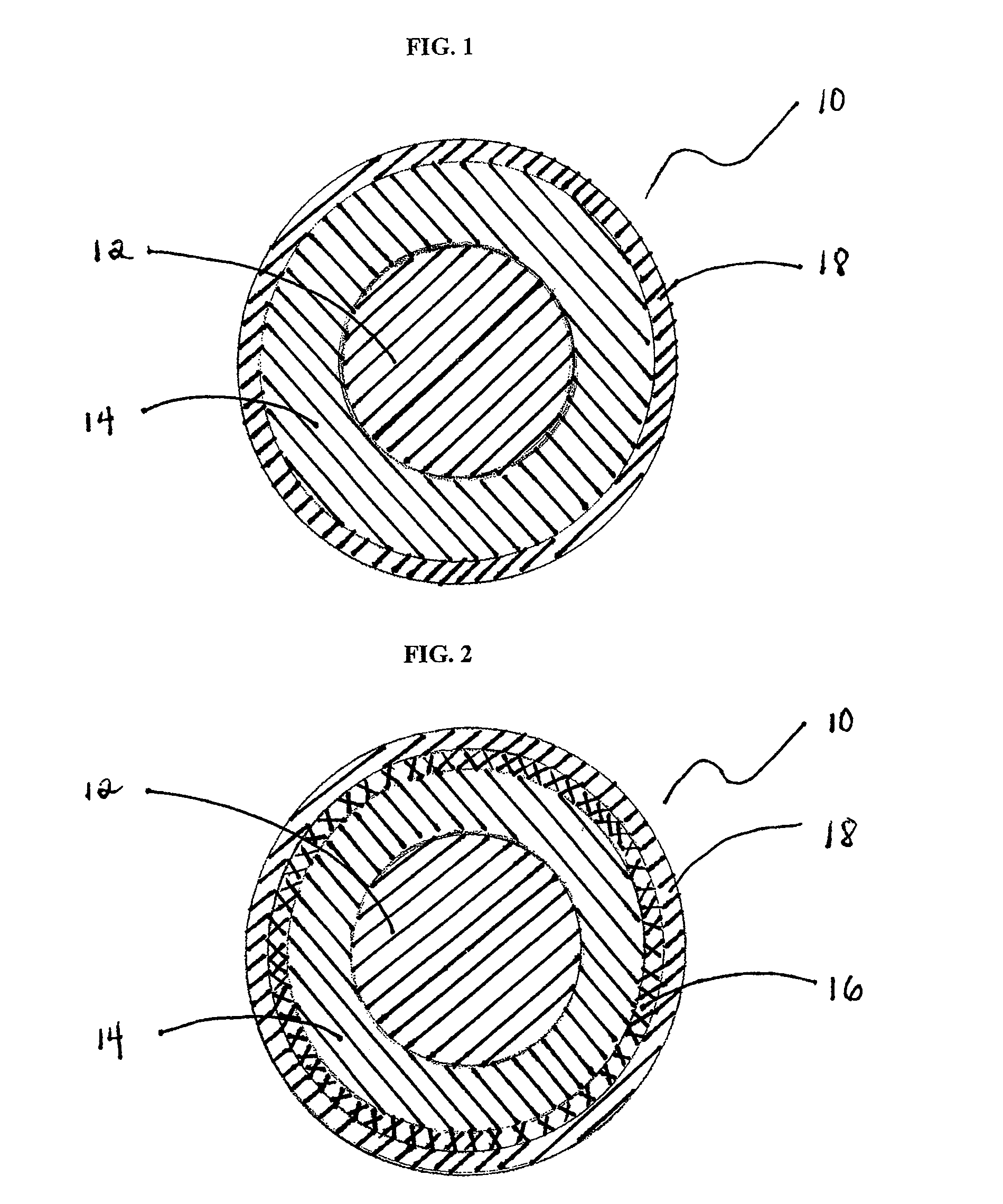
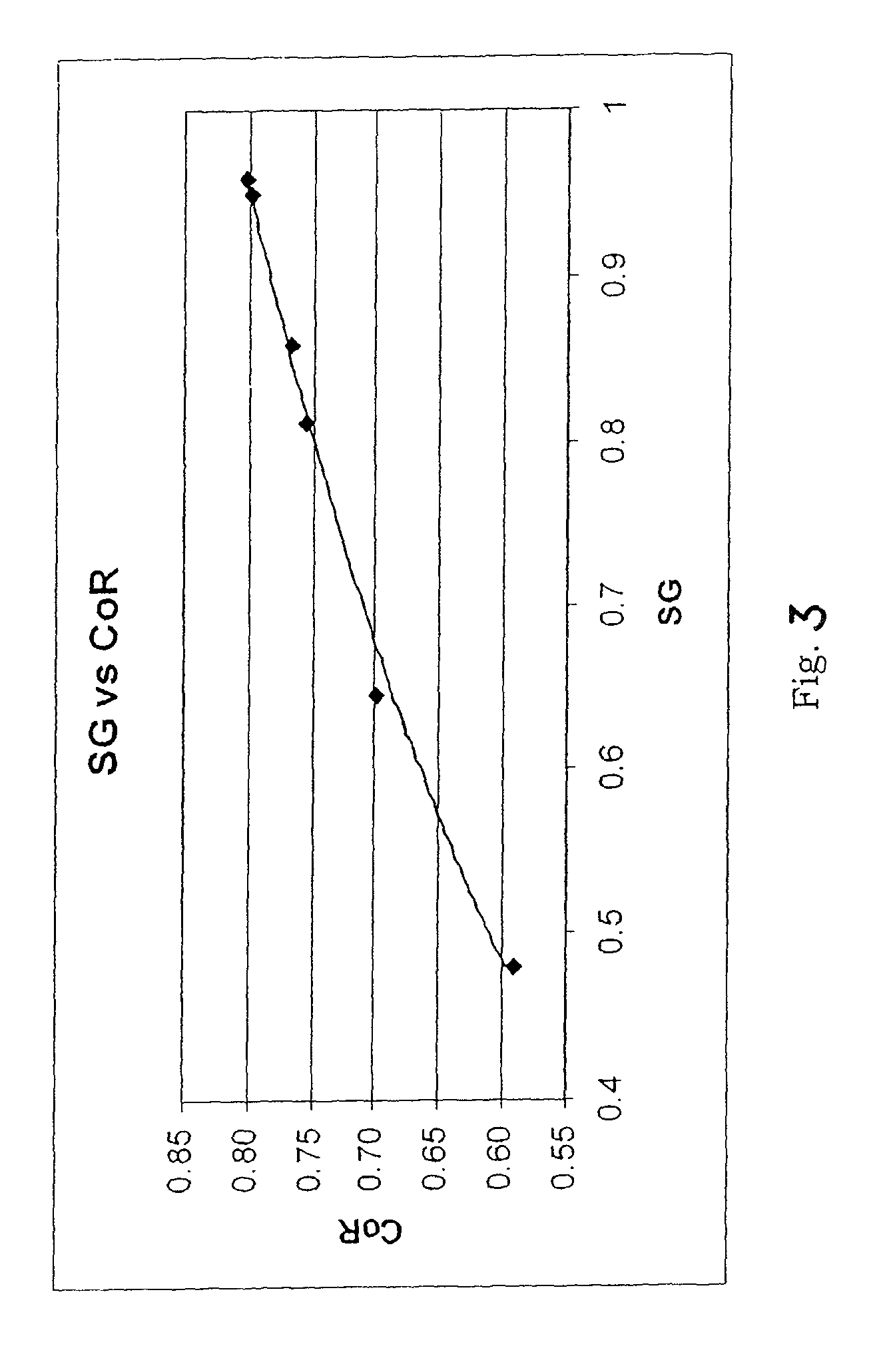
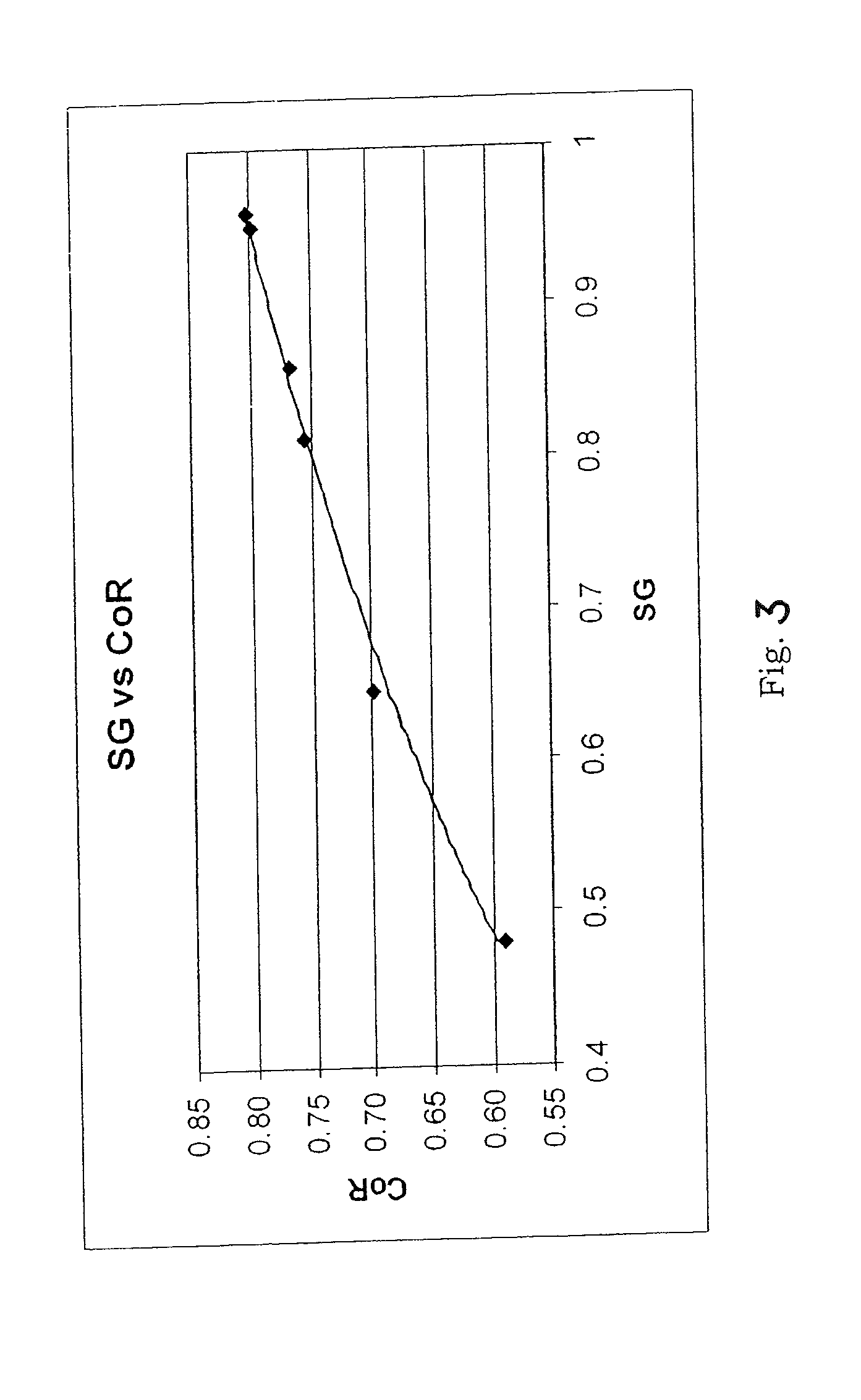
Foam-core golf balls
InactiveUS7452291B2Reduce decreaseIncrease in moment of inertiaGolf ballsSolid ballsEngineeringGolf Ball
A golf ball with a controlled moment of inertia and controlled spin rate is disclosed. The increase in moment of inertia is preferably accomplished by a reduction in the specific gravity or weight of the core, e.g., by foaming. Preferably, this reduction is less than about 15% in specific gravity or less than about 25% in weight to minimize the reduction in the coefficient of restitution of the core.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
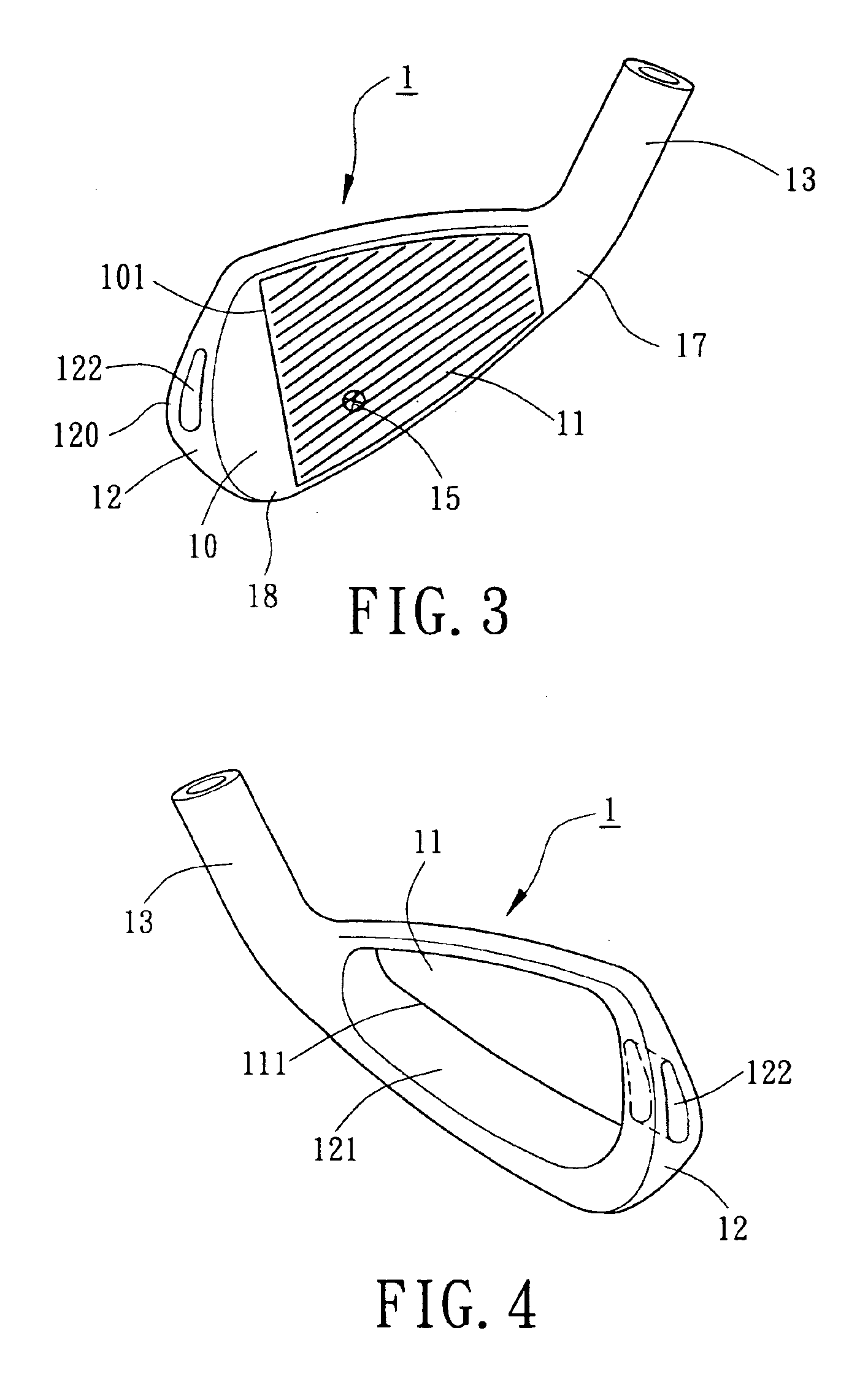
Golf club head
InactiveUS6932717B2Increased inertial momentImprove the strike effectGolf clubsRacket sportsEngineeringGolf Ball
A golf club head includes a golf club head body, a striking plate mounted to a front side of the golf club head body, and a perimeter wall extending rearward along a perimeter of the golf club head body. At least one hole is defined in a toe of the perimeter wall to reduce the weight of the upper part of the golf club head body, thereby shifting the center of gravity of the golf club head downward toward the heel and thereby increasing the inertial moment of the golf club head.
Owner:FUSHENG PRECISION
Foam-core golf balls
A golf ball with a controlled moment of inertia and controlled spin rate is disclosed. The ball has an intermediate layer positioned between the core and the cover and the intermediate layer has a reduced specific gravity. Preferably, this reduction is less than about 30% in specific gravity and the reduction in the coefficient of restitution is less than about 2%.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Combination inertial sensor based on multi-component atom interferometer and measurement method of combination inertial sensor
ActiveCN103837904ARealize synchronized measurementsHighly integratedAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEarthquake monitoringLaser light
The invention discloses a combination inertial sensor based on a multi-component atom interferometer and a measurement method of the combination inertial sensor, and relates to the technical field of inertial measurement through atom interference. The combination inertial sensor comprises a first inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer, a second inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer and a vacuum communication cavity, wherein the first inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer and the second inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer are the same in structure. The vacuum communication cavity is communicated with an atom interference area of the first inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer and an atom interference area of the second inertial-moment-sensitive cold atom interferometer in the horizontal direction. According to the measurement method, multi-frequency laser light is used for simultaneously and independently manipulating two types of alkali metal atoms in the same physical unit, wherein the acceleration and the gravity gradient of one type of alkali metal atoms are measured through a three-pulse pi / 2-pi-pi / 2 Raman laser sequence, and the rotating speed of the other type of alkali metal atoms is measured through a four-pulse pi / 2-pi-pi-pi / 2 Raman laser sequence. Synchronous measurement of a plurality of inertial moments is realized through a simplex physical device at the same time, and the combination inertial sensor based on the multi-component atom interferometer and the measurement method of the combination inertial sensor can play an important role in inertial navigation, resource exploration, earthquake monitoring, physical geographical research and other fields.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Cost-effective system and method for detecting, classifying and tracking the pedestrian using near infrared camera
ActiveUS20120229643A1Improve accuracyLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsObject basedSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
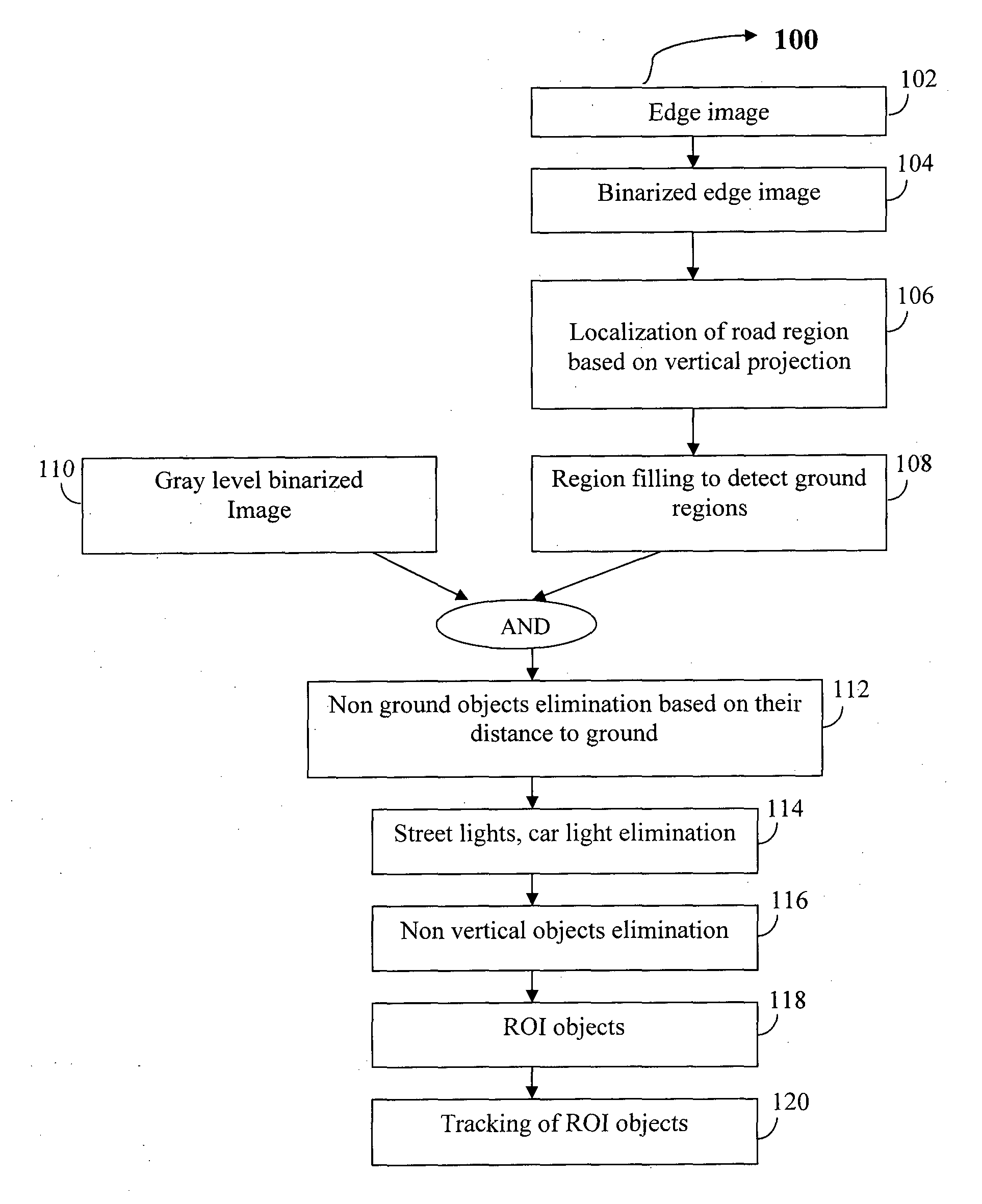
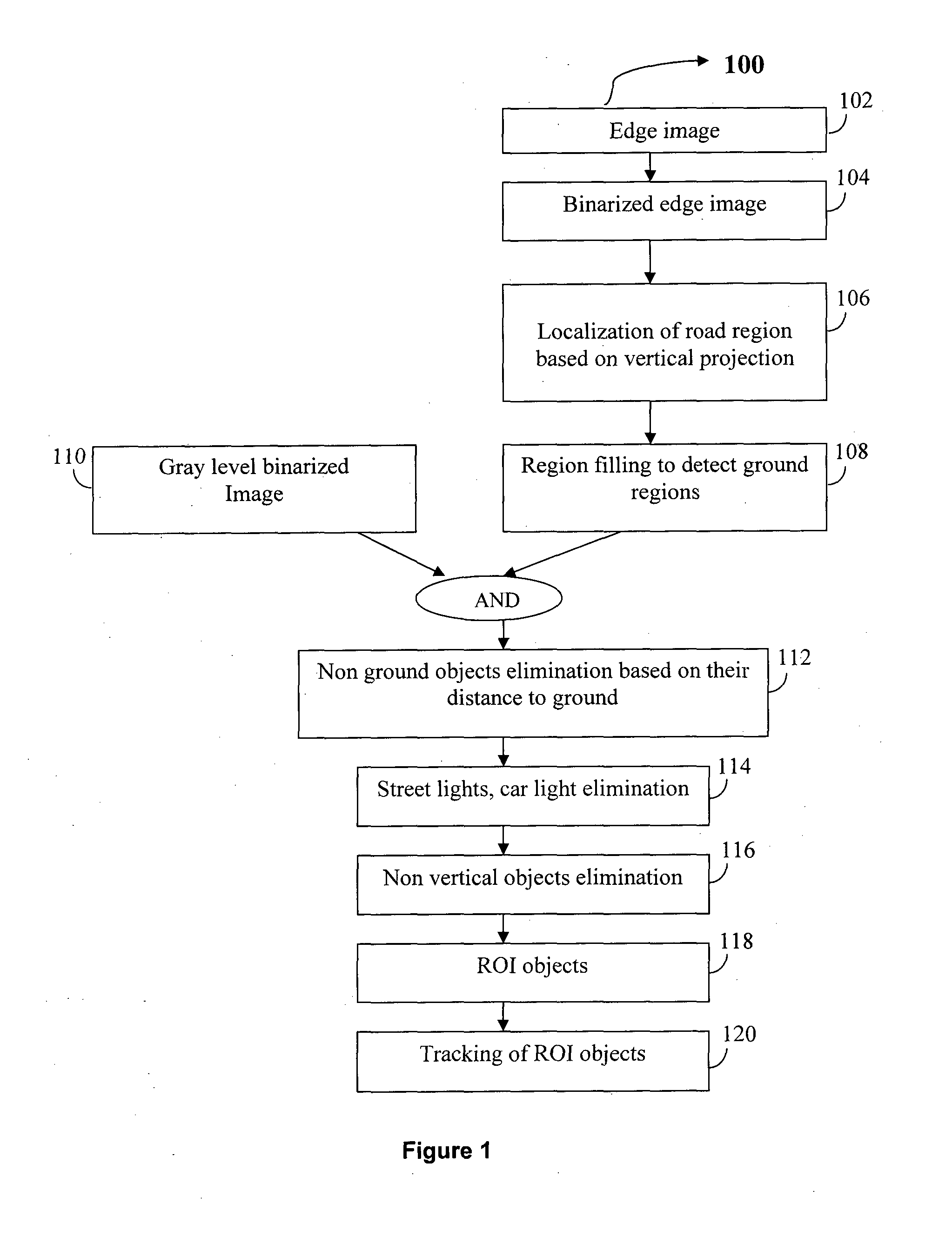
A cost effective method for detecting, classifying and tracking the pedestrian present in front of the vehicle by using images captured by near infrared (IR) camera disposed on the vehicle, the said method comprises the processor implemented steps of: detecting the road to focus of attention for filtering the region of interest (ROI) objects in the said image by estimating the ground region characterized by identifying smooth regions connected to bottom most part of the image; eliminating the non-ground objects based on their distance to ground; filtering the non-ROI objects based on the shape of such objects by computing the signal to noise ratio (SNR) which is a measure of regularity of the component based on its periodicity of its contour for each of such non-ROI objects; eliminating the non-vertical objects by computing inertial moment relative to x and y axis with respect to the centre of mass of such non-vertical objects; classifying the pedestrians in the analyzed frame of the image based their shape; and tracking the movement of the classified pedestrian using mean shift algorithm.
Owner:TATA CONSULTANCY SERVICES LTD
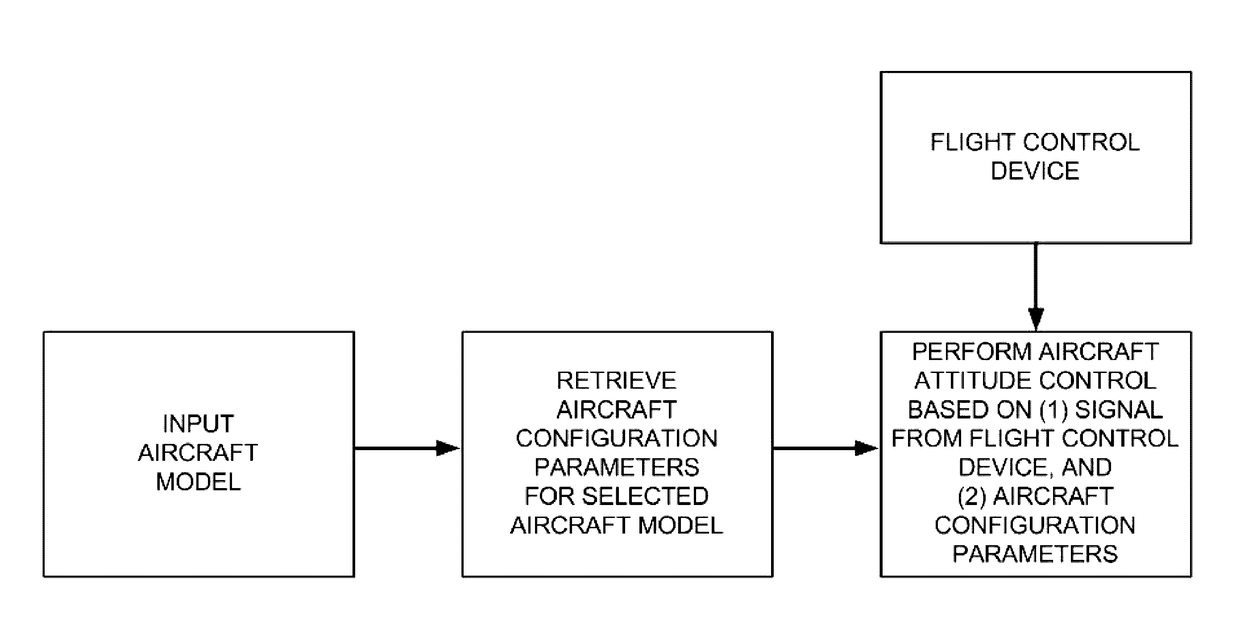
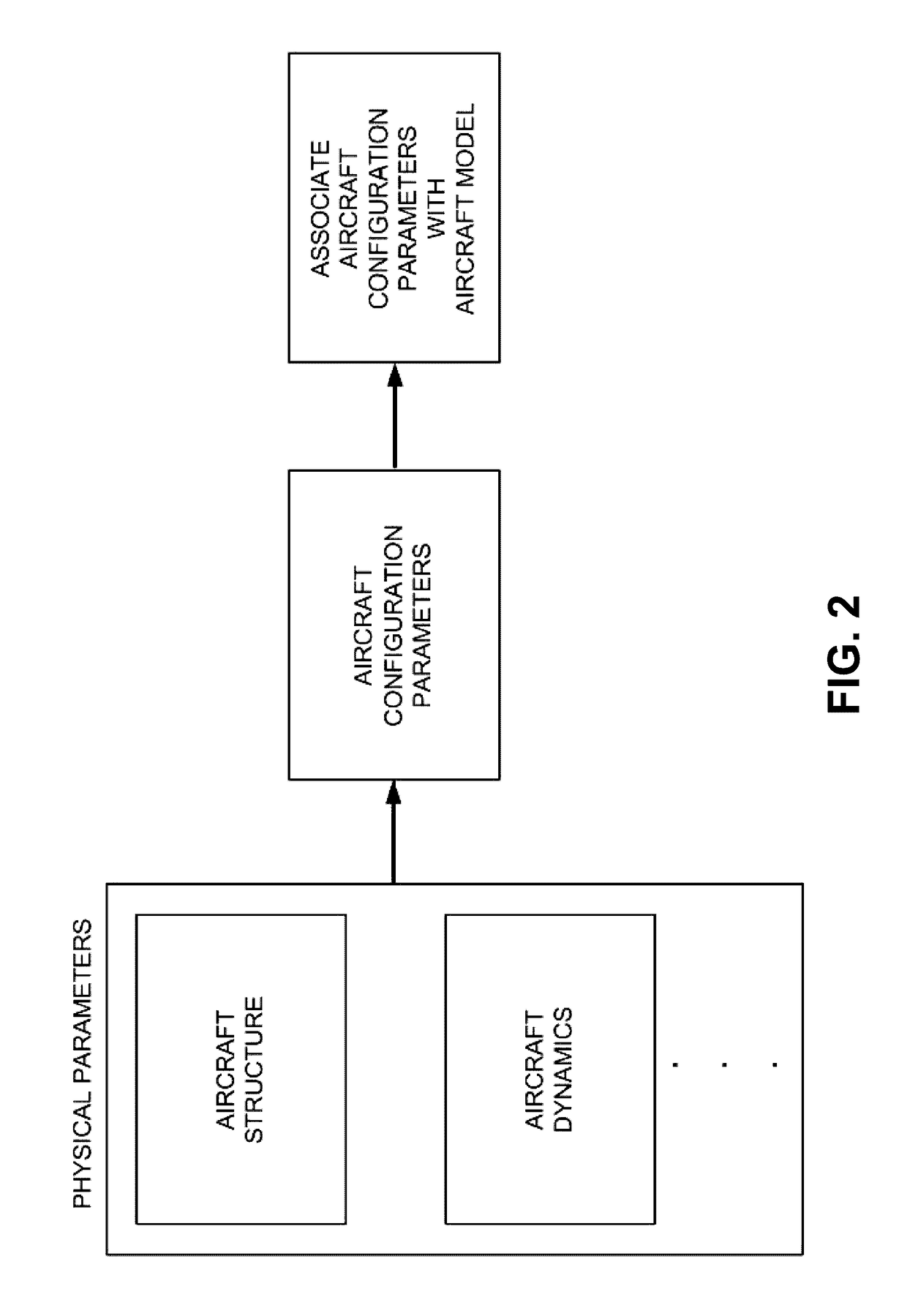
Aircraft attitude control methods
Systems and methods are provided for aircraft attitude control. The aircraft attitude control may take physical parameters of the aircraft into account. For example, one or more aircraft configuration parameters, such as moment of inertia, motor lift curve, and / or axial distance may be calculated and / or taken into account based on the aircraft physical parameters. The aircraft configuration parameters may include non-linear parameters. The control systems may include feedback control systems, and may optionally use a feedforward and feedback control for angular acceleration.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
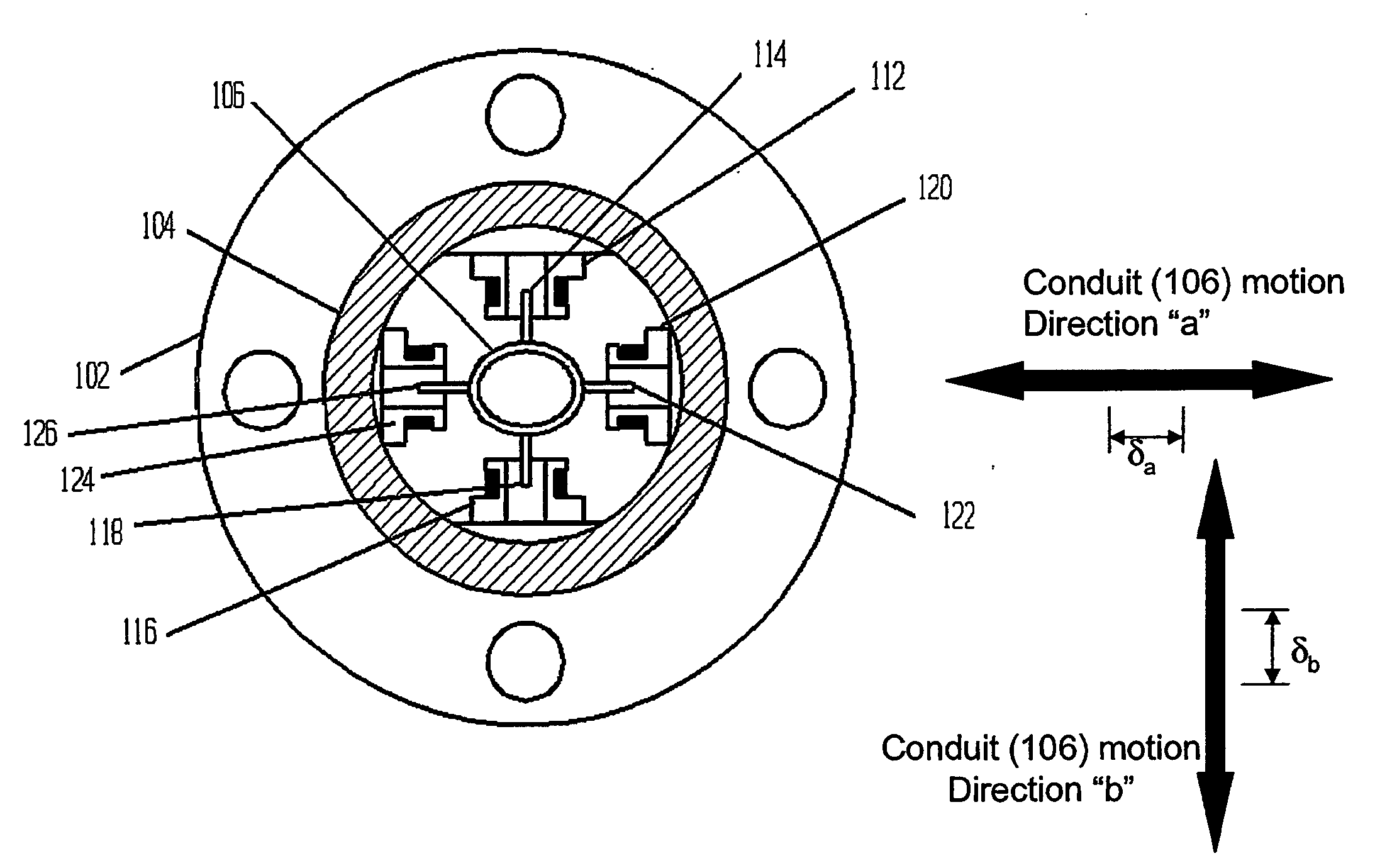
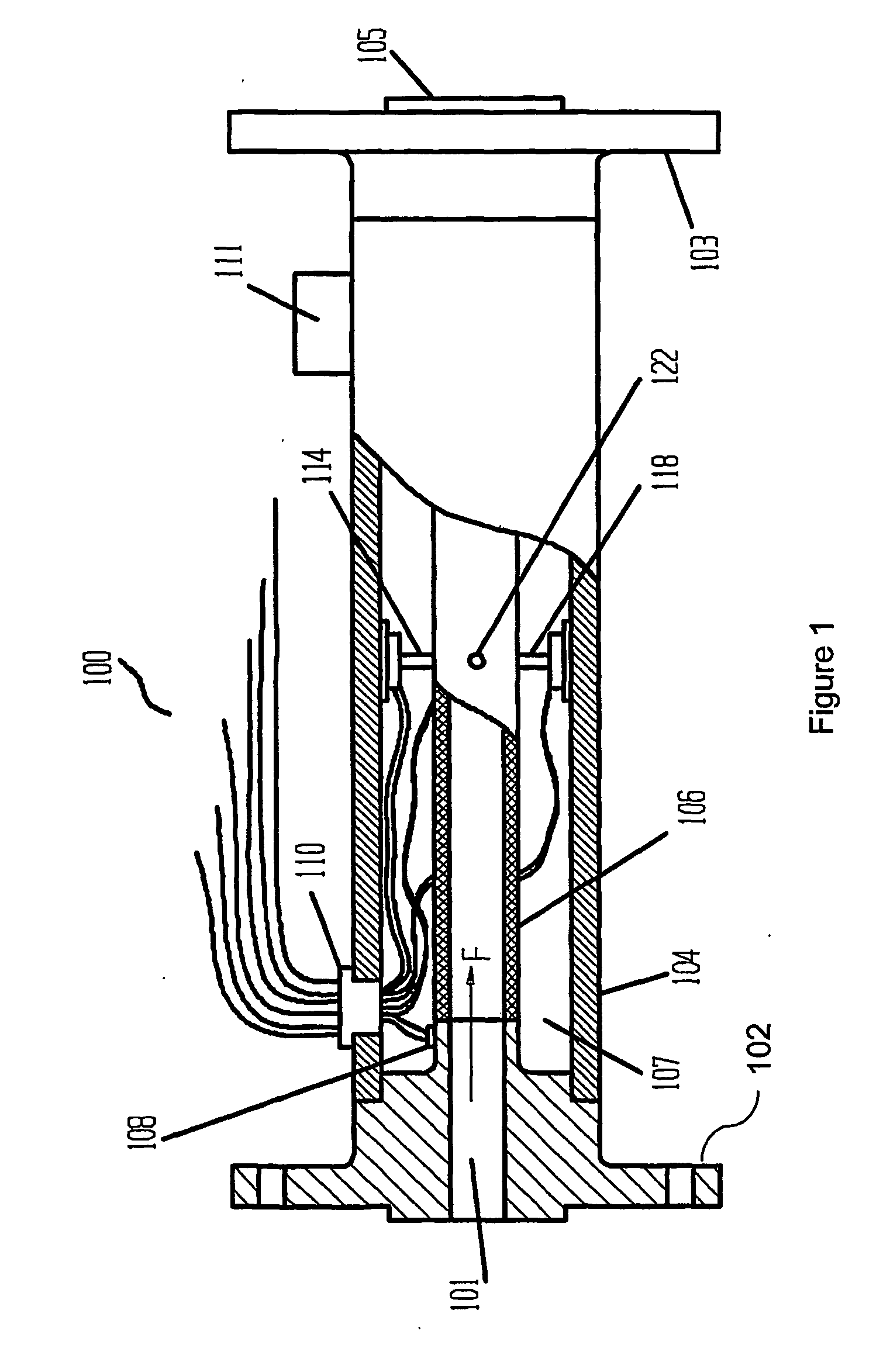
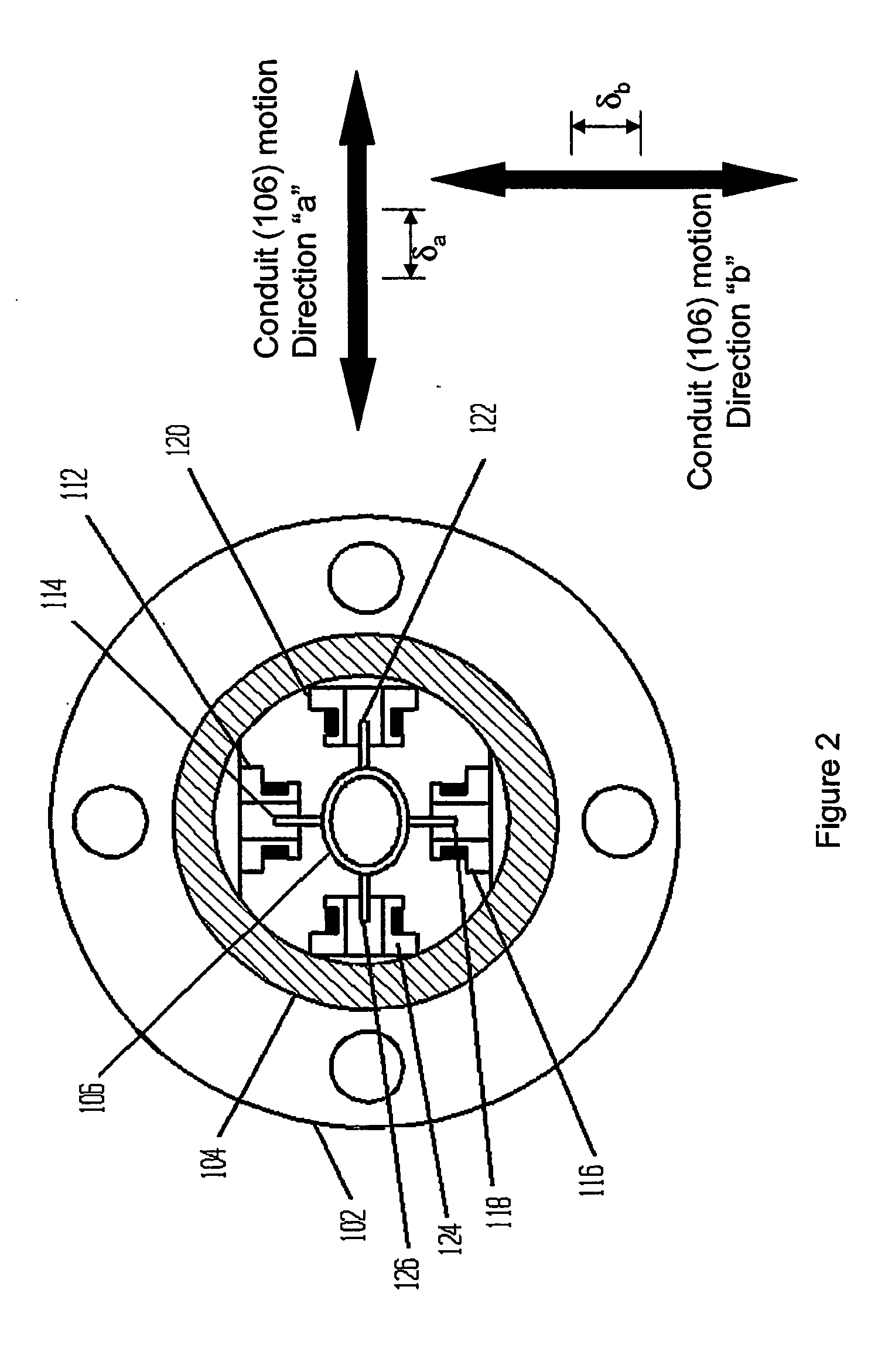
Precise pressure measurement by vibrating an oval conduit along different cross-sectional axes
A conduit (106), with geometry designed to enhance pressure sensitivity, is vibrated at resonance in two modes along different cross-sectional axes (a, b). Measuring the change in the frequency ratio squared of the modes yields a substantially linear relationship to pressure that is substantially immune to other material properties and other environmental factors. Moments of inertia in different cross-sectional axes are related to pressure as a result of the elliptical or oral cross section of the conduit (106).
Owner:CARPENTER BRENT L
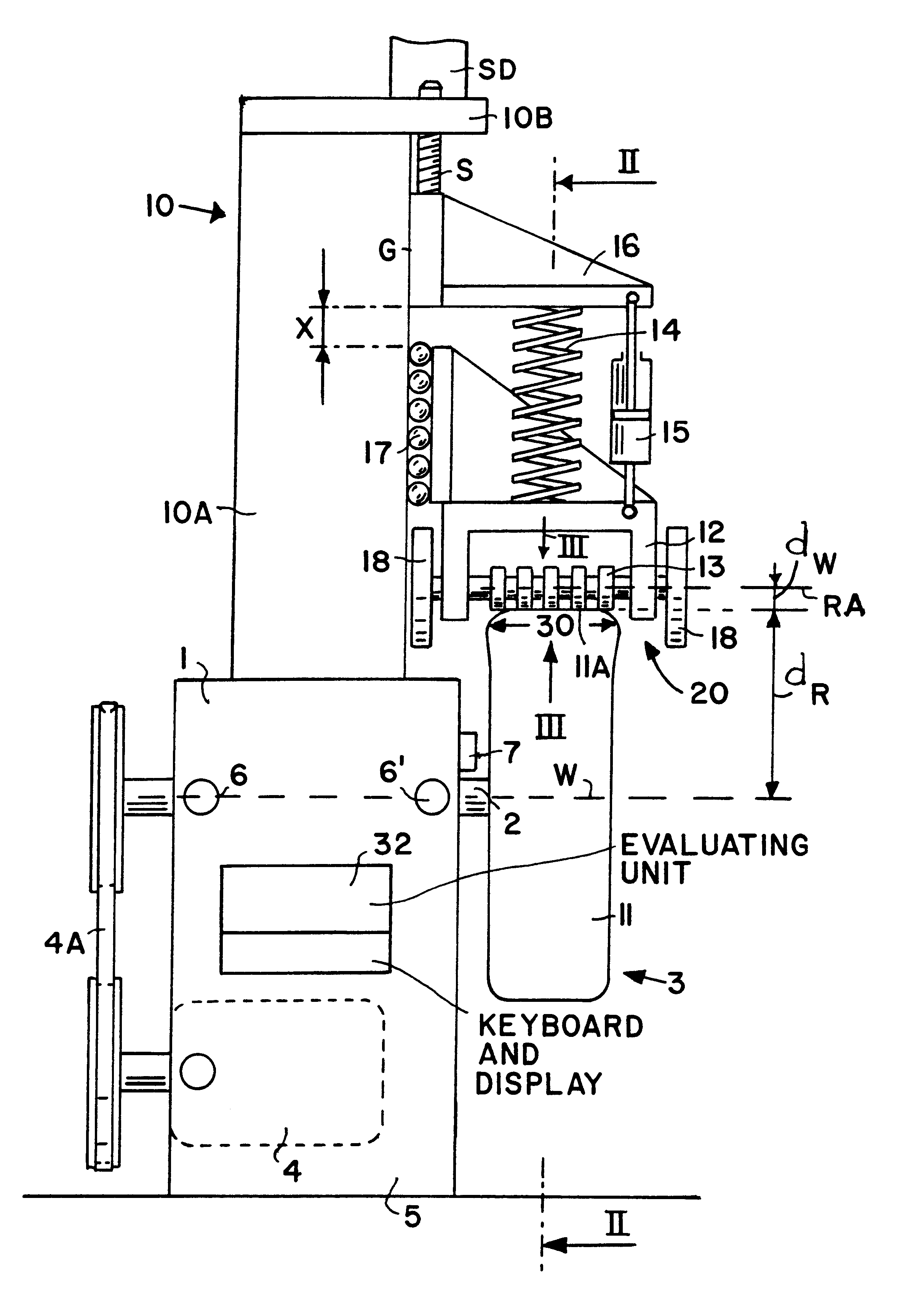
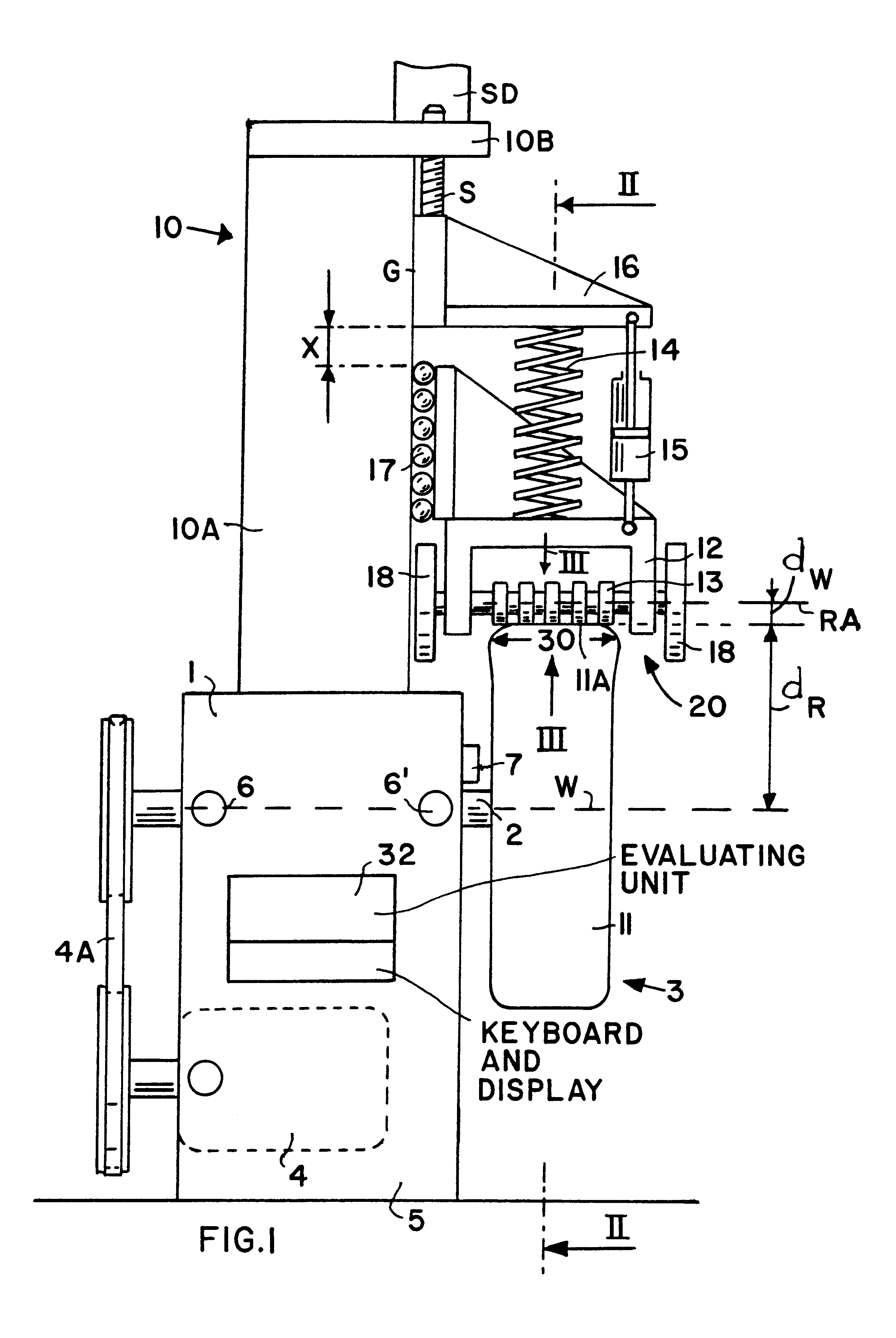
Method and apparatus for reducing vibrations transmitted to a vehicle from a wheel unit
InactiveUS6360593B1High simulationSimpler to precisely determineStatic/dynamic balance measurementUsing mechanical meansBrakeDynamic balance
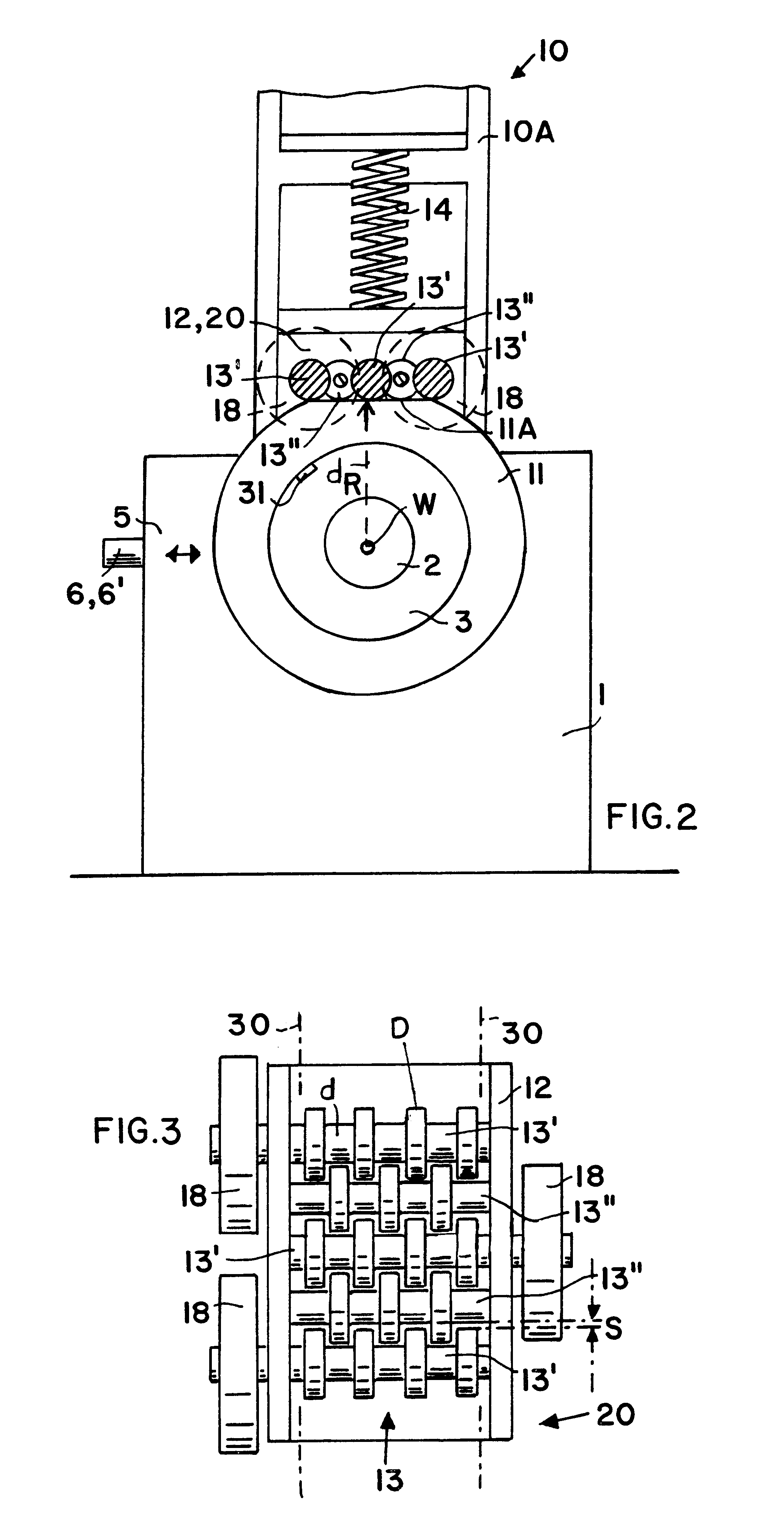
Vibrations generated by the wheel units of a vehicle are reduced by a low pulsating operation that optimally simulates actual vehicle operating conditions. For this purpose the mass moment of inertia of the wheel unit and of rotating components such as the hub and the brake disc are taken into account. The wheel unit is rotatably mounted on a balancing spindle (2) in a measuring apparatus to determine the mass and angular location of balancing weights (31). The vibrations are measured at a speed that corresponds to a typical travel speed of a vehicle. A loading mechanism including a roller shoe (20) applies a force to the tire tread surface through a spring damping (14, 15) to optimally simulate the conditions of a roadway. The roller shoe (20) has rollers (13) with sections of larger and smaller diameters so that neighboring rollers intermesh. The combined masses of the rollers, as reduced to the roller radius dw, corresponds to the rotational mass of the vehicle wheel as reduced to the tread radius (dR). It is also possible to disengage the contact force from the tread surface for dynamically balancing the wheel unit under load-free conditions. Thus, wheel-balancing steps under loaded and load free conditions can be done on one machine.
Owner:SCHENCK ROTEC GMBH
Single column maritime wind power generation device with circumferential stabilizing column
InactiveCN102146873AIncrease the moment of inertiaAchieve protectionMachines/enginesWind energy generationOcean bottomOpen sea
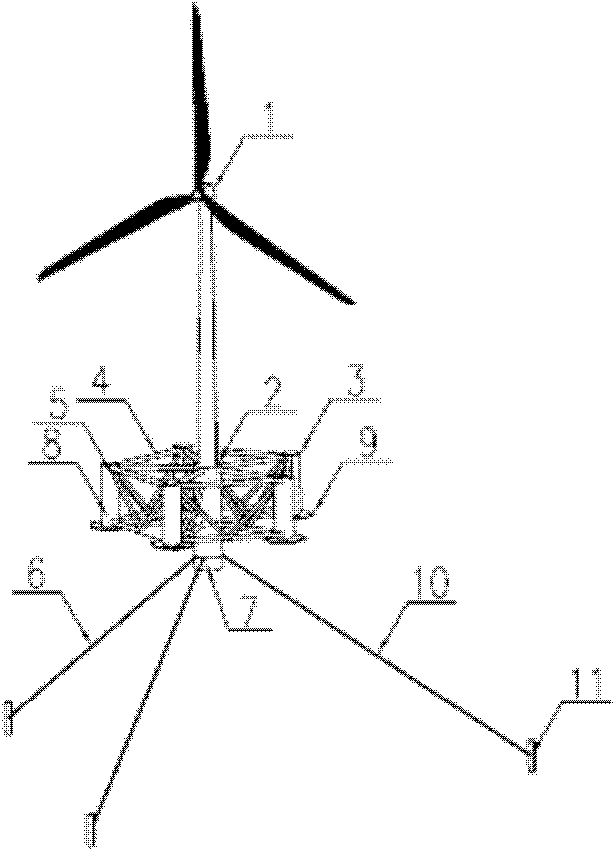
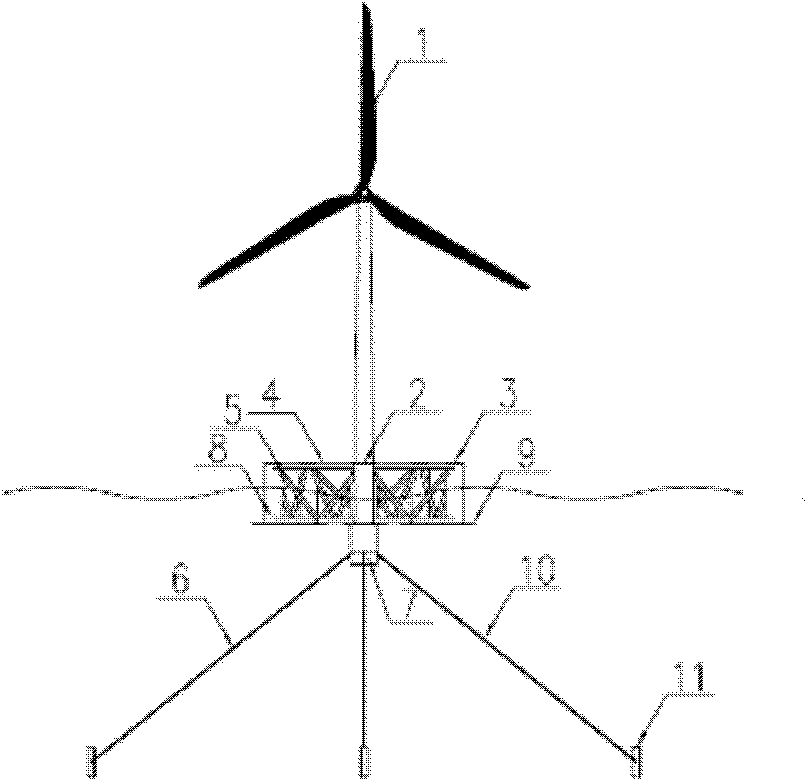
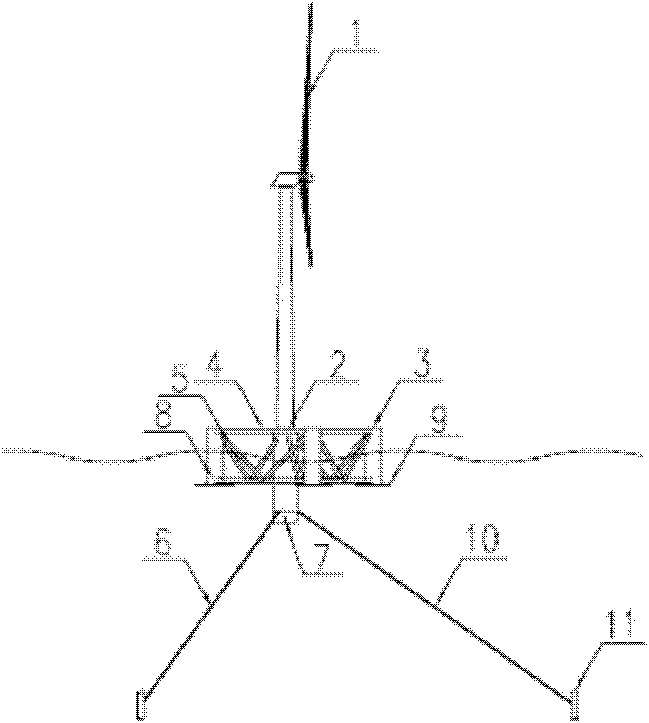
The invention provides a single column maritime wind power generation device with a circumferential stabilizing column, and belongs to the technical field of ocean energy resource utilization. The single column maritime wind power generation device with the circumferential stabilizing column comprises a wind power generation set, a single column base, the circumferential stabilizing column, a supporting structure, a berthing system and a fixed ballast system; the wind power generation set is fixed on the single column base; the circumferential stabilizing column is fixed at the periphery of the single column base; both ends of the supporting structure are connected with the circumferential stabilizing column and the single column base respectively; the middle part and the bottom of the single column base are connected with the berthing system and the fixed ballast system respectively; and the berthing system is connected with the seabed. By arranging the circumferential stabilizing column, a larger waterline plane inertial moment can be obtained in a smaller waterline plane area; meanwhile, due to the low gravity center of the single column base, the stability requirement is met and the high water power performance is gained; therefore, a stable, economic and flexible floating base is provided for the wind power generation set, so the single column maritime wind power generation device with the circumferential stabilizing column is particularly applicable to deep water regions of the open sea.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Golf putter with improved moment of inertia, aim and feel
InactiveUS20050239574A1Undesirable torsional vibrationFeel goodGolf clubsRacket sportsVisibilityEngineering
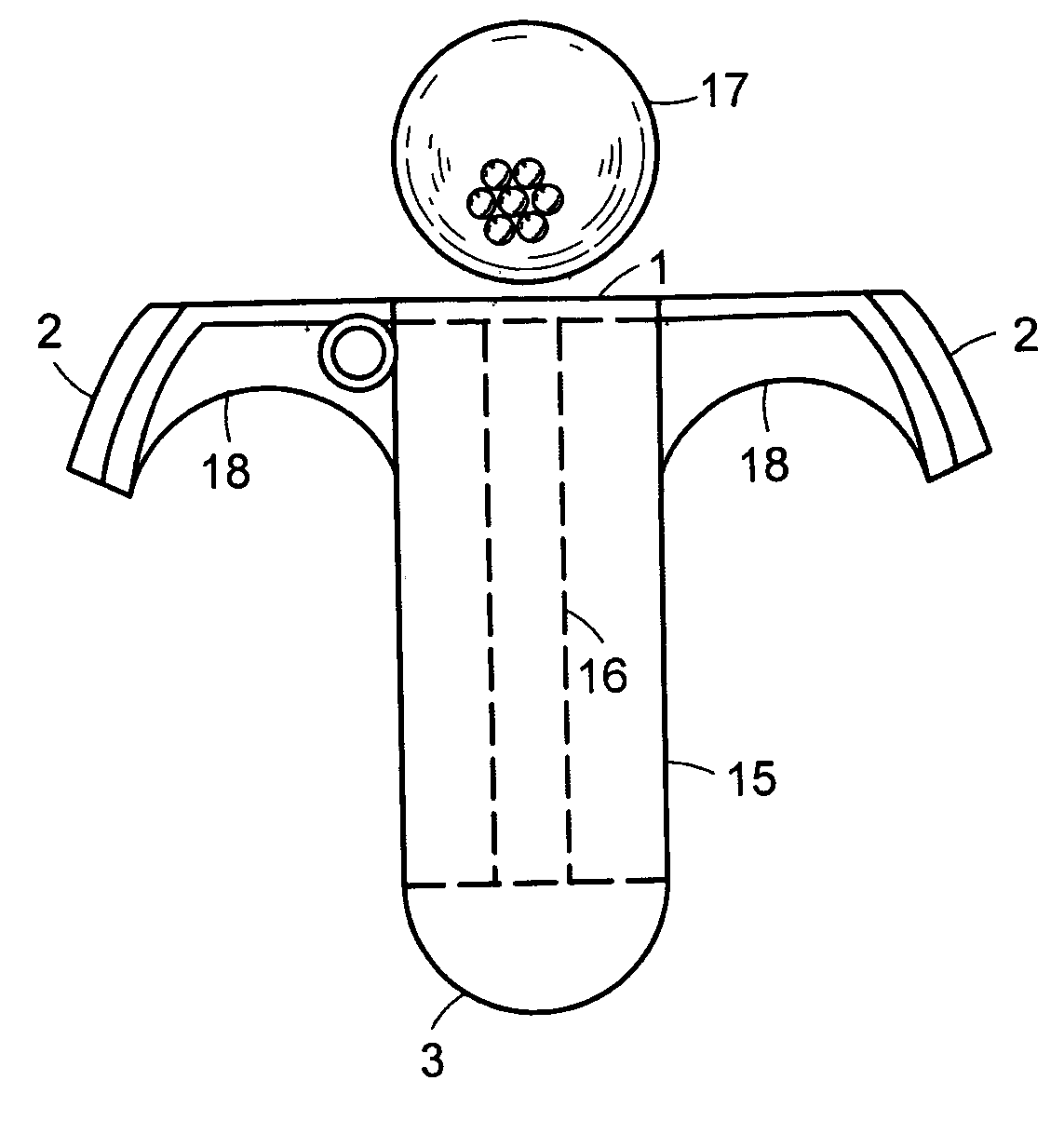
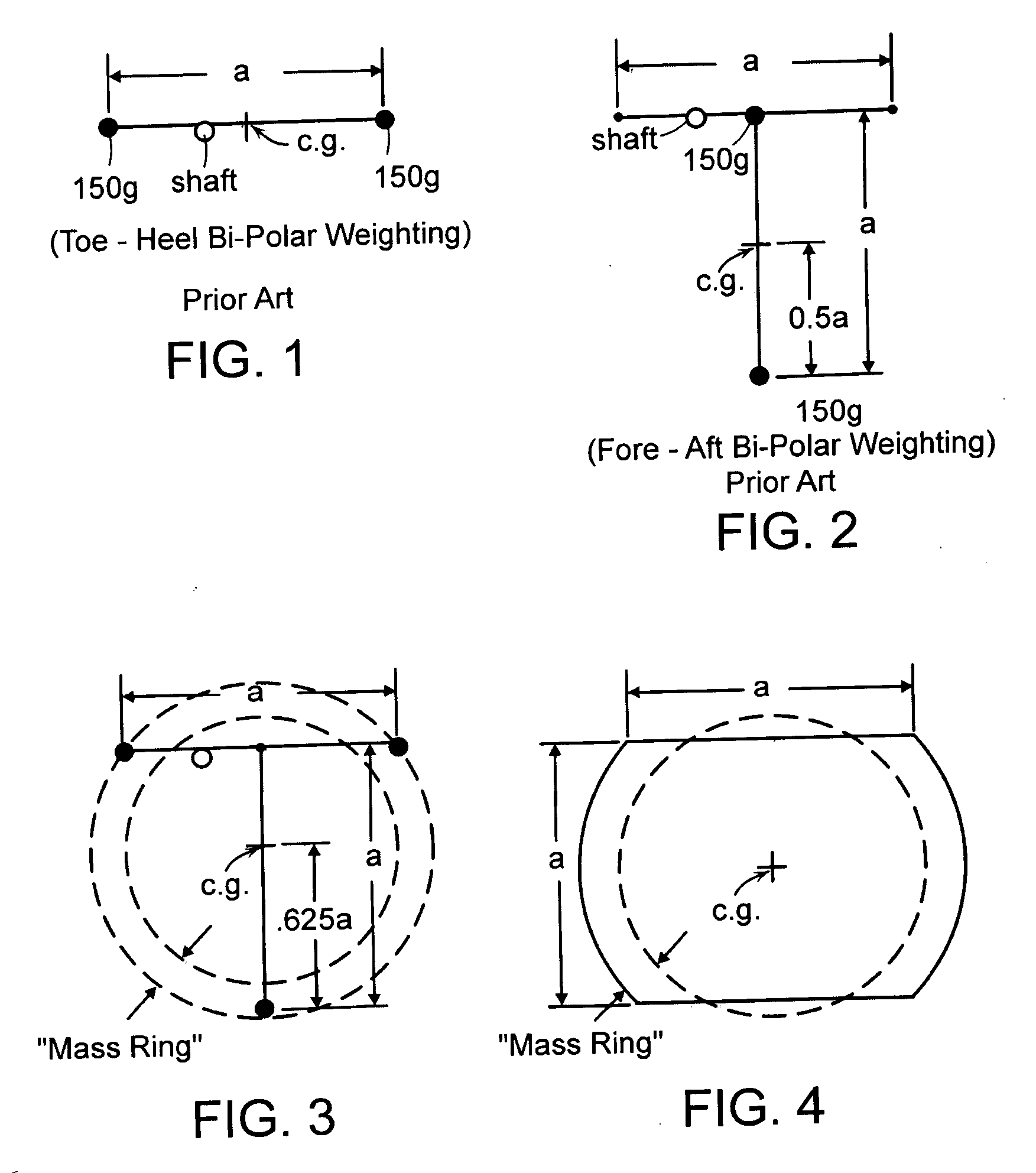
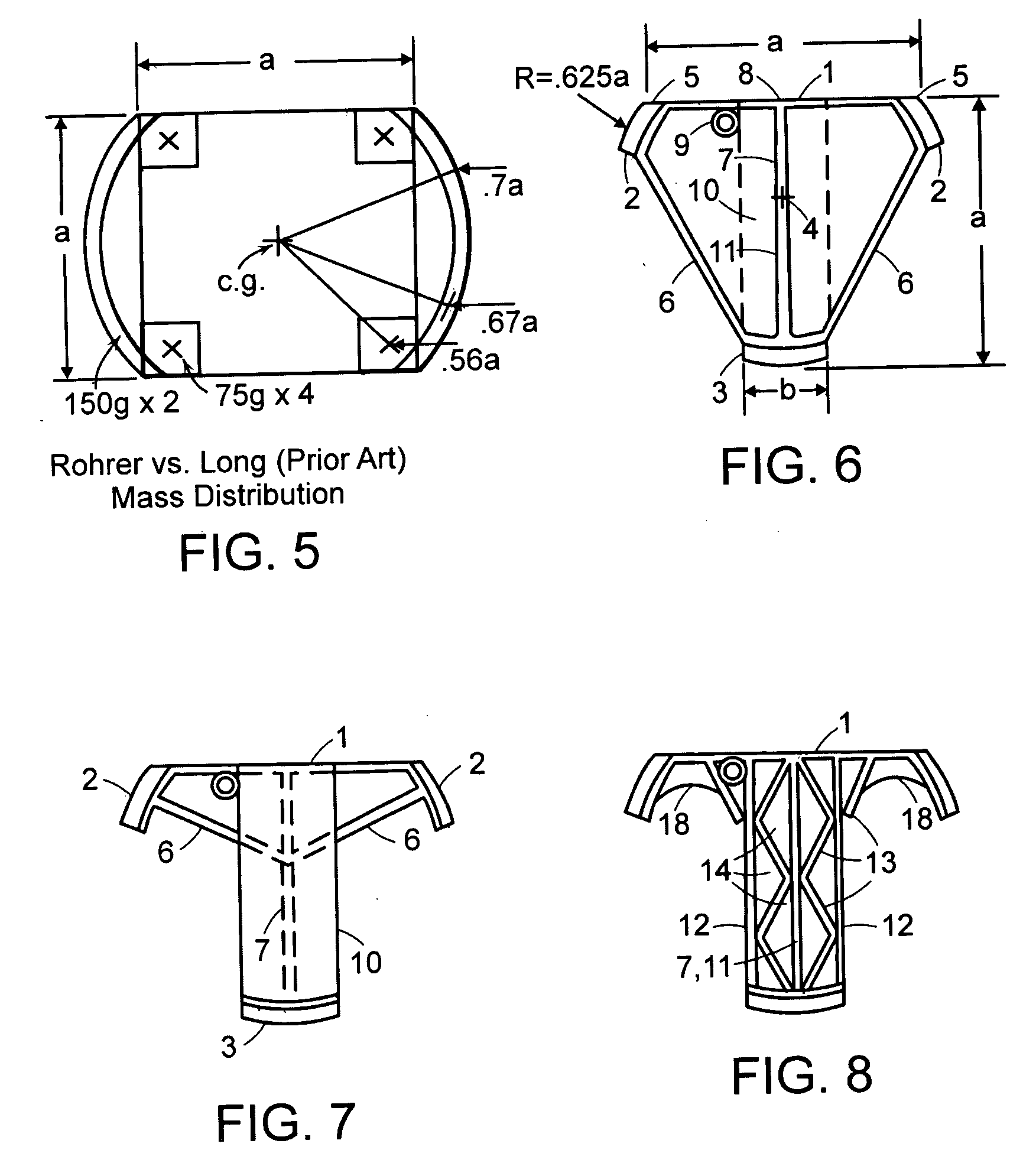
A golf putter in which most of the clubhead mass is distributed at three or more individual or one or more arcuate locations within a “Mass Ring” approximately equidistant from, and as remote as possible from, the clubhead planar center of mass with the clubshaft axis preferably forward of the clubhead center of mass thus maximizing both putter and clubhead planar moment of inertia for improved putter performance during mis-hits. Maximum remote mass is achieved by interconnecting the remote high mass areas (Mass Ring) with the putterface striking area and the putter shaft connection point with a light weight rigid open (see thru) truss system so arranged to enhance the visibility of the Sighting Field and / or aim or Sight Line on the putterhead while preventing undesirable vibration of individual clubhead members.
Owner:ROHRER TECH
Model for predicting resilience of bar subjected to two roll straightening
ActiveCN104866641AAccurately reflectAccurately describe the stress-strain relationshipSpecial data processing applicationsStress distributionTension compression
The invention relates to a method for predicting resilience of a bar subjected to two roll straightening, and belongs to the technical field of two-roll straightening machines. The method comprises the followings steps: firstly, determining the offset of a stress neutral layer when the rod is subjected to straightening; then, determining a deformation-hardening coefficient and tension-compression stress distribution according to different straightening processes and deformation characteristics of rods in different specifications; finally, determining the model for predicting rebound bending moment and straightening rebound deflection by combining a pure bending and rebound theory, wherein the rebound deflection delta is related to the following variables of R, sigma<t>, lambda, xi, psi, kappa, I, E, L, B, n, R0, Rw, P and tau; R represents a rod radius; sigma<t> represents the yield limit; lambda represents a hardening coefficient; xi represents an elastic region ratio; psi represents a neutral layer offset radius ratio; k represents an anti-bend rate; I represents rod section moment of inertia; E represents modulus of elasticity; L represents the distance between the two end points in three-point bending; B represents a plastic coefficient; n represents a hardening index; R0 represents an initial bending radius; Rw represents an anti-bend radius; P represents straightening force; tau represents a correction coefficient. According to the method, a straightening and deformation process can be truly reflected, and the straightening theory can be perfected; resilience in the straightening process can be accurately predicted, and bases for the roll shape design and process parameter establishment are provided.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
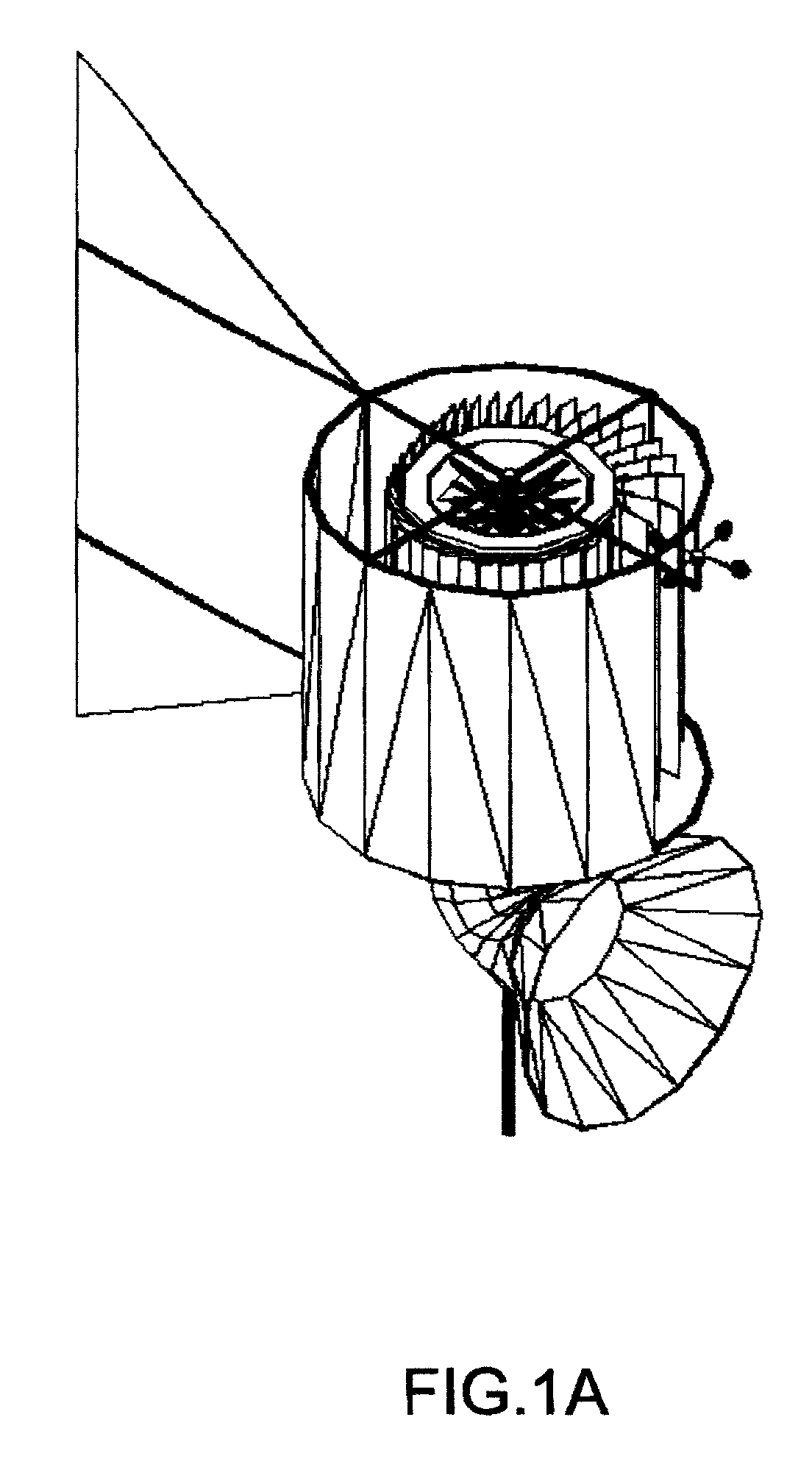
Vertical axis variable geometry wind energy collection system
A device to convert the kinetic energy of wind into kinetic energy in the form of a rotating mass (FIG. 9) and to then selectively harvest and convert the kinetic energy of the rotating mass into electrical energy using both permanent magnet and electromagnet generators (FIG. 33). The conversion of the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical kinetic energy of the rotating mass is maximized through mechanical means by varying the physical moment of inertia of the rotating mass programatically based upon real time sensor data (FIG. 27A,27B). The conversion of the kinetic energy of the rotating mass into electrical energy is maximized through the programatical control of the field coil current of the electromagnet generator based upon real time sensor data (FIG. 62).
Owner:AARON MICHAEL SCOTT
Metal laminate structure and method for making
Laminates consisting of a high-damping core material sandwiched between two stiff, weldable skins. The laminate structures have increased resonant frequencies, improved damping characteristics, do not outgas, and may have a decreased inertial moment. The laminates are comprised of 100% metal constituents, and do not rely on epoxy or low-melting point solders. To make the laminate structures, a first alloyable metal is deposited on the surface of a dissimilar metal. The coated surface is then placed in contact with a second alloyable metal and allowed to interdiffuse at elevated temperatures. The metals are chosen such that diffusion creates an alloy with a melting point lower than either of the constituents. The processing temperature is set so that the alloy melts but leaves the base metals in solid form, causing a thin layer of liquid to form and wet both sides of the interface. External pressure is applied to the opposing base metals in such a way as to induce flow of the liquid layer and disrupt any oxide layers present on the surface of one or more of the base metals. Continued diffusion elevates the melting temperature of the liquid phase and causes it to solidify isothermally, creating a bond between the base metals. Highly polished surfaces on the base metals comprising the laminate structure are not required because the applied pressure causes the metal (in thin sheet form) to deform and create the intimate metal-metal contact necessary for diffusion. Moreover, the liquid flow helps to fill gaps between the parent materials and further mitigates the need for polished surfaces.
Owner:INTRL PLEX TECH INC
Computer simulation prediction method of in-car vibration and noise of car
InactiveCN105279327ALow costShorten the development cycleSpecial data processing applicationsNoise, vibration, and harshnessCombustion
The invention aims to provide a computer simulation prediction method of the in-car vibration and noise of a car. The computer simulation prediction method comprises the following steps: A: calculating the reciprocating inertial force and the reciprocating inertial moment of a crank mechanism of an engine; B: according to the combustion pressure of the engine, calculating a moment generated by air pressure; C: processing engine load into frequency domain load according to orders; D: establishing an NVH (Noise Vibration and Harshness) finite element simulation model of a complete car, preliminarily judging the correctness of a model according to a modality, and loading the load onto an engine centroid in the model; E: calculating a response curve of the in-car vibration and noise, and comparing the response curve with a target value; F: according to the response curve of the in-car vibration and noise and the target value, finding a peak point which affects NVH performance to carry out contribution analysis; and G: according to a contribution analysis result, carrying out structure improvement to lower a noise or vibration peak. The computer simulation prediction method can predict and solve problems before manufacture cost is generated, a great quantity of cost is saved, and a development period is shortened.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Rotary engine with counter-rotating housing and output shaft mounted on stationary spindle
InactiveUS6761144B2Eliminate needPropellersInternal combustion piston enginesClassical mechanicsRotary engine
A counter-rotating rotary-piston engine has an output shaft with a cylindrical inner cavity rotatably mounted on a single support spindle in the frame of an aircraft. The output shaft extends substantially through the length of the engine block, which is suitably journaled on the shaft or the spindle to permit its counter-rotation. Internal combustion power is transmitted to the output shaft by means of an inner rotary piston fixed to the shaft which cooperates in conventional manner with an outer working chamber in the engine block, thereby producing concurrent rotation of the shaft and counter-rotation of the engine block. Dual propellers mounted on the shaft and on the block improve thrust performance, balance the torques and moments of inertia of the two counter-rotating masses, and virtually eliminate any resultant torque to the aircraft.
Owner:SCHWAM PAUL A
Fan tower inherent frequency analyzing method based on conservation of mechanical energy
Provided is a fan tower inherent frequency analyzing method based on conservation of mechanical energy. According to the method, a tower is regarded as a beam of a variable cross-section with one end fixed and the other end having concentrated mass and inertia moment, the fan tower is divided into a few sections, each section is signified by a constant-section beam, the rigidity of the beam is determined by adopting an equivalent rigidity method, a certain offset distance exists between a top mass center and the center of the beam, the mentioned parameters are regarded as the analyzing basis of the fan tower, and influences of relative parameters on the inherent frequency of the tower are determined by determining a first stage bending inherent frequency analyzing model and a first stage torsional inherent frequency analyzing model respectively.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST
Method for monitoring torsional vibration damper
ActiveCN1865891AInternal-combustion engine testingMachine gearing/transmission testingMoment of inertiaTorsional vibration
The invention discloses a method for monitoring a torsional vibration damper. The torsional vibration damper has a connecting part (2) connectable to a shaft and a vibration rotating body (3) connected to the connecting part (2) in a rotationally elastic manner. The connecting part (2) and the vibration rotating body (3) ) is digitally measured and converted in the computing station to output characteristic values. In order to ensure favorable monitoring conditions, the invention proposes to determine the relative twisting angle between the two parts (2, 3) and furthermore determine the vibration rotation by simultaneously measuring the angle of rotation of the connecting part (2) and the vibration rotating body (3). The rotational angular acceleration of the body (3), taking into account any changes in the angular velocity of the connecting part (2), and with the help of a vibrating rotating body (3) by constructing a predetermined mass moment of inertia the torsional stiffness and torsional damping are calculated and displayed as characteristic values .
Owner:盖斯林格集团有限公司
Foam-core golf balls
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Golf putter head
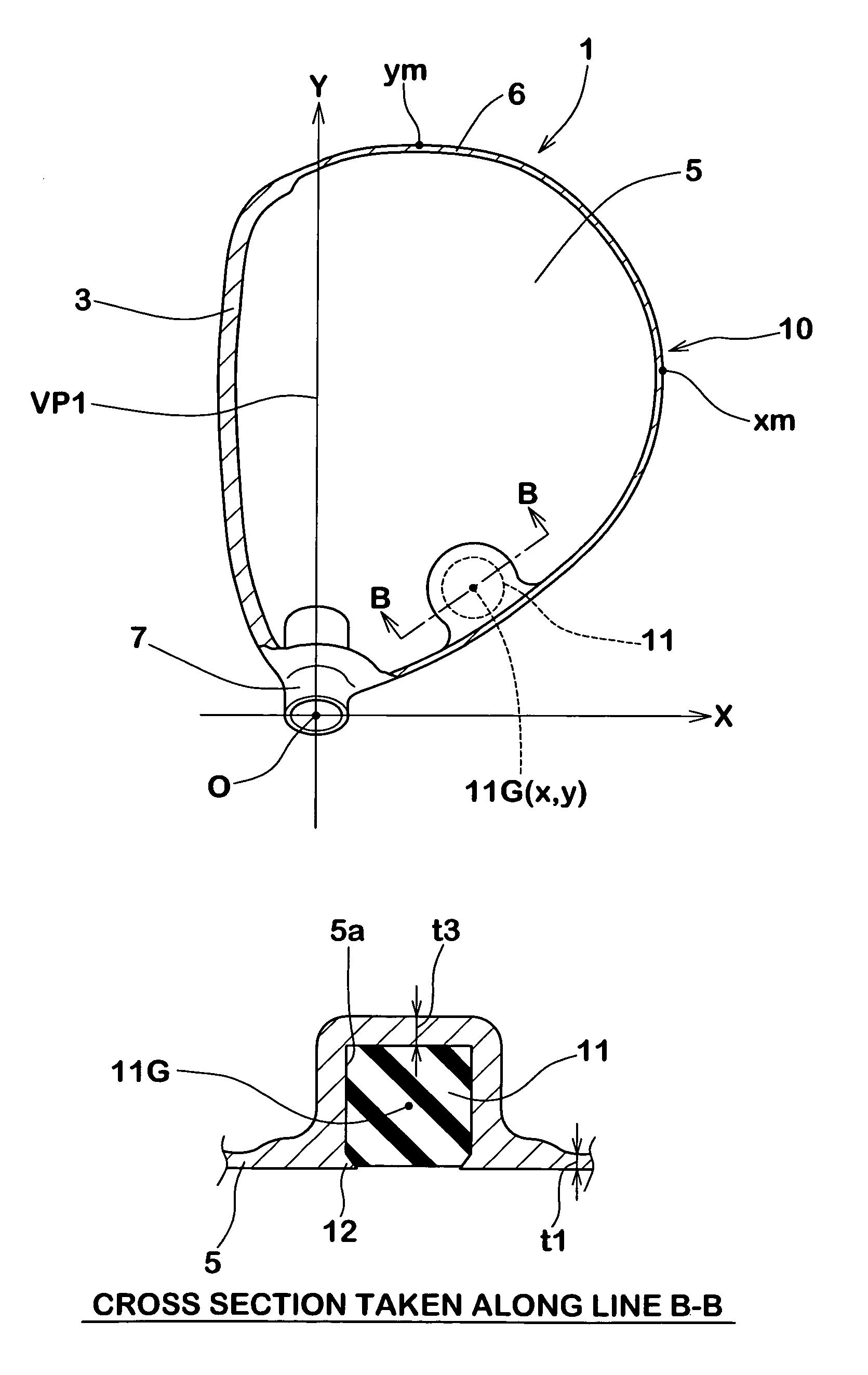
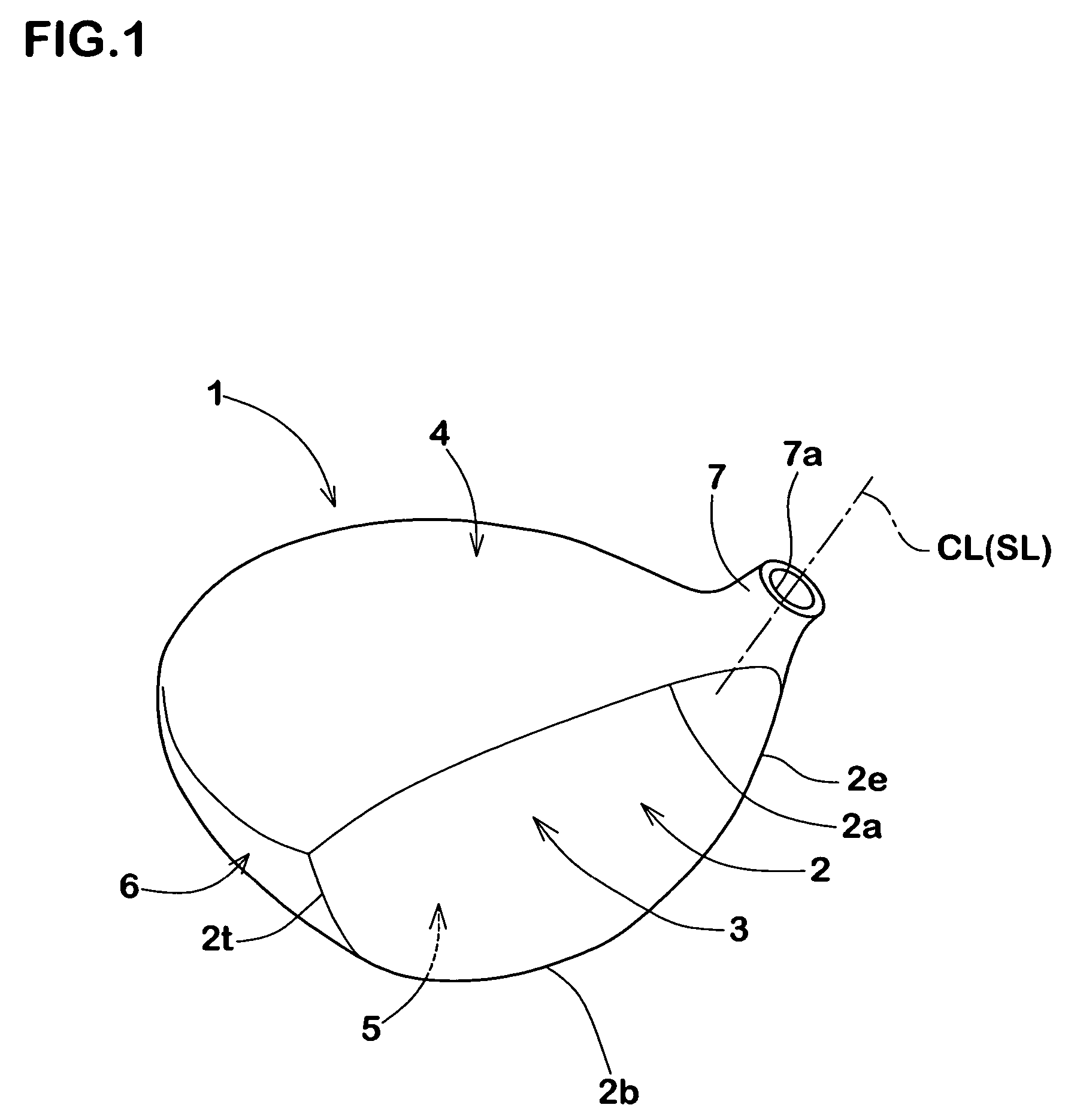
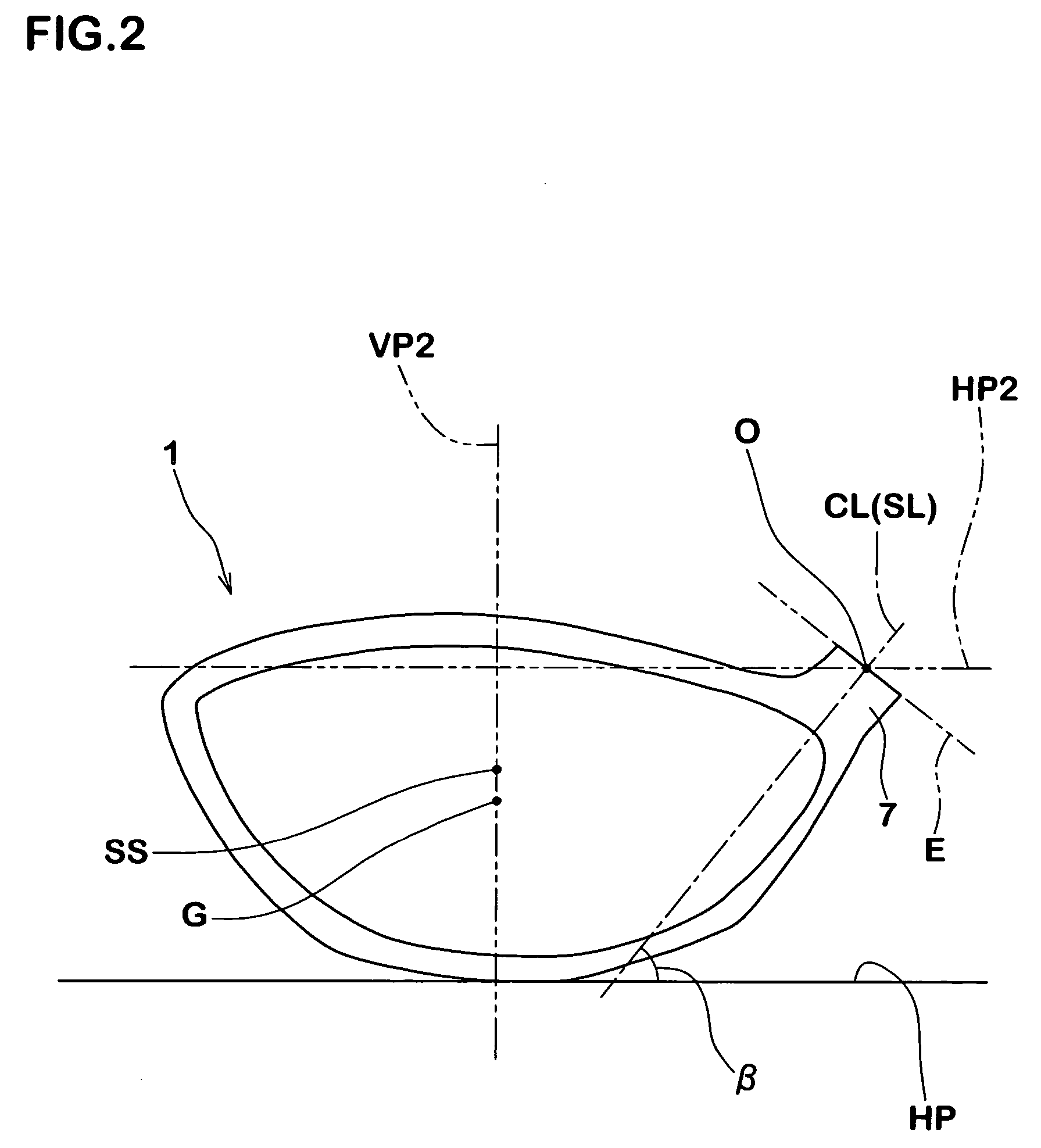
The present invention is a golf putter head wherein the second moment among the three inertial moments described below shows a maximum value in a state in which the head is placed on a horizontal plane at a specified lie angle and loft angle:First moment: inertial moment about a first axis which passes through the center of gravity of the head, and which is parallel to the face surface and said horizontal plane;Second moment: inertial moment about a second axis which is an axis in the vertical direction that passes through the center of gravity of the head; andThird moment: inertial moment about a third axis which passes through the center of gravity of the head, and which is perpendicular to said first axis and perpendicular to said second axis.
Owner:DUNLOP SPORTS CO LTD
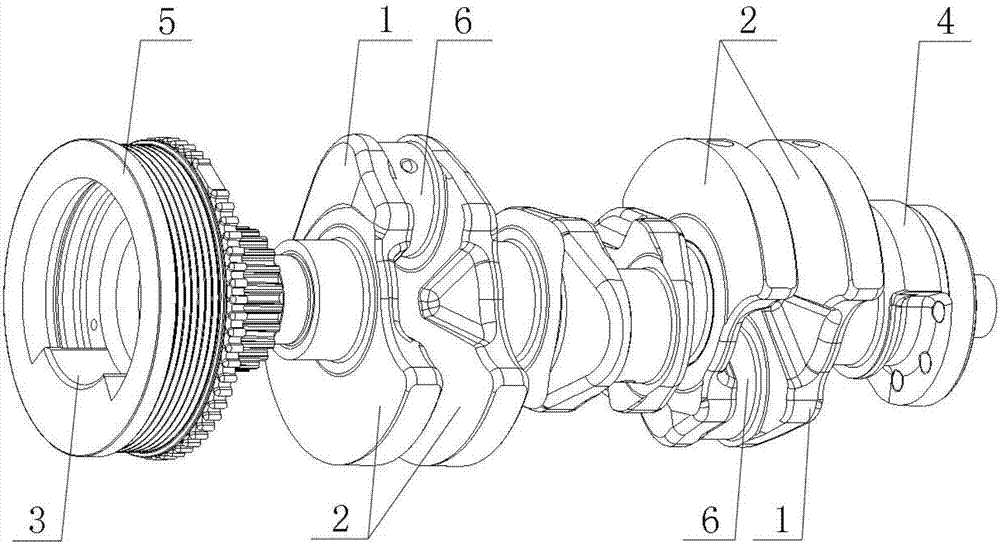
Vehicle, engine and crankshaft balance structure of engine
InactiveCN107237861AMeeting Basic Balance Water GoalsImprove universalityRotating vibration suppressionInertia force compensationEngineeringMoment of inertia
The invention discloses a crankshaft balance structure, which includes balance weights respectively arranged on several groups of crank arms with equal weight, and also includes a first counterweight arranged at the front end of the crankshaft and a second counterweight arranged at the rear end of the crankshaft. The mass of the first balance weight and the second balance weight are equal, the direction of the center of mass is opposite, and the direction of the center of mass of one of them is the same as the direction of the center of mass of the balance weight on the adjacent crank arm. In this way, the balance of the inertial force is maintained through the characteristics of the first counterweight and the second counterweight being equal in weight and reversed, and at the same time, one of them is in the same direction as the center of mass of the counterweight on the adjacent crank arm, so that the rotational inertia moment can be achieved Full balance and semi-balance of reciprocating inertia moment meet the basic balance design goal of the crankshaft system. Compared with the existing technology, there is no need to change the structure of the front and rear parts of the engine (such as the flywheel), which improves the universality and versatility . The invention also discloses an engine and a vehicle, the beneficial effects of which are as described above.
Owner:BEIQI FOTON MOTOR CO LTD
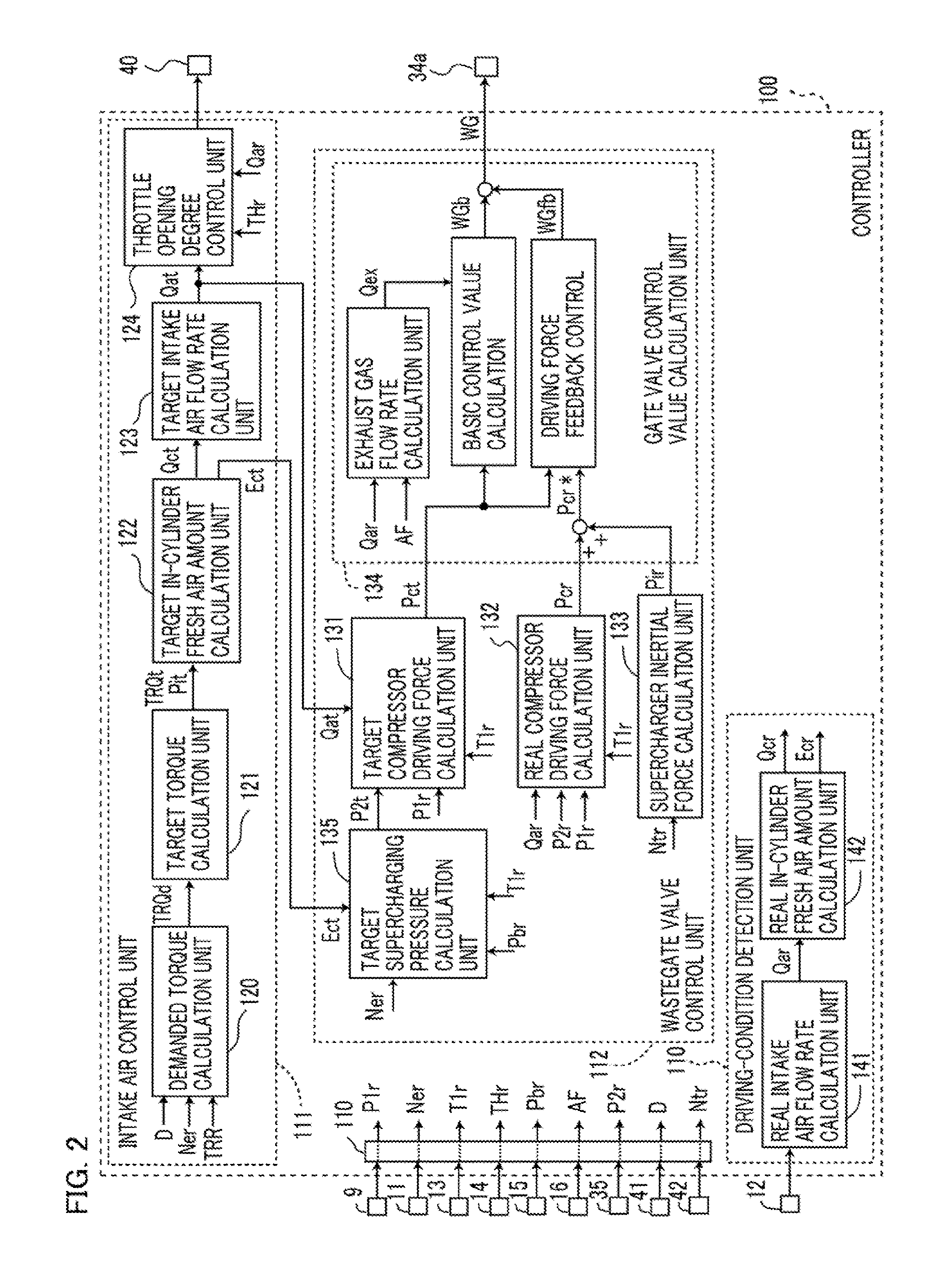
Controller for supercharger-equipped internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20170051663A1Stable feedback responseReduce in quantityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringActuator
A controller, for a supercharger-equipped internal combustion engine, that can improve the feedback response of compressor driving force is provided. In a controller, inertial force produced by an inertial moment of a supercharger is calculated, based on a real rotation speed of the supercharger; then, driving force feedback control is implemented in which a gate valve control value, which is a control value for a gate valve actuator, is changed so that an addition value obtained by adding the inertial force to the real compressor driving force approaches a target compressor driving force.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP +1
Metal laminate structure and method for making
InactiveUS20050011937A1Lower melting temperatureHigh melting temperatureWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaEpoxyLiquid layer
Laminates consisting of a high-damping core material sandwiched between two stiff, weldable skins. The laminate structures have increased resonant frequencies, improved damping characteristics, do not outgas, and may have a decreased inertial moment. The laminates are comprised of 100% metal constituents, and do not rely on epoxy or low-melting point solders. To make the laminate structures, a first alloyable metal is deposited on the surface of a dissimilar metal. The coated surface is then placed in contact with a second alloyable metal and allowed to interdiffuse at elevated temperatures. The metals are chosen such that diffusion creates an alloy with a melting point lower than either of the constituents. The processing temperature is set so that the alloy melts but leaves the base metals in solid form, causing a thin layer of liquid to form and wet both sides of the interface. External pressure is applied to the opposing base metals in such a way as to induce flow of the liquid layer and disrupt any oxide layers present on the surface of one or more of the base metals. Continued diffusion elevates the melting temperature of the liquid phase and causes it to solidify isothermally, creating a bond between the base metals. Highly polished surfaces on the base metals comprising the laminate structure are not required because the applied pressure causes the metal (in thin sheet form) to deform and create the intimate metal-metal contact necessary for diffusion. Moreover, the liquid flow helps to fill gaps between the parent materials and further mitigates the need for polished surfaces.
Owner:INTRL PLEX TECH INC
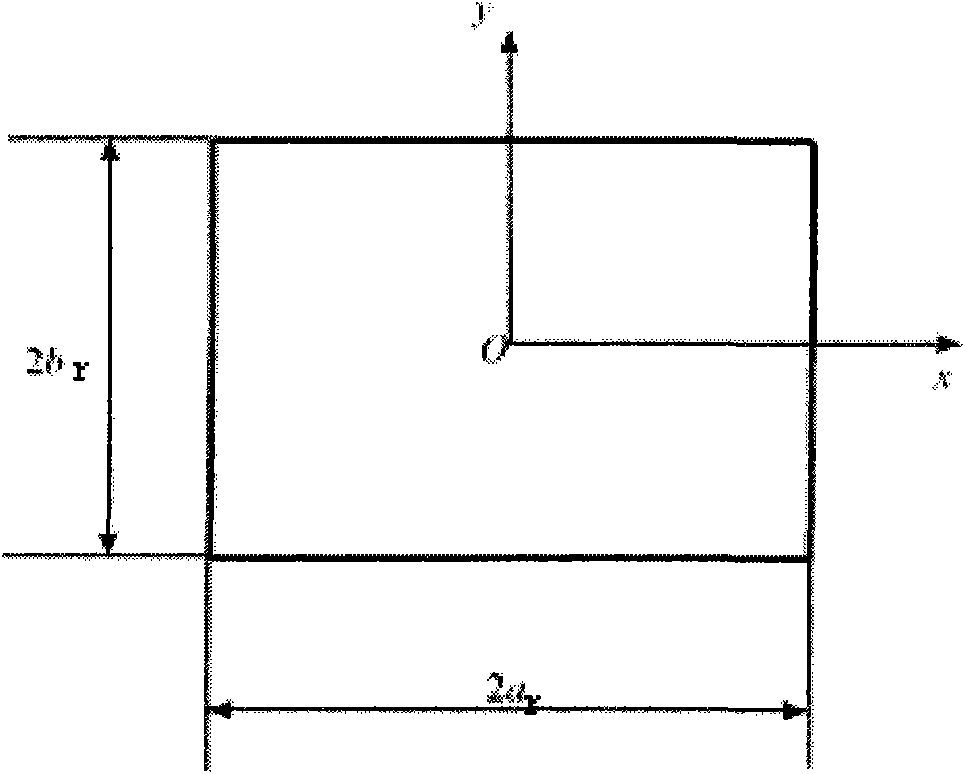
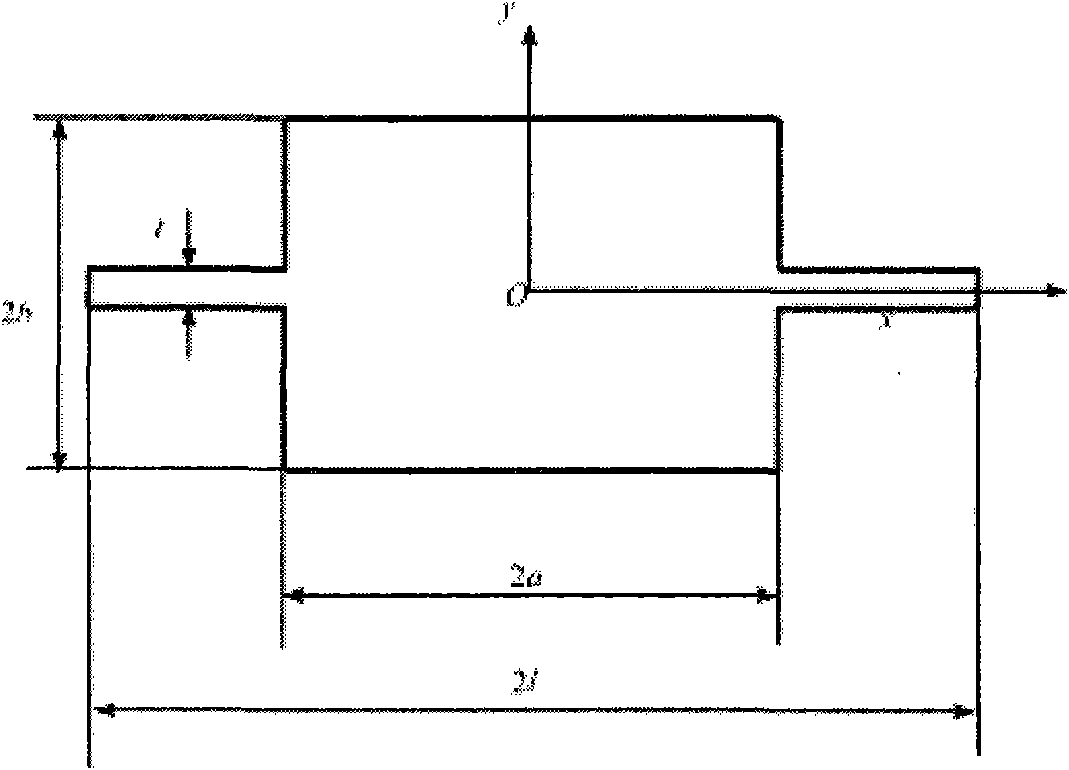
Method for determining sectional dimension of rectangular beam with lugs
ActiveCN102411652AHigh precisionImprove design efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsSize determinationPhysics
The invention belongs to the field of structural mechanics and relates to a method for determining the sectional dimension of a rectangular beam which is provided with lugs and used for flutter model design. The method for determining the sectional dimension of the rectangular beam with the lugs is characterized by comprising the following steps of: calculating the half width ar and the half height br of a rectangular section when a rectangular beam without any lug has a vertical inertia moment Ix and a polar inertia moment J which have preset values; adjusting the preset polar inertia momentJ; calculating the half width a and the half height b; and calculating the sectional half width l of the rectangular beam with the lugs when the rectangular beam with the lugs has a lateral inertia moment Iy and the lug thickness t which have the preset values. By the method, the precision of sectional rigidity of a model is improved, the uncertainty of model design is reduced, the time required by determining the sectional dimension is shortened, and the efficiency of designing a flutter model is improved.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Calibration device for test measuring beam of wave load of ship
ActiveCN106546408ACompact structureReasonable structureHydrodynamic testingInertial momentWave loading
The invention relates to a calibration device for a test measuring beam of the wave load of a ship. The calibration device comprises two loading support stools arranged separately, a support is arranged on the loading support stools, the measuring beam is arranged in the support, the two ends of the measuring beam are sleeved by loading frames respectively, and counterweights are applied to the bottoms of the loading frames. The calibration device is compact and reasonable in structure and convenient to operate; via the special-purposed calibration device, vertical and horizontal inertial moments and torque can be obtained convenient and rapidly and are similar to those of a practical ship, and it can be ensured that the torsional center is similar to that of the practical ship; and the calibration device can calibration relation between strains of different measuring profiles of the test measuring bean and the wave loads born by a profile of a hull.
Owner:CHINA SHIP SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH CENTER (THE 702 INSTITUTE OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDUSTRY CORPORATION)
Metal laminate structure and method for making
InactiveUS6572984B2Automatic conveying/guiding stockWelding/soldering/cutting articlesEpoxyInertial moment
Laminates consisting of a high-damping core material sandwiched between two stiff, weldable skins. The laminate structures have increased resonant freguencies, improved damping characteristics, do not outgas, and may have a decreased inertial moment. The laminates are comprised of 100% metal constituents, and do not rely on epoxy or low-melting point solders.
Owner:INTRL PLEX TECH INC
Method of measuring moment of inertia of washing machine drum and washing machine implementing the method
ActiveCN102277706AImprove measurement accuracyEliminate measurement errorsOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusSynchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous motor
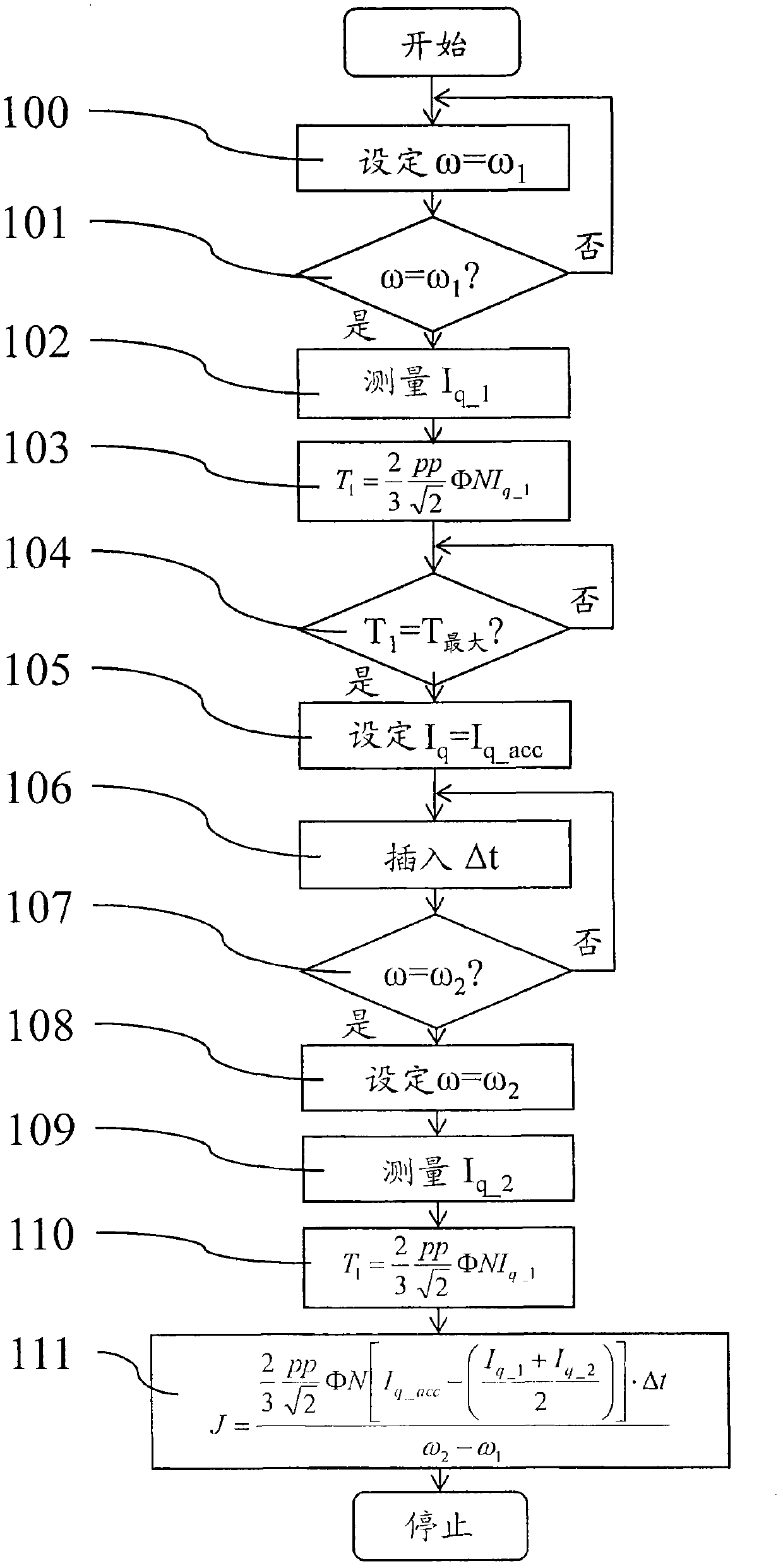
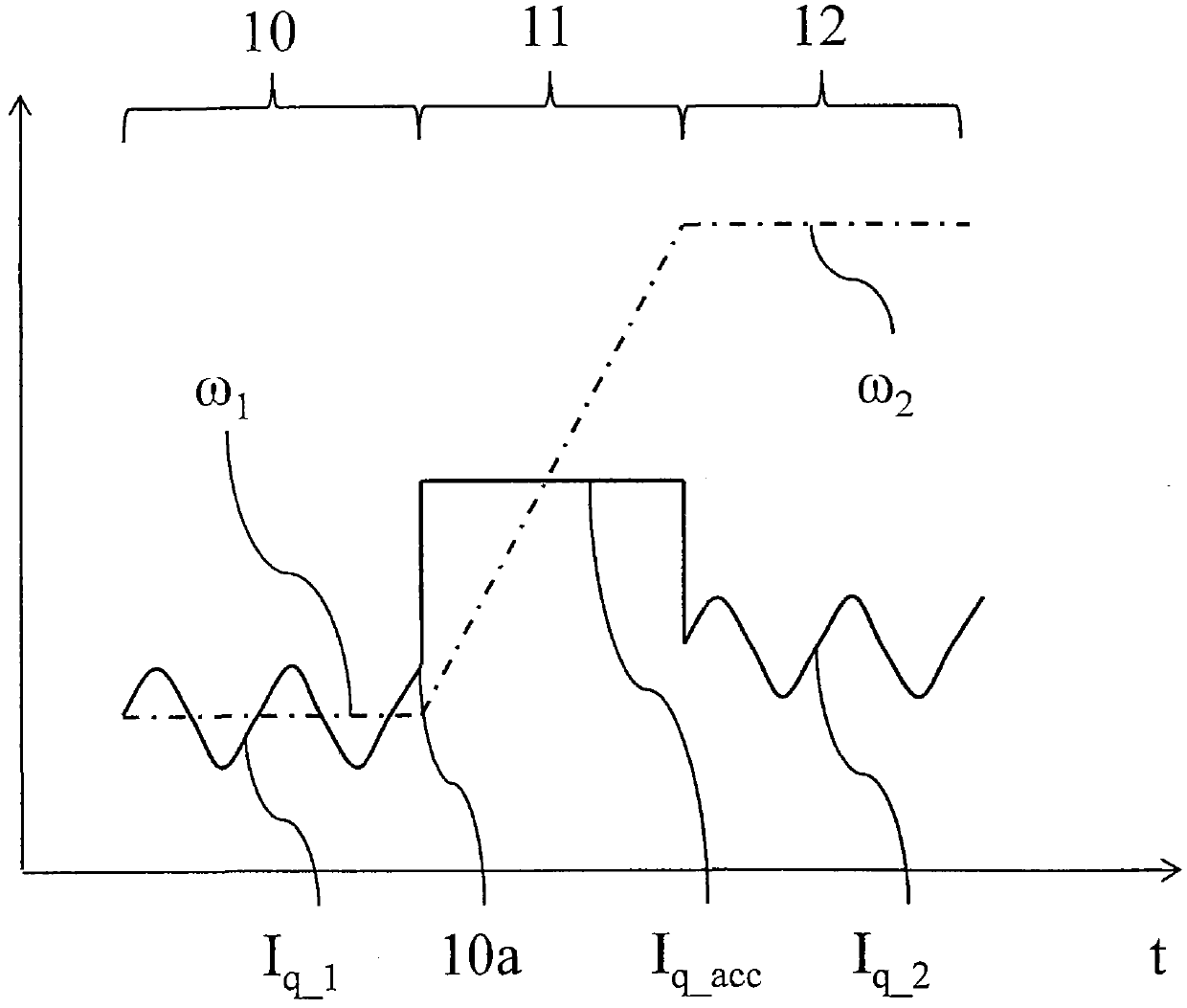
A method of measuring a moment of inertia of a drum of a washing machine and a washing machine implementing the method, the method comprising the steps of: rotating the drum by a permanent magnet synchronous motor so that the drum reaches a first rotational angular velocity (100-101) ; at said first angular velocity, determining (104) a synchronization point in a periodic signal representing said torque delivered by said synchronous motor; Moment starts the acceleration transient of the drum (105); when the second angular velocity is reached, terminates the acceleration transient (107); obtains the duration of the acceleration transient (106); according to the following formula, based on the An indirect measurement of the moment of inertia of the drum is performed by the value of the torque supplied to the drum during an acceleration transient, the value of the duration of the transient, and the change in angular velocity in the transient:
Owner:ASKOLL HLDG SRL
Foam-core golf balls
A golf ball with a controlled moment of inertia and controlled spin rate is disclosed. In one embodiment, the golf ball comprises a core, an intermediate layer and a cover, wherein the intermediate layer comprises a foamed highly neutralized polymer, has its specific gravity reduced to less than about 1.05, wherein the reduction in the specific gravity of the intermediate layer is less than about 25% to minimize the reduction in the coefficient of restitution of the golf ball to about 6% or less.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
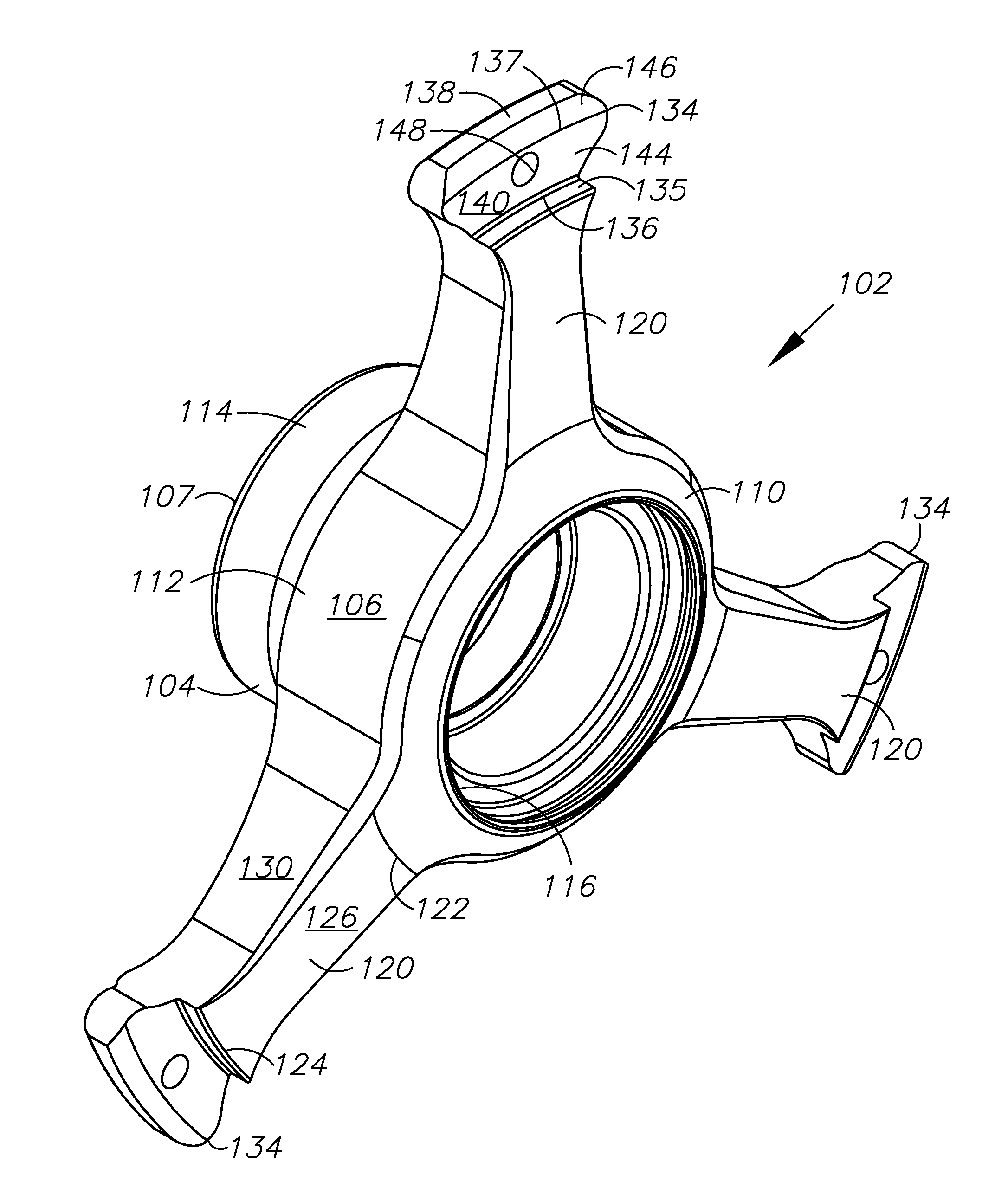
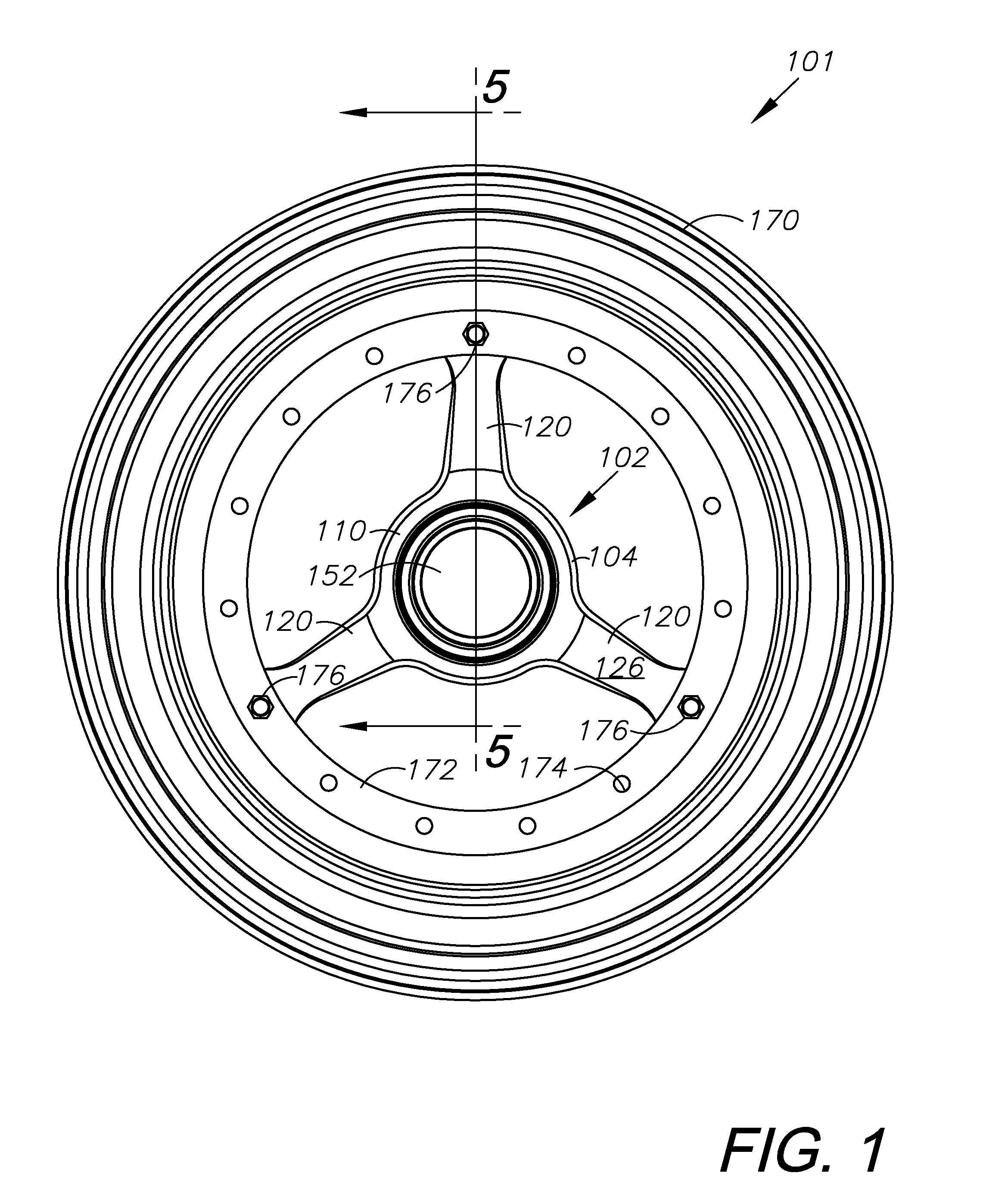
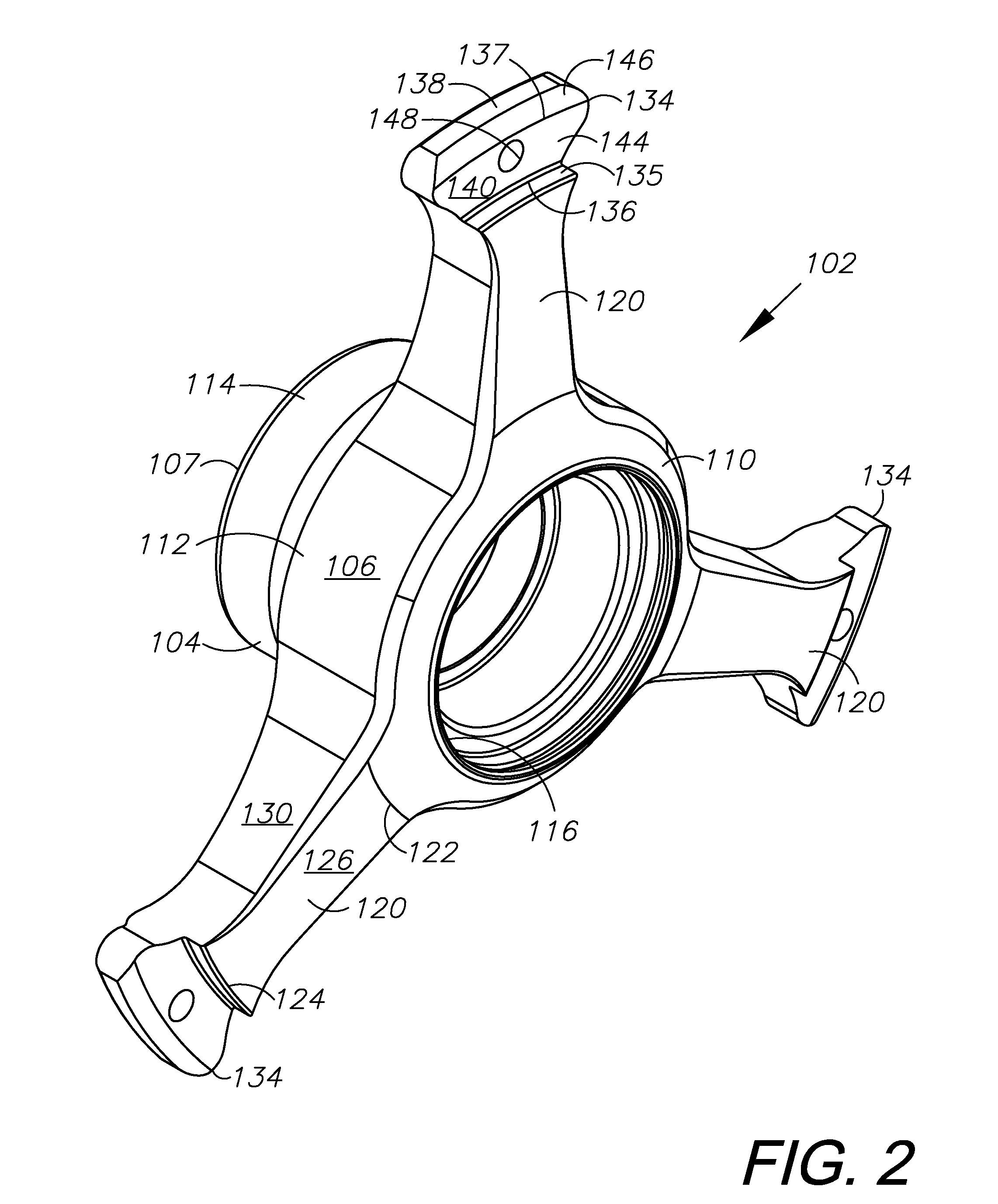
Wheel hub
InactiveUS20100320830A1Decreases mass weightDecreases static weightHubsSpoked wheelsMoment of inertiaEngineering
A hub for a wheel having a low mass and low moment of inertia includes a tubular body with a bore having, and three radially-extending arms that terminate with a tab. The hub is adapted for mounting on the radial flange of a wheel rim. The arms are space 120 degrees apart and extend from the body tapering from a relatively thick and wide portion to a relatively narrow and thin portion. A bore in the tab receives a fastener for securing the tab to the flange. Mounting hardware including spacers, bearings, O-rings, and an oil seal are secured within the body bore for mounting the hub onto the spindle of a vehicle steering mechanism. A hub nut and cotter pin secures the hub to the spindle. A center cap covers the open end of the body. The hub may optionally include three flanges for mounting a brake rotor.
Owner:WELD RACING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com