Magnetron radiating element, magnetron and microwave cooking device
A heat dissipation element and cooking device technology, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, discharge tubes, and time-of-flight electronic tubes, can solve problems such as insufficient heat dissipation of the sleeve, loss of heat dissipation effect of the heat dissipation plate, and limited coaxiality, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Embodiment 1: A magnetron heat dissipation element with better combination of processing simplicity and heat dissipation effect.
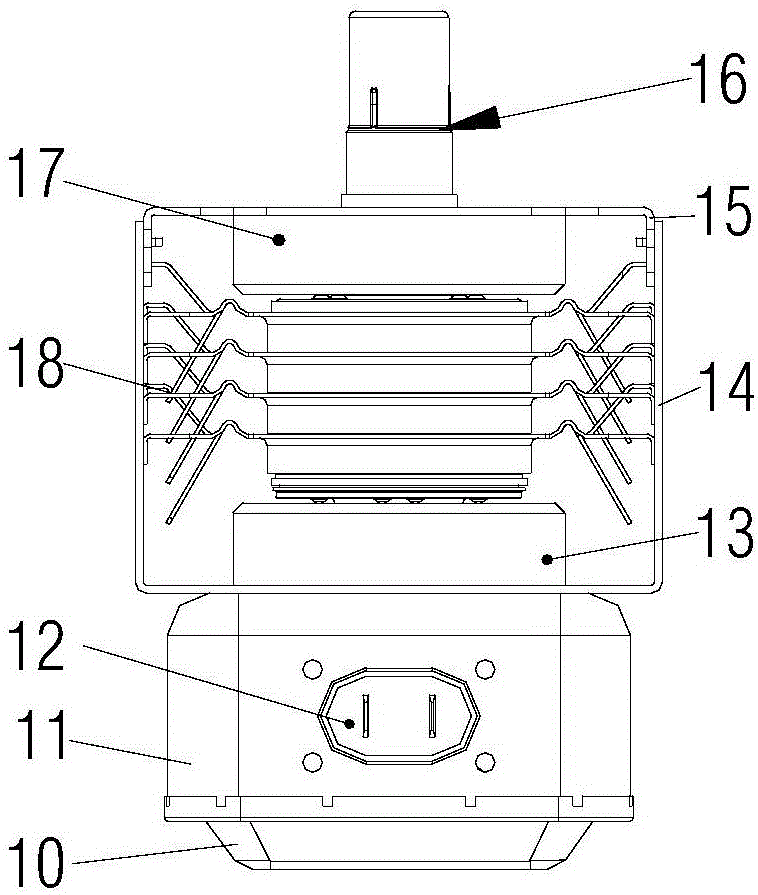
[0043] like Figure 4 and Figure 6 As shown in , the magnetron cooling element according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention includes a central cooling body 105 . exist Figure 4 to Figure 7 In the first specific embodiment of the magnetron heat dissipation element shown in , the central heat dissipation body 105 has a rectangular cross-section (such as Figure 6 As shown in , including a square cross-section), a cylindrical central assembly hole that is coated and bonded to the outer wall of the anode cylinder is formed on the central radiator 105, and the inner hole wall of the central assembly hole is the contact surface 104, The contact surface 104 is attached to the outer wall of the anode cylinder to conduct heat conduction therewith.
[0044] Along the axial direction of the anode cylinder, the height of the centra...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Embodiment 2: A heat dissipation element for a magnetron with priority given to the heat dissipation effect.
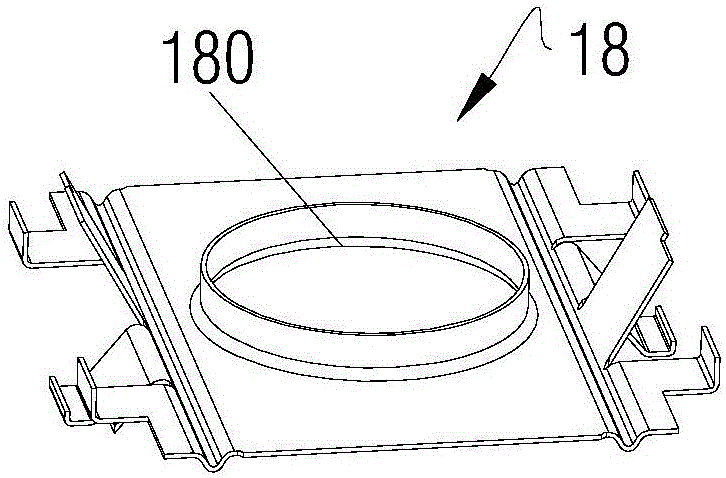
[0055] like Figure 9-11 As shown in , the difference from the previous embodiment is that, along the radial direction of the anode cylinder, the central radiator 105 has a circular cross-section, so that the thickness of the central radiator 105 is uniform, close to the thin-walled sleeve structure (compared to In embodiment 1, the center radiator 105 is thicker at the four corners of the rectangular cross-section and thinner near the midpoint of the side length), this structure is more conducive to the heat conduction from the outer wall of the anode cylinder to the center radiator 105 Dissipate through the cooling fins. Moreover, the formed central air channel 102 is an annular band structure, and when the cooling air flows through the central air channel 102 , it is more fully mixed with the hot air in the central air channel 102 , and the heat dissipation...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3: A heat dissipation element for a magnetron that gives priority to processing simplicity.
[0059] like Figure 12 to Figure 14 As shown, the only difference between it and Embodiment 1 is that the second middle air passage is omitted, so that the central radiator 105 only has the first middle air passage on both sides of the cooling air blowing direction.
[0060] As described in Example 1, the second middle air channel is an integral extrusion-molded structure with rear row of cutters. Canceling the second middle air channel can correspondingly save the process of material removal, and only need to drill the center after extrusion molding. Only holes are needed, and the manufacturing process and material costs are reduced.
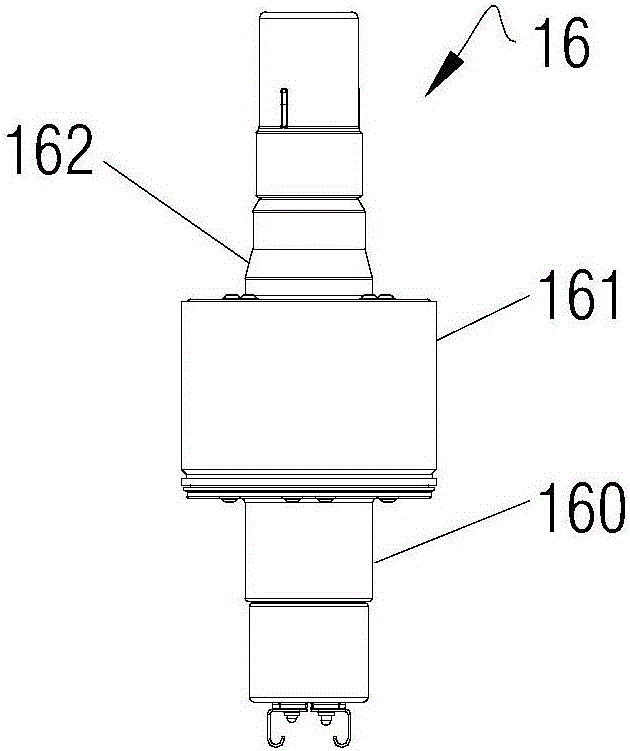
[0061] In addition, the present invention also provides a magnetron ( Figure 8 It can represent the installation structure of the magnetron in the first two embodiments, and the structure of the magnetron formed by the installation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com