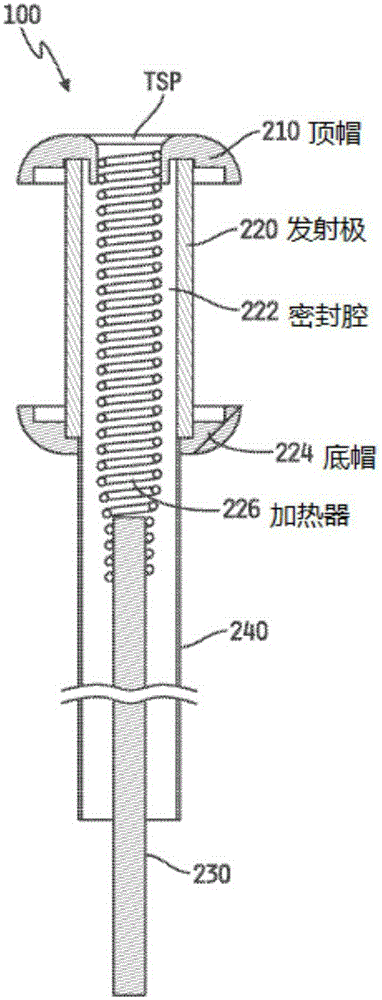
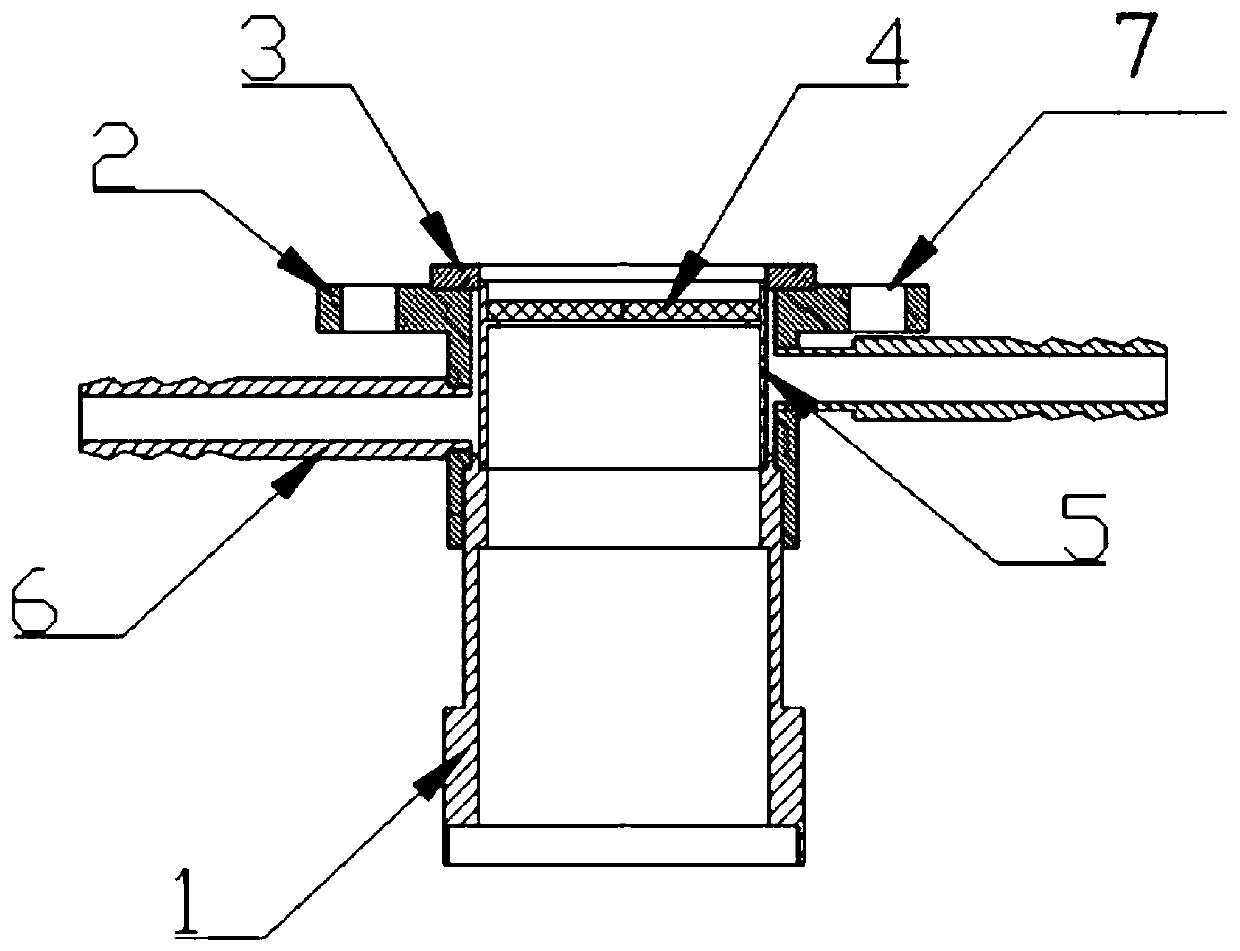
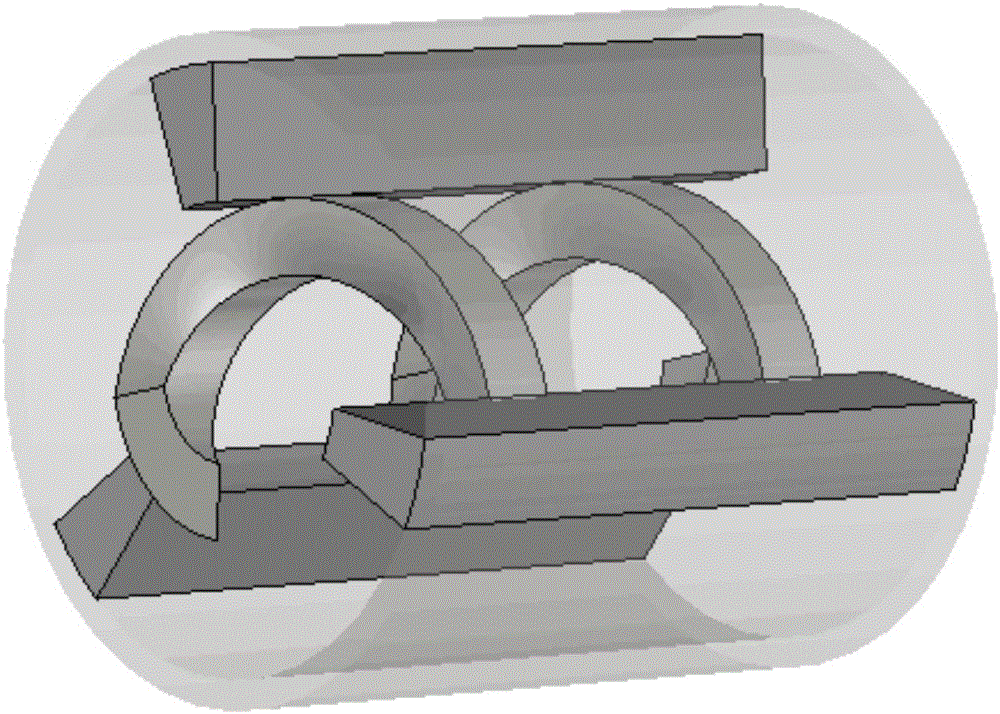
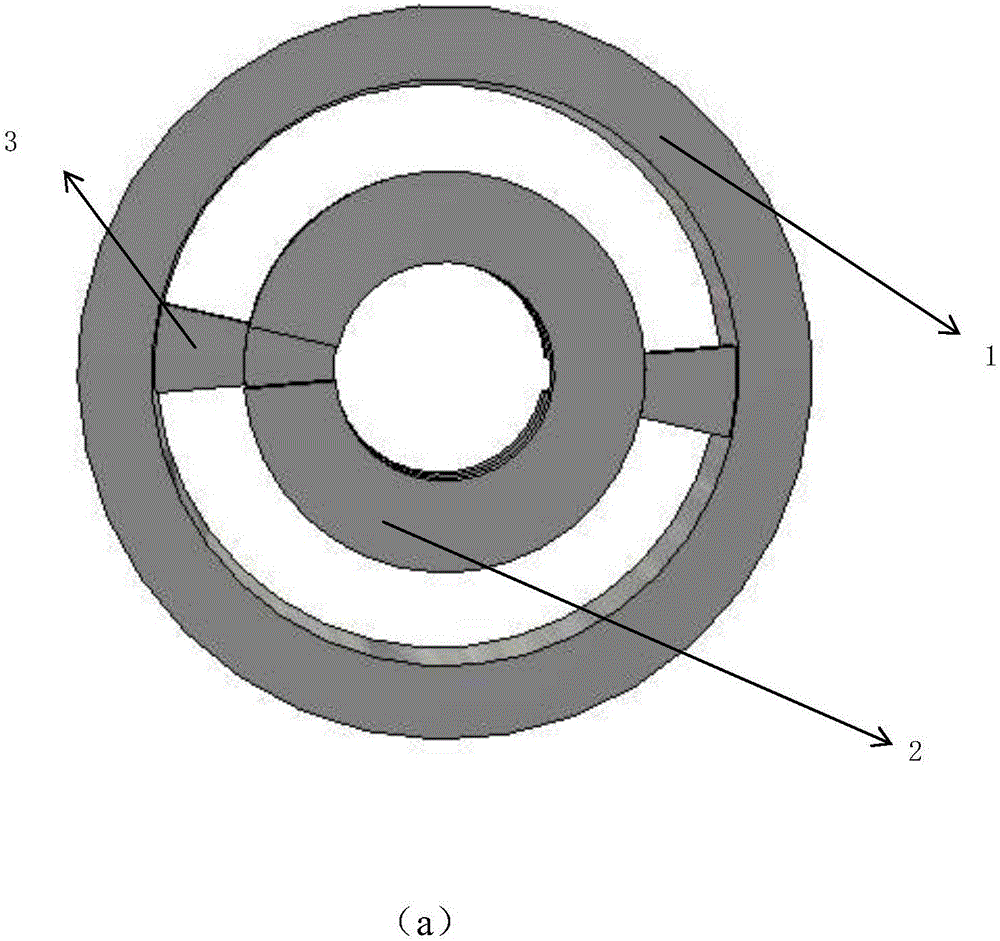
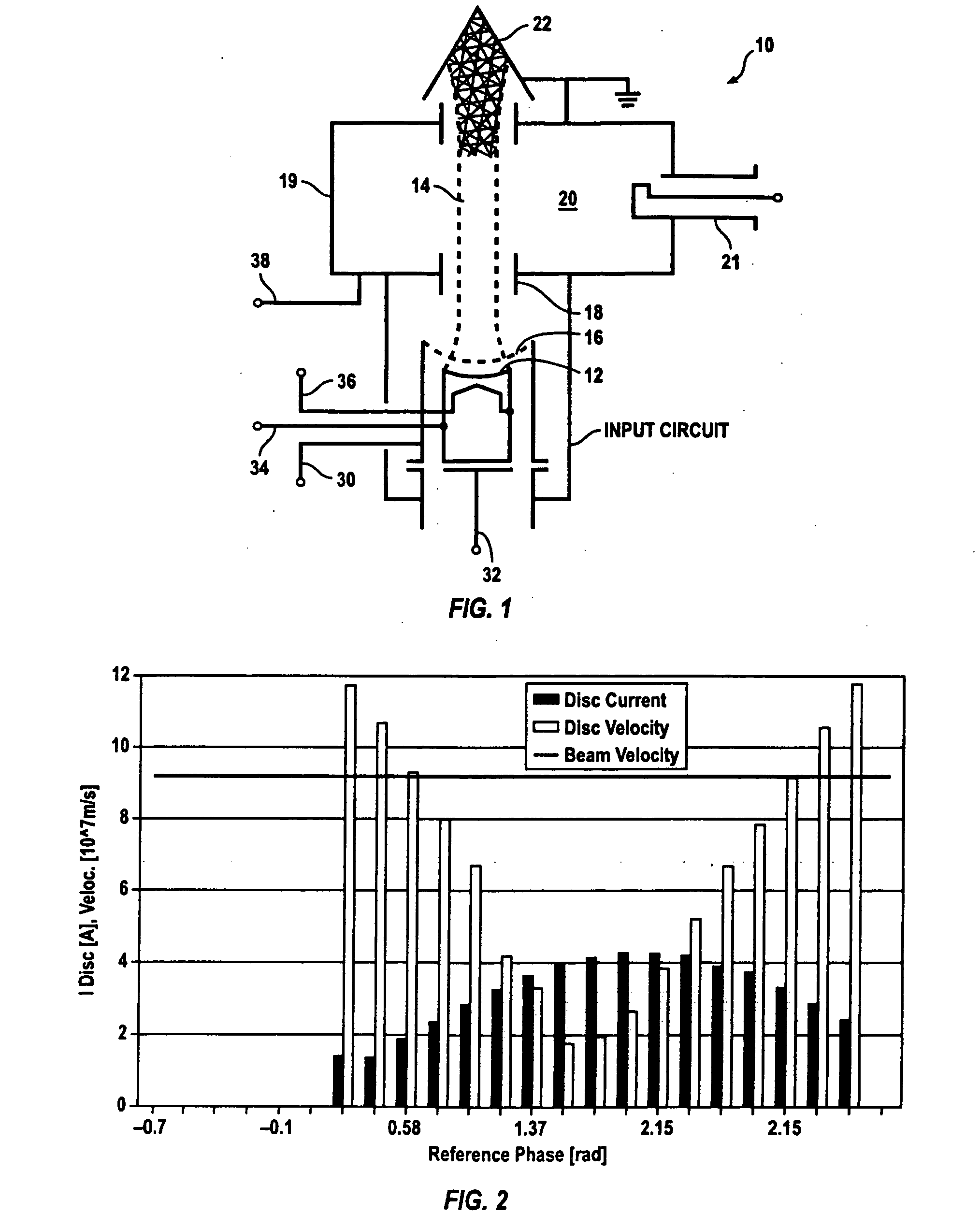
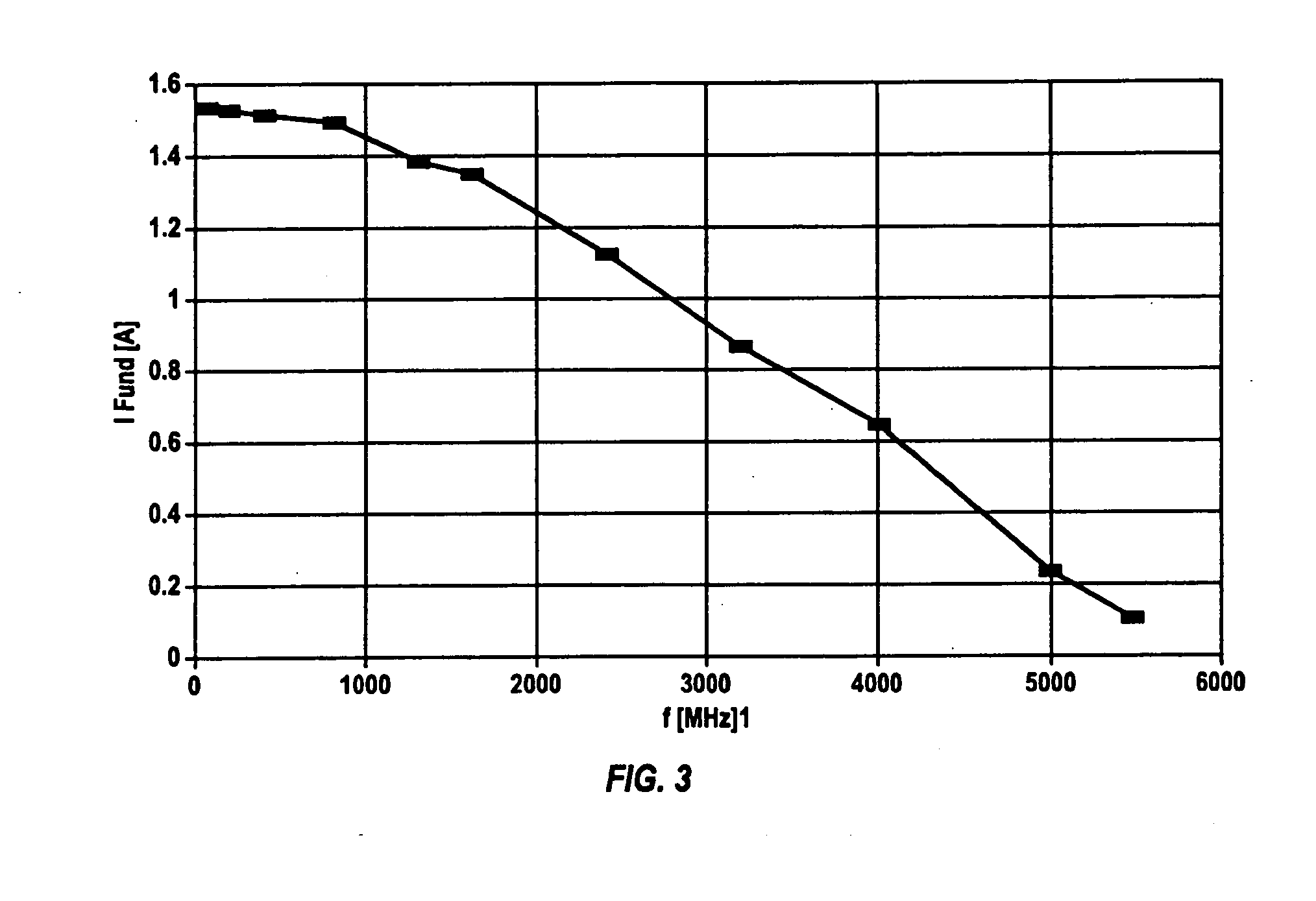
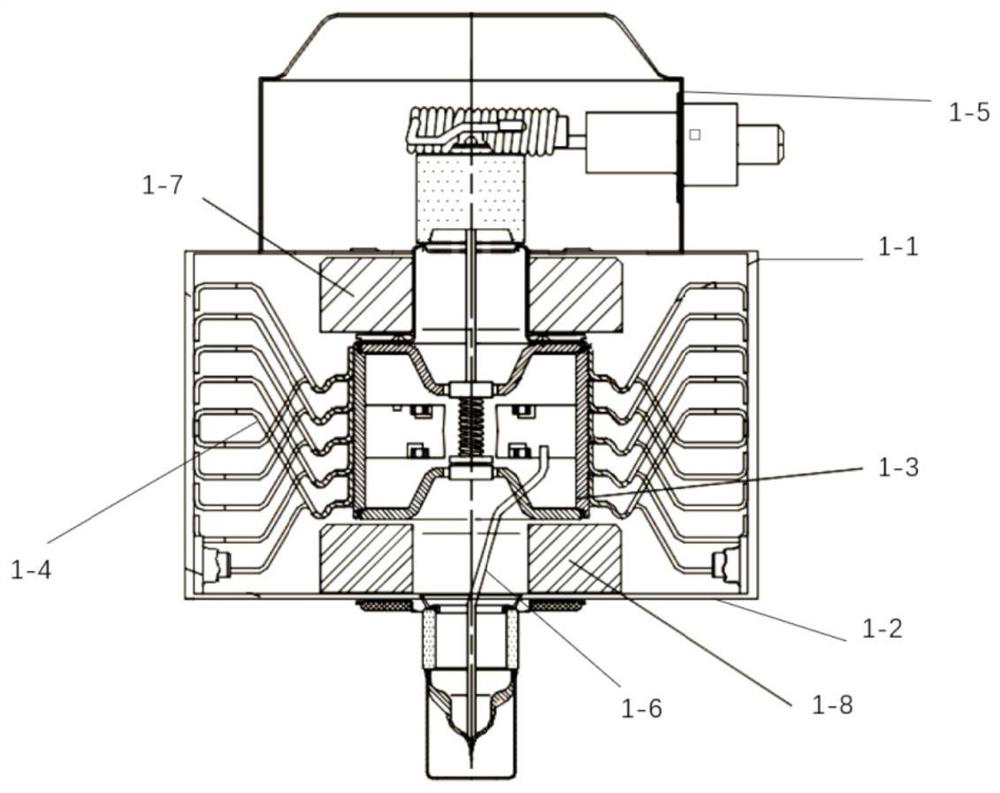
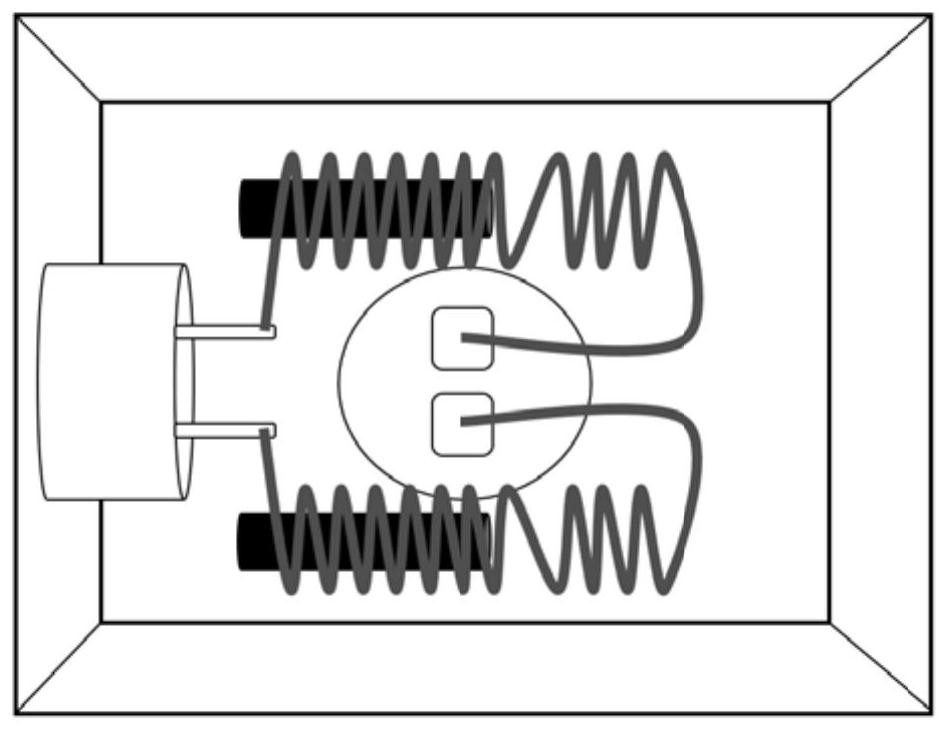
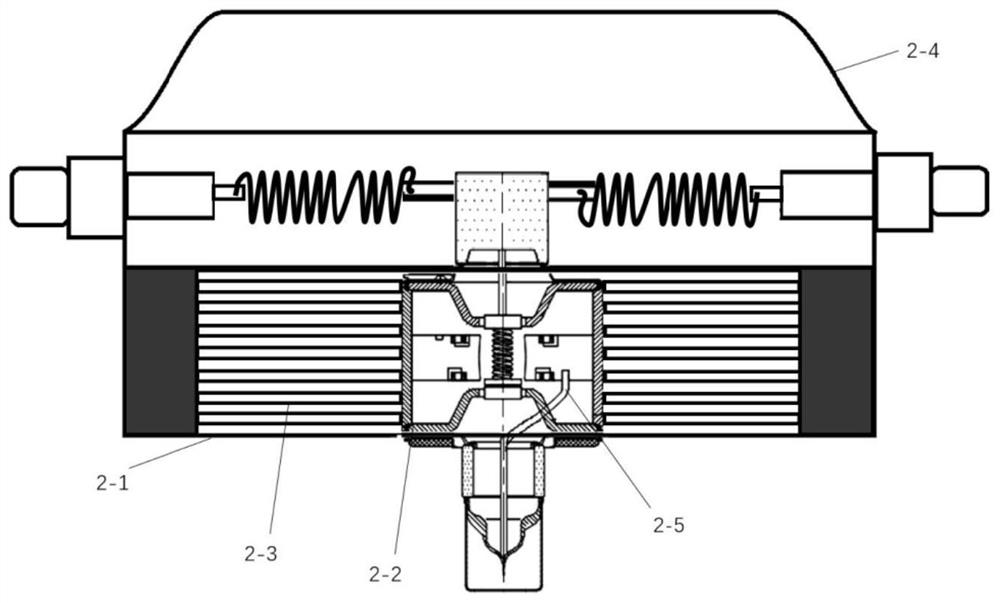
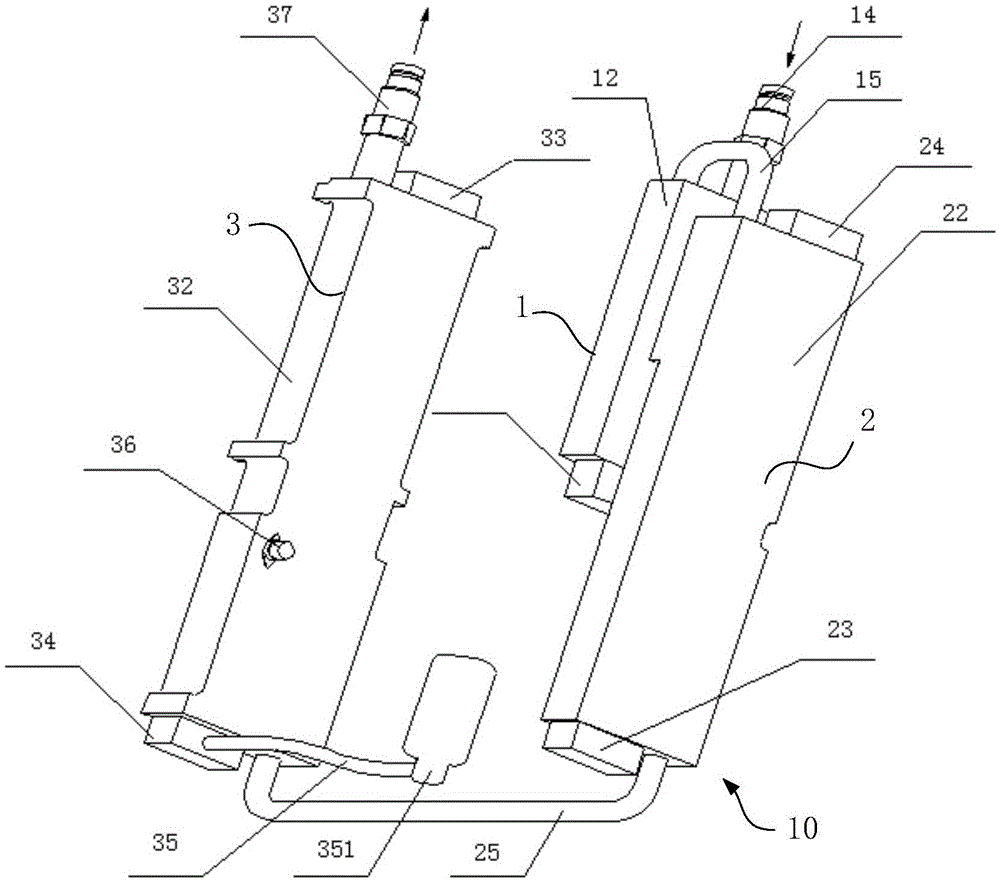
Patents
Literature
89results about "Transit-tube cooling methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
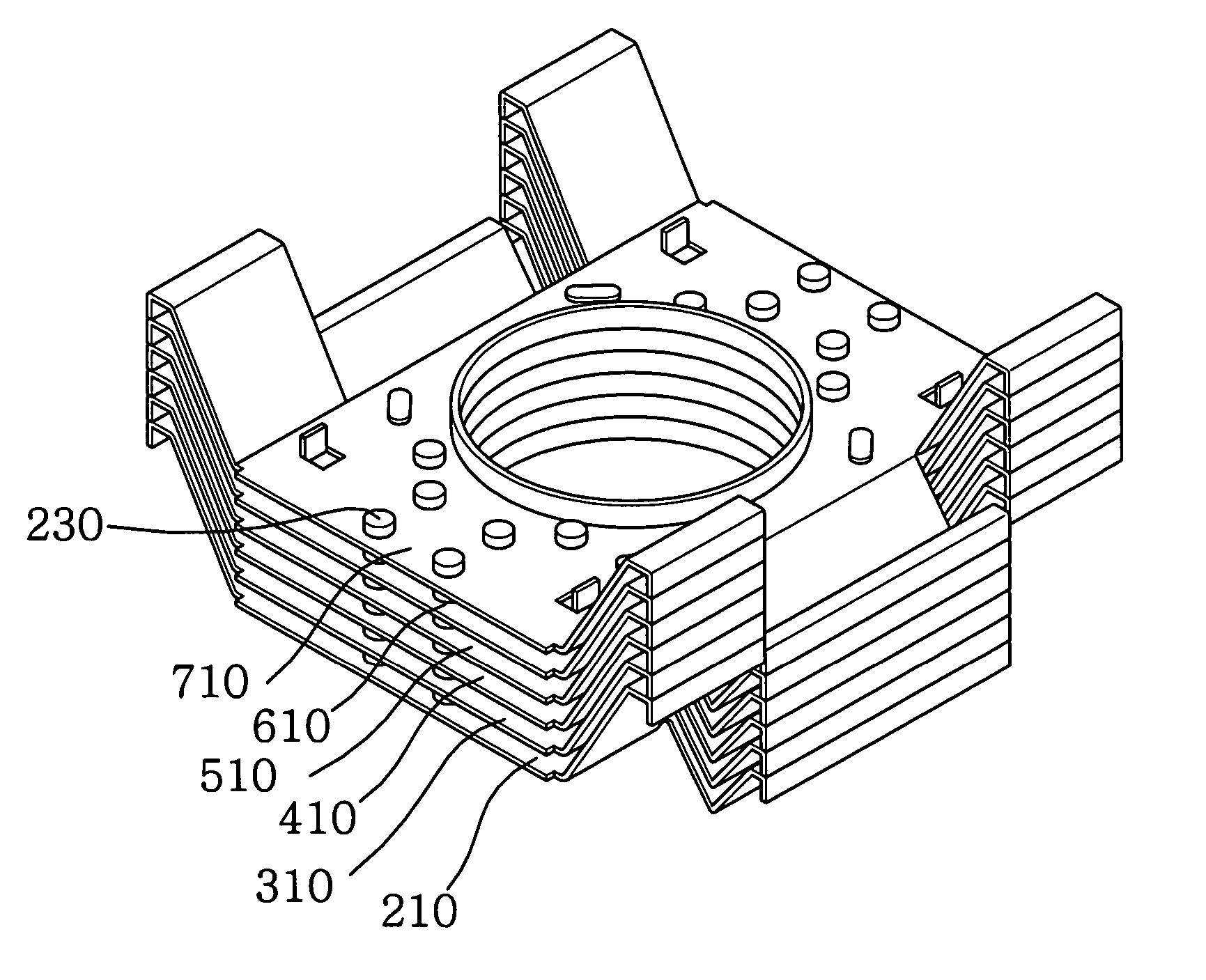
Magnetron cooling fin
InactiveUS20060049766A1Improve cooling efficiencySimple structureMagnetronsSolid-state devicesEngineeringHeat sink
A magnetron cooling fin is disclosed, characterized in that a plurality of turbulence-promoting protrusions are provided on one side of a planar body that has a boss-type through-hole in which an anode is coupled and a plurality of coupling pieces outwardly extending and bent at edges of the planar body, whereby, with inflow air undergoing flow separation at top ends of the turbulence-promoting protrusions and coming again into contact with the planar body, an existing temperature boundary gets thinned and a friction coefficient gets increased, thereby improving a heat transfer rate and an cooling efficiency.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
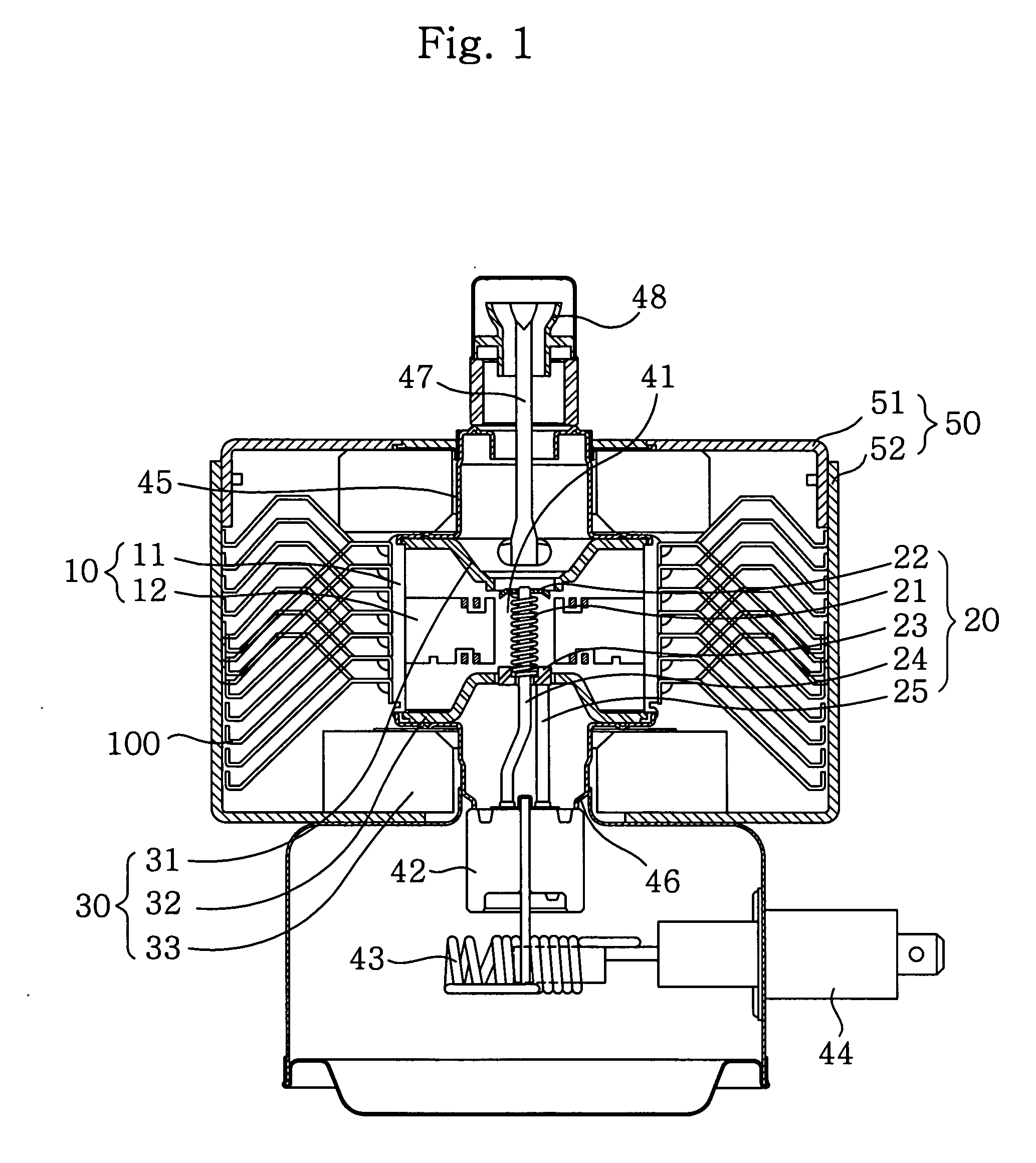
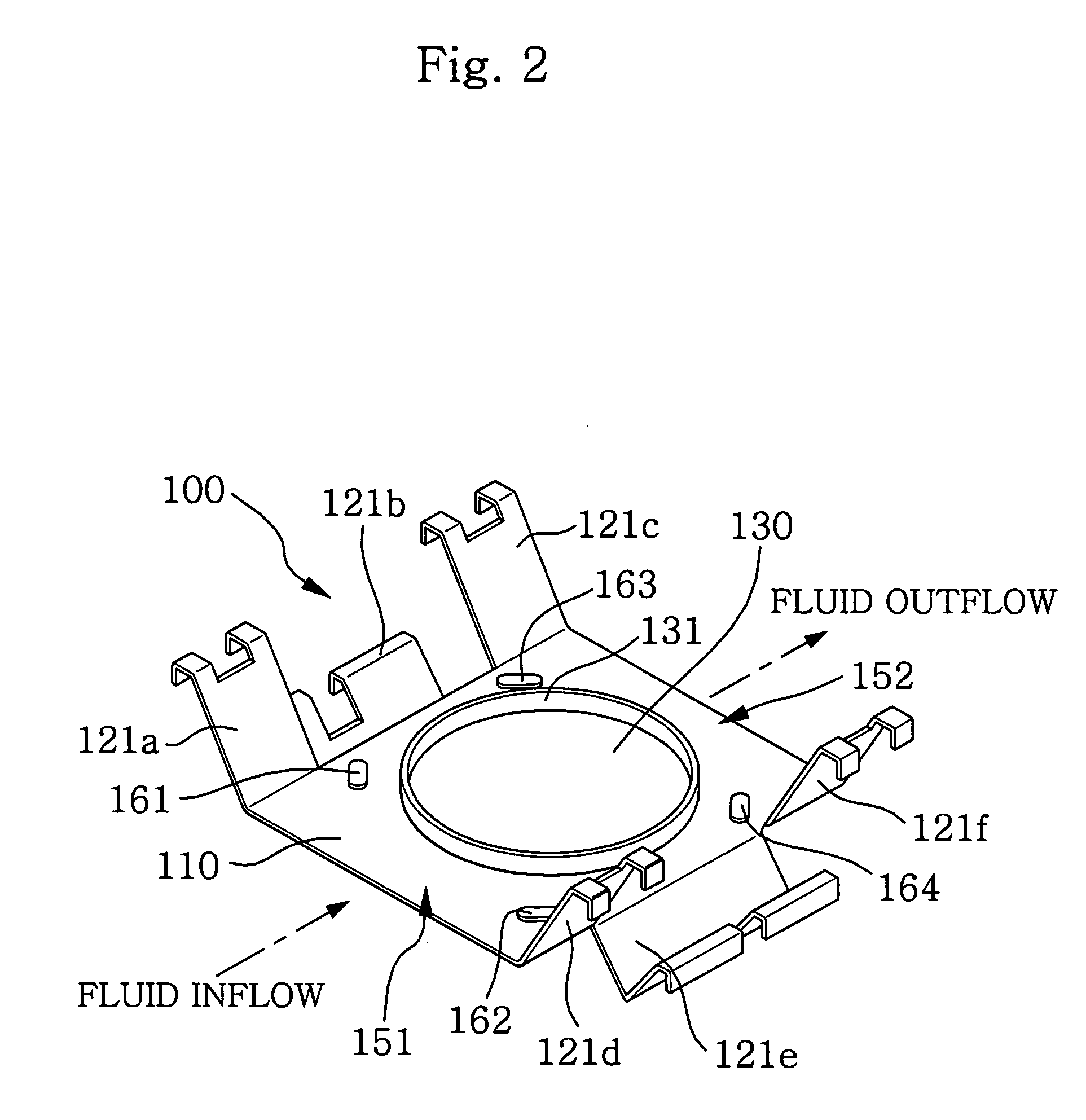
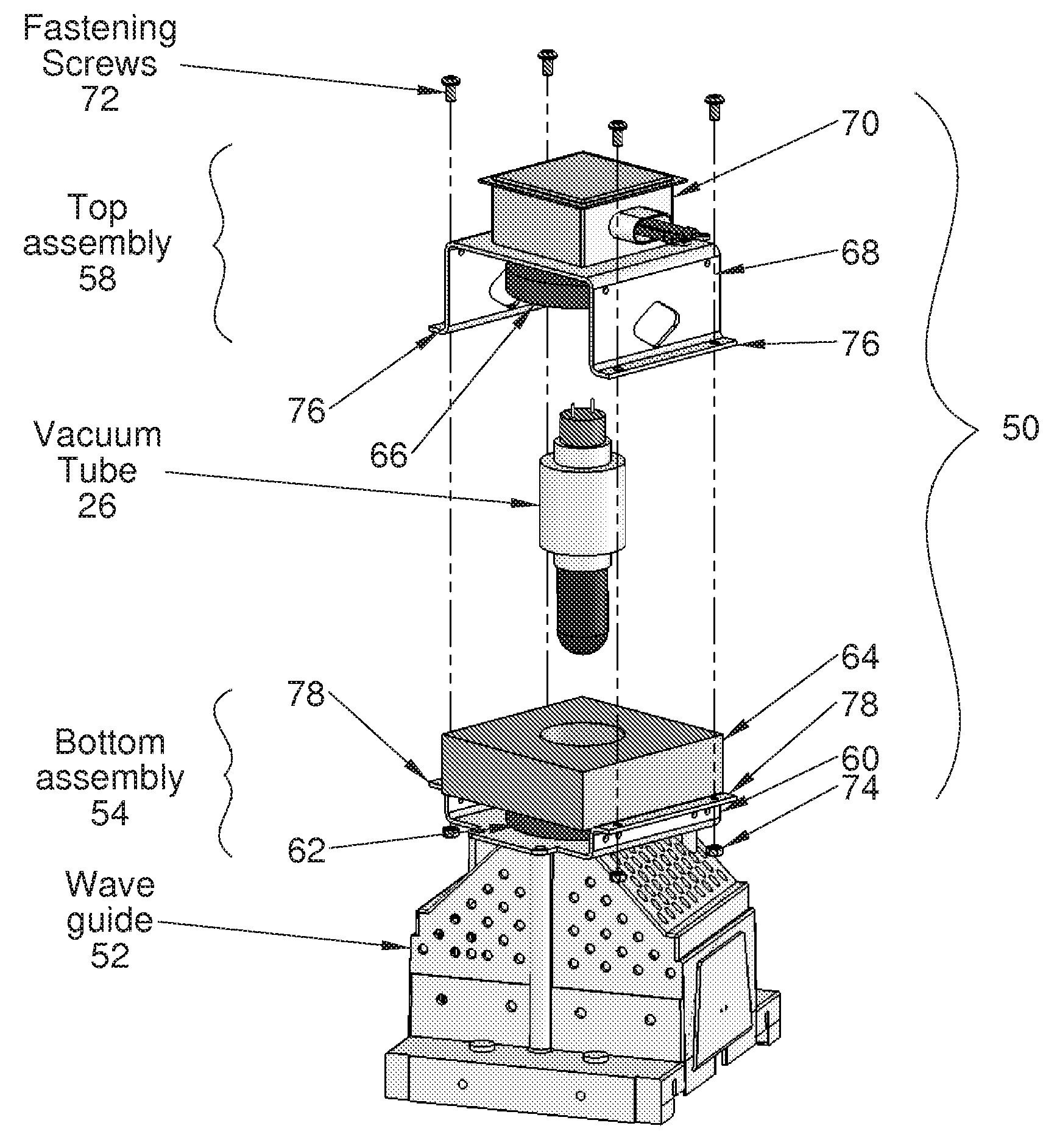
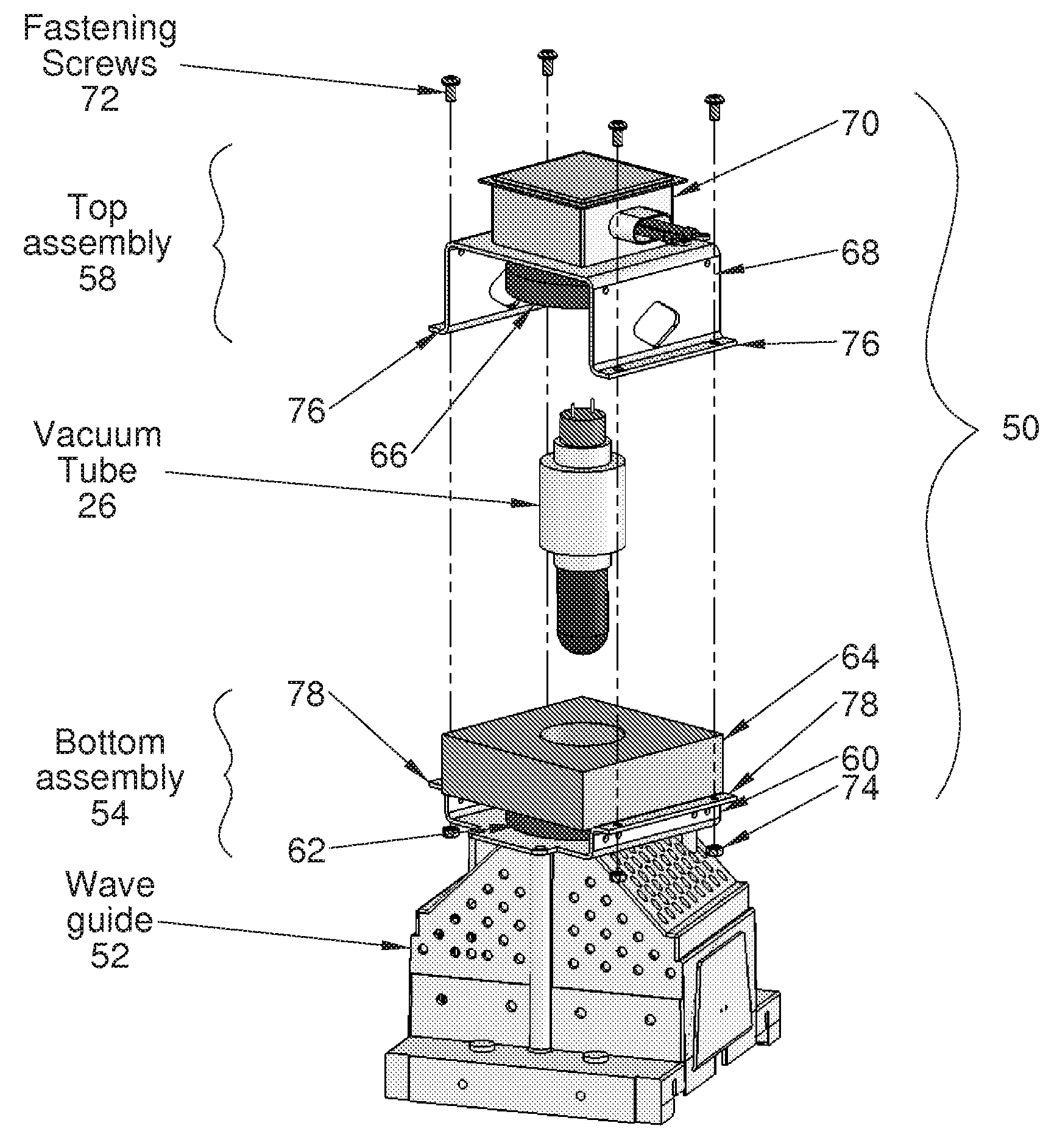
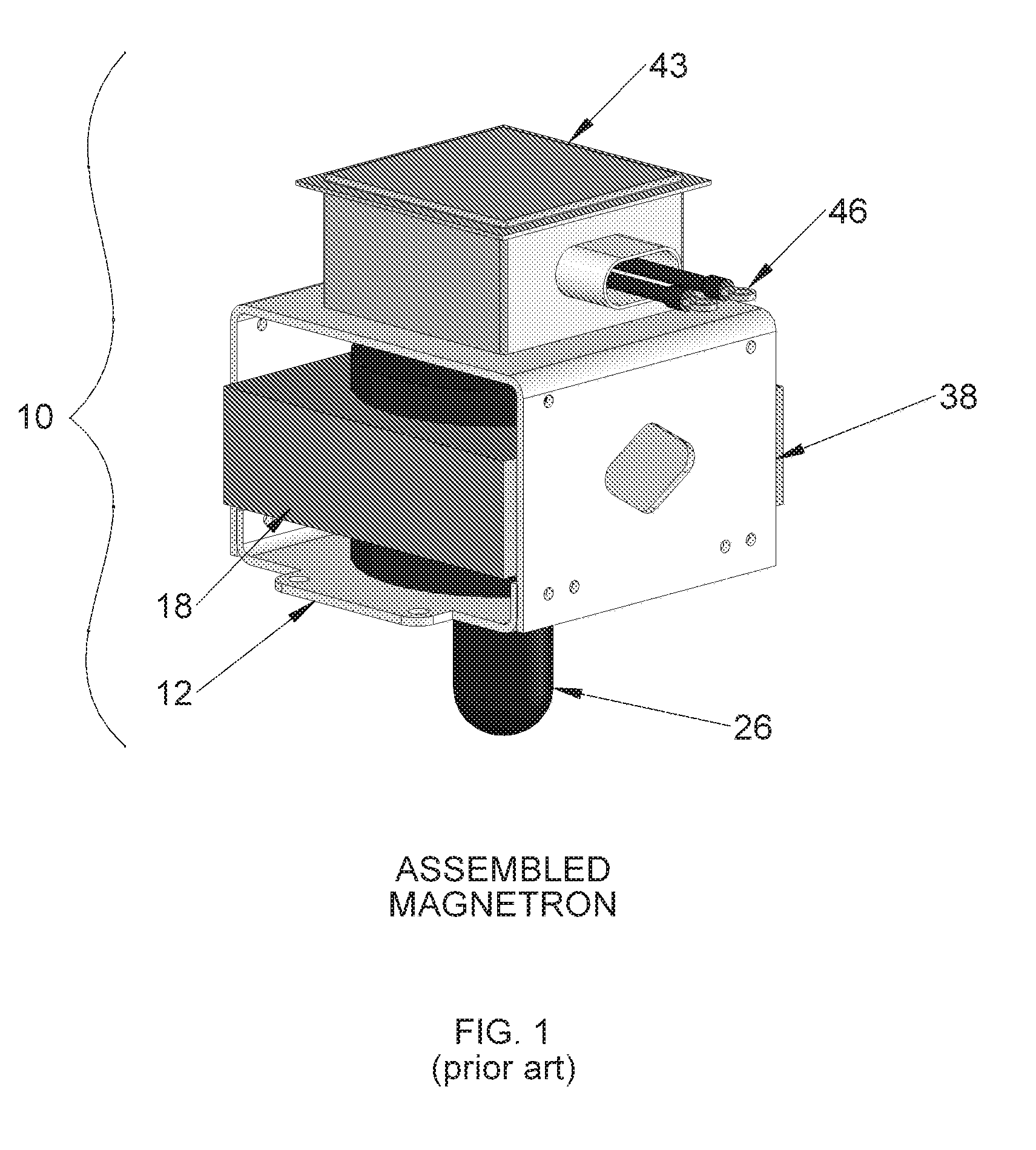
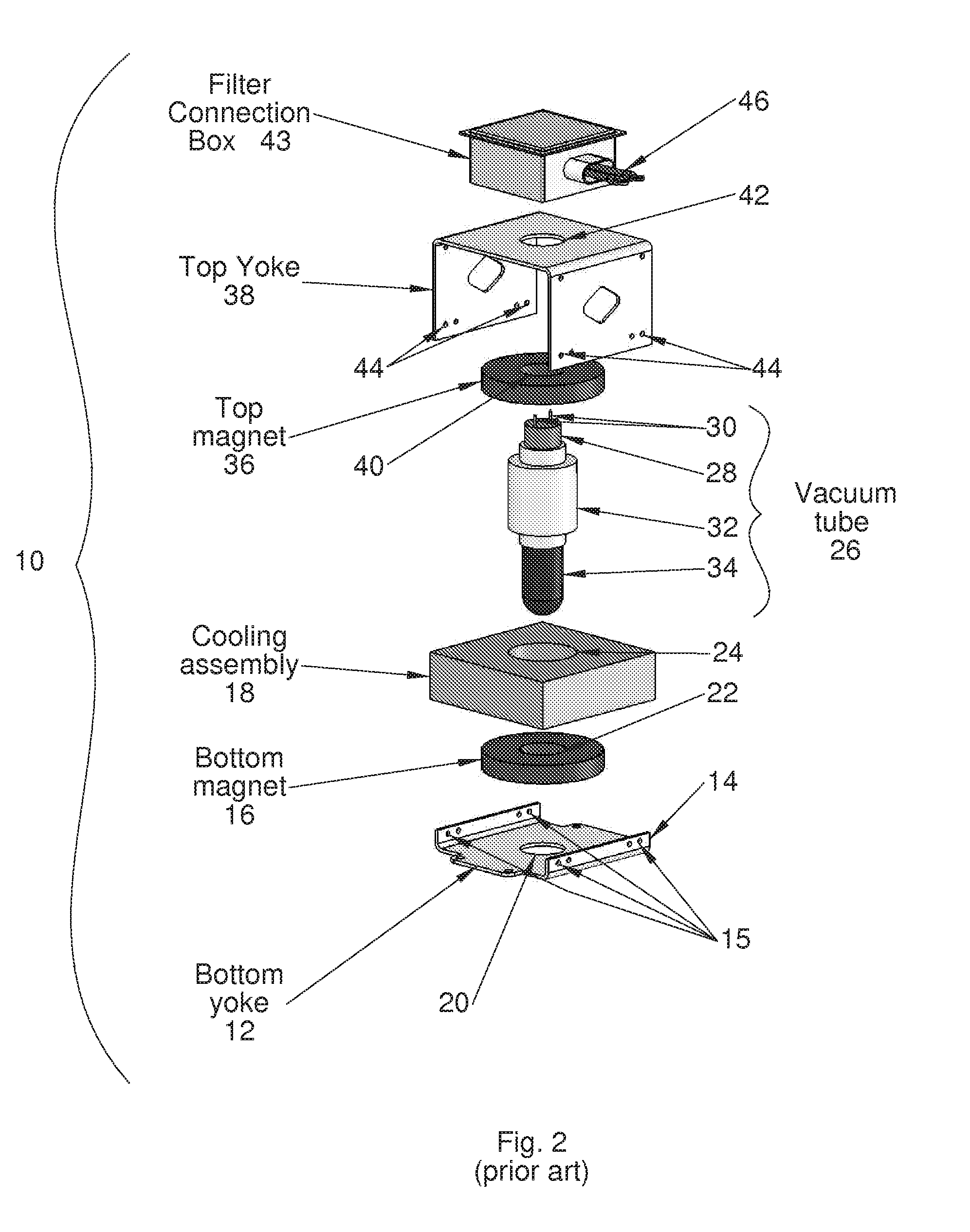
Modular magnetron
InactiveUS20110012508A1Reduce electromagnetic interferenceMagnetronsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsEngineeringVacuum tube
A modular magnetron for use in UV curing lamp assembly is disclosed. The modular magnetron includes a vacuum tube having a vacuum tube body, a top assembly, and a bottom assembly. The top assembly is configured to substantially overlay the vacuum tube. The bottom assembly is configured to substantially extend about the vacuum tube, the vacuum tube being positioned to partially protrude from the bottom assembly, the bottom assembly including a cooling assembly configured to employ a flexible clamp-type fitting about the vacuum tube body for substantially maintaining thermal and electrical conductivity. The top assembly is configured to be releasably fastened to the bottom assembly about the vacuum tube with removable fasteners.
Owner:HERAEUS NOBLELIGHT AMERICA
Traveling-wave valve arrangement
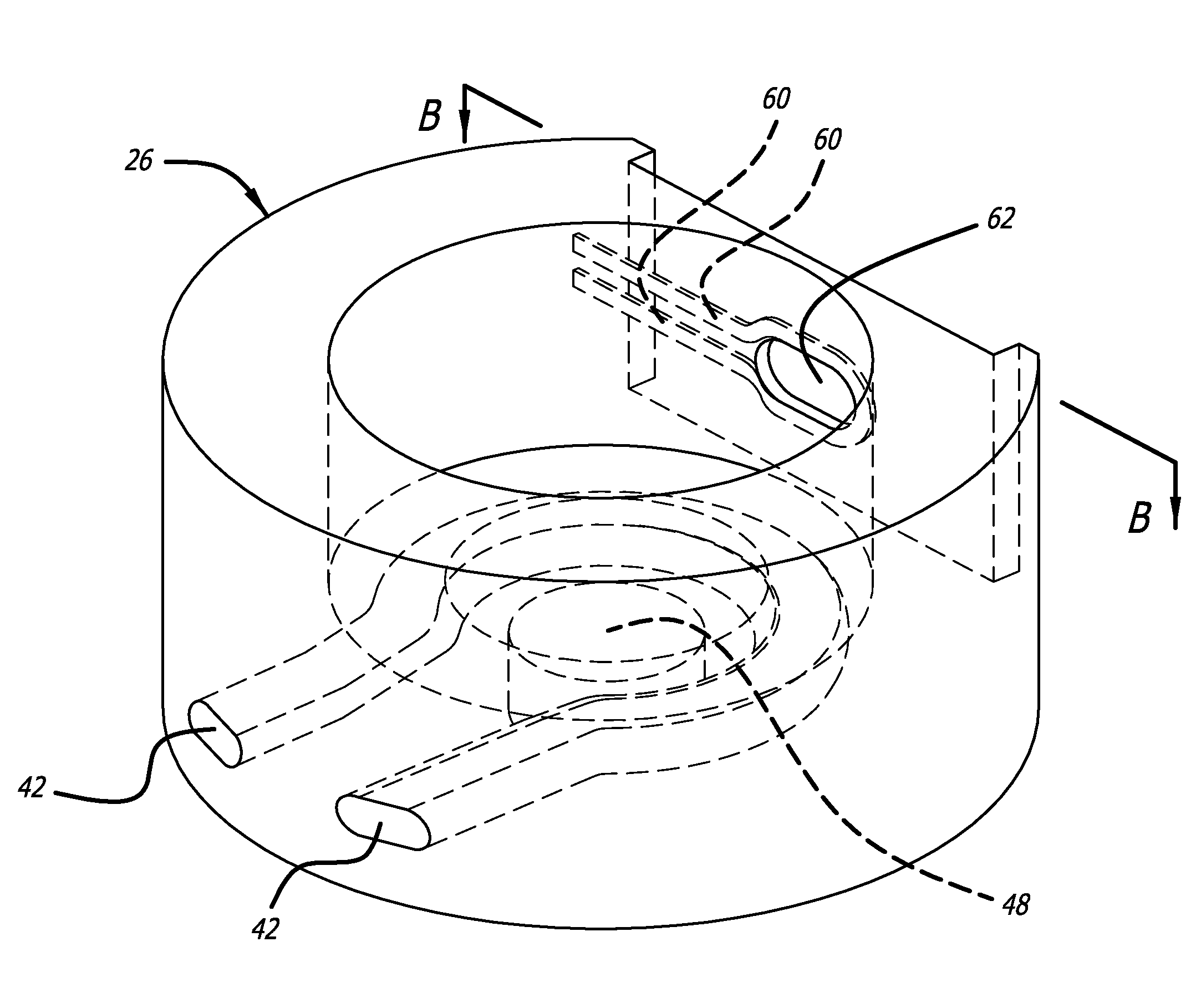
InactiveUS6486604B1Reduce heatLong signal pathTravelling-wave tubesDischarge tube main electrodesActive coolingMechanical engineering
For a traveling-wave valve arrangement with a traveling-wave valve and a linearizing circuit arrangement, it is proposed to design the linearizing circuit arrangement and the traveling-wave valve as one constructional unit and, for the thermal protection of the linearizing circuit arrangement in the simultaneous presence of a high permissible temperature of the valve housing, to maintain the circuit arrangement by means of an active cooling element at a nondamaging temperature lower than the one of the wall of the valve or of a common wall. The cooling element is preferably a Peltier element.
Owner:THALES ELECTRON DEVICES
Method and apparatus for radio frequency cavity
ActiveUS7411361B2Fast heat conductionAvoid failureStability-of-path spectrometersAdditive manufacturing apparatusPhotocathodeEngineering
In an electron accelerator, a conductive housing defines a cavity. Photoelectrons are emitted from a photocathode into the cavity when light is applied to the photocathode. Via an opening formed in a wall of the conductive housing, the photoelectrons are output to the outside of the cavity. Coolant is flowed through a flow path formed in the wall of the conductive housing, to suppress a temperature rise of the conductive housing. The wall of the conductive housing is made by a metal additive manufacturing technique in such a way as to produce a flow path that has a gentle trajectory without discontinuities in gradient.
Owner:RADIABEAM TECH
Magnetron cooling fin
InactiveCN1744264AIncrease the heat exchange areaSpeed up heat exchangeSolid-state devicesTransit-tube collectorsEngineeringHeat sink
A magnetron cooling fin is disclosed, characterized in that a plurality of turbulence-promoting protrusions are provided on one side of a planar body that has a boss-type through-hole in which an anode is coupled and a plurality of coupling pieces outwardly extending and bent at edges of the planar body, whereby, with inflow air undergoing flow separation at top ends of the turbulence-promoting protrusions and coming again into contact with the planar body, an existing temperature boundary gets thinned and a friction coefficient gets increased, thereby improving a heat transfer rate and an cooling efficiency.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
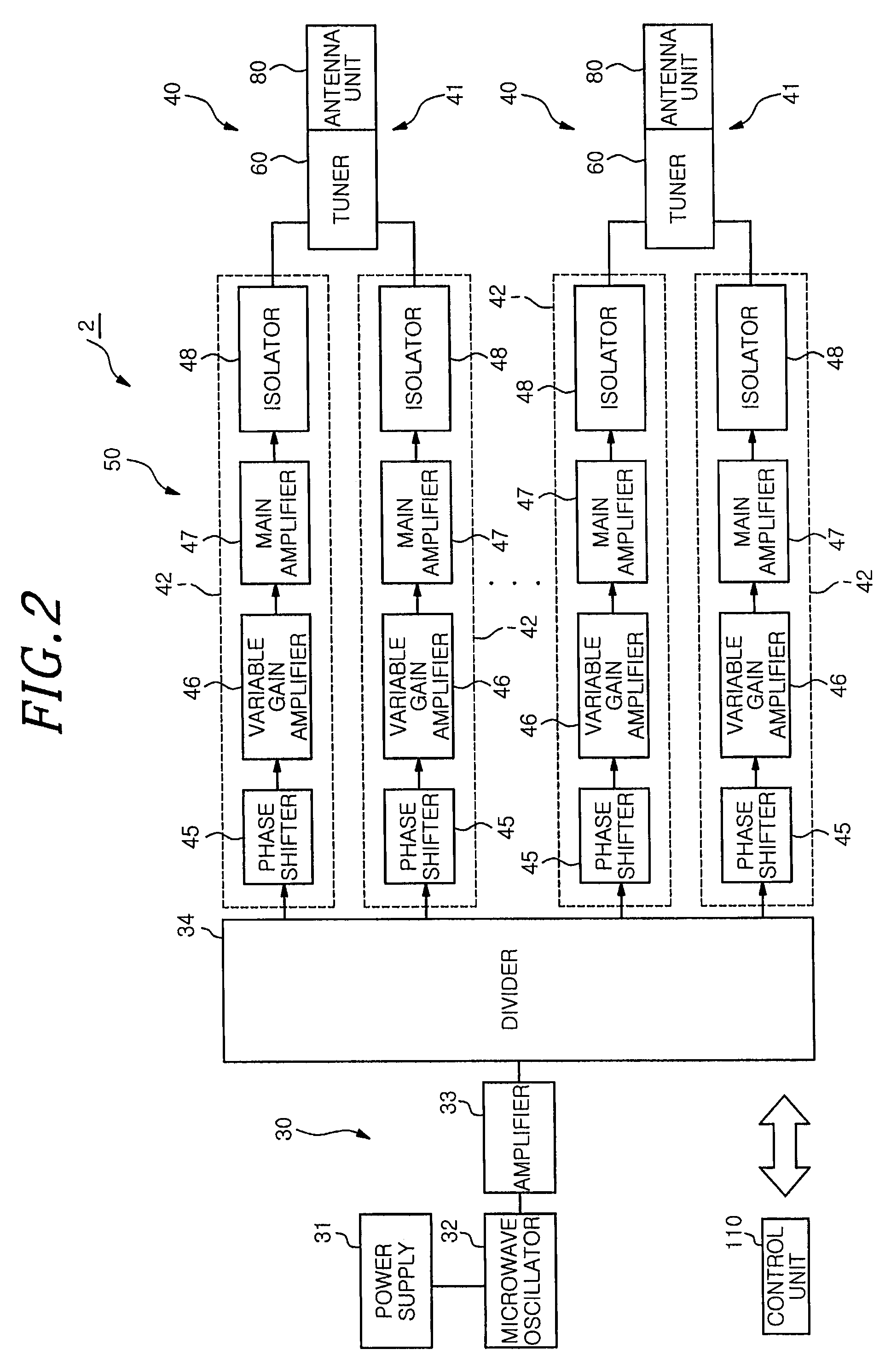
Microwave introducing mechanism, microwave plasma source and microwave plasma processing apparatus
ActiveUS9281154B2Reduce thermal effectsAntenna supports/mountingsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorEngineering
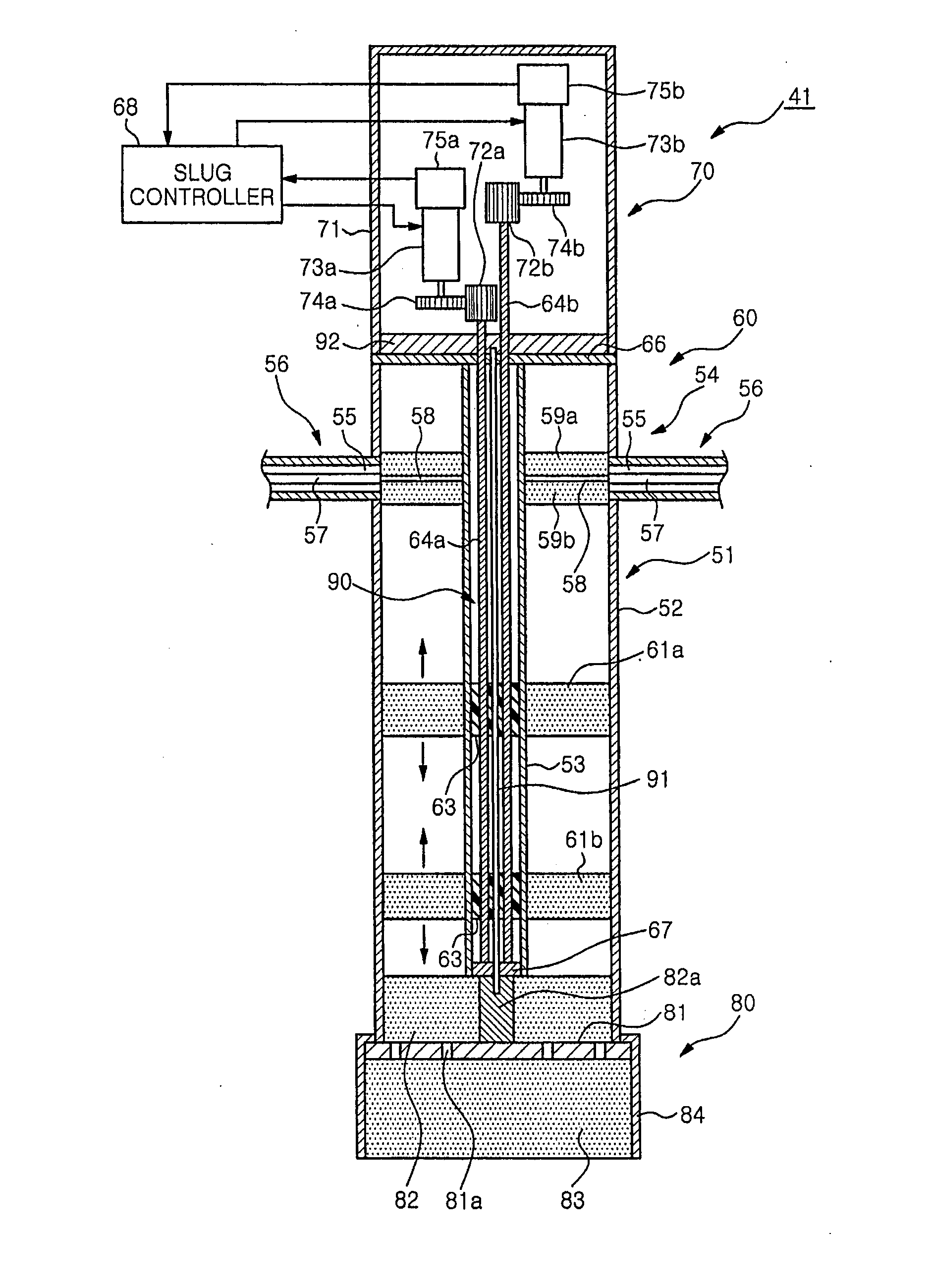
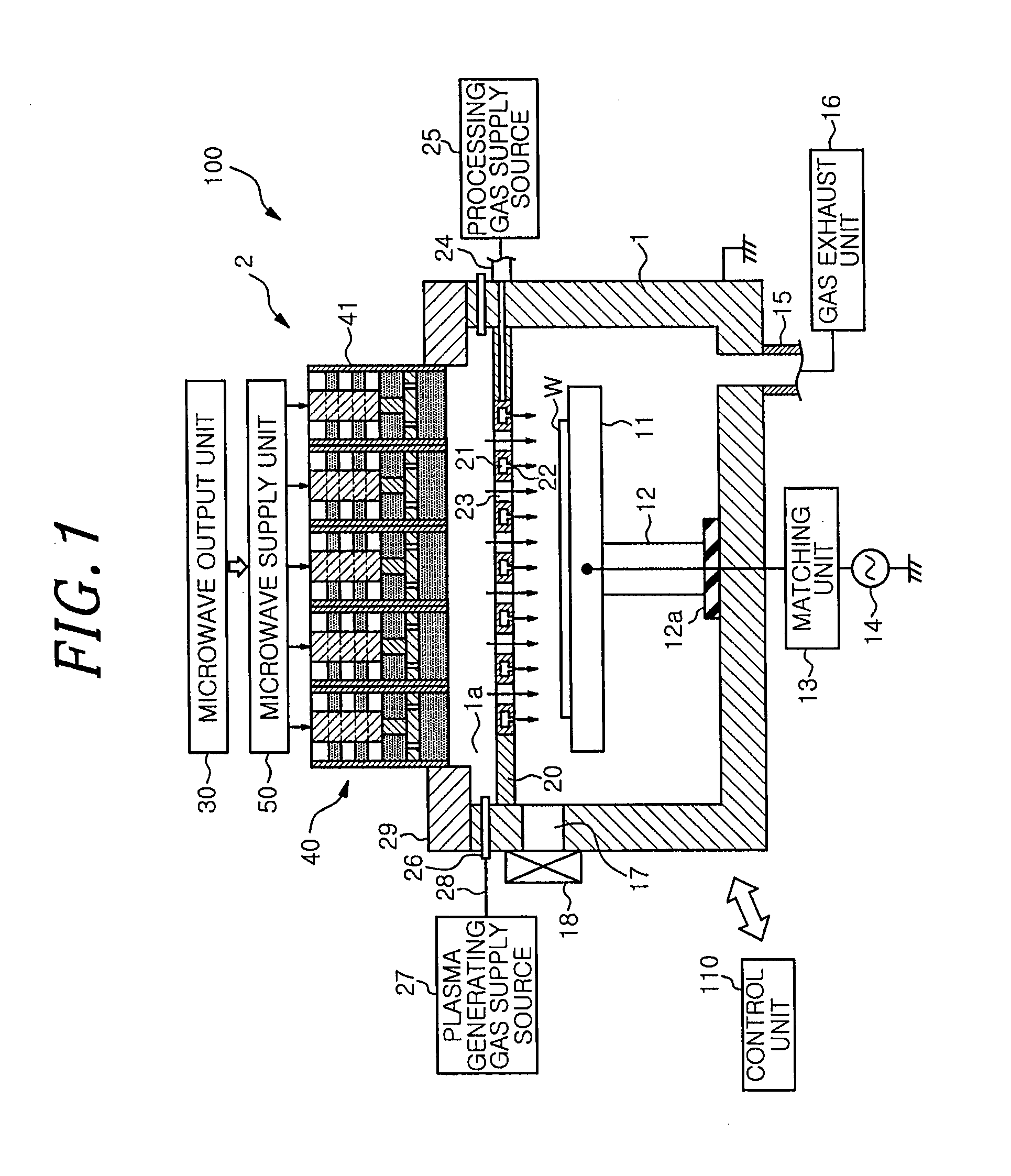
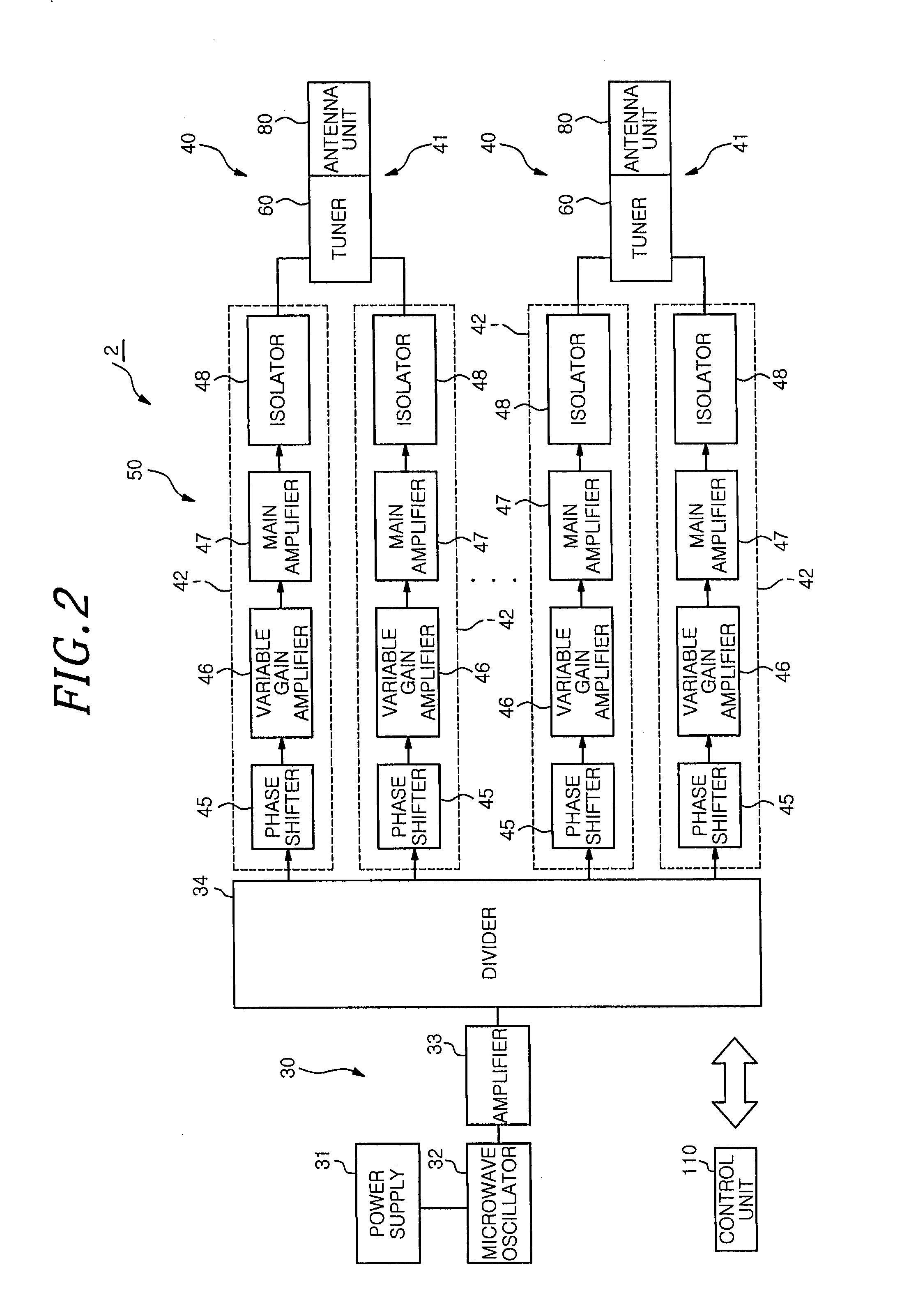
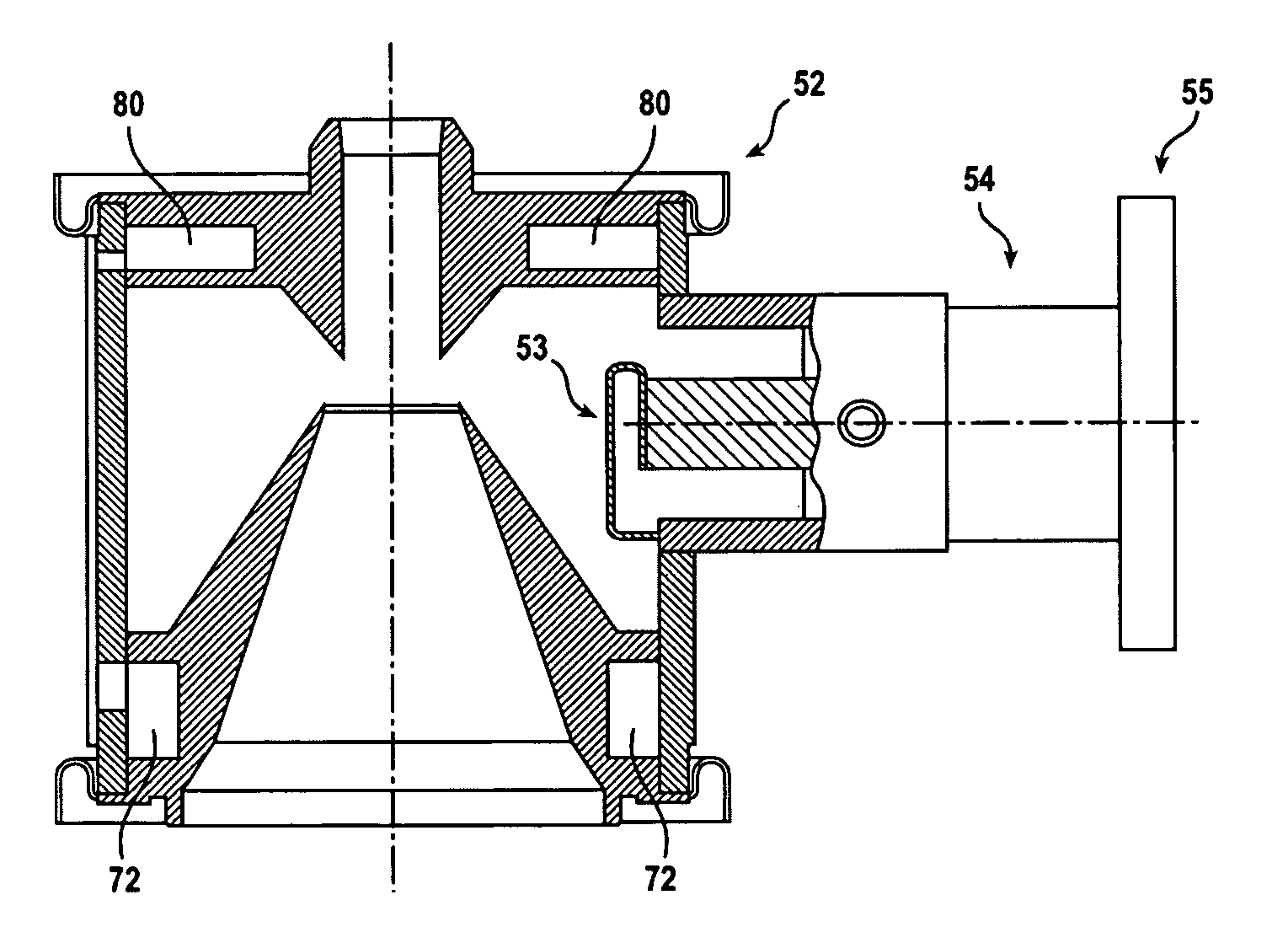
The microwave introducing mechanism includes an antenna unit having a planar antenna radiating a microwave into a chamber; a tuner for performing impedance matching; and a heat dissipation device for dissipating a heat from the antenna unit. The tuner has a tuner main body including a tubular outer conductor and a tubular inner conductor to serve as a part of a microwave transmission line; slugs provided between the outer conductor and the inner conductor to be movable along a longitudinal direction of the inner conductor; and a driving device for moving the slugs. The heat dissipation device has a heat pipe configured to transfer the heat of the antenna unit from its heat input end to its heat dissipation end.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Modular magnetron
InactiveUS8264150B2Reduce electromagnetic interferenceMagnetronsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsVacuum tubeFastener
A modular magnetron for use in UV curing lamp assembly is disclosed. The modular magnetron includes a vacuum tube having a vacuum tube body, a top assembly, and a bottom assembly. The top assembly is configured to substantially overlay the vacuum tube. The bottom assembly is configured to substantially extend about the vacuum tube, the vacuum tube being positioned to partially protrude from the bottom assembly, the bottom assembly including a cooling assembly configured to employ a flexible clamp-type fitting about the vacuum tube body for substantially maintaining thermal and electrical conductivity. The top assembly is configured to be releasably fastened to the bottom assembly about the vacuum tube with removable fasteners.
Owner:HERAEUS NOBLELIGHT AMERICA
Method and apparatus for radio frequency cavity
ActiveUS20080129203A1Avoid failureFast heat conductionAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransit-tube cooling methodsManufacturing technologyPhotocathode
In an electron accelerator, a conductive housing defines a cavity. Photoelectrons are emitted from a photocathode into the cavity when light is applied to the photocathode. Via an opening formed in a wall of the conductive housing, the photoelectrons are output to the outside of the cavity. Coolant is flowed through a flow path formed in the wall of the conductive housing, to suppress a temperature rise of the conductive housing. The wall of the conductive housing is made by a metal additive manufacturing technique in such a way as to produce a flow path that has a gentle trajectory without discontinuities in gradient.
Owner:RADIABEAM TECH
Novel broadband high-average-power air cooling structure output window
InactiveCN104465274AWorking bandwidthIncreased power capacityTransit-tube cooling methodsTransit-tube coupling devicesElectricityMicrowave
The invention discloses a novel broadband high-average-power air cooling structure output window and relates to an output window of a microwave and millimeter-wave electric vacuum device, in particular to a broadband high-average-power output window of a gyro traveling wave tube. According to the output window, one layer of window plate or double layers of window plates adopted in the prior art are replaced with three layers of window plates, the three layers of window plates are arranged on a window plate installation ring at intervals, ventilation holes connected with cavities between the adjacent window plates are formed in the window plate installation ring, the window plates are cooled through the ventilation holes, and then the operation bandwidth of the output window is effectively expanded and the power capacity of the output window is effectively improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Magnetron
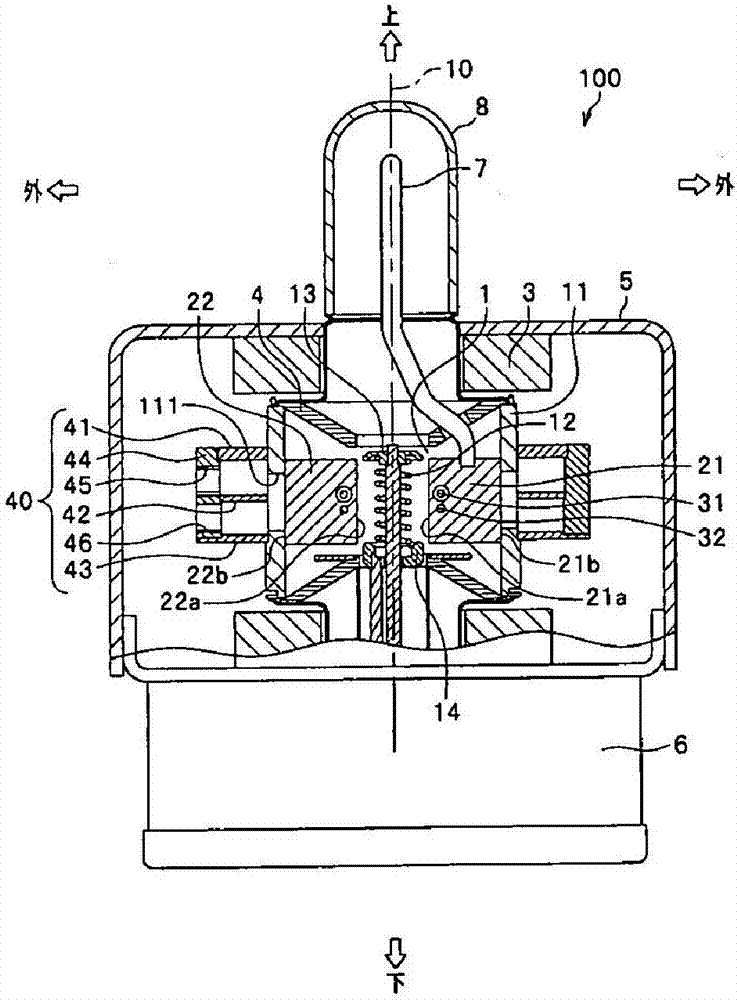
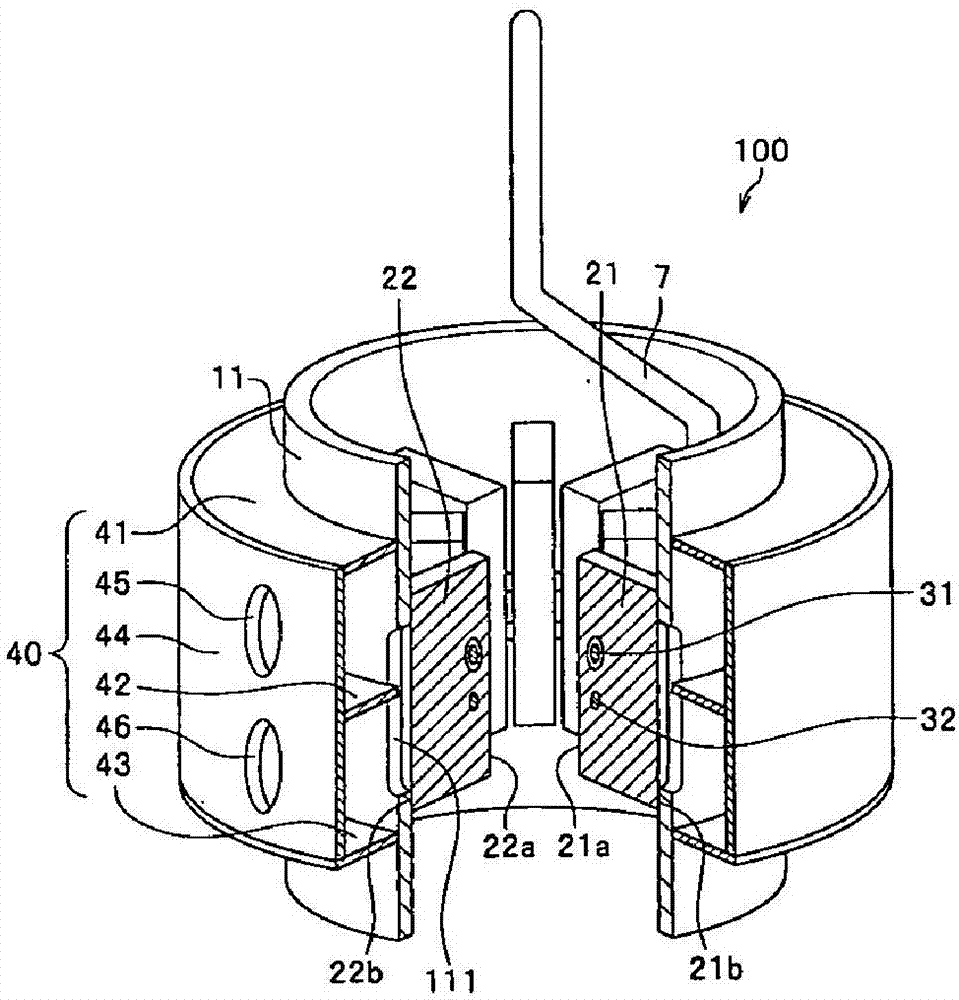
ActiveCN107887241AImprove cooling effectTransformers/inductances coolingMagnetronsEngineeringCoolant
A magnetron includes an anode cylinder extending in a cylindrical shape along a central axis and a plurality of plate-like vanes at least each one end of which is fixed to the anode cylinder, extending from an inner face of the anode cylinder toward the central axis, in which the anode cylinder includes refrigerant flow paths for directly applying a refrigerant to the plate-like vanes. The refrigerant flow paths 111 are openings formed so that end surfaces (joint end faces of the plate-like vanes) of the plate-like vanes are exposed, which allow the refrigerant to directly contact the plate-like vanes.
Owner:HIATACHI POWER SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Magnetron with relatively fixed yoke and cooling block by means of a cushioning material and fixing member
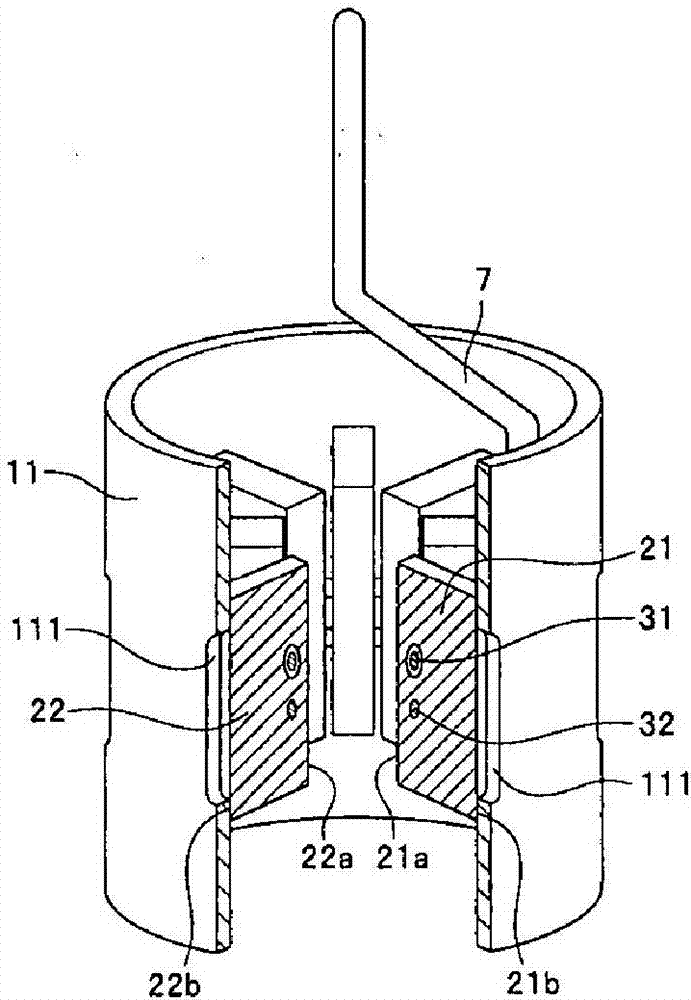
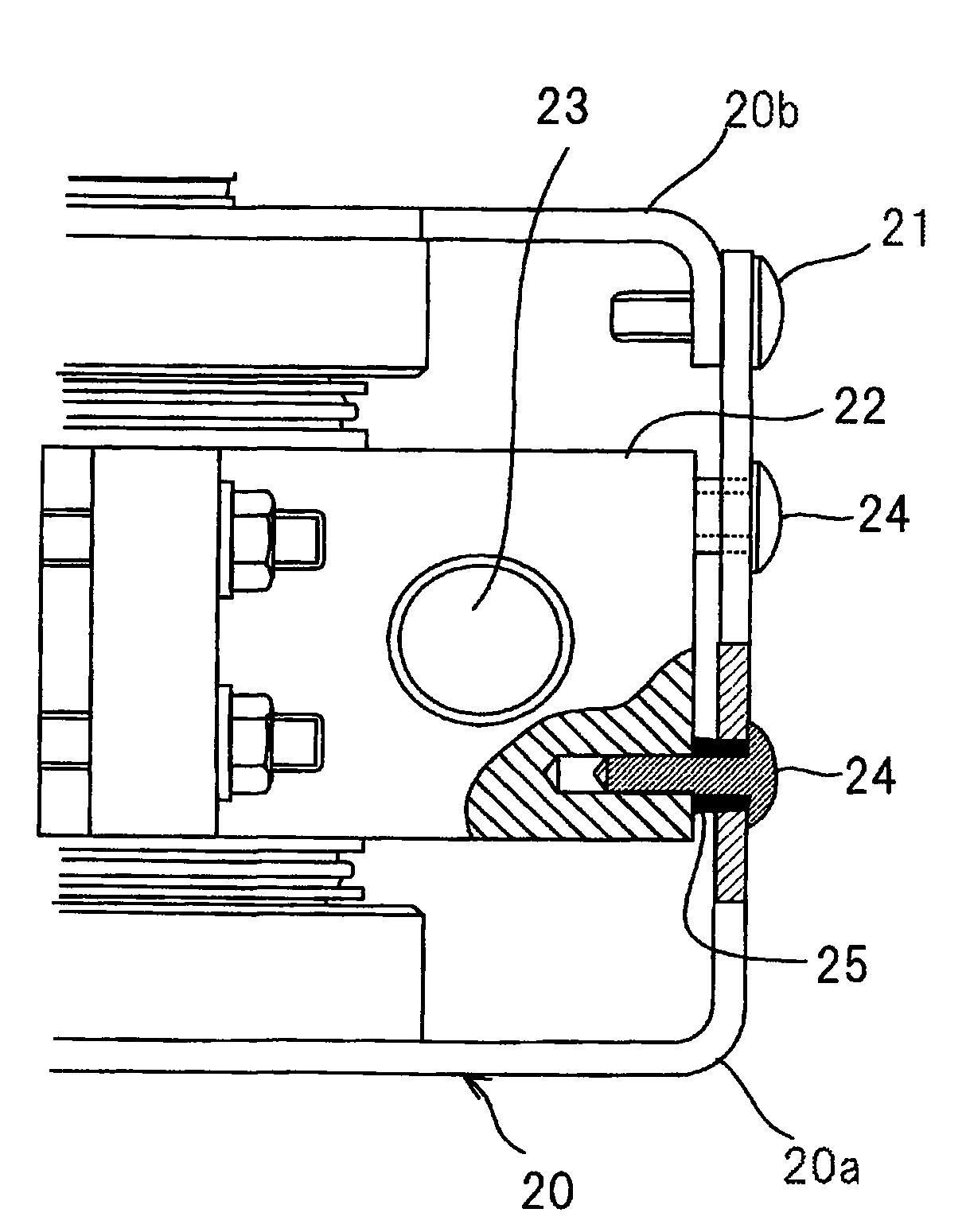
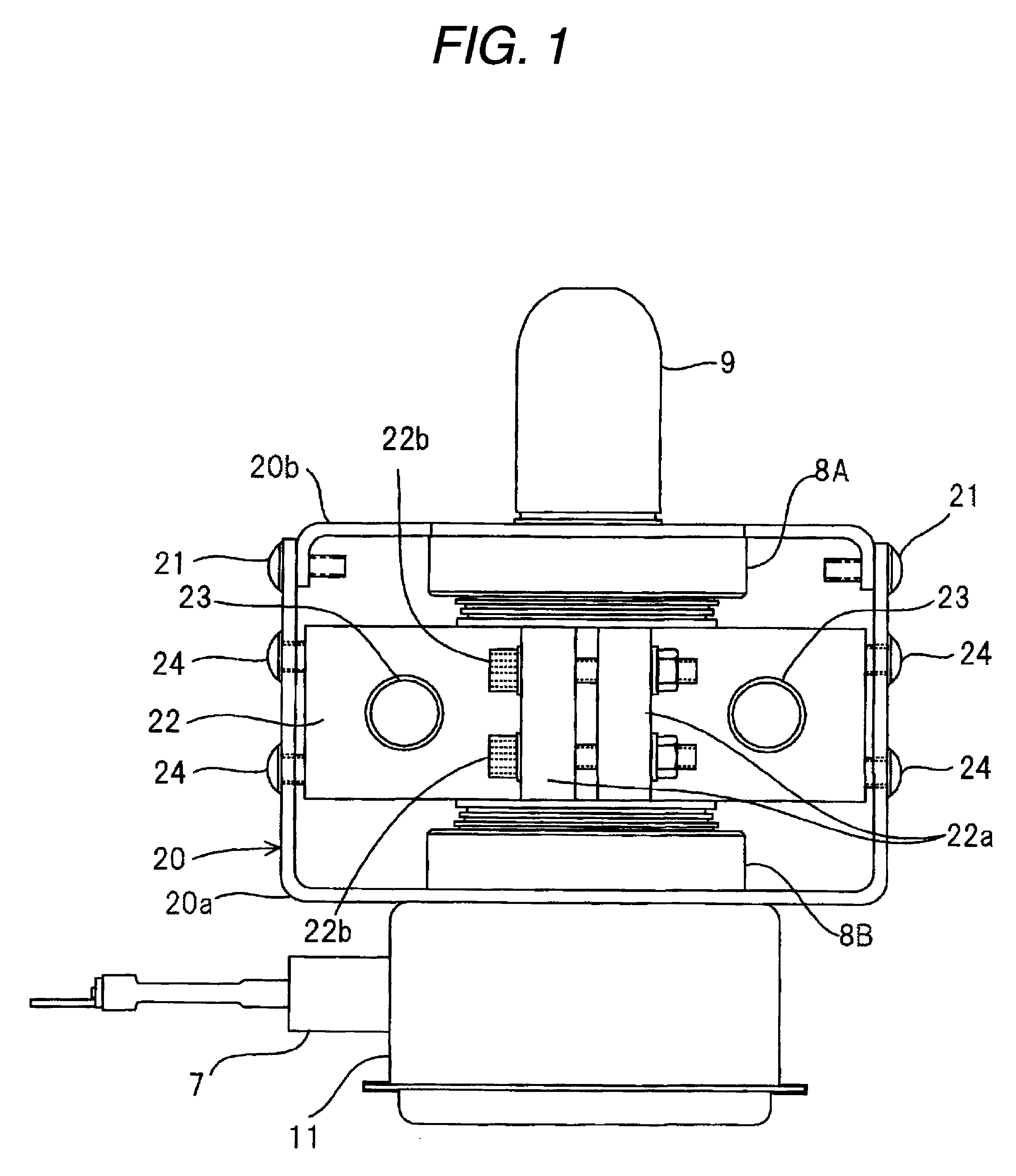
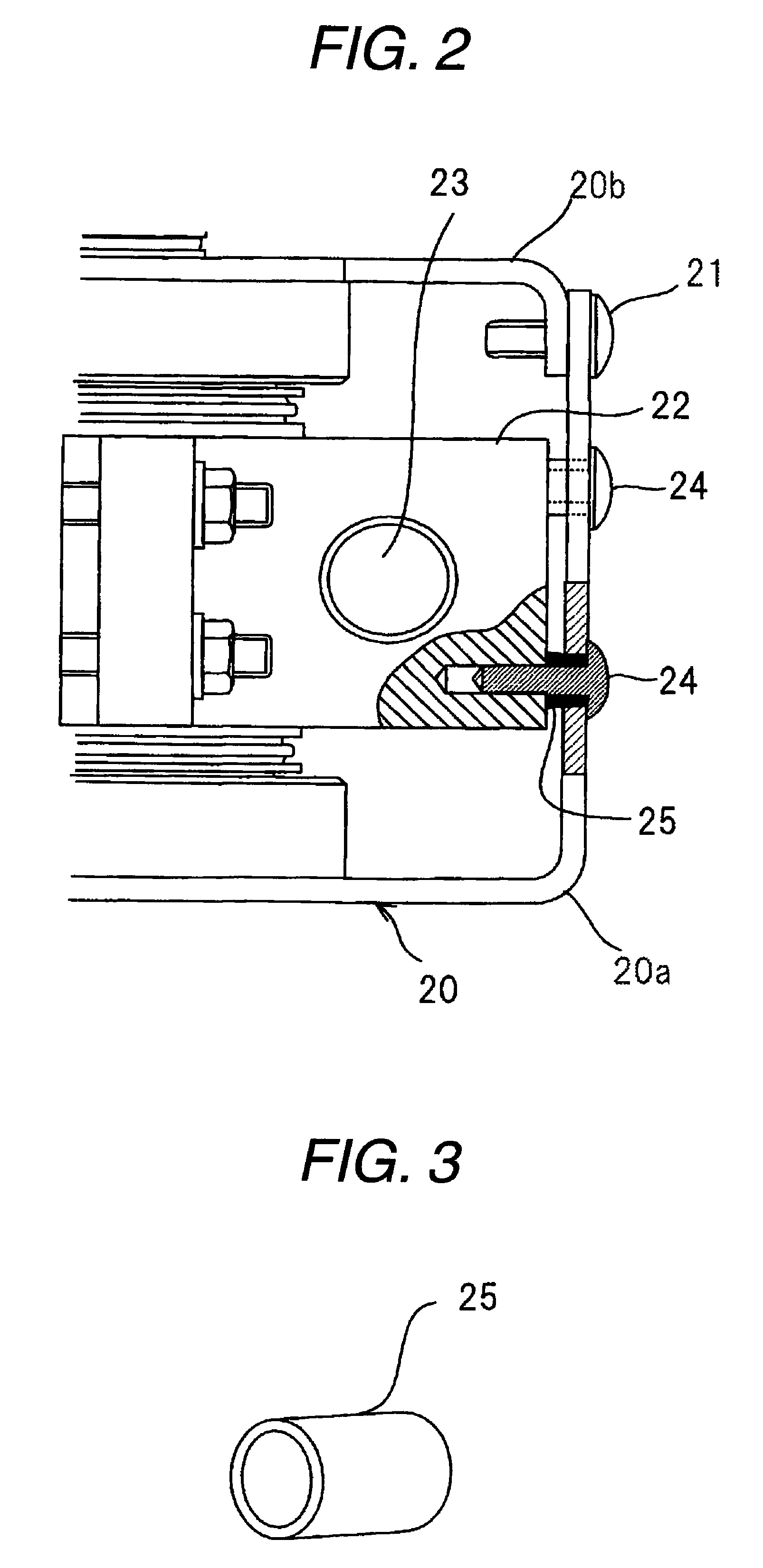
InactiveUS7855495B2Increase resistanceImprove vibrationTransit-tube vessels/containersMagnetronsCushioningEngineering
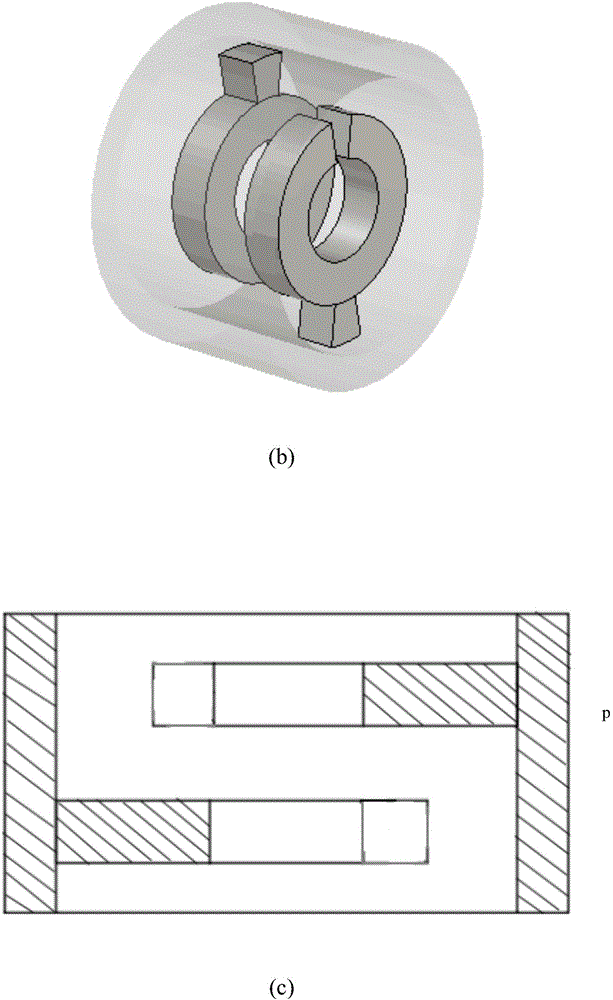
A gap is provided between a cooling block 22 and a magnetic yoke 20. A cushioning material 25 is interposed in the gap to fix the cooling block 22 relatively to the magnetic yoke 20 by screws. Thus, even when metals having a large difference in tendency of ionization are used in the cooling block 22 and the magnetic yoke 20, the corrosion of the metals hardly arises. Further, the cushioning material 25 is provided in the gap between the cooling block 22 and the magnetic yoke 20, so that an impact or vibration to an anode tubular member 10 can be mitigated and the disconnection and deficiency of the filament of a cathode structural member can be reduced. Further, since a dimensional unevenness of the cooling block 22 or the magnetic yoke 20 can be absorbed by the cushioning material 25, the dimensional accuracy of parts does not need to be improved to make an assembly easy.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Microwave introducing mechanism, microwave plasma source and microwave plasma processing apparatus
ActiveUS20130180661A1Reduce thermal effectsAntenna supports/mountingsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorEngineering
The microwave introducing mechanism includes an antenna unit having a planar antenna radiating a microwave into a chamber; a tuner for performing impedance matching; and a heat dissipation device for dissipating a heat from the antenna unit. The tuner has a tuner main body including a tubular outer conductor and a tubular inner conductor to serve as a part of a microwave transmission line; slugs provided between the outer conductor and the inner conductor to be movable along a longitudinal direction of the inner conductor; and a driving device for moving the slugs. The heat dissipation device has a heat pipe configured to transfer the heat of the antenna unit from its heat input end to its heat dissipation end.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
L-band inductive output tube
InactiveUS7145297B2Magnetic resonance acceleratorsTransit-tube cooling methodsAtmospheric pressureWave band
An inductive output tube (IOT) operates in a frequency range above 1000 MHz. An output window may be provided to separate a vacuum portion of the IOT from an atmospheric pressure portion of the IOT, the output window being surrounded by a cooling air manifold, the manifold including an air input port and a plurality of apertures permitting cooling air to move from the port, through the manifold and into the atmospheric pressure portion of the IOT. The output cavity may include a liquid coolant input port; a lower circular coolant channel coupled to receive liquid coolant from the liquid coolant input port; a vertical coolant channel coupled to receive liquid coolant from the lower circular coolant channel; an upper circular coolant channel coupled to receive liquid coolant from the vertical coolant channel; and a liquid coolant exhaust port coupled to receive liquid coolant from the upper circular coolant channel.
Owner:COMM & POWER IND
Magnetron
InactiveCN105190822AImprove performanceTransit-tube vessels/containersTransit-tube cathodesResonant cavityEngineering
A 4G magnetron is disclosed. The magnetron may include an anode comprising a cylindrical member and anode vanes disposed within the cylindrical member which define resonant cavities therebetween, and a dispenser cathode, suitable for heating and located coaxially within said anode. The magnetron may operate in a temperature range of about 850-1050 DEG C. The magnetron may include conductive cooling. The magnetron may comprise inventive anode and cathode structures. A method for preparing a plurality of magnetron tubes substantially simultaneously is further provided.
Owner:朴秀用
Gyrotron energy coupling window
ActiveCN111489946AImprove heat resistanceIncrease output power capacityNuclear energy generationTransit-tube cooling methodsEngineeringContinuous wave
The embodiment of the invention provides a gyrotron energy coupling window. The gyrotron energy coupling window comprises a window support cylinder, a window positioning flange adapter plate, a windowsealing cylinder and cooling water joints, wherein the window support cylinder is arranged at the bottom of the window sealing cylinder, the window positioning flange adapter plate is connected to the window positioning flange adapter plate in a sleeving mode, and the window support cylinder, the window sealing cylinder and the window positioning flange adapter plate are welded in an airtight mode; and at least two cooling water joints communicated with the interior of the window positioning flange adapter plate are further arranged on an outer side of the window positioning flange adapter plate. The gyrotron energy coupling window overcomes the problems that in the prior art, when a gyrotron works at high power and continuous waves, due to electron energy consumption, a large amount of heat energy is deposited on a cavity wall and an energy coupling window, the temperature of a window piece is too high, the thermal stress is too large, the output power, the mode purity and the stability of the gyrotron are reduced, and the gyrotron is scrapped due to the fact that the window piece is broken under severe conditions.
Owner:HUADONG PHOTOELECTRIC TECHN INST OF ANHUI PROVINCE
Slow wave structure for high-power output of traveling wave tubes
InactiveCN106653524AImprove the problem of high power outputSolve the problem of too small coupling impedanceTransit-tube cooling methodsTransit-tube coupling devicesElectricityWave structure
The invention discloses a slow wave structure for high-power output of traveling wave tubes, and belongs to the field of microwave electric vacuum. The slow wave structure comprises a cylindrical metal shell, a plurality of concentric open metal rings arranged in the shell, and a metal support structure for fixing the metal rings. The support structure of the slow wave structure is made of a metal material, and can achieve a function of heat dissipation to a certain extent. Within the working frequency range, the slow wave structure has a much larger coupling impedance curve than a helix slow wave structure, and can achieve well and effective interaction and exchange of energy. The problem that the coupling impedance of a general slow wave structure is too small is solved to a certain extent. The slow wave structure of the invention is easy to machine. The problem concerning high power output of traveling wave tubes with larger bandwidth is well improved. The application scope of travelling wave tubes is expanded.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Magnetron
A magnetron, comprising a cylindrical anode with a resonant space formed inside and a cathode therein, magnets installed on the top and bottom of the anode, a magnetic yoke arranged outside the anode and the magnet to form a closed cycle, and a cooling device, the The cooling device includes the main cooling device that constitutes the heat release path from the anode, and the auxiliary cooling device that constitutes the direct or indirect heat release path from the magnet, wherein the main cooling device is an anode heat conductor, one end of which is close to the outer surface of the anode The other end passes through the magnetic yoke and is exposed to the outside air. The auxiliary cooling device includes a magnet heat conductor close to the outer surface of the magnet. One side of the magnet heat conductor is in contact with the shell of the magnetron, or it is close to the magnetic The magnetic yoke heat conductor on the outer surface of the choke plate, one side of the magnetic yoke heat conductor is in contact with the shell of the magnetron.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Magnetoelectric tube device and its production method
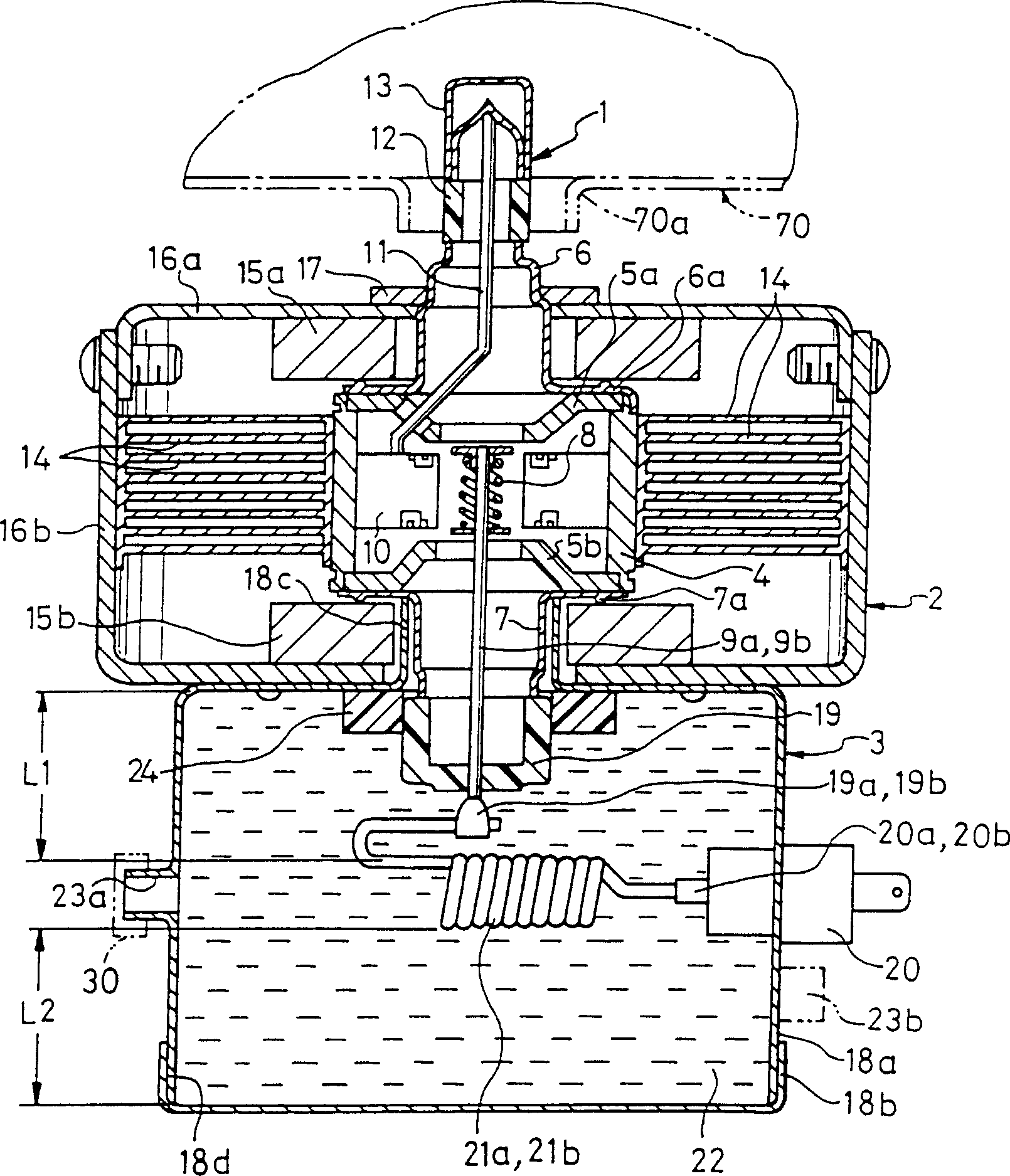
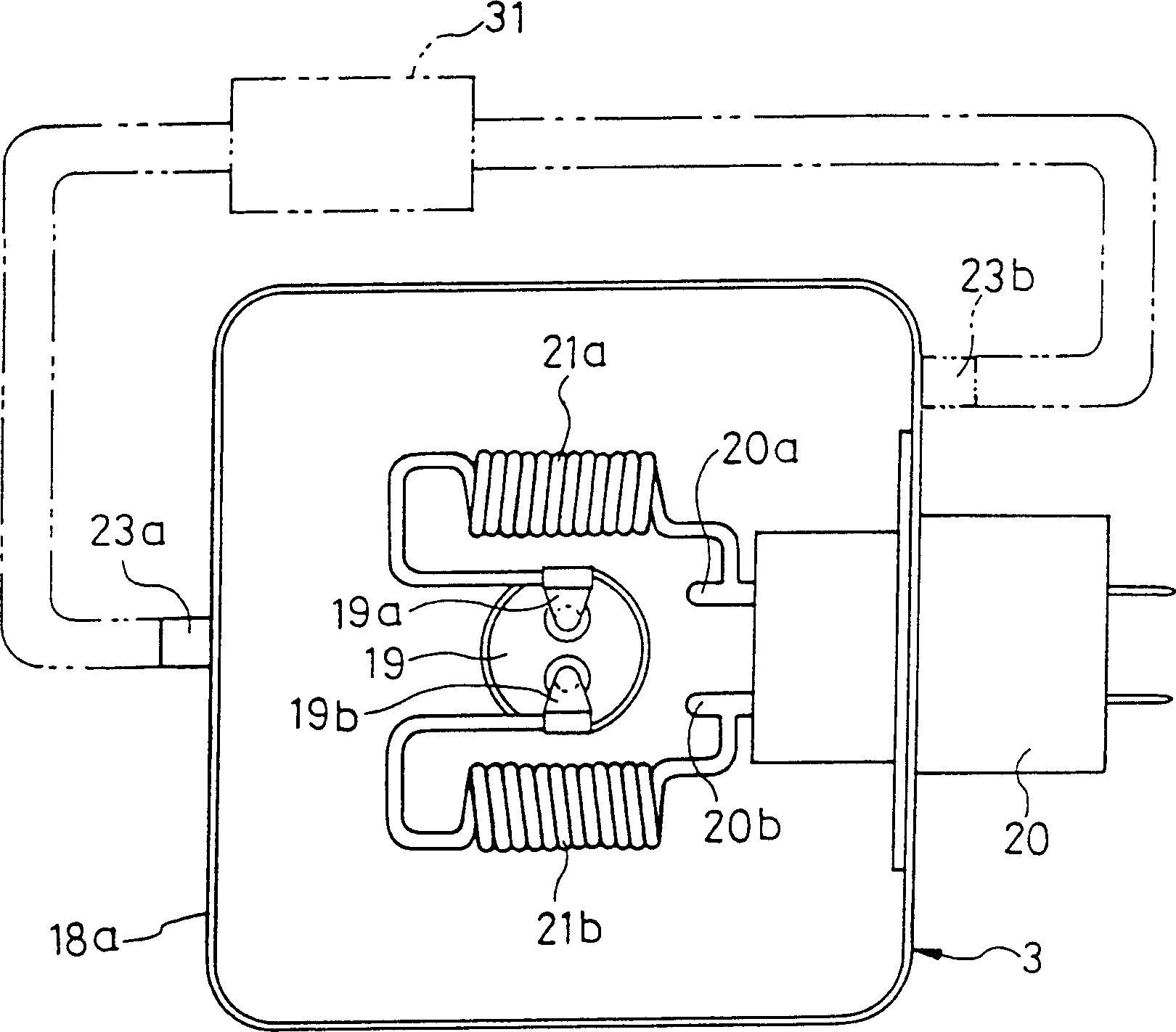
InactiveCN1290142CAvoid pollutionTransit-tube leading-in arrangementsMagnetronsEngineeringRadio wave
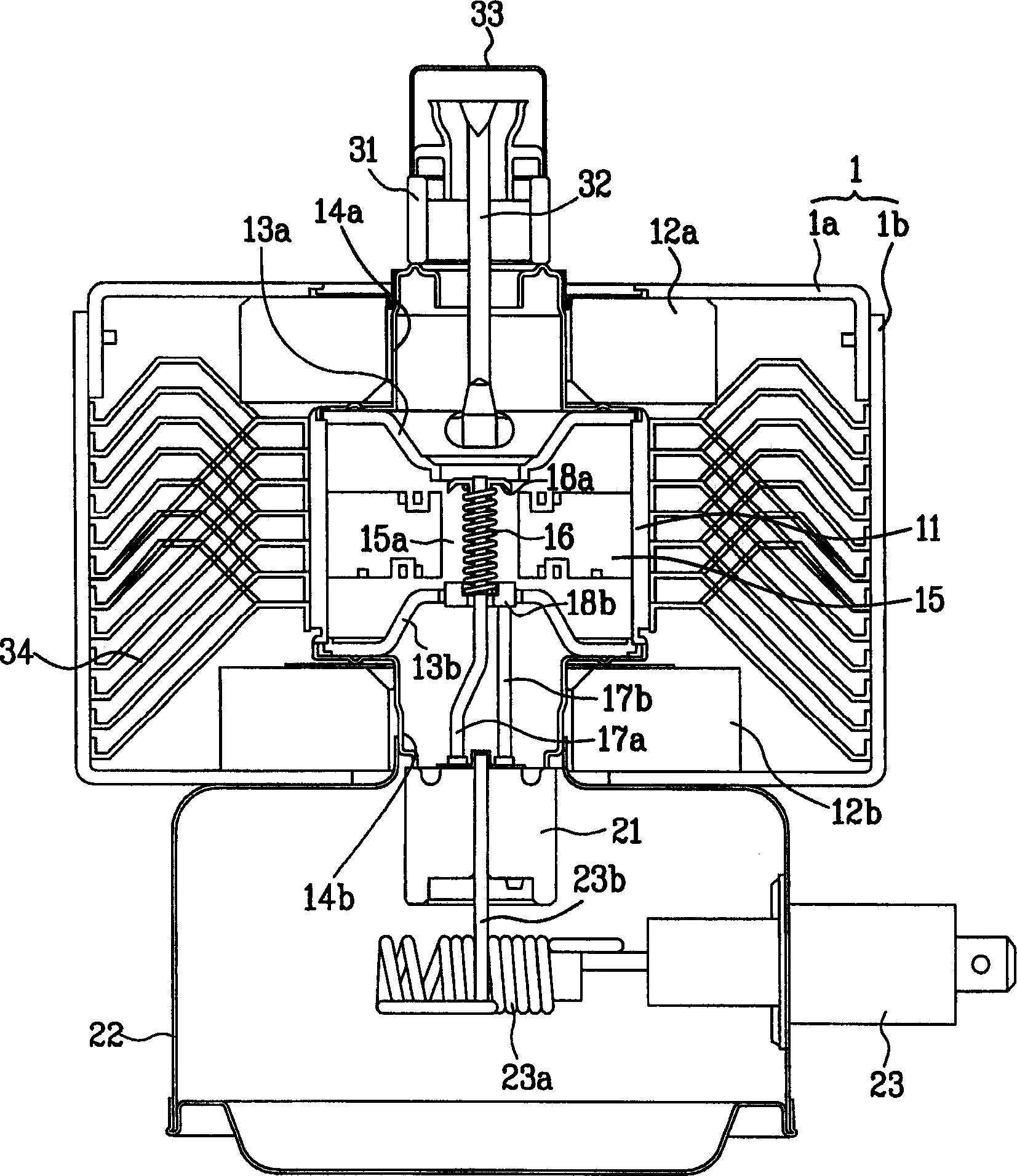
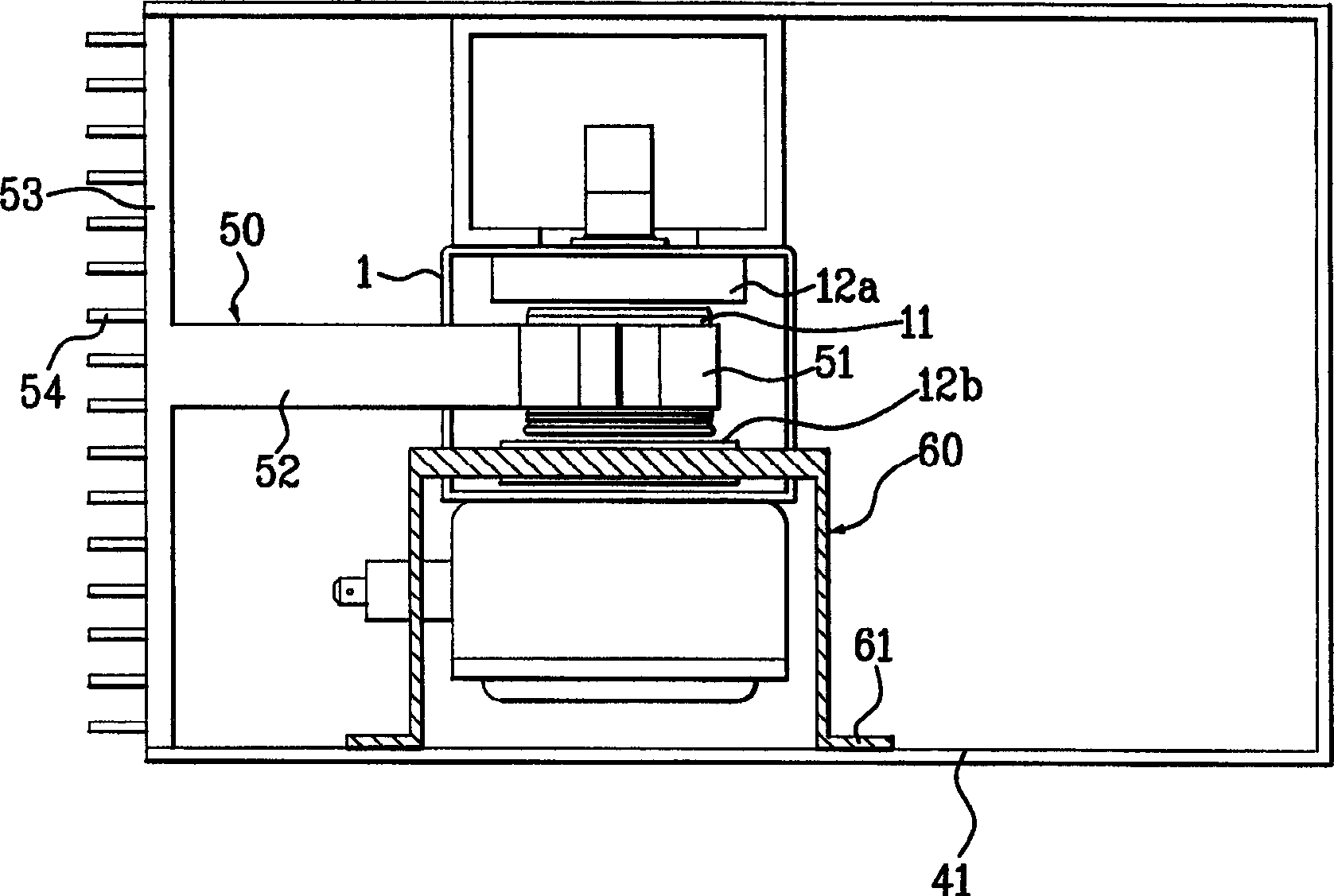
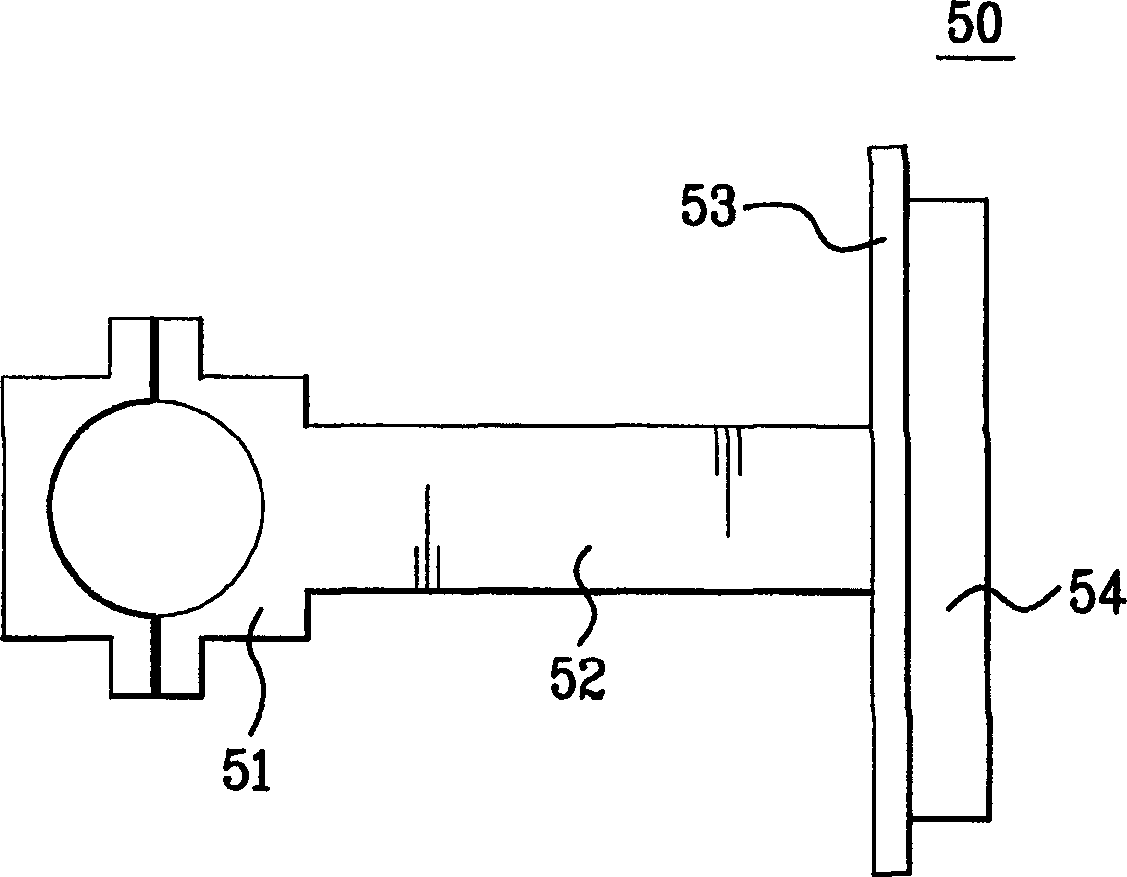
A magnetron apparatus and a manufacturing method therefor according to the present invention comprises a magnetron (1) having a tubular anode (4) and a cathode (8), a magnetic circuit (2) having first and second magnets (15a, 15b) disposed around the upper and lower opening end portions of the tubular anode, respectively, and a yoke (16b) disposed enclosing the tubular anode and the first and second magnets, and a radio wave leakage preventor (3) having a filter case (18a, 18b) and LC filter circuit components (20, 20a, 20b) disposed inside the filter case, wherein at least the filter case is filled with an insulating cooling liquid.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Output waveguide window for Ka-waveband high-power space traveling-wave tube
ActiveCN111524769ASimple structureImprove cooling effectTransit-tube vessels/containersTransit-tube cooling methodsWave tubeMechanical engineering
The invention provides an output waveguide window for a Ka-waveband high-power space traveling wave tube. The window comprises a window piece, a sealing piece, a waveguide flange and a transition waveguide, and is characterized in that the sealing piece sleeves the outer side of the window piece and is connected with the circumference of the window piece in a sealing manner; the waveguide flange is connected with the upper side of the sealing piece; the transition waveguide sleeves the lower side of the sealing piece and is hermetically connected with the sealing piece; and a vacuum cavity isformed in the sealing piece, the waveguide flange and the transition waveguide. The structure is simple, the reliability is high, and the requirements of small standing wave, temperature impact resistance, mechanical vibration resistance and good heat dissipation performance of the traveling wave tube are met.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
Magnetron
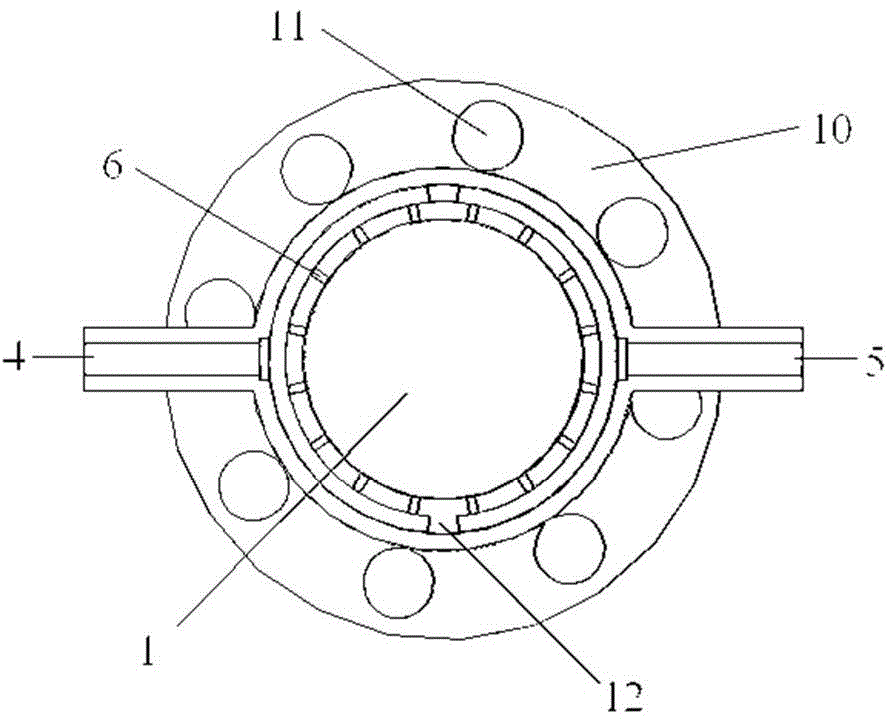
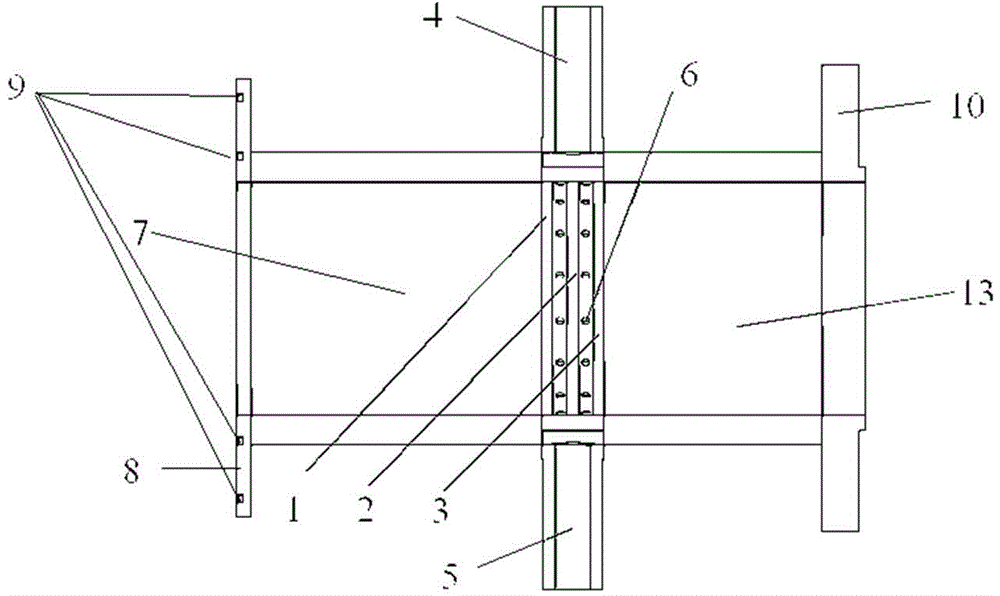
ActiveCN108091532AImprove cooling efficiencyImprove heat transfer efficiencyMagnetronsTransit-tube cooling methodsHeat conductingBlack ball
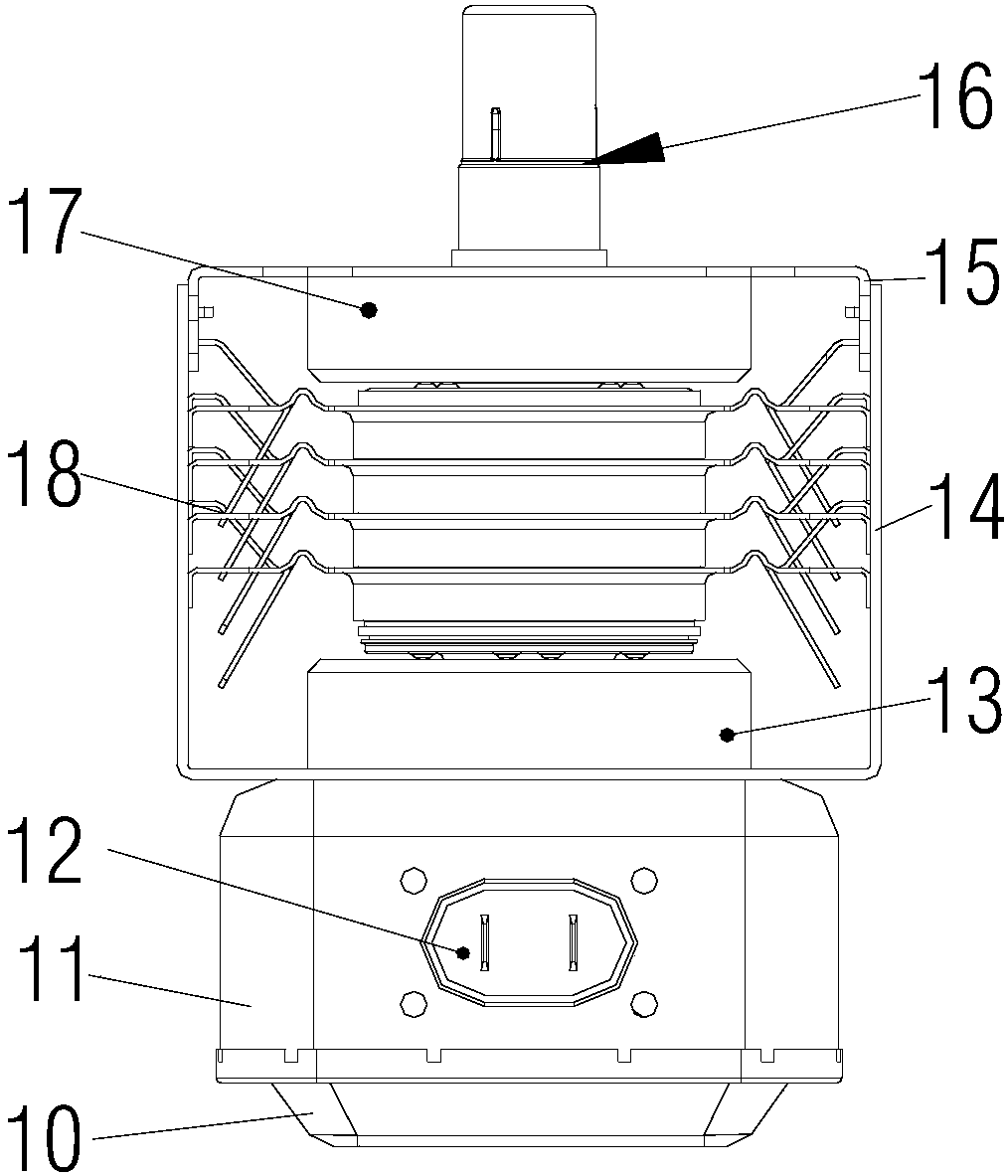
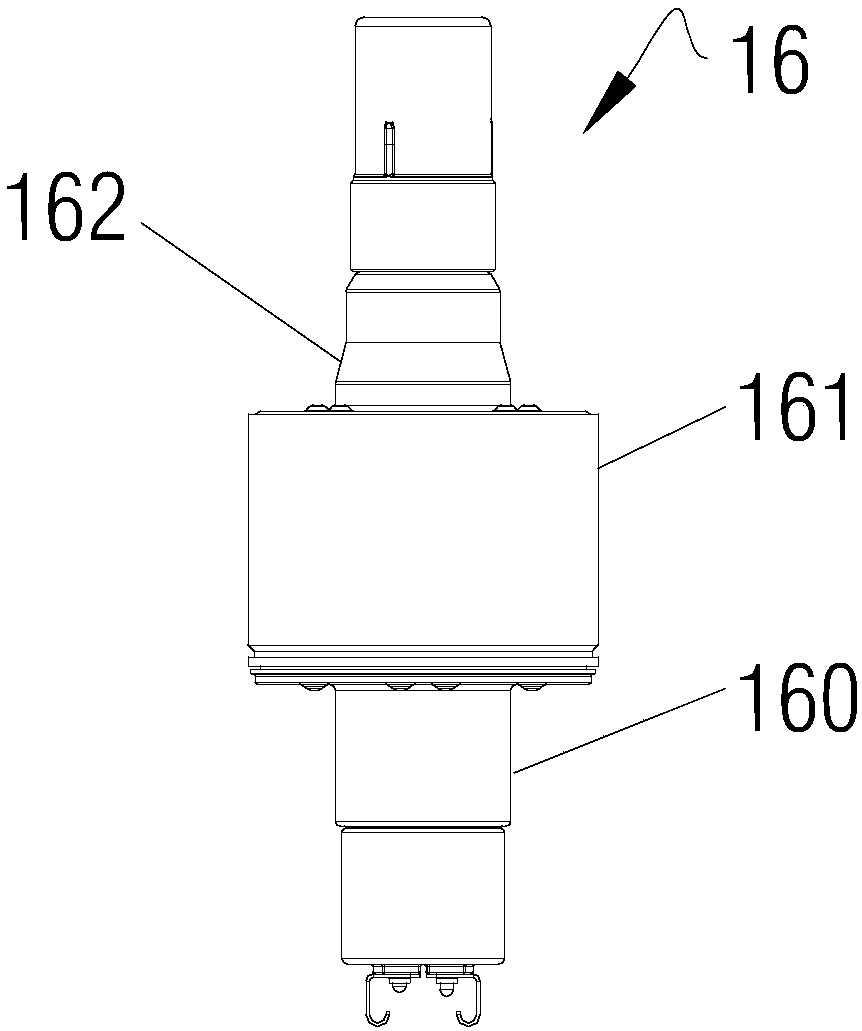
The invention, which relates to the field of magnetron structure, discloses a magnetron comprising a magnetron heat-dissipating element for dissipating heat from the magnetron. The magnetron heat-dissipating element consists of a central heat-conducting body (1) coating and being in contact with the outer side wall of an anode cylinder (161), a heat transferring plate (2) extending externally fromthe central heat-conducting body (1), and a plurality of cooling fin groups that are arranged on at least one plane of the heat transferring plate (2) vertically and are spaced at intervals. A direct-current air duct is formed corresponding between each two adjacent cooling fin groups. According to the magnetron, while the structure of the magnetron heat-dissipating element and the mounting structures of the magnetron heat-dissipating element and a black ball assembly are simplified to a certain extent, the heat transfer efficiency between the anode cylinder and the magnetron heat-dissipatingelement and inside the magnetron heat-dissipating element are improved, so that the heat radiation efficiency of the magnetron is enhanced.
Owner:GUANGDONG WITOL VACUUM ELECTRONICS MFR
Heat dissipation module for magnetron and magnetron having same
PendingCN108389765AMiniaturizationConducive to high powerMagnetronsTransit-tube cooling methodsMiniaturizationEngineering
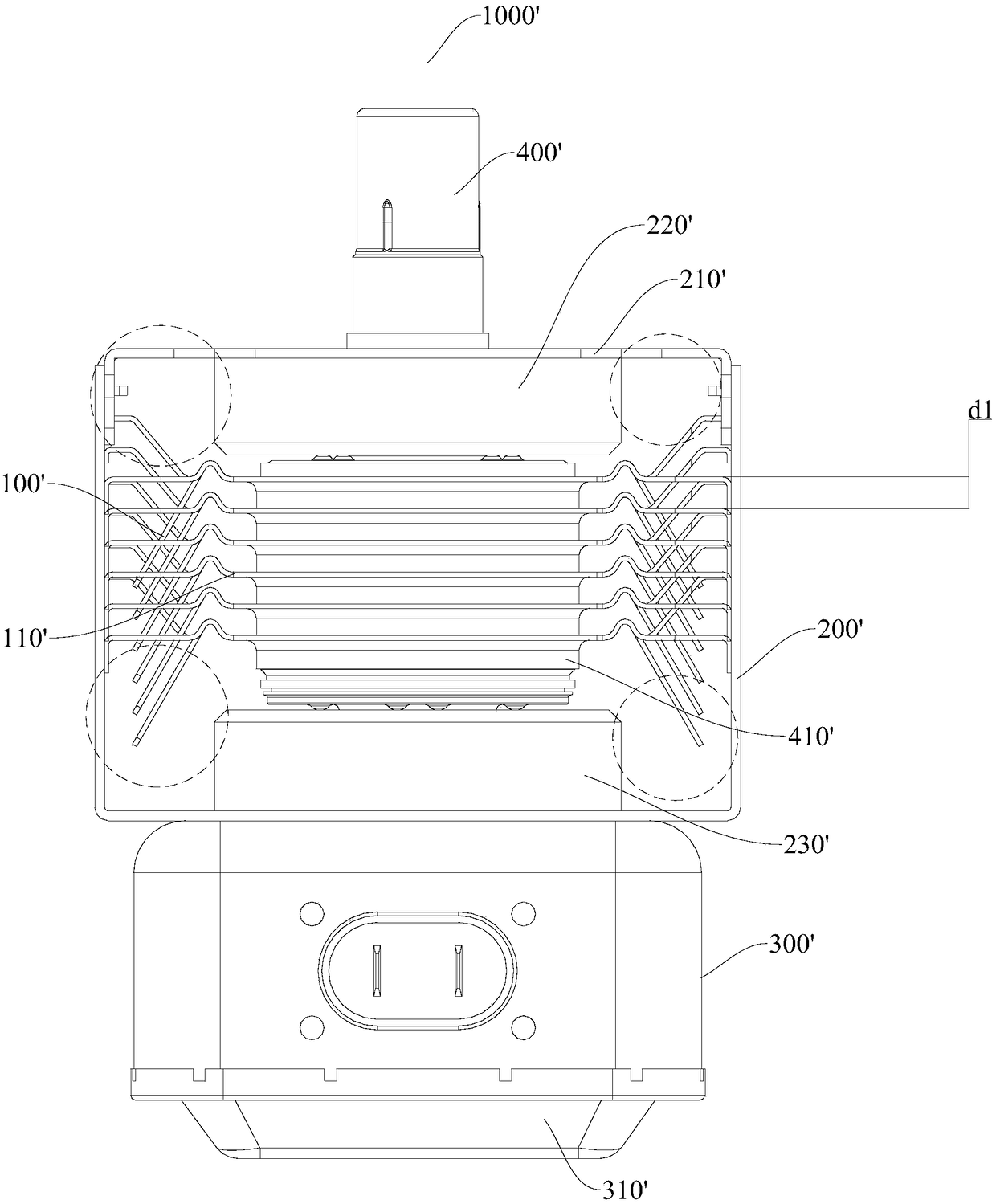
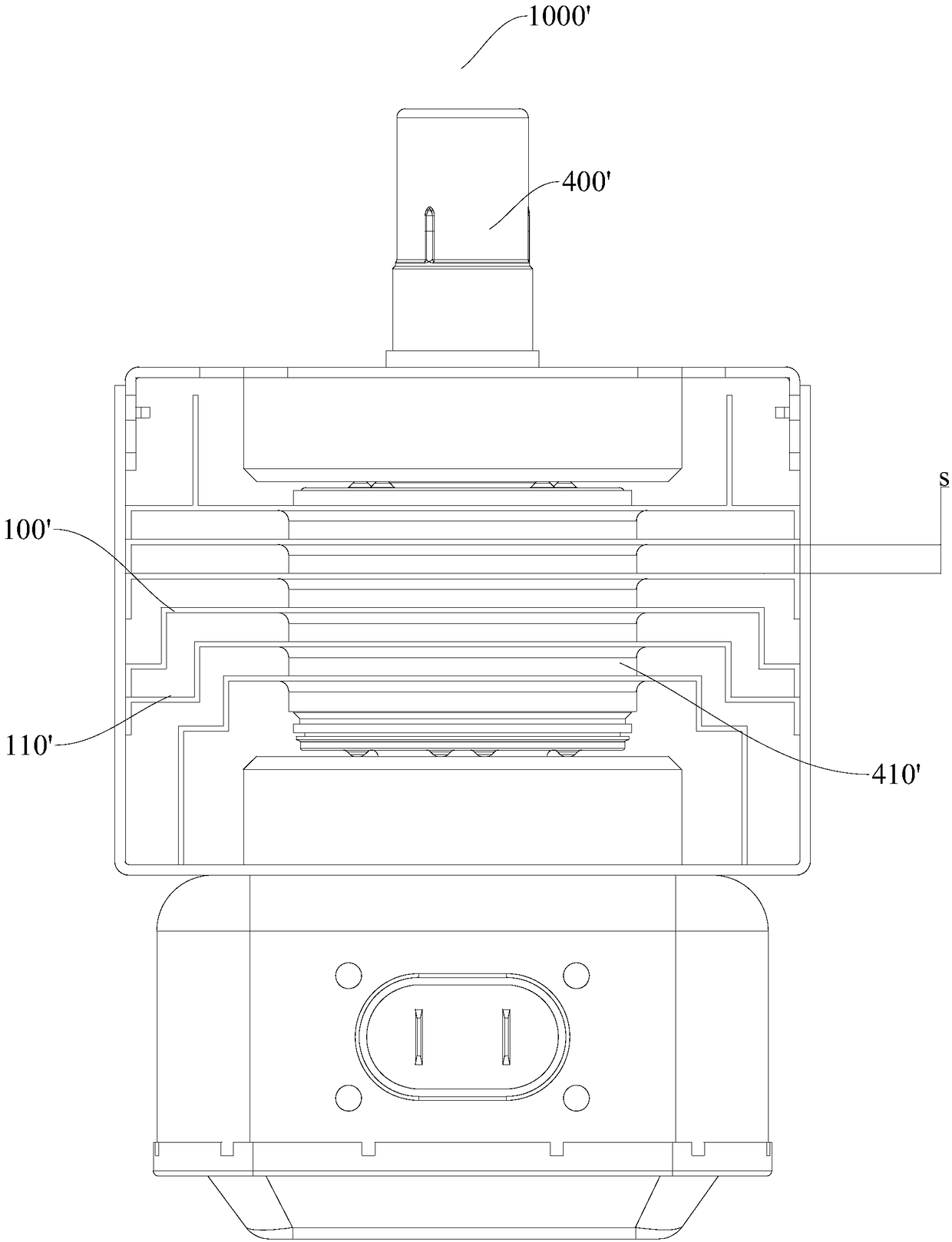
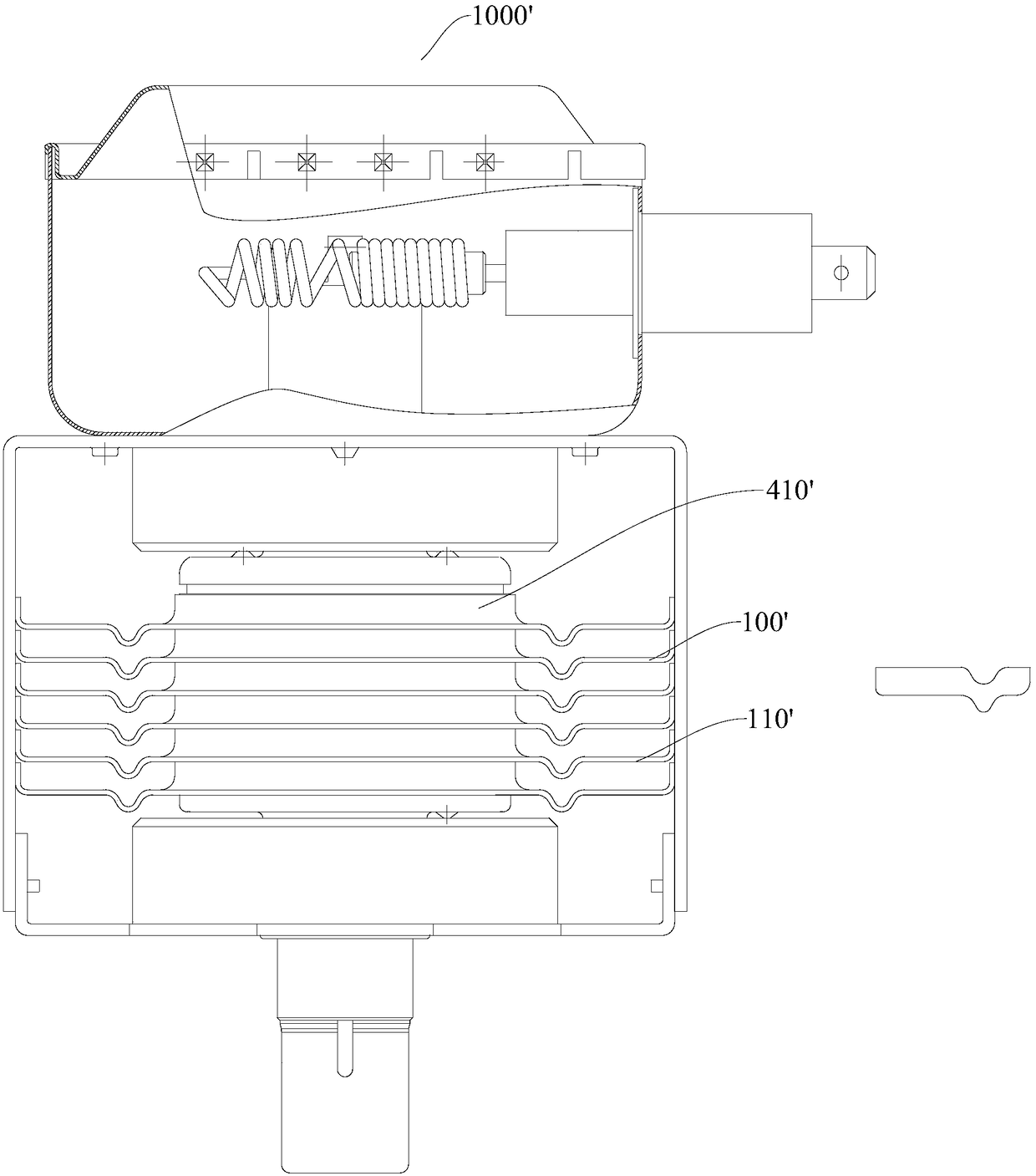
The present invention discloses a heat dissipation module for a magnetron and a magnetron having the same. The heat dissipation module comprises: an intermediate cooling fin; an upper cooling fin arranged above the intermediate cooling fin and arranged with the intermediate cooling fin at intervals in a vertical direction, wherein the left side of the upper cooling fin is towards the left and is obliquely extended upwards, and the right side of the upper cooling fin is towards the right and is obliquely extended upwards; and a lower cooling fin arranged below the intermediate cooling fin and arranged with the intermediate cooling fin at intervals in a vertical direction, wherein the left side of the lower cooling fin is towards the left and is obliquely extended downwards, the right side of the lower cooling fin is towards the right and is obliquely extended downwards, and the intermediate cooling fin, the upper cooling fin and the upper cooling fin are respectively provided with coaxial anode holes. The heat dissipation module for a magnetron can fully utilize the heat dissipation space and the cold wind of the magnetron to have a good heat dissipation effect and facilitate miniaturization and high power of the magnetron.
Owner:GUANGDONG WITOL VACUUM ELECTRONICS MFR
Heat sink apparatus for microwave magnetron
ActiveUS20200176213A1Improve cooling effectHeat dissipationMagnetronsTransit-tube cooling methodsMicrowaveEngineering
A heat sink apparatus for a microwave magnetron includes a thermal conduction seat, a first heat-fin set, and at least one first heat pipe. One end of the first heat pipe protrudes into the thermal conduction seat, while another end of the first heat pipe protrudes into the first heat-fin set. An antenna of the microwave magnetron is to penetrate through the thermal conduction seat.
Owner:TSENG TON RONG +1
An electromagnetic wave oscillator
ActiveCN109148242BReduce emission densityReduce lossTransit-tube cathodesTransit-tube cooling methodsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Microwave frequency structure for microwave tube with beam-containing device with permanent magnets and enhanced cooling
ActiveUS8427057B2High strengthImprove cooling effectTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube cooling methodsMicrowave tubeLight beam
The invention relates to a microwave frequency structure for microwave tube comprising a cylindrical vacuum jacket and a device for containing an electron beam in the axis of revolution of the cylindrical jacket. The containing device comprises at least two rows, each containing permanent magnets, each row being aligned either side of and equidistant to the beam-containment axis, the at least two rows containing permanent magnets being of parallelepipedal shapes and having a magnetic polarization parallel to one of its edges in a plane transversal to the axis, their direction of magnetization in the row changing alternately from one containing magnet to another next containing magnet, or preceding containing magnet, to create an alternating periodic magnetic field along the containment axis.
Owner:THALES SA
Magnetron
A magnetron includes a cooling block (10) having an annular continuous portion with opposite end portions (12a, 12b) opposed to each other, the cooling block being secured to an outer peripheral surface of the cylindrical anode body, the cooling block having a coolant circulation pathway defined therein, a tightening member (15) engageable with the opposite end portions of the cooling block to tighten the cooling block by reducing a distance between the opposite end portions of the cooling block, and a pair of pipe joints (14) each connected to a portion of the cooling block adjacent to one of the opposite end portions so as to communicate with the coolant circulation pathway. The tightening member is disposed between connecting portions of the pair of pipe joints with the cooling block so as to extend in a direction inclined with respect to a plane including an annular direction of the cooling block.
Owner:PANASONIC INTPROP MANAGEMENT CO LTD
L-band inductive output tube
InactiveUS20070080762A1Transit-tube cooling methodsTubes with multiple resonatorAtmospheric pressureWave band
An inductive output tube (IOT) operates in a frequency range above 1000 MHz. An output window may be provided to separate a vacuum portion of the IOT from an atmospheric pressure portion of the IOT, the output window being surrounded by a cooling air manifold, the manifold including an air input port and a plurality of apertures permitting cooling air to move from the port, through the manifold and into the atmospheric pressure portion of the IOT. The output cavity may include a liquid coolant input port; a lower circular coolant channel coupled to receive liquid coolant from the liquid coolant input port; a vertical coolant channel coupled to receive liquid coolant from the lower circular coolant channel; an upper circular coolant channel coupled to receive liquid coolant from the vertical coolant channel; and a liquid coolant exhaust port coupled to receive liquid coolant from the upper circular coolant channel.
Owner:COMM & POWER IND
Distributed radiation coupling loss circuit applied to gyrotron traveling wave tube
ActiveCN114512387AImprove efficiencyIncrease output energyTransit-tube cooling methodsTransit-tube coupling devicesCoupling lossMicrowave
The invention discloses a distributed radiation coupling loss circuit applied to a gyrotron traveling wave tube, and belongs to the technical field of microwave and millimeter wave vacuum devices. According to the invention, self-oscillation of a TE11 mode and backward wave oscillation of a TE21 mode can be effectively suppressed. Meanwhile, high-power electromagnetic energy generated due to beam-wave interaction is guided into the rhombic waveguide and can be absorbed by the attenuation materials tightly attached to the side walls of the two wide edges of the rectangular waveguide. The surface area of the continuous attenuation material tightly attached to the side walls of the two wide edges of the rectangular waveguide is far larger than that of an attenuation ceramic ring in a high-frequency interaction circuit of a traditional medium-loaded gyrotron traveling wave tube, so that the heat dissipation area is increased; the problem that the medium loading section of the traditional medium loading gyrotron traveling wave tube absorbs excessive energy to generate high temperature and then overheat and exhaust gas is solved. Therefore, the beam-wave interaction efficiency, the stability and the power capacity of the gyrotron traveling wave tube are effectively improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Heat storage device of travelling wave tube
InactiveCN106169402AIncrease loading capacityImprove sealingTransit-tube collectorsTransit-tube cooling methodsEngineeringPhase-change material
The invention discloses a heat storage device of a travelling wave tube. The heat storage device of the travelling wave tube comprises a phase-change material, a base and a cover plate, wherein the base is provided with a storage cavity for accommodating the phase-change material, an assembly upper end surface arranged at the top part of the storage cavity, to-be-welded walls of the base, an injection hole, a sealing hole, an assembly lower end surface in contact with a bottom plate of the travelling wave tube, a cooling surface and sealing bolts for sealing the injection hole and the sealing hole, wherein the to-be-welded walls of the base are arranged on the periphery of the inner wall at the top part of the storage cavity; the cooling surface is arranged at the bottom part of the base and is in close fit with a collector of the travelling wave tube; the cover plate comprises a bottom surface of the cover plate and the to-be-welded walls of the cover plate; the bottom surface of the cover plate is in contact with the assembly upper end surface; and the to-be-welded walls of the cover plate are welded with the corresponding to-be-welded walls of the base. By the heat storage device of the travelling wave tube, the travelling wave tube is in specific working time; the highest temperature of a storage part after absorbing heat does not exceed 150 DEG C; the sealing effect of the phase-change material is good; and normal use of the travelling tube is effectively ensured.
Owner:CHENGDU GUOGUANG ELECTRIC
Miniaturized magnetron structure
ActiveCN111739773ASmall sizeStable jobTransit-tube leading-in arrangementsMagnetronsMiniaturizationEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of vacuum electronic devices, and particularly provides a miniaturized magnetron structure. According to the present invention, a neodymium iron boron or samarium cobalt permanent magnet material placed on an external support of a magnetron is adopted to replace an original ferrite magnetic ring so as to ensure the magnetic field intensity in an interaction space. The ferrite magnetic ring is not needed in the magnetron structure, and a neodymium iron boron or samarium cobalt permanent magnet is placed on the external support of the magnetron, so that the height and the width of the magnetron can be greatly reduced, and the magnetron structure is cuboid-shaped and can be matched with the shapes and the structures of the cooling fins and a filtering assembly synchronously, especially the filtering assembly. According to the invention, the output of an original same-direction choking coil from one end is improved into the output of a heterodromous choking coil from the left end and the right end, so that the miniaturized magnetron structure can stably work while being matched with a magnetic circuit structure. In conclusion, the invention provides the novel magnetron structure, and the miniaturization design of the magnetron structure is further realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Cooling device for travelling-wave tube amplifier
ActiveCN105470072AImprove cooling effectTransit-tube cooling methodsAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention relates to a cooling device for a travelling-wave tube amplifier. The cooling device comprises a first cooling plate, a second cooling plate and a third cooling plate, wherein the first cooling plate, the second cooling plate and the third cooling plate are all internally provided with cooling liquid runners, the cooling liquid runners in the first cooling plate, the second cooling plate and the third cooling plate are sequentially communicated so that a cooling liquid can sequentially pass through the first cooling plate, the second cooling plate and the third cooling plate, and the first cooling plate, the second cooling plate and the third cooling plate are sequentially used for cooling a high-voltage power supply of the amplifier, a power factor corrector (PFC) power supply and a travelling-wave tube. By the cooling device, the problems that the travelling-wave tube amplifier is instable in running, a component is thermally damaged and the service lifetime of a system is reduced caused by slow cooling speed and low cooling rate in an air-cooling mode are solved.
Owner:SICHUAN JIUZHOU ELECTRIC GROUP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com