Patents
Literature
849 results about "Coolant channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods of cooling process chamber components
ActiveUS20120273162A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce total powerElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringCoolant channel
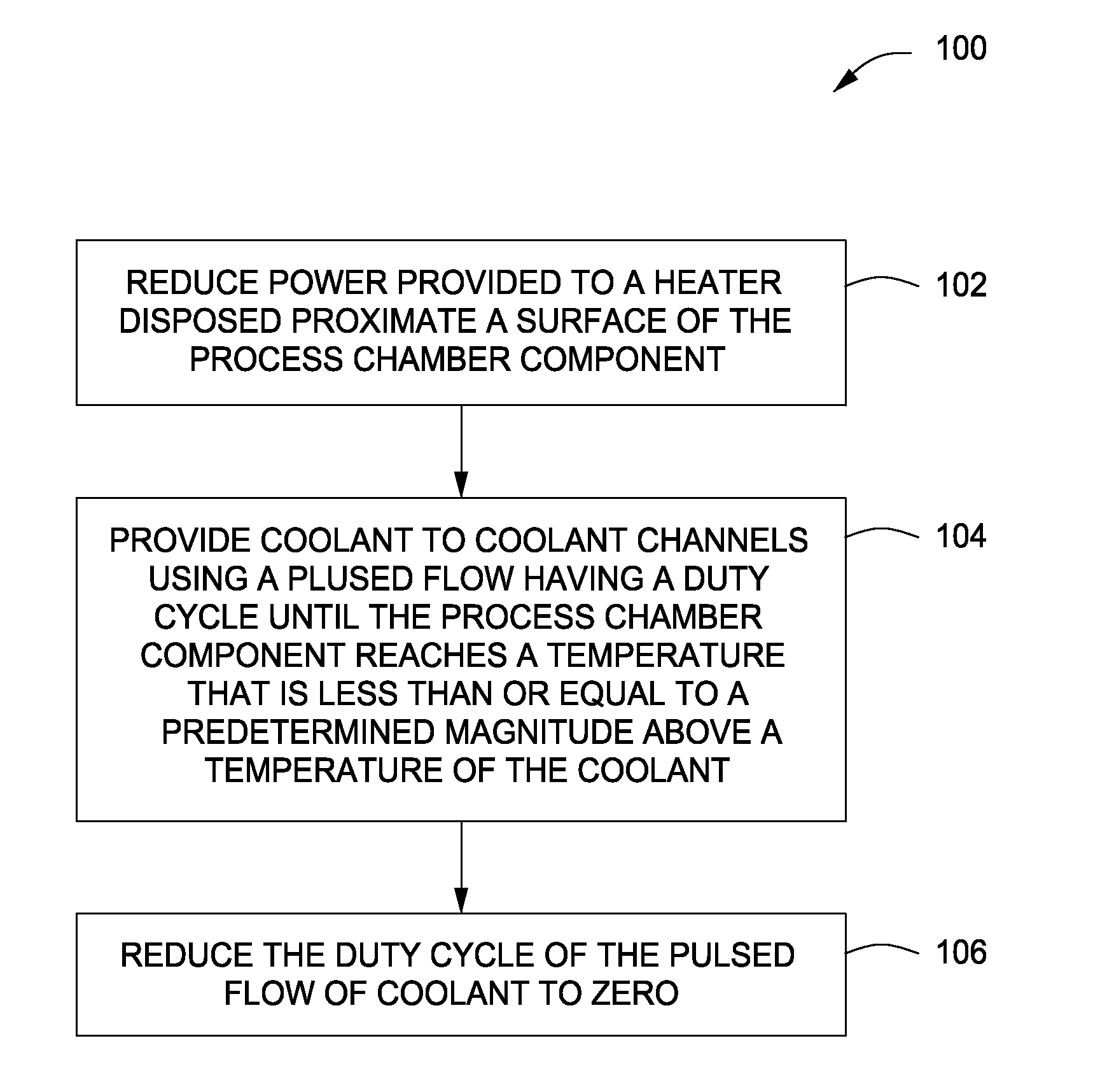
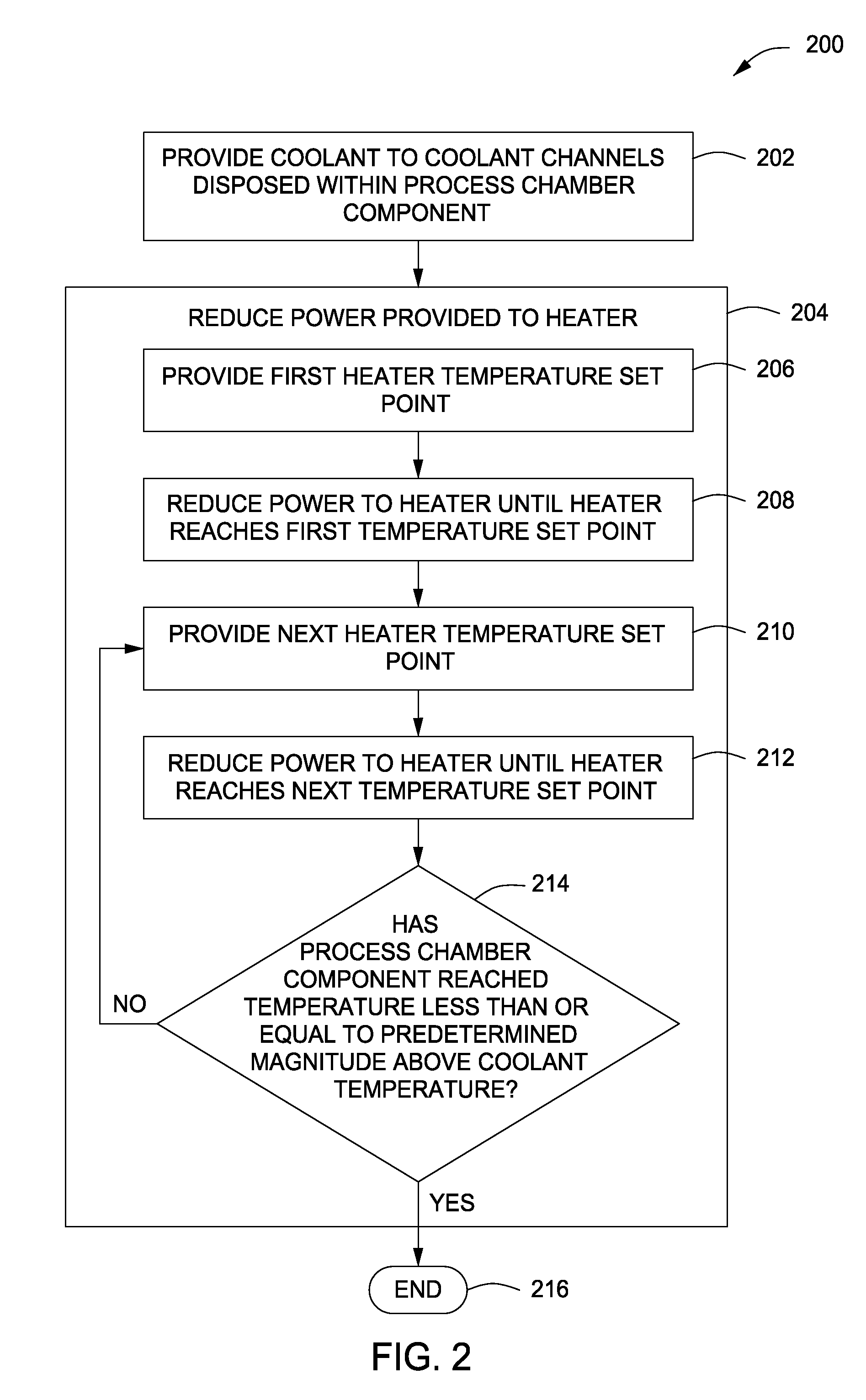
Methods for cooling process chamber components are provided herein. In some embodiments, a method of cooling a process chamber component may include reducing a power provided to a heater disposed proximate a surface of the process chamber component to reduce an amount of heat provided to the component by the heater; providing a coolant to coolant channels disposed within the process chamber component using a pulsed flow having a duty cycle until the process chamber component reaches a temperature that is less than or equal to a predetermined magnitude above a temperature of the coolant; and after the process chamber component reaches the temperature less than or equal to the predetermined magnitude above a temperature of the coolant, reducing the duty cycle of the pulsed flow of the coolant to zero.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
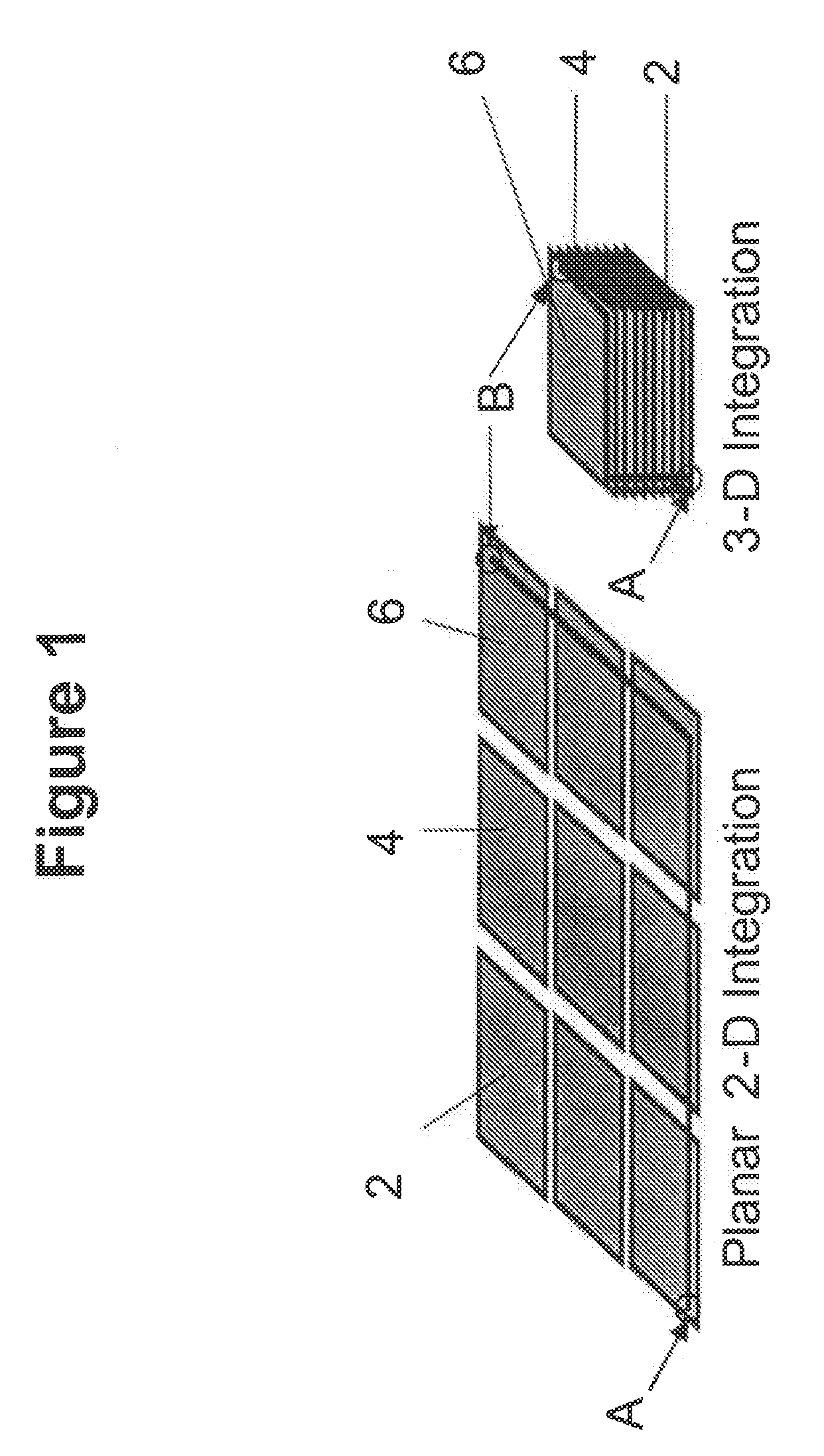
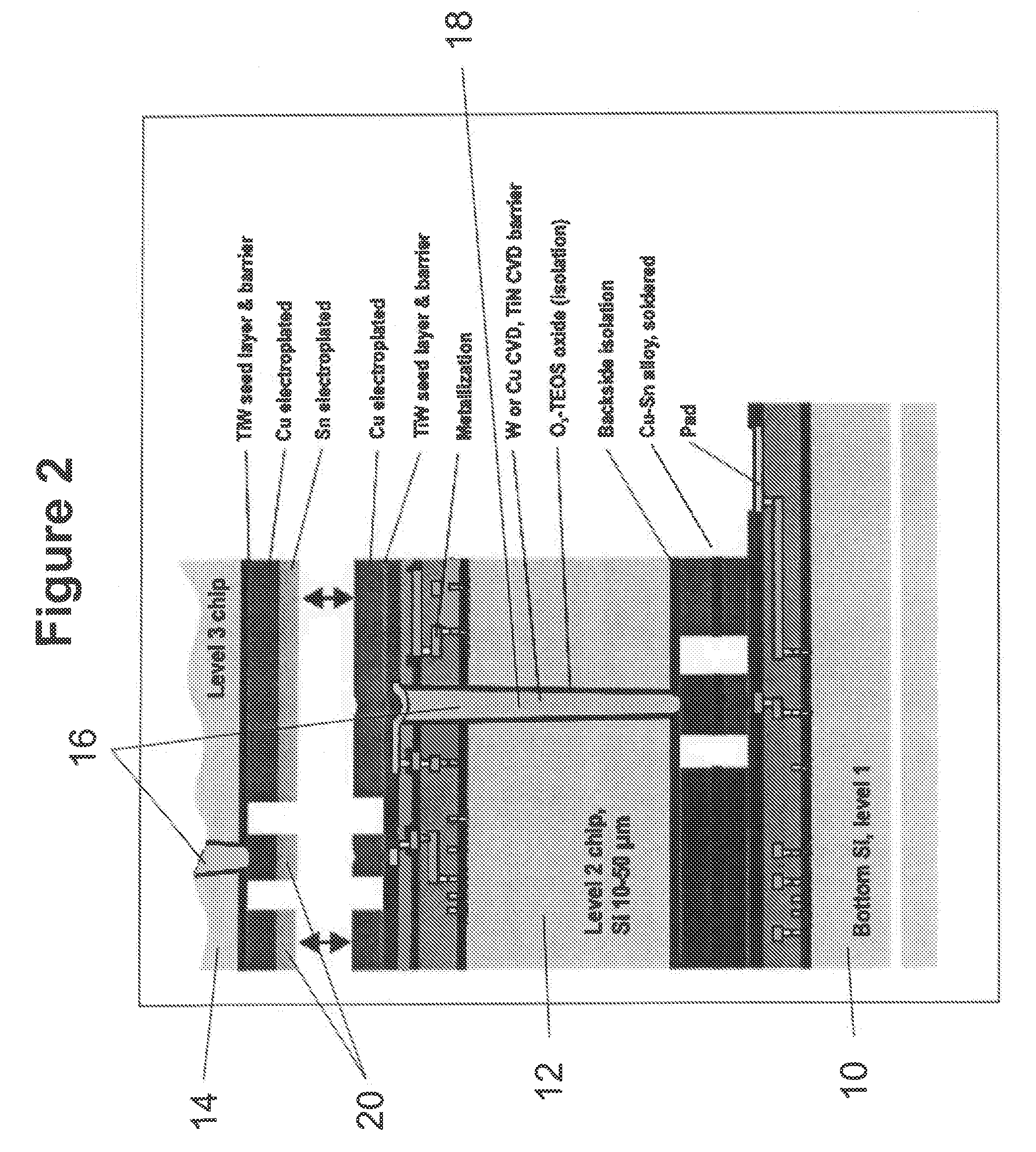
Structure and process for electrical interconnect and thermal management
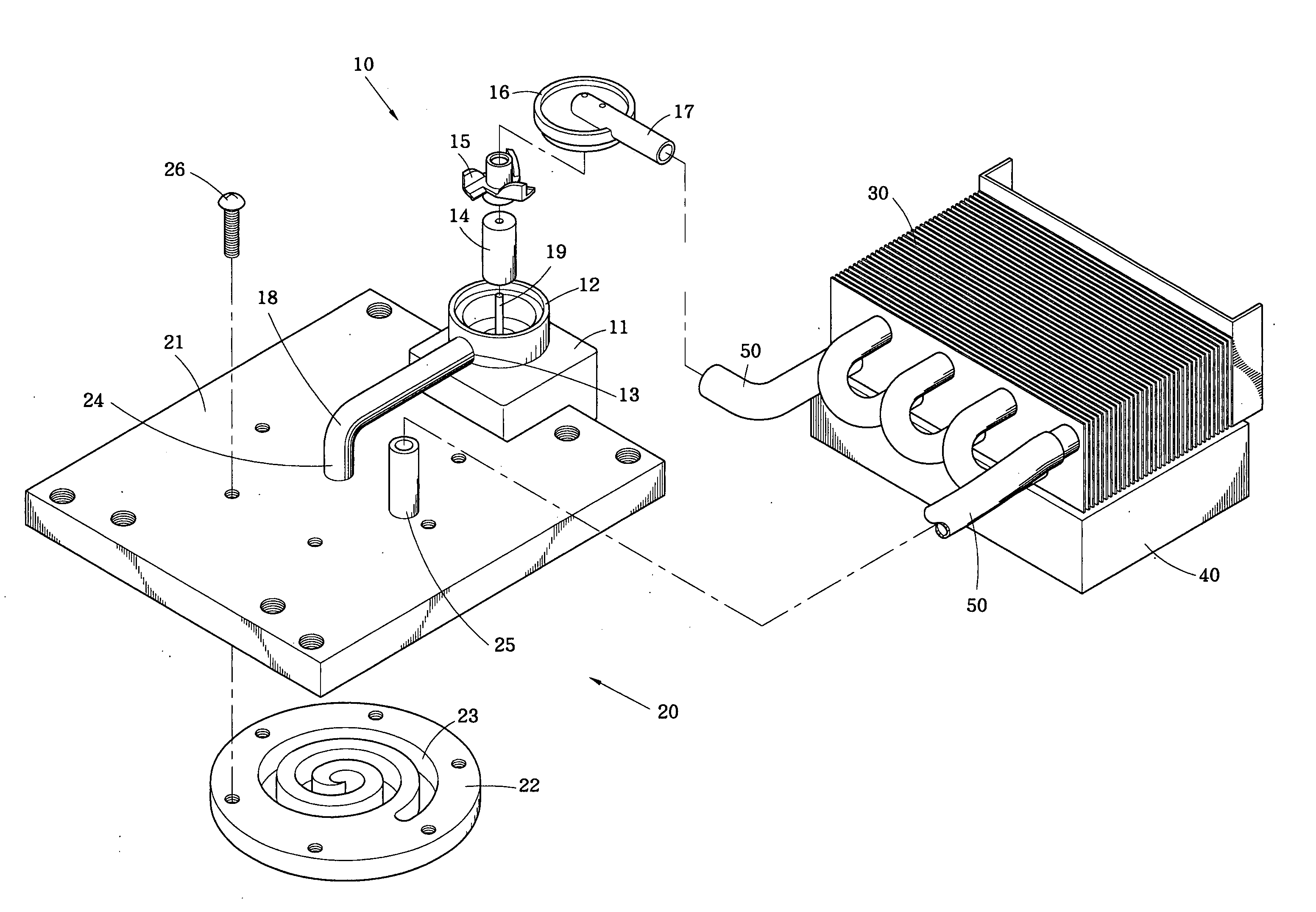
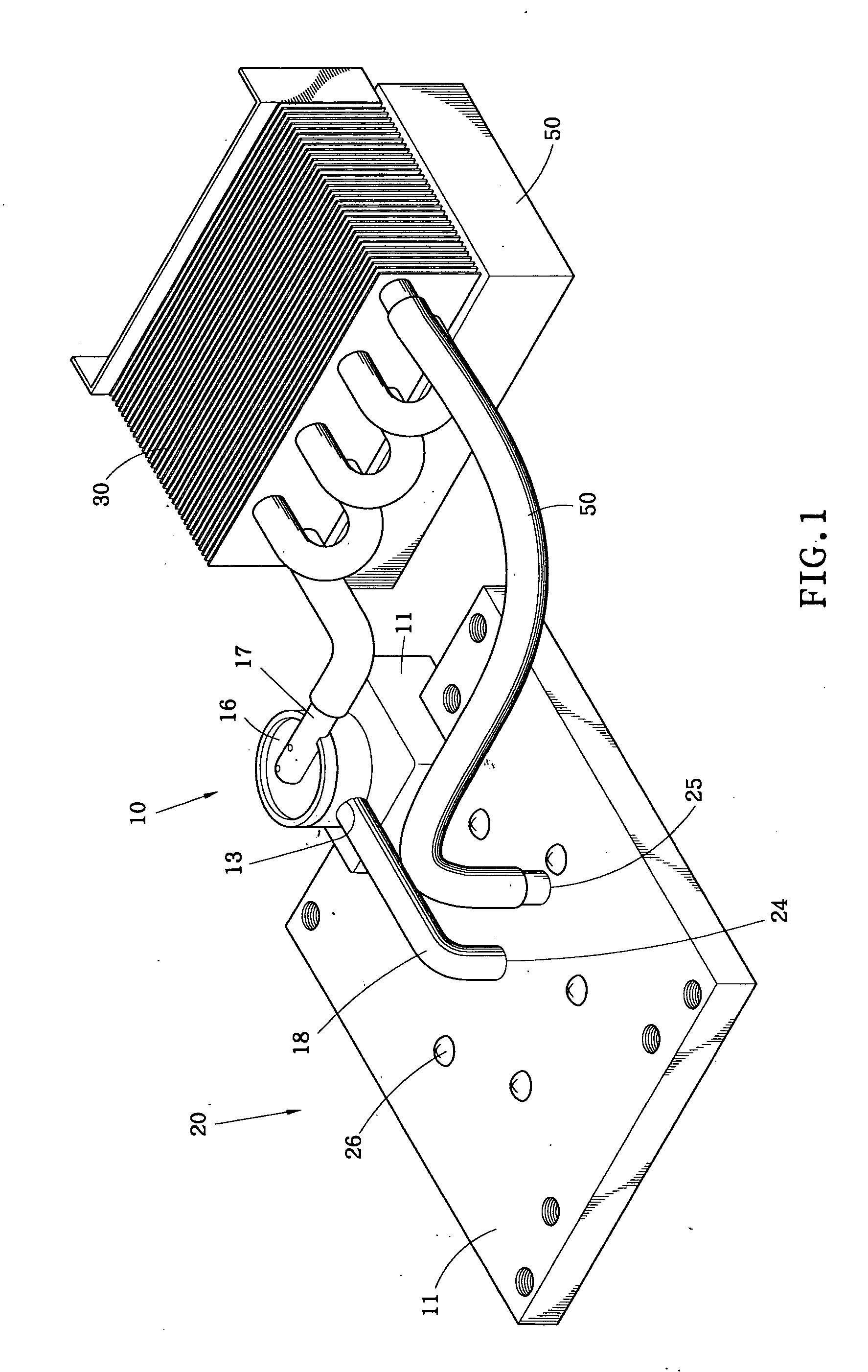
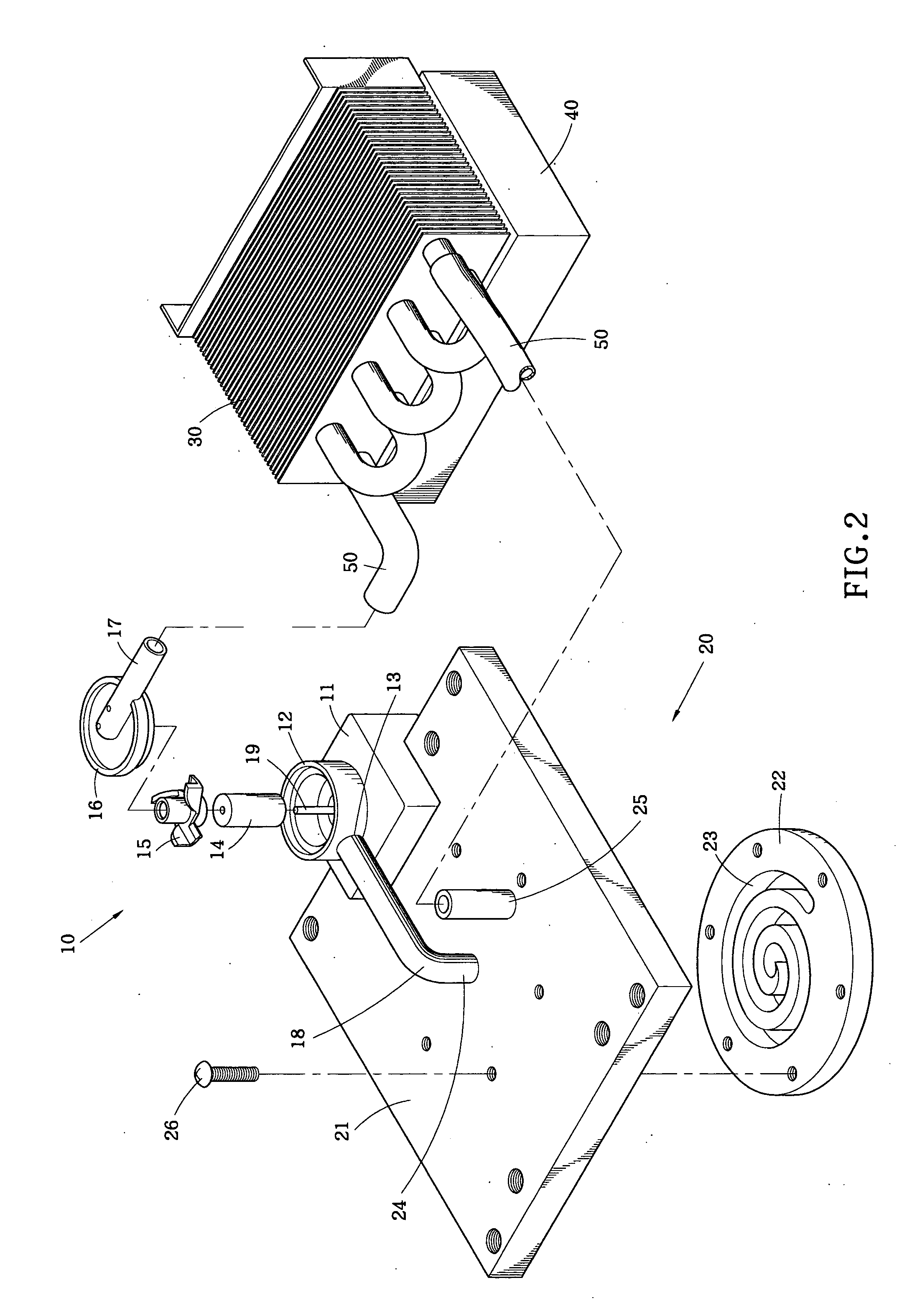
ActiveUS20090057879A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectrical interconnect
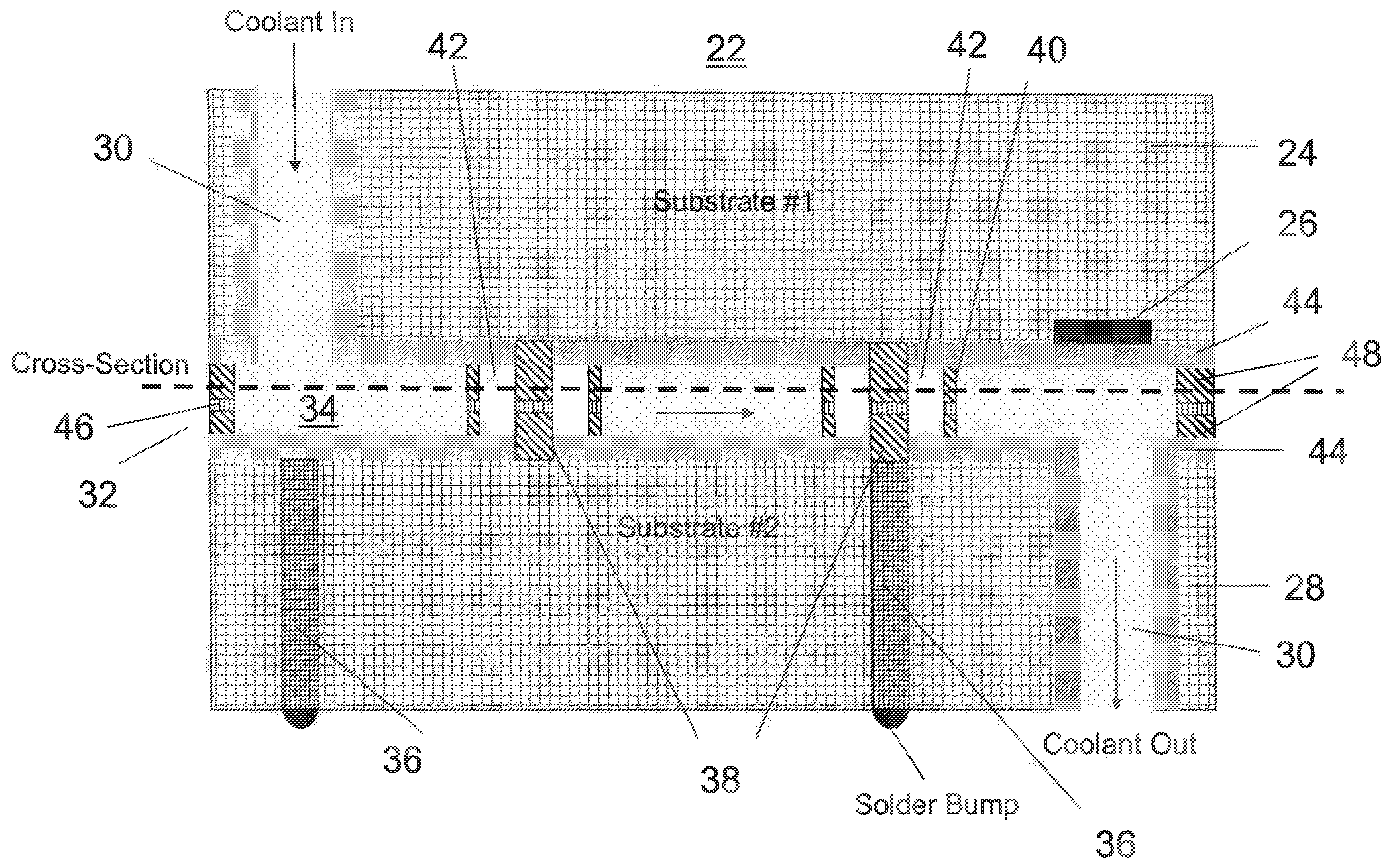
A structure and method for thermal management of integrated circuits. The structure for thermal management of integrated circuits includes first and second substrates bonded together, at least one of the first and second substrates including at least one circuit element, an entrance through-hole having a length extending through a thickness of at least one of the first substrate and the second substrate, an exit through-hole having a length extending through a thickness of at least one of the first substrate and the second substrate, a bonding element forming a seal between the first and second substrates and forming a space between the first and second substrate, and a coolant channel formed in the space between the first and second substrates such that a fluid entering the entrance through-hole transits the coolant channel and the exit through-hole to provide cooling to the circuit element. The method supplies a fluid through the entrance through-hole, flows the fluid through the coolant channel between the first substrate and second substrates, and removes the fluid from the coolant channel through the exit through-hole.
Owner:MICROSS ADVANCED INTERCONNECT TECH LLC
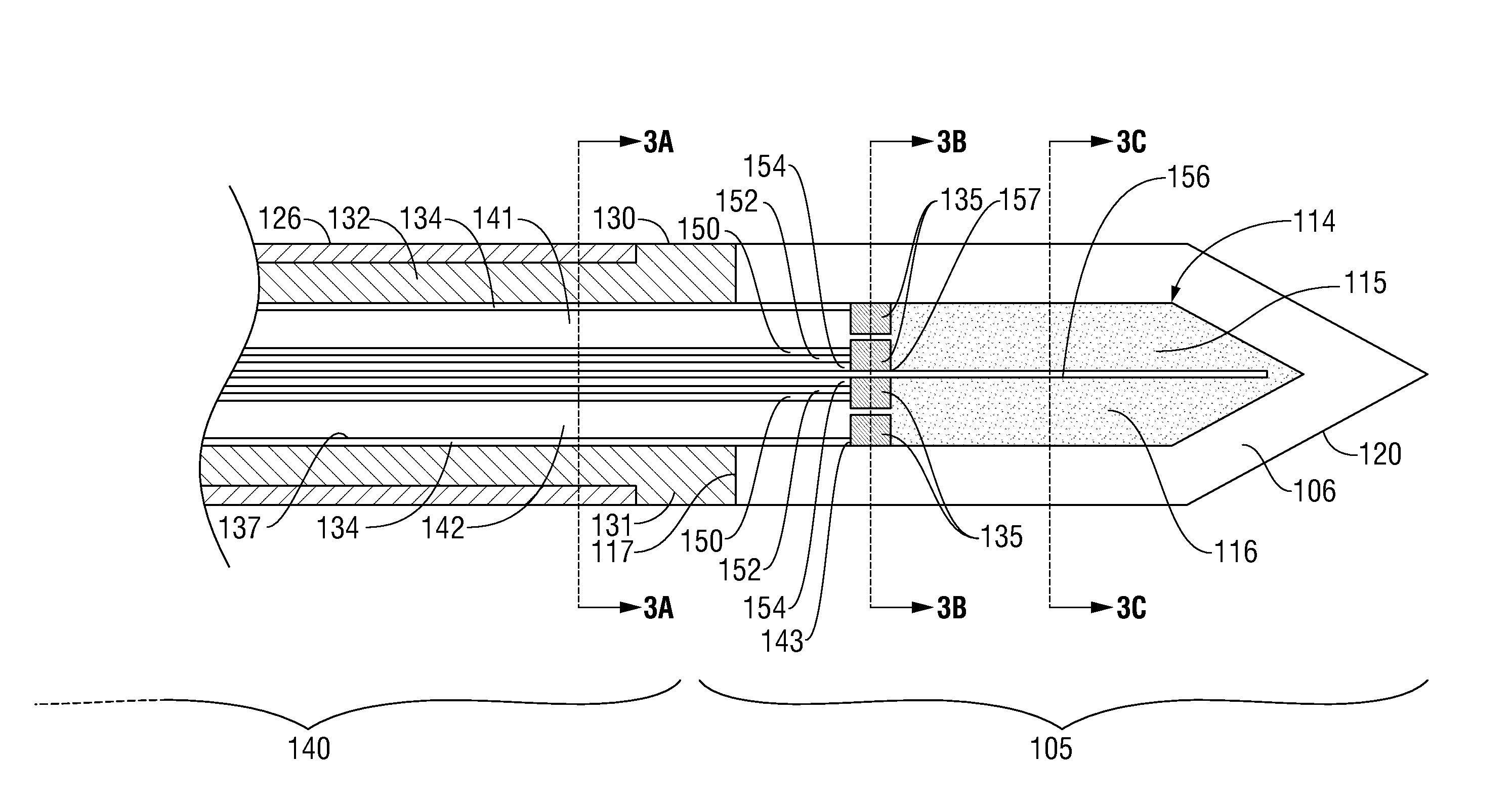
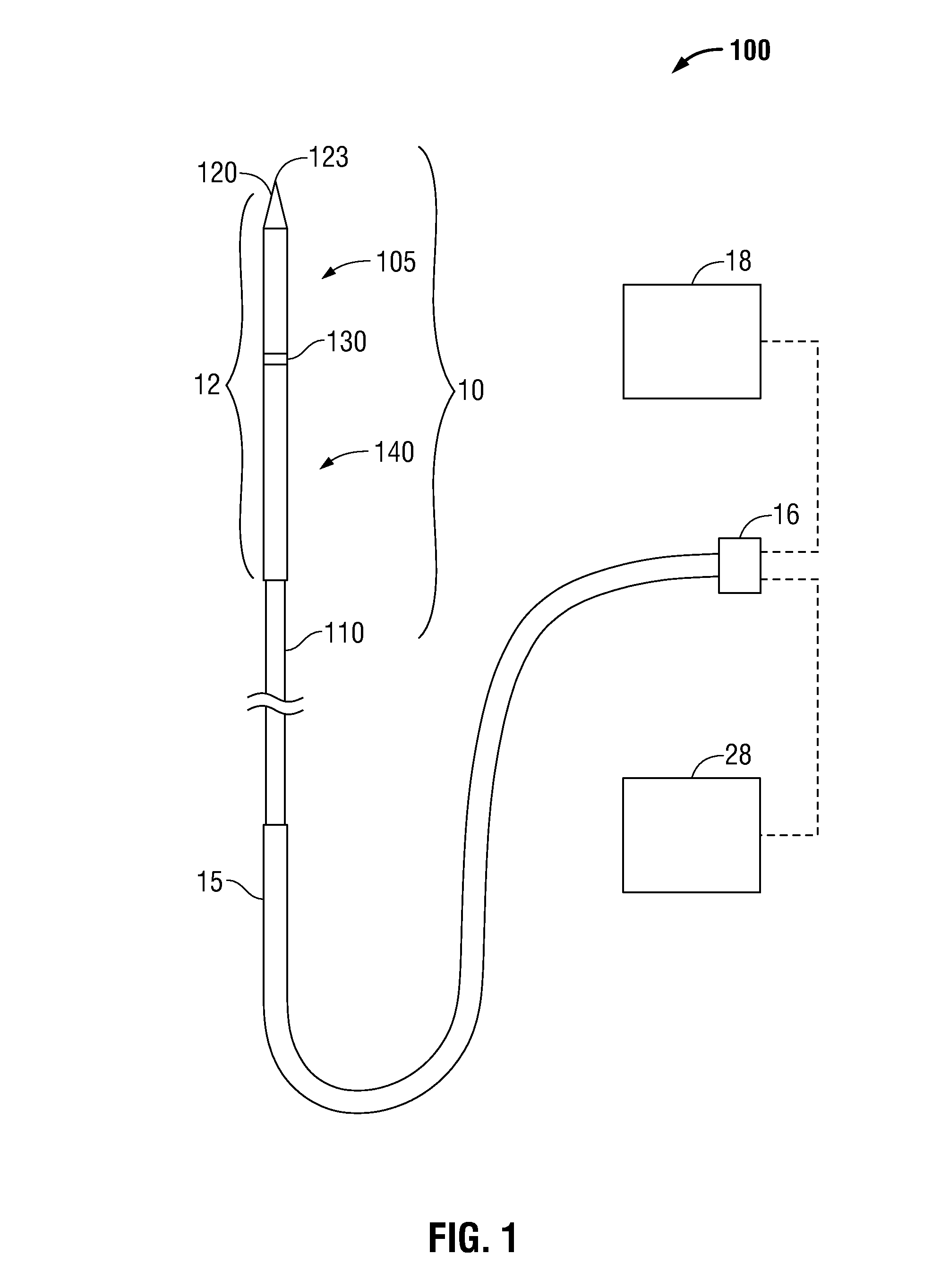
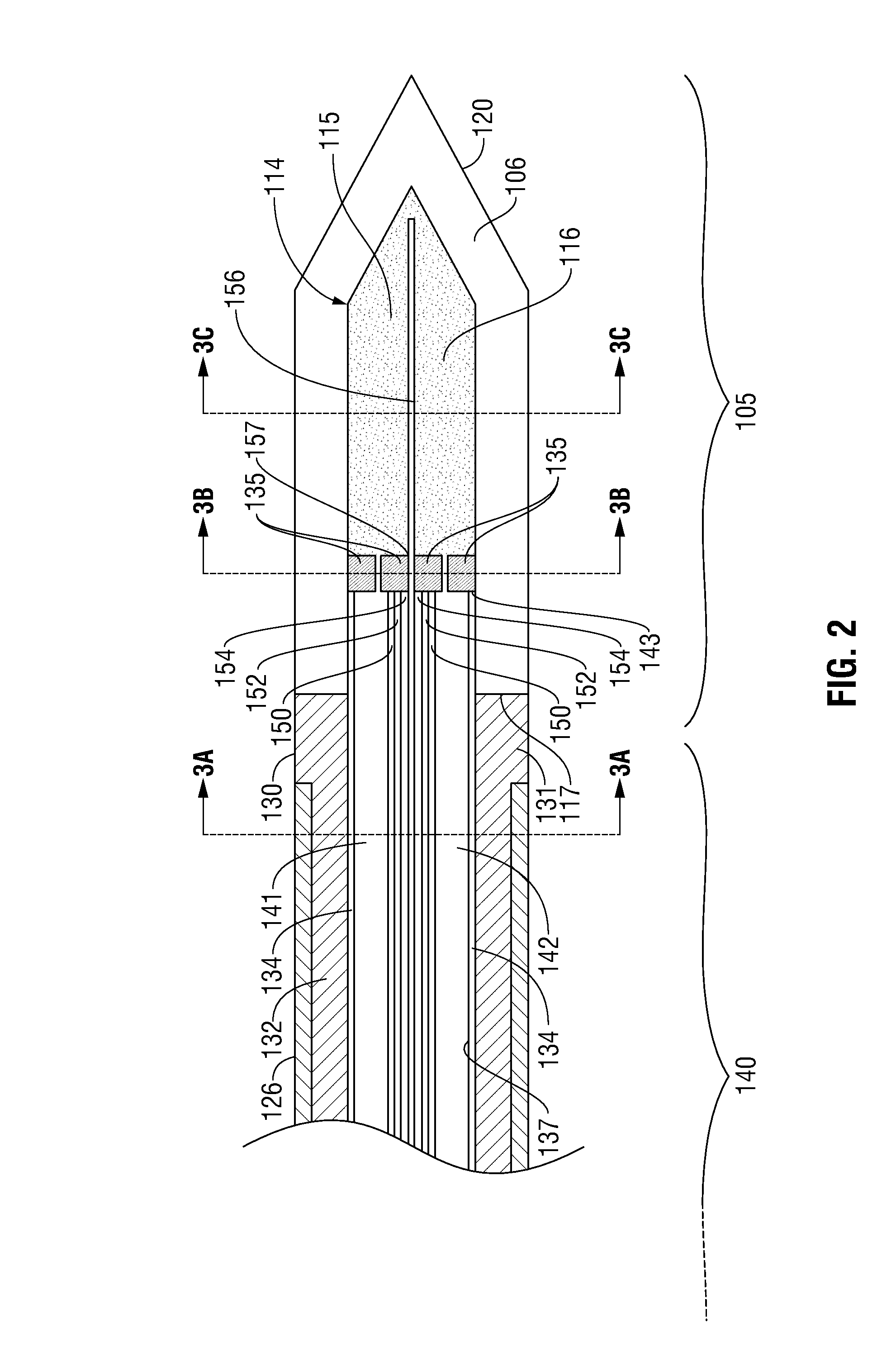
Perfused Core Dielectrically Loaded Dipole Microwave Antenna Probe
ActiveUS20110066144A1Improve power delivery performance powerImprove power power handlingElectrotherapySurgical needlesCouplingCooling chamber
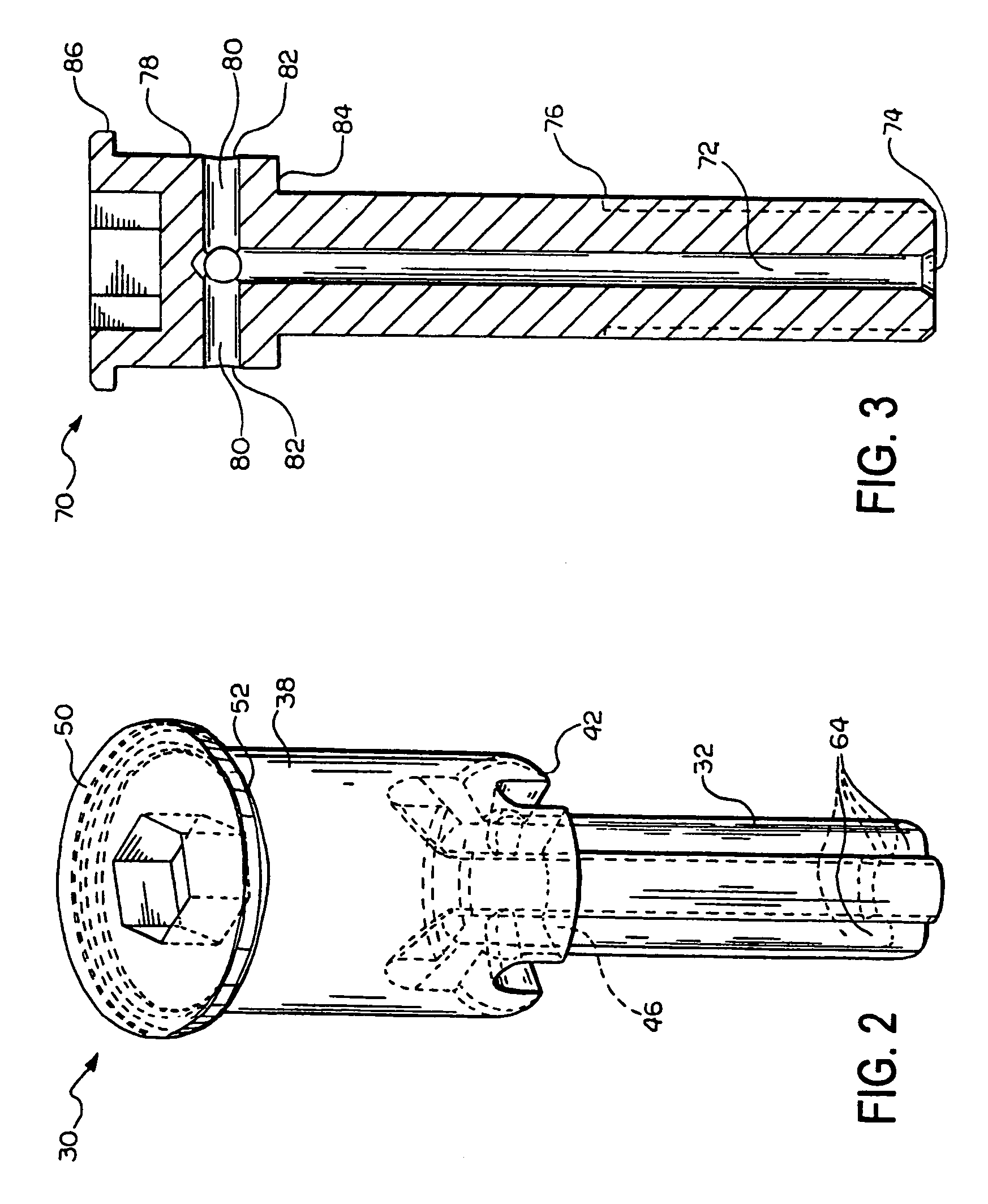
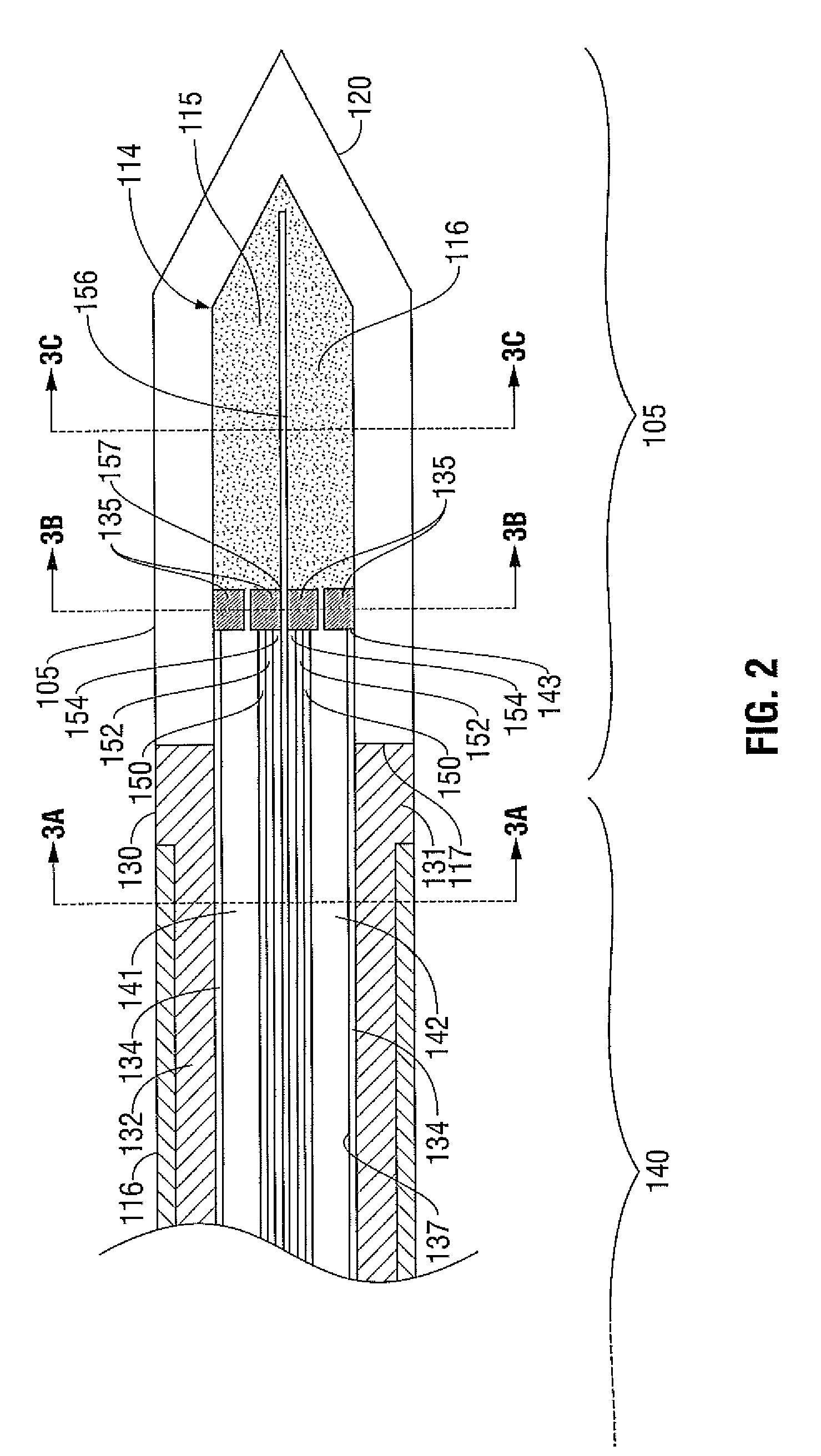
A microwave surgical ablation probe having an arrangement of coolant channels in fluid communication with a cooling chamber disposed within the distal end of the probe is disclosed. A hypotube having one or more longitudinal ribs extending radially inward from an inner surface thereof is coaxially disposed around a coaxial feedline. The longitudinal ribs of the hypotube engage an outer sheath of the feedline to define a fluid inflow channel to deliver coolant to the cooling chamber, and a fluid outflow channel to receive fluid from the cooling chamber. The cooling chamber may be formed from porous ceramic or porous metallic material that provides structural support to the probe while permitting coolant to circulate therethrough. The probe includes dielectric and choke members that are adapted to control the microwave radiation pattern (e.g., ablation shape), and which may provide improved coupling of the probe to tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Apparatus and method for adjusting coolant flow resistance through liquid-cooled electronics rack(s)
InactiveUS20110056675A1Improve heat transfer performanceOvercomes shortcomingTemperatue controlElectrical apparatus contructional detailsLine tubingCoolant flow
Apparatuses and methods are presented for adjusting coolant flow resistance through one or more liquid-cooled electronics racks. Flow restrictors are employed in association with multiple heat exchange tube sections of a heat exchange assembly, or in association with a plurality of coolant supply lines or coolant return lines feeding multiple heat exchange assemblies. Flow restrictors associated with respective heat exchange tube sections (or respective heat exchange assemblies) are disposed at the coolant channel inlet or coolant channel outlet of the tube sections (or of the heat exchange assemblies). These flow restrictors tailor coolant flow resistance through the heat exchange tube sections or through the heat exchange assemblies to enhance overall heat transfer within the tube sections or across heat exchange assemblies by tailoring coolant flow. In one embodiment, the flow restrictors tailor a coolant flow distribution differential across multiple heat exchange tube sections or across multiple heat exchange assemblies.
Owner:IBM CORP
Liquid cooling manifold with multi-function thermal interface
ActiveUS20100104938A1Cell temperature controlCell component detailsCompressible materialThermal management system
A liquid cooling manifold assembly for use in the thermal management system of a battery pack is provided. The liquid cooling manifold assembly includes a coolant channel portion through which the coolant channels run, and a dual layer thermal interface interposed between the coolant channel portion and the cells of the battery pack. The outer material layer of the dual layer thermal interface is comprised of an electrically non-conductive, high dielectric material that is preferably tear resistant, deformable and has a high tensile strength and a relatively low surface friction. The inner material layer of the dual layer thermal interface is comprised of a highly compressible material.
Owner:TESLA INC
Gas showerhead, method for making the same and thin film growth reactor
ActiveUS20130299009A1Easy to manufactureImprove utilization efficiencyValve members for heating/coolingHollow article cleaningEngineeringReaction chamber
The present application provides a gas showerhead including a gas distribution and diffusion plate and a water cooling plate, the gas distribution and diffusion plate includes several columns of first gas diffusion passages connecting to a first reactant gas source and several columns of second gas diffusion passages connecting to a second reactant gas source; the water cooling plate having cooling liquid passages is arranged below the gas distribution and diffusion plate, and the water cooling plate is provided with first gas outlet passages provided for the reactant gas in the first gas diffusion passages to flow out and second gas outlet passages provided for the reactant gas in the second gas diffusion passages to flow out, so as to isolatedly feed at least two reactant gases into a reaction chamber.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FAB EQUIP INC CHINA
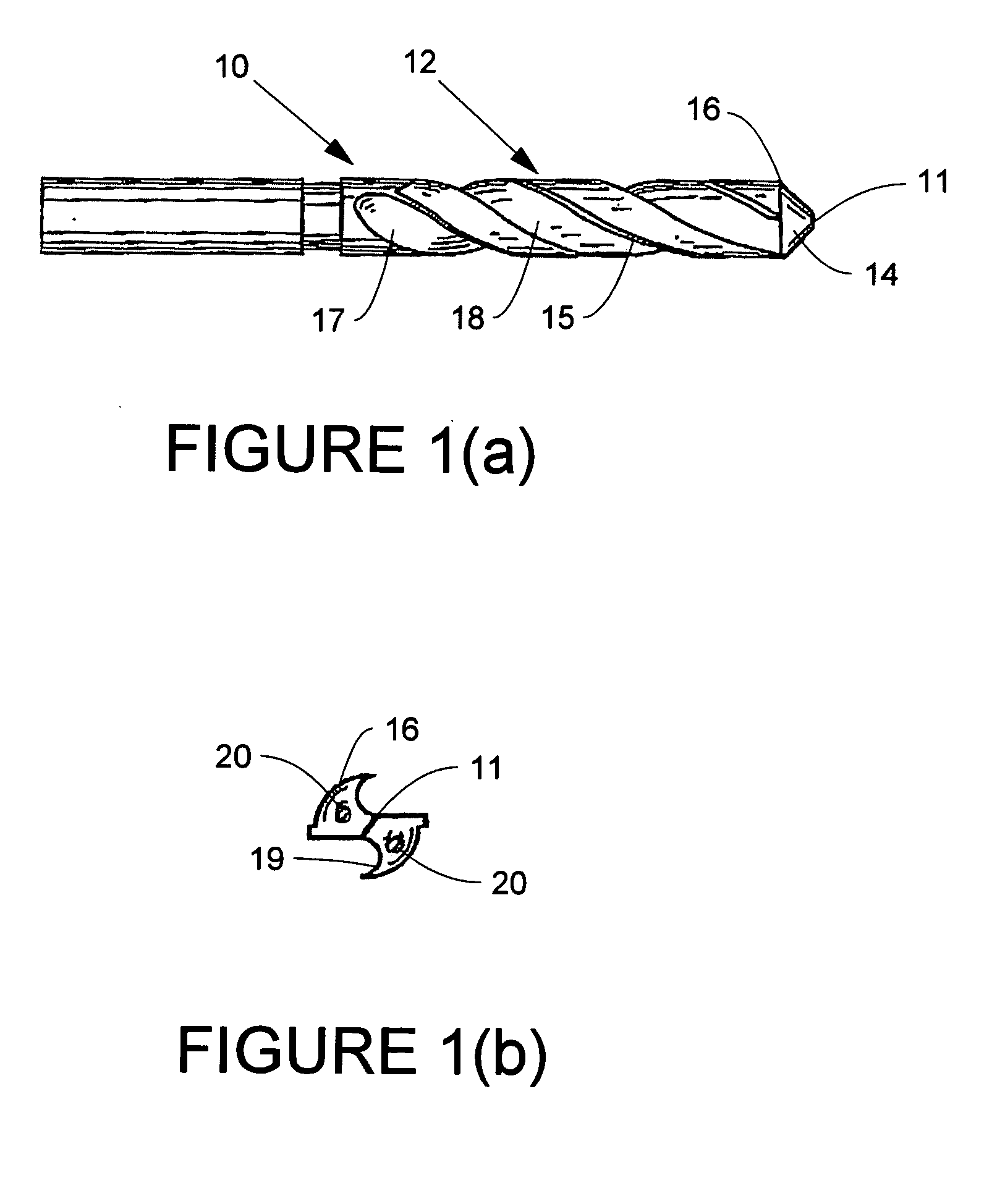
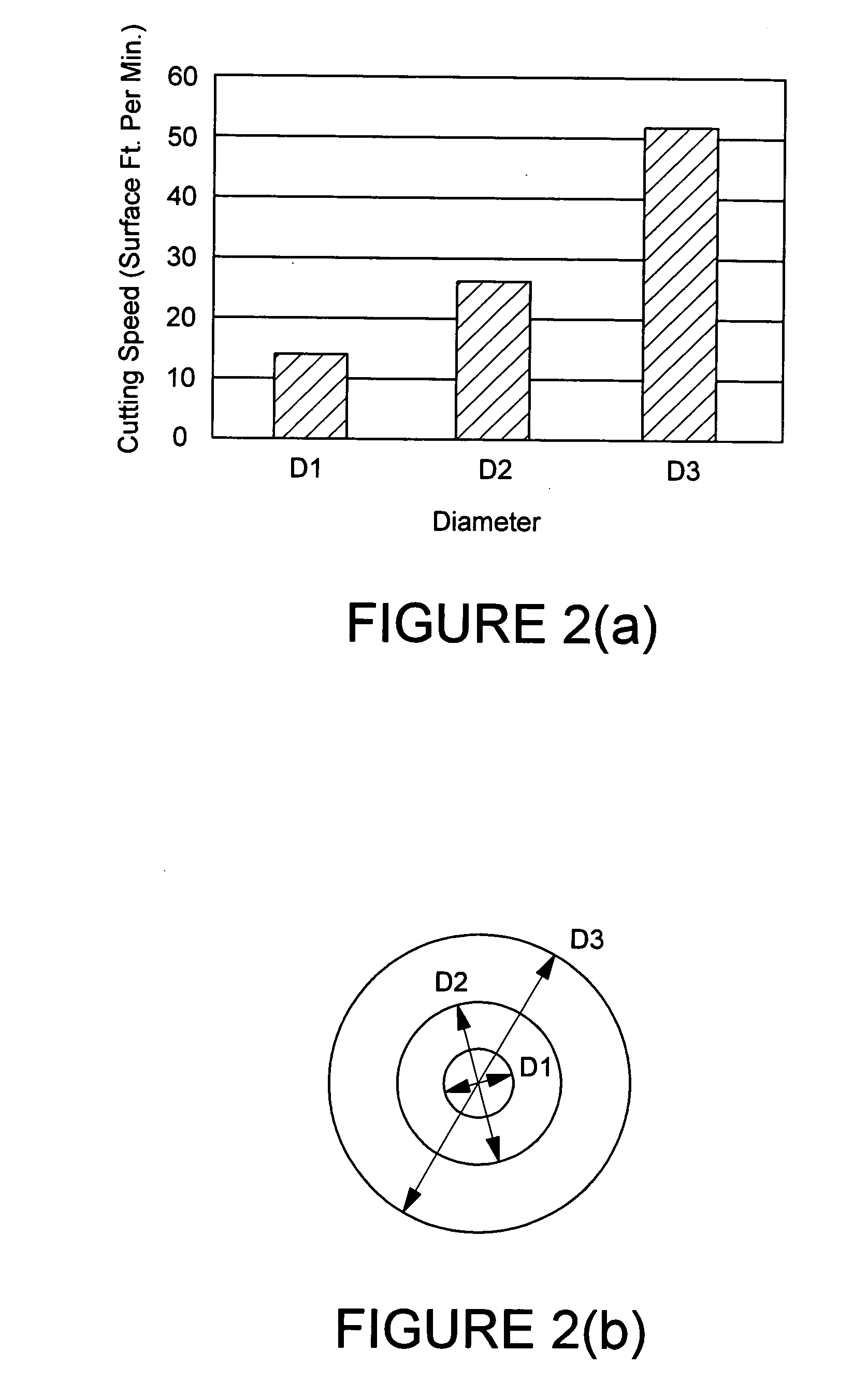
Cutter blade with integral coolant passages
InactiveUS6634835B1Low heat generationHeat dissipationMetal working apparatusGear teeth manufacturing toolsHobbingCarbide
A hob type cutter blade for use in a hobbing process. The cutter blade is formed with at least one cooling passage that permits the flow of coolant through the cutter blade to the contact surface reducing the heat generation as well as dissipating any heat already produced during the hobbing operation. During manufacturing, the cooling passage is sintered into the carbide cutter blade without the addition of separate operation.
Owner:DANA AUTOMOTIVE SYST GRP LLC
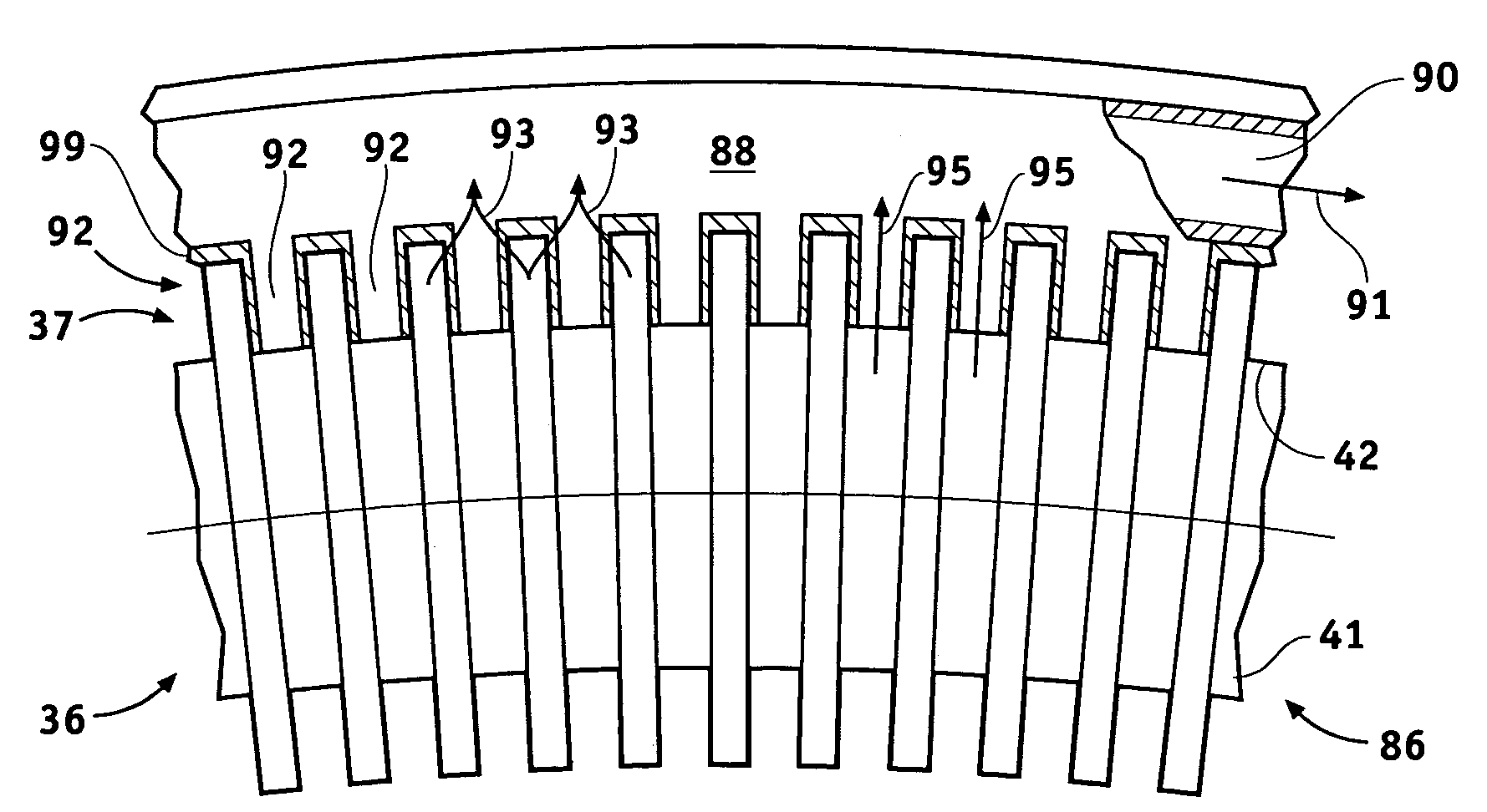
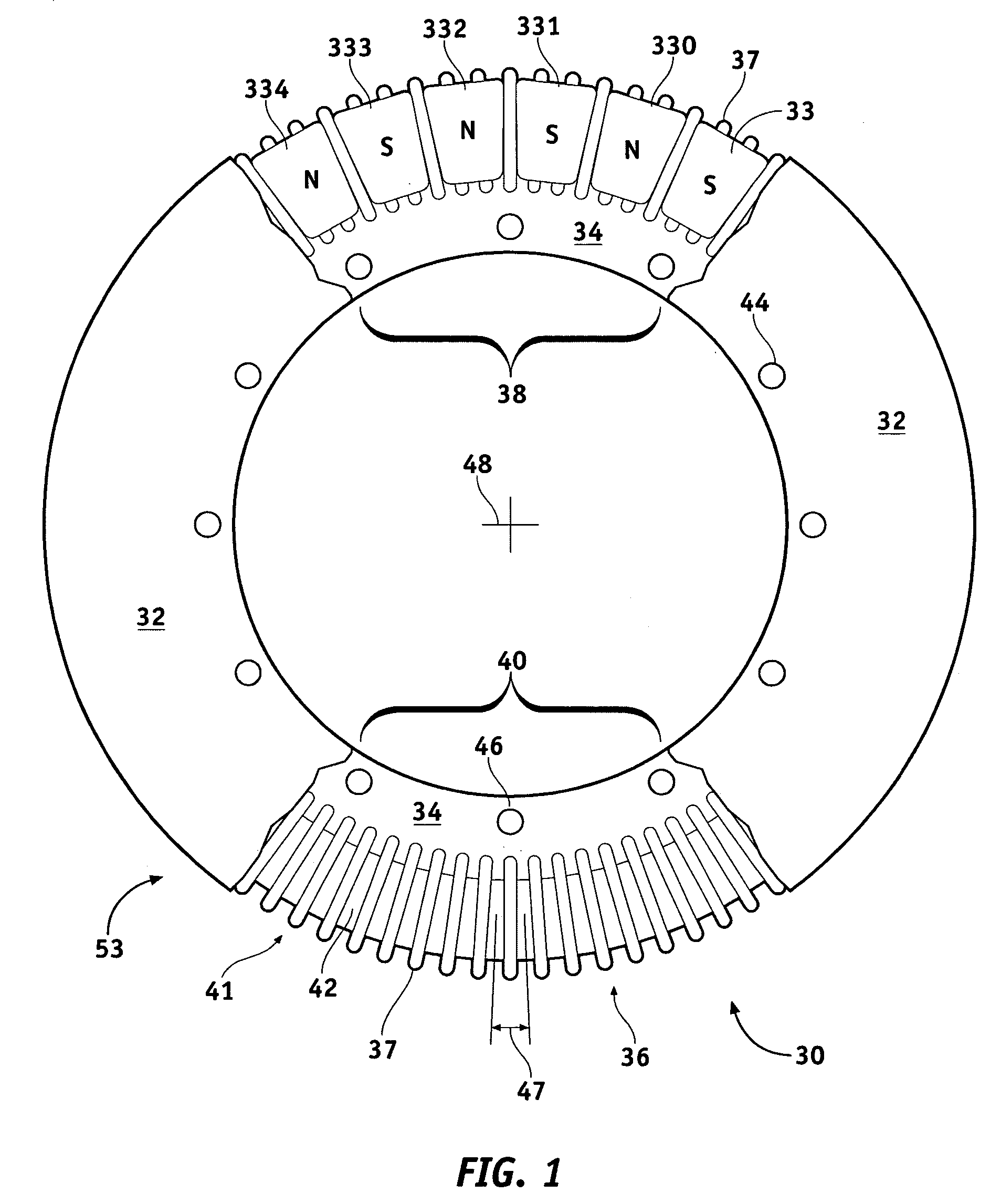
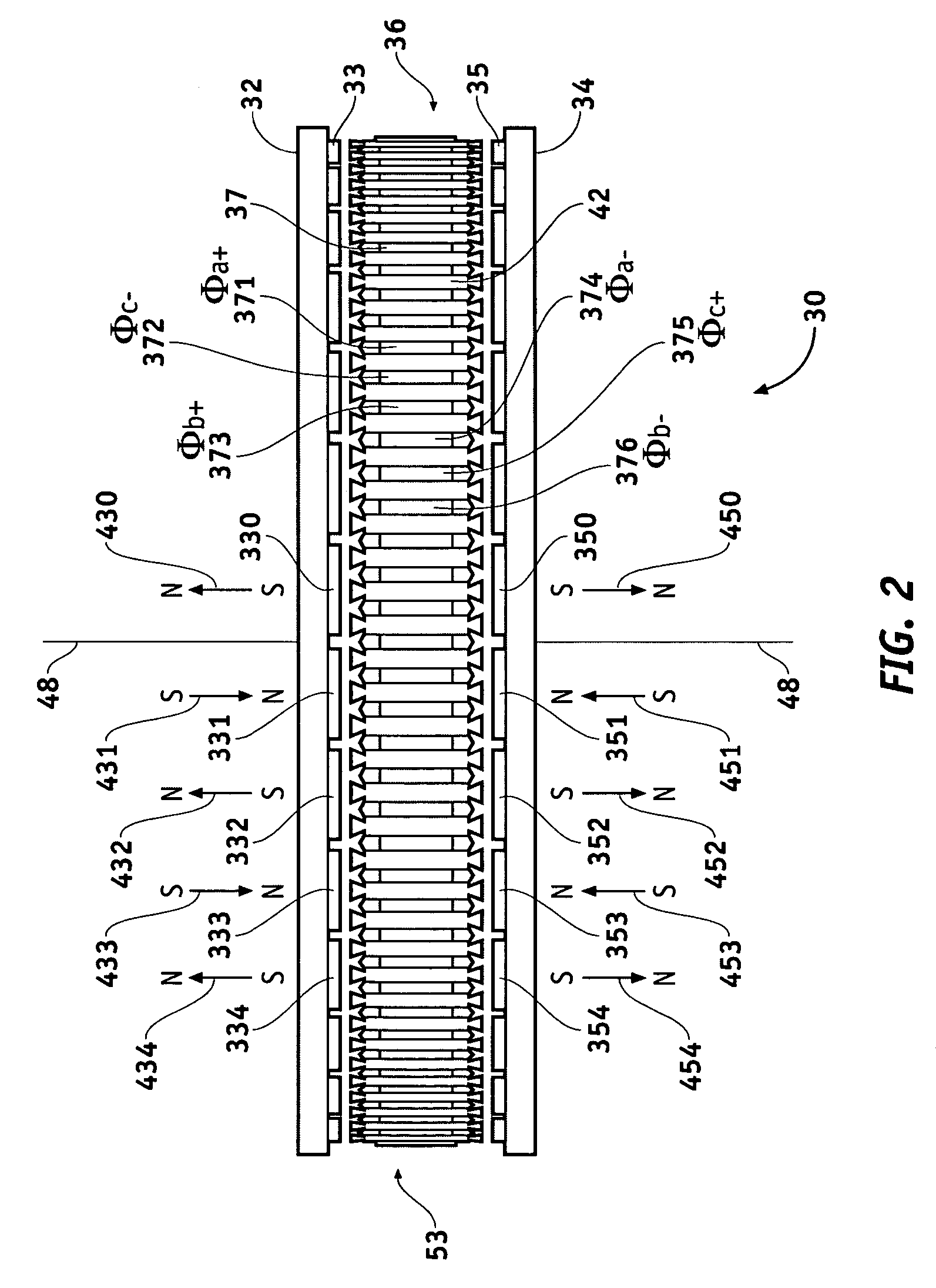
Cooling and handling of reaction torque for an axial flux motor
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
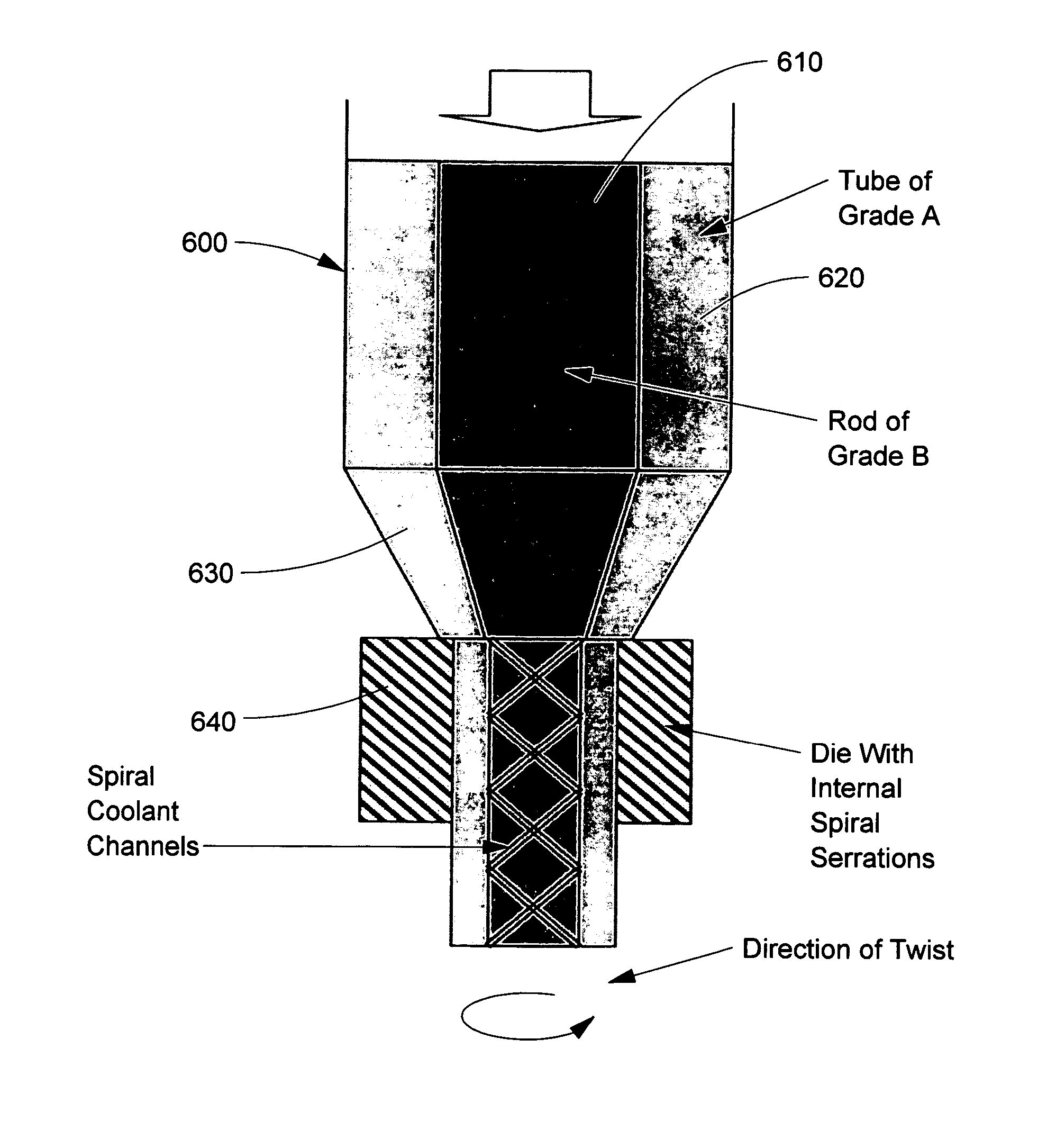
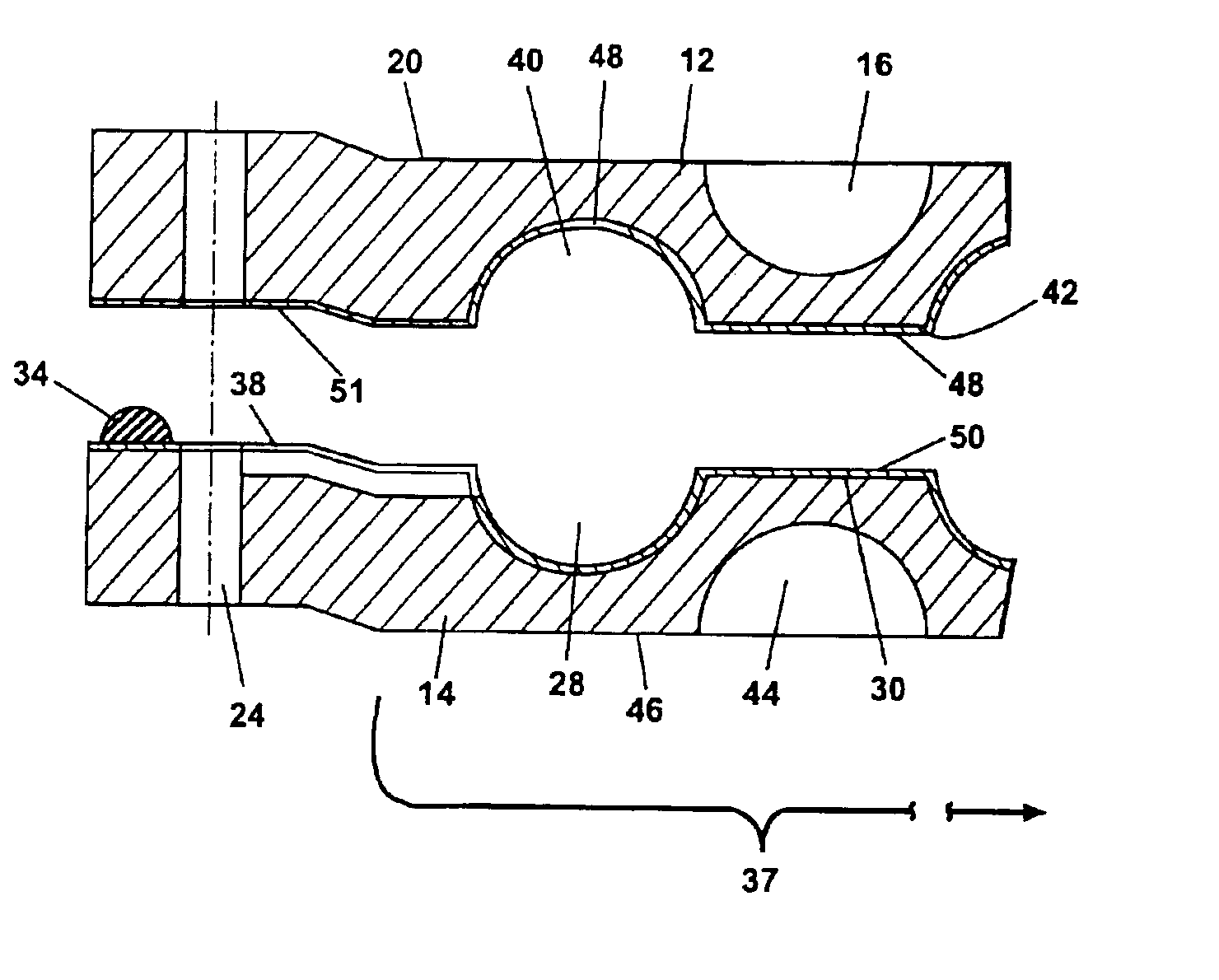
Composite article with coolant channels and tool fabrication method
Embodiments of the present invention include composite articles comprising at least a first region and a second region and methods of making such articles. The first region may comprise a first composite material, wherein the first region comprises less than 5 wt. % cubic carbides by weight, and the second region may comprise a second composite material, wherein the second composite material differs from the first composite material in at least one characteristic. The composite article may additionally comprise at least one coolant channel. In certain embodiments, the first and second composite material may individually comprise hard particles in a binder, wherein the hard particles independently comprise at least one of a carbide, a nitride, a boride, a silicide, an oxide, and solid solutions thereof and the binder comprises at least one metal selected from cobalt, nickel, iron and alloys thereof. In specific embodiments, the first composite material and the second composite material may individually comprise metal carbides in a binder, such as a cemented carbide.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
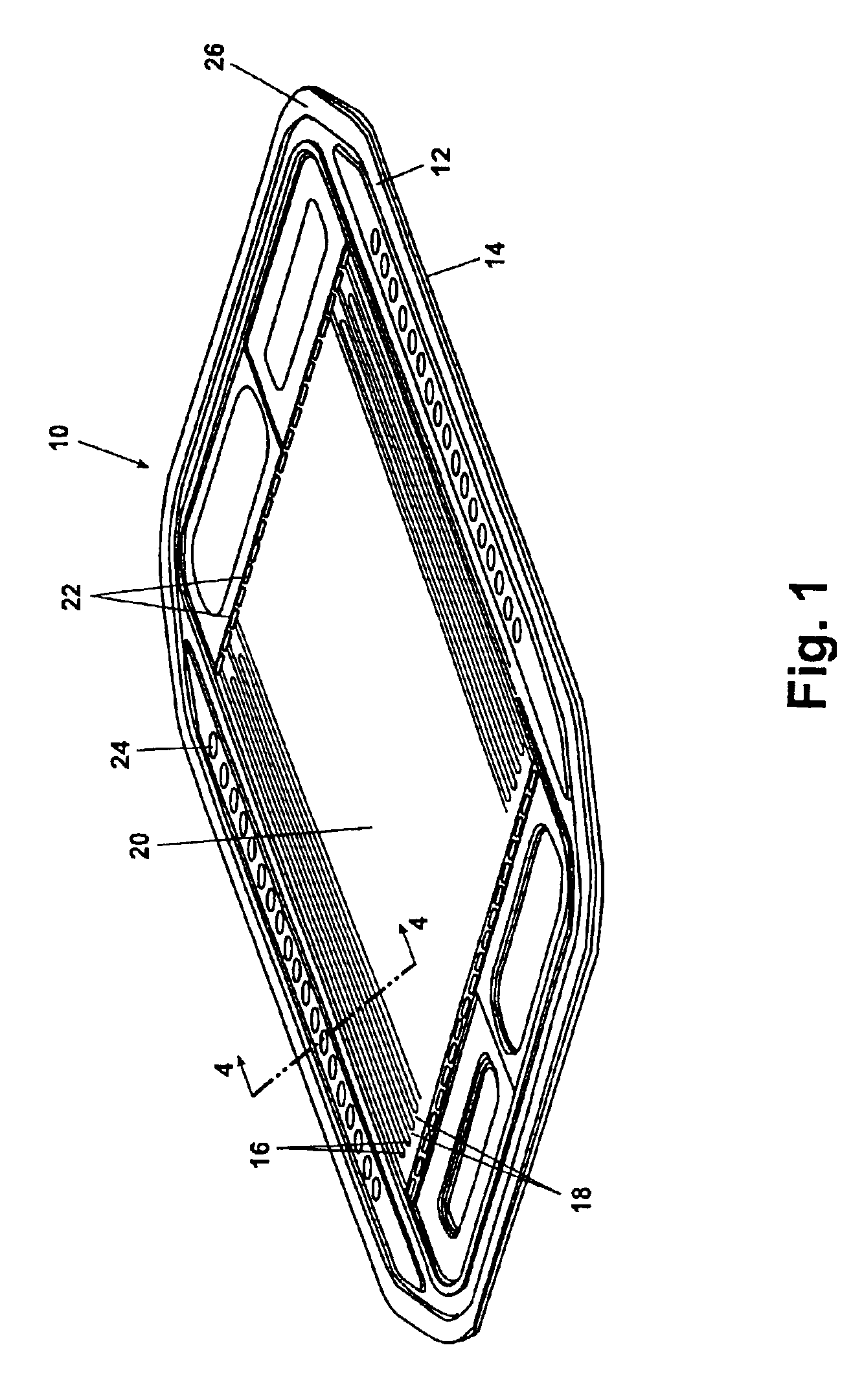
Joining of bipolar plates in proton exchange membrane fuel cell stacks
InactiveUS6887610B2Reduce material costsAvoid contactFuel cells groupingElectrode carriers/collectorsEngineeringProton exchange membrane fuel cell
A bipolar plate assembly for a proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack advantageously connects electrically conductive plate surfaces, without the requirement to weld or braze the plate pairs. Each plate has alternating coolant channels and lands formed on an inside facing surface. An electrically conductive layer is deposited over at least the coolant channels and lands. Pairs of plates are aligned having facing electrically conductive layers. A fluid seal is disposed between the inside facing surfaces about a perimeter of the coolant channels. Each plate pair is compressed to form a plurality of electrical bond lines between adjacent lands within the perimeter seal. The perimeter seal prevents stack reactant gas oxygen from contacting and oxidizing the electrically conductive layer. A dielectric coolant is also used to reduce oxidation of the electrically conductive layer.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Compact high efficiency gasifier
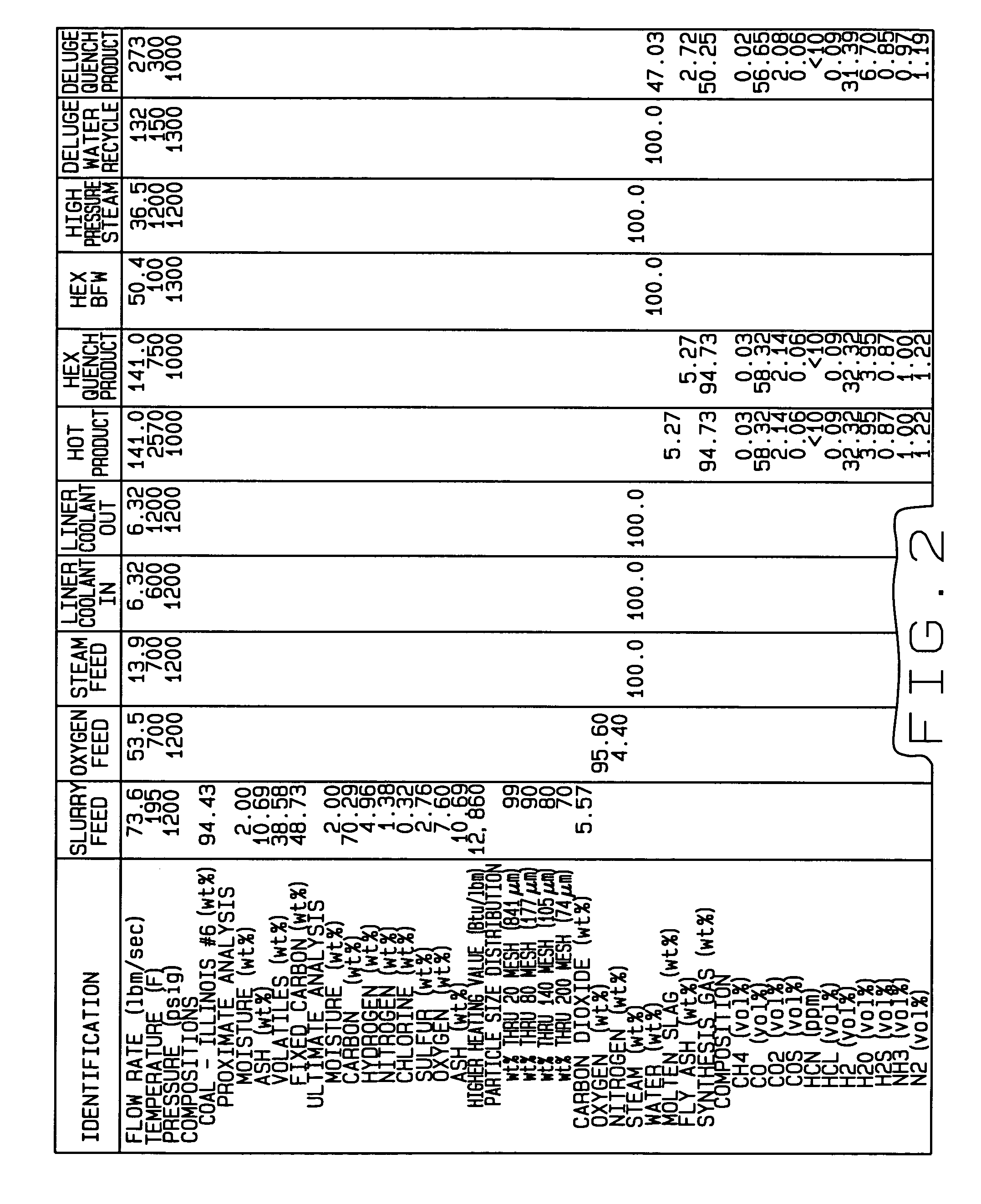
ActiveUS7547423B2Improve efficiencyEffectively ‘free floating’Gasifier mechanical detailsEnergy inputParallel plateCoolant flow
A gasifier system is provided that includes a gasification chamber spool that has a ceramic matrix composite (CMC) liner adapted to form a solidified slag protective layer on an interior surface of the liner from molten slag flowing through the gasification chamber spool. The gasification system additionally includes a heat exchanger (HEX) quench spool that also includes a CMC liner adapted to form a solidified slag protective layer on an interior surface of the liner from molten slag flowing through the HEX quench spool. Additionally, the HEX quench spool includes a parallel plate HEX core having a plurality of CMC panels. The CMC panels are adapted to form a solidified slag protective layer on exterior surfaces of each respective CMC panel from molten slag flowing through the HEX quench spool. Furthermore, each CMC panel includes a plurality of internal coolant channels adapted to exchange sensible waste heat from the hot product flowing through the HEX quench spool with a coolant flowing through the internal coolant channels. The sensible waste heat absorbed by the coolant is recovered by the gasification system by utilizing the heated coolant in various operational phases of the gasification system.
Owner:THE BOEING CO +1
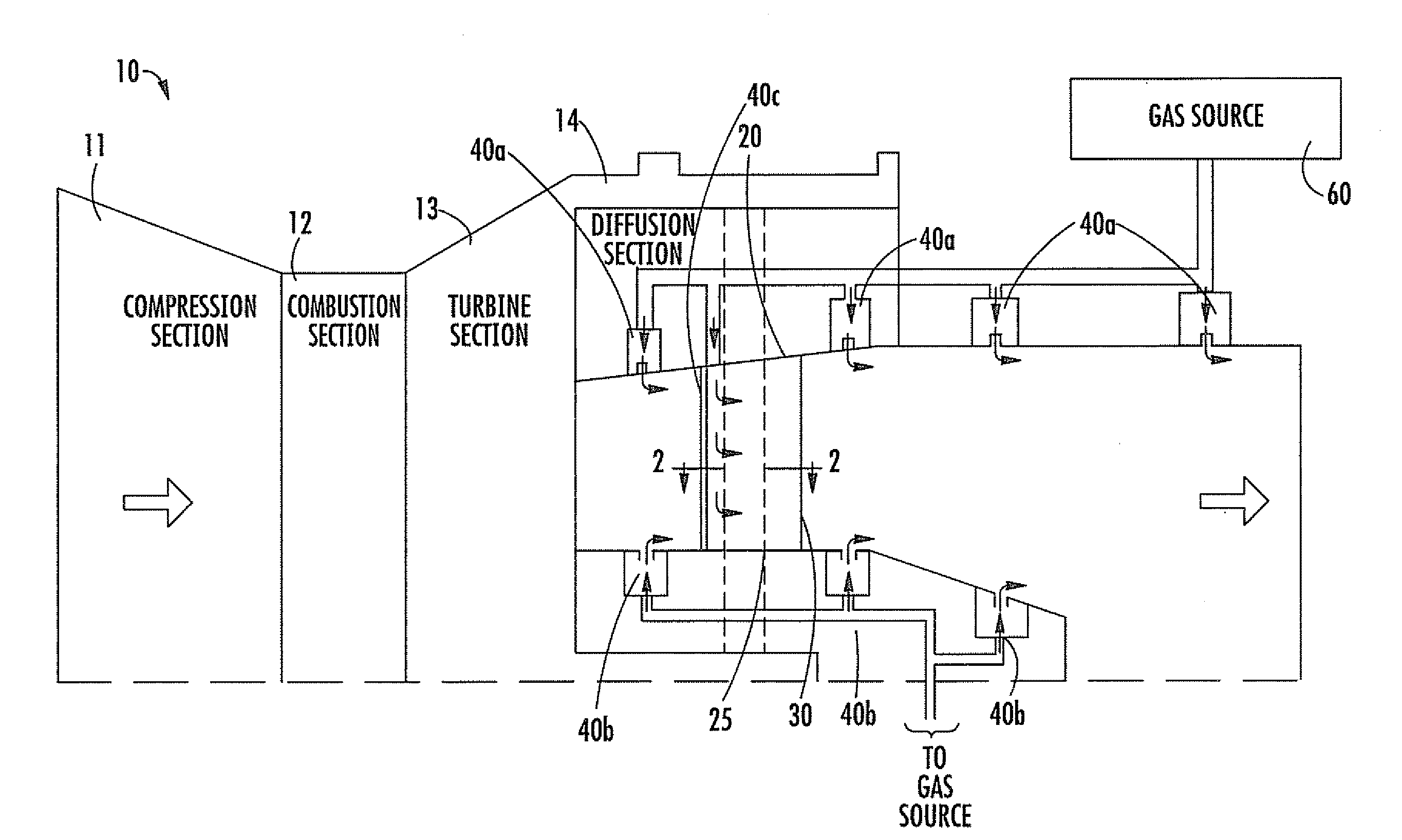
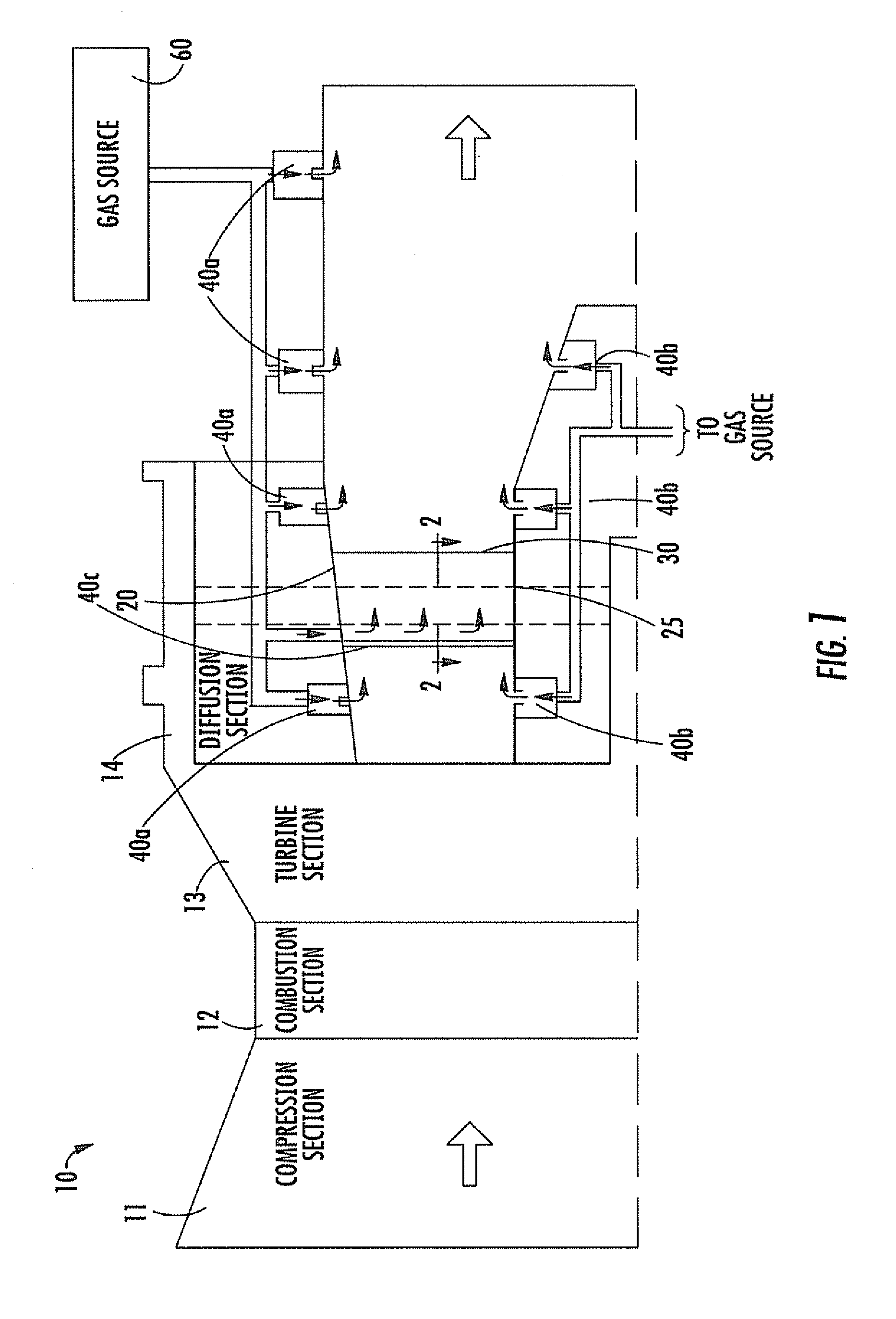
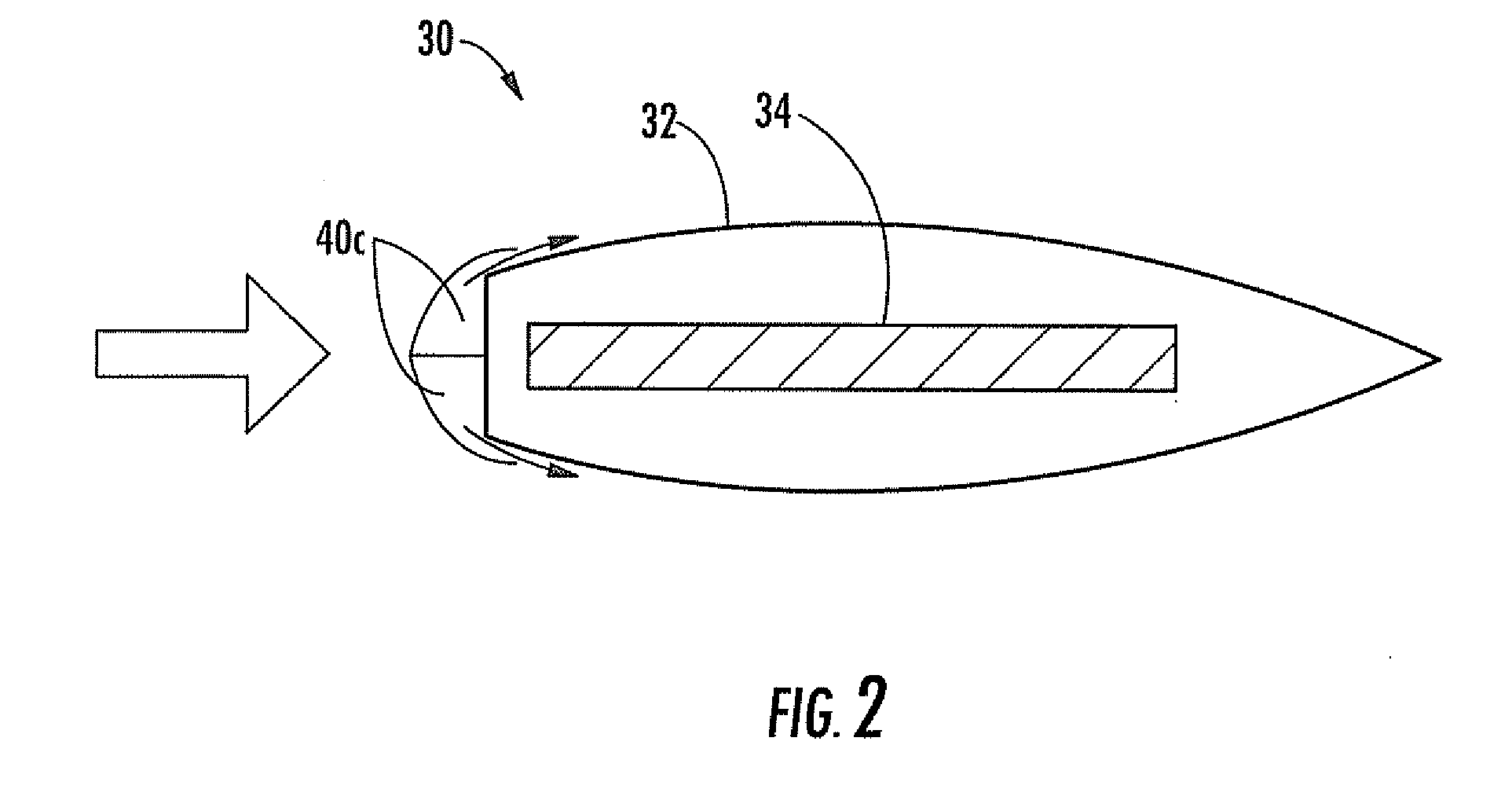
Combustion Turbine Including a Diffuser Section with Cooling Fluid Passageways and Associated Methods
InactiveUS20090263243A1Easy to attachImprove cooling effectPump componentsRotary non-positive displacement pumpsCombustionTurbine
A combustion turbine includes a compressor section, a combustion section downstream from the compressor section, and a turbine section downstream from the combustion section. A diffuser section is downstream from the turbine section and has an outer wall, an inner wall, and at least one strut member extending therebetween. The outer wall has at least one first gas passageway therein, the inner wall has at least one second gas passageway therein, and the at least one strut member has at least one third gas passageway therein. The at least one first, second and third gas passageways deliver gas therethrough to assist attachment of a boundary layer to adjacent surfaces of the outer wall, the inner wall, and the at least one strut, respectively.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
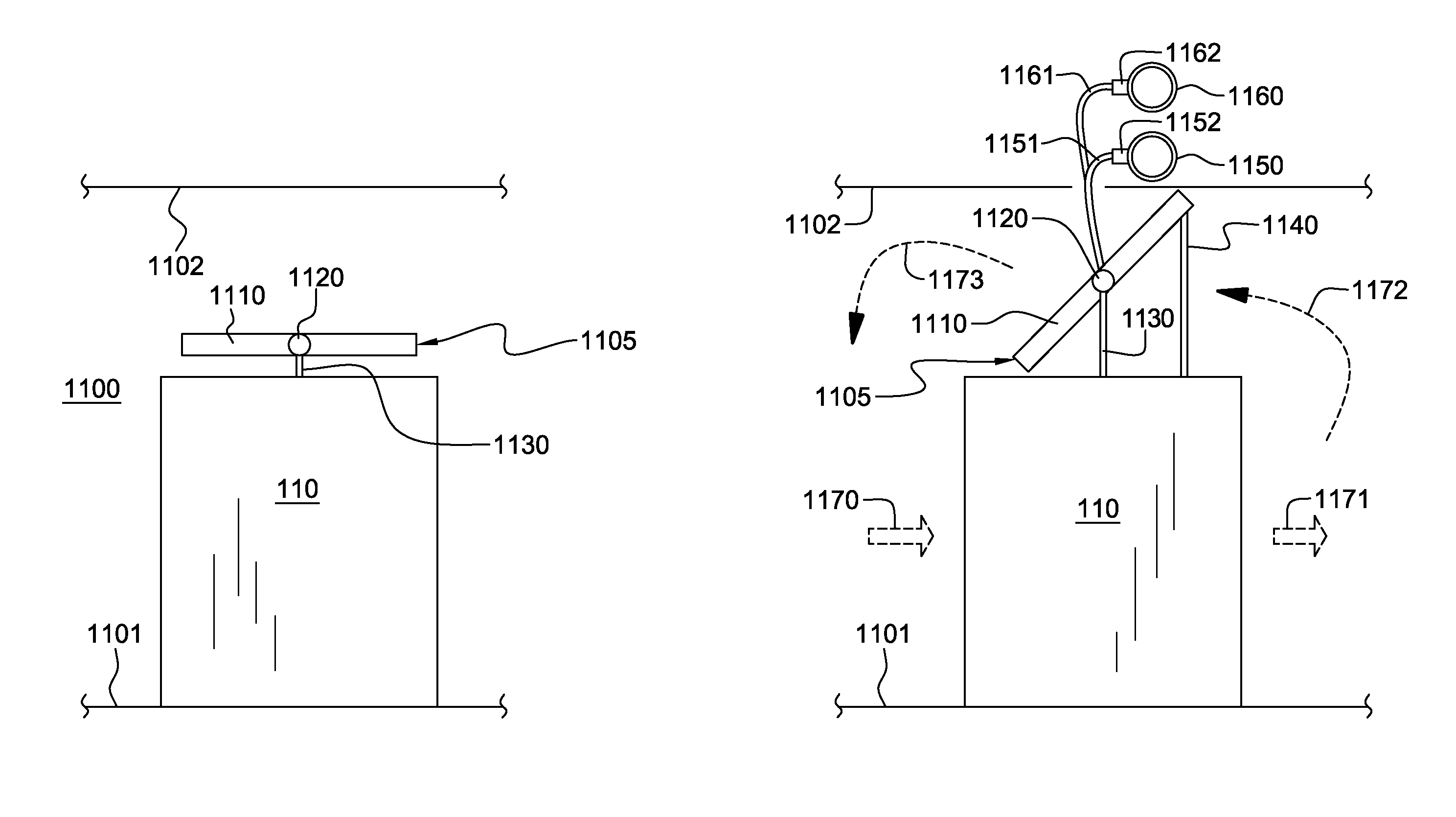
Apparatus and method for facilitating cooling of an electronics rack
Apparatus and method are provided for facilitating cooling of air passing through an electronics rack. The apparatus includes a heat exchange assembly hingedly mounted above and external to the rack, such that air passing above the rack from an air outlet side to an air inlet side thereof passes through the heat exchange assembly, and is cooled. The heat exchange assembly includes a support structure to support hinged mounting of the assembly above the rack, and an air-to-liquid heat exchanger coupled to the support structure. The heat exchanger has an inlet plenum and an outlet plenum in fluid communication with respective connect couplings which facilitate connection of the plenums to coolant supply and return lines, respectively. The heat exchanger also includes heat exchange tube sections, each of which has a coolant channel with an inlet and an outlet coupled to the inlet and outlet plenums, respectively.
Owner:IBM CORP
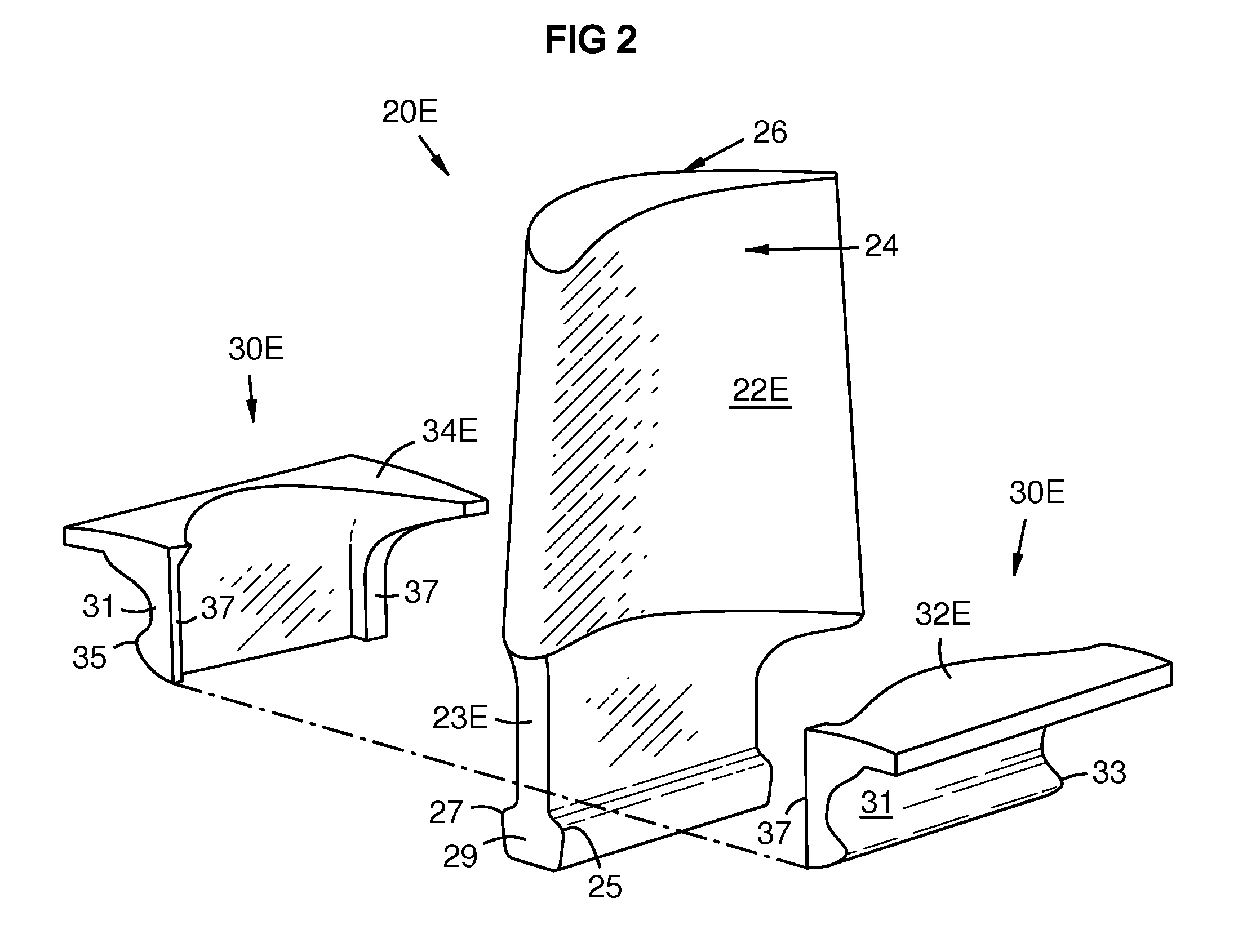
Modular turbine airfoil and platform assembly with independent root teeth
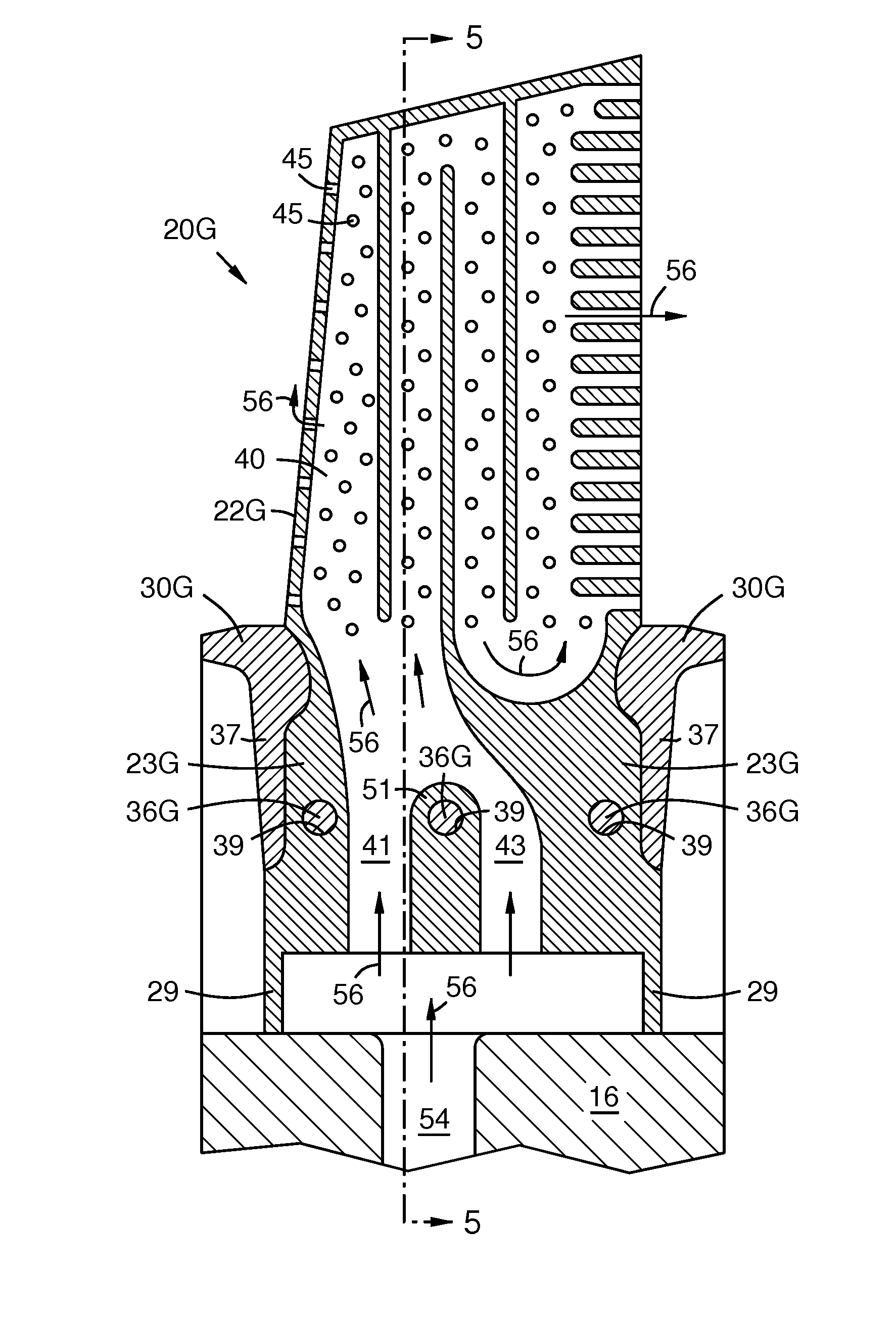
A turbine airfoil (22E-H) extends from a shank (23E-H). A platform (30E-H) brackets or surrounds a first portion of the shank (23E-H). Opposed teeth (33, 35) extend laterally from the platform (30E-H) to engage respective slots (50) in a disk. Opposed teeth (25, 27) extend laterally from a second portion of the shank (29) that extends below the platform (30E-H) to engage other slots (52) in the disk. Thus the platform (30E-H) and the shank (23E-H) independently support their own centrifugal loads via their respective teeth. The platform may be formed in two portions (32E-H, 34E-H), that are bonded to each other at matching end-walls (37) and / or via pins (36G) passing through the shank (23E-H). Coolant channels (41, 43) may pass through the shank beside the pins (36G).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
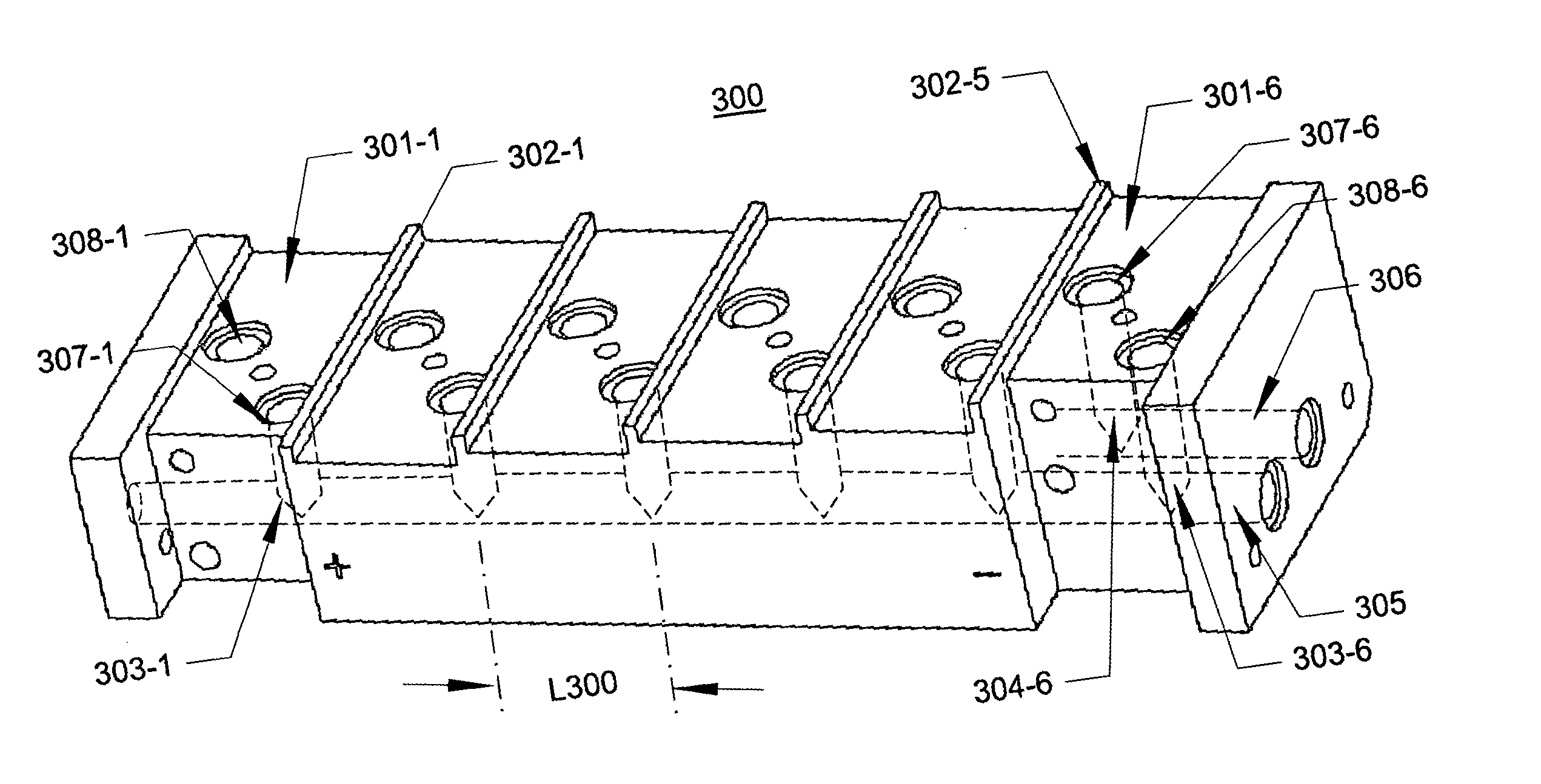
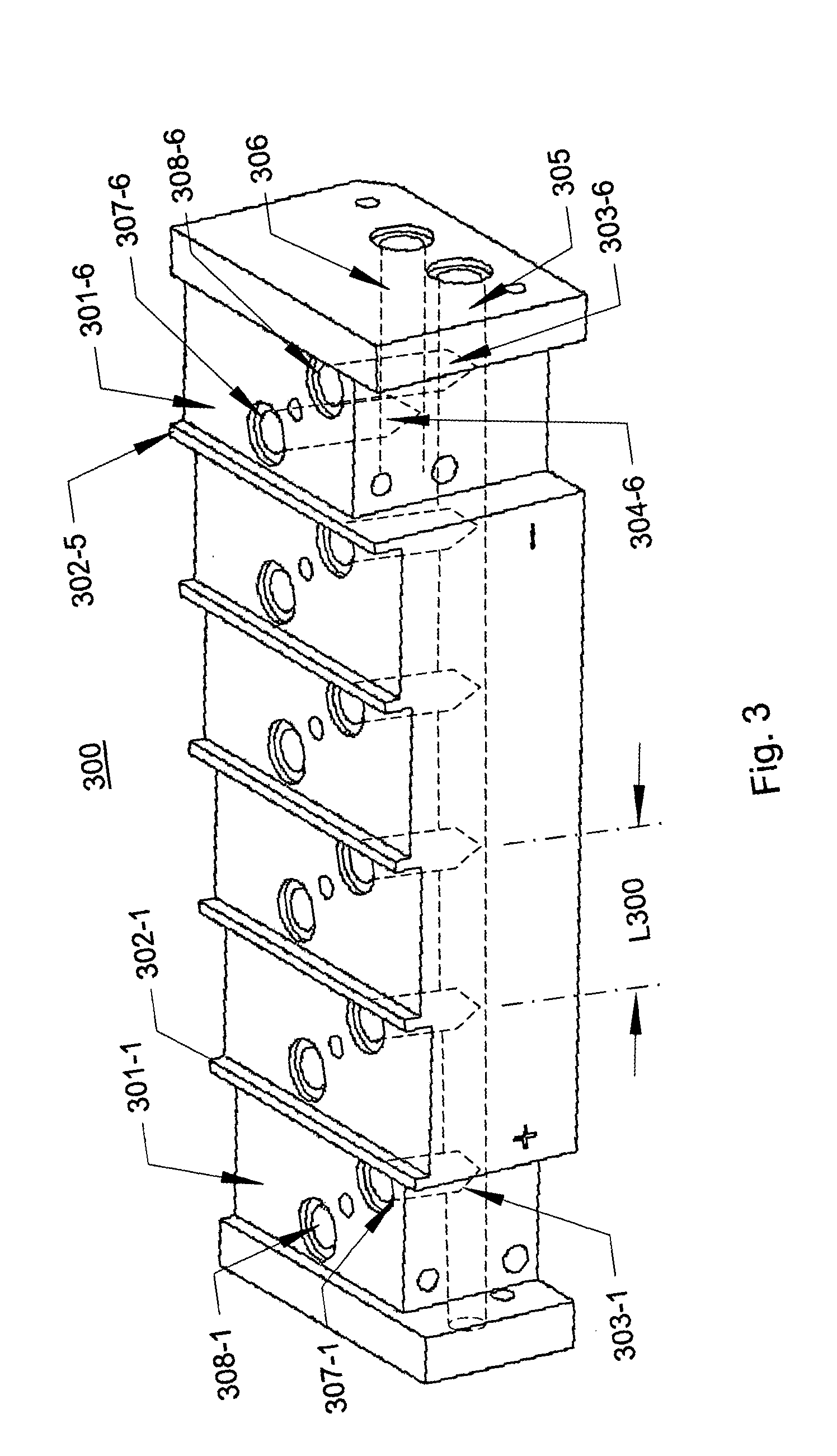
Stepped manifold array of microchannel heat sinks
ActiveUS20050063433A1Reduce corrosionClosely spacedSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsEngineeringLaser beams
An assembly for providing a concentrated, vertically stacked array of laser beams from a horizontally offset array of electrically serially-connected metallic microchannel heat sinks each bearing a laser diode bar. The heat sinks are mounted on horizontally offset planes of the manifold which has coolant channels serving adjacent heat sinks that are separated from each to increase the electrical resistance of the fluid path between adjacent ones of said heat sinks. Stepped optical deflectors re-arrange the horizontally emitted laser beams into vertical stack.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
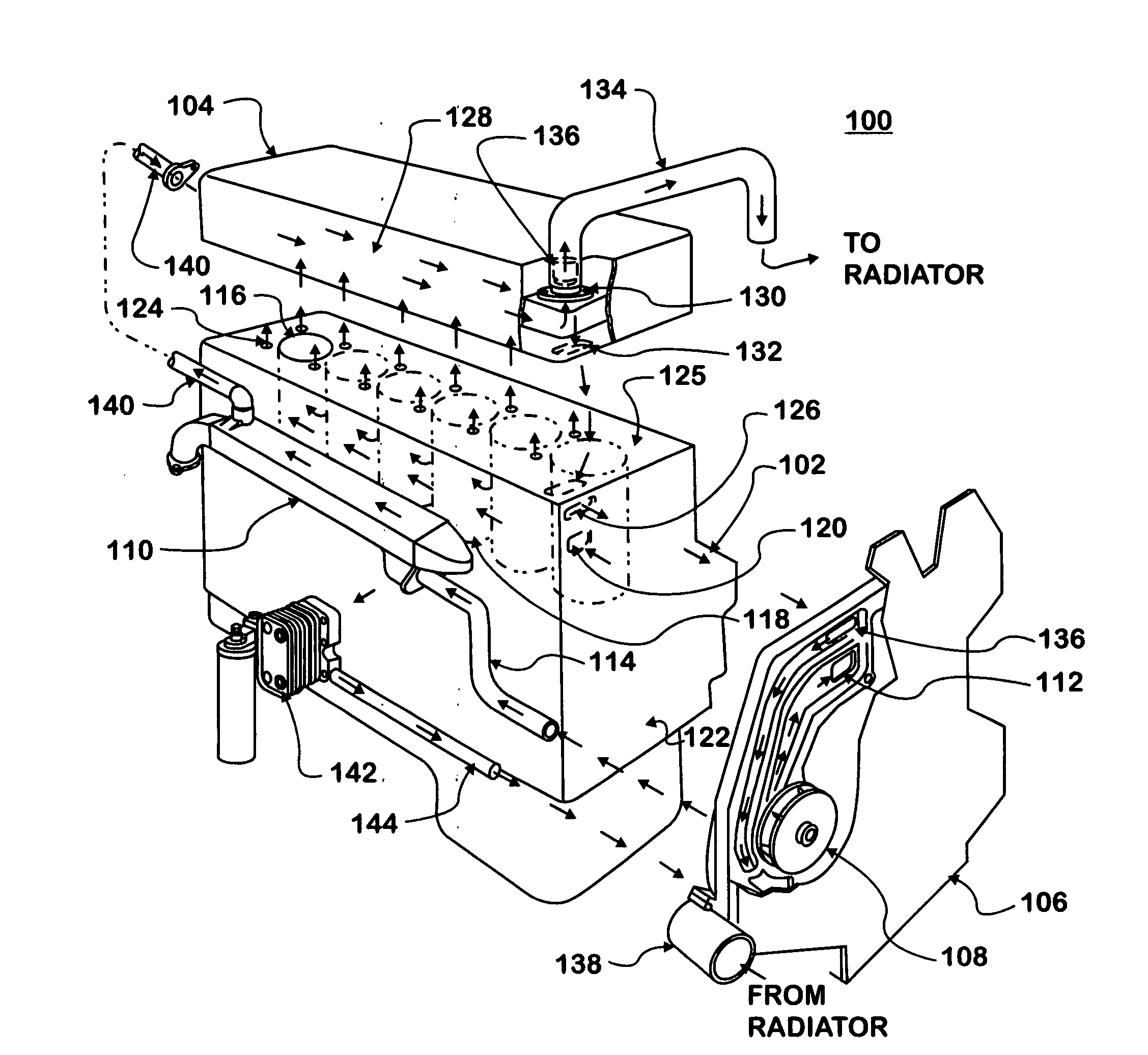
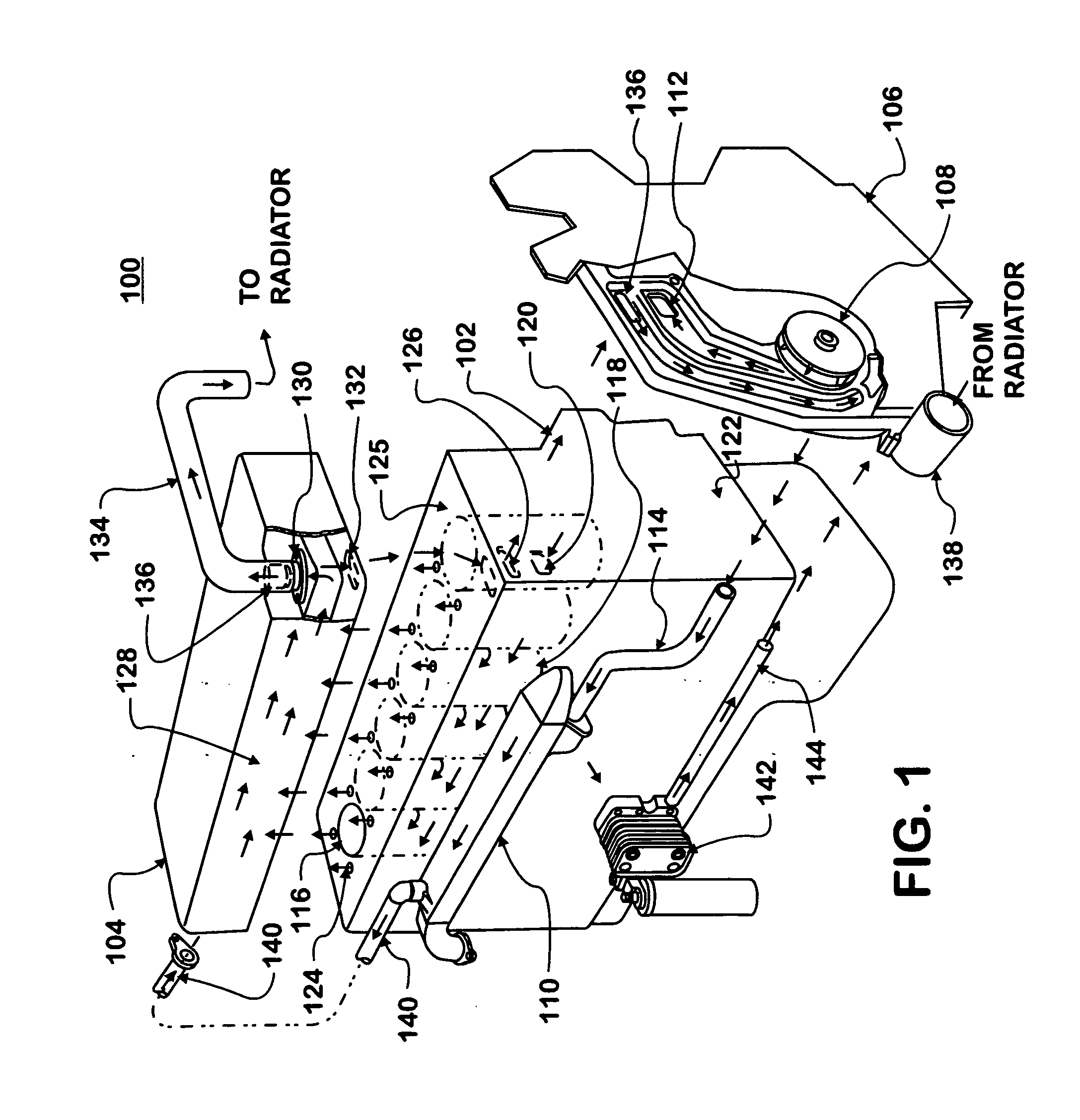
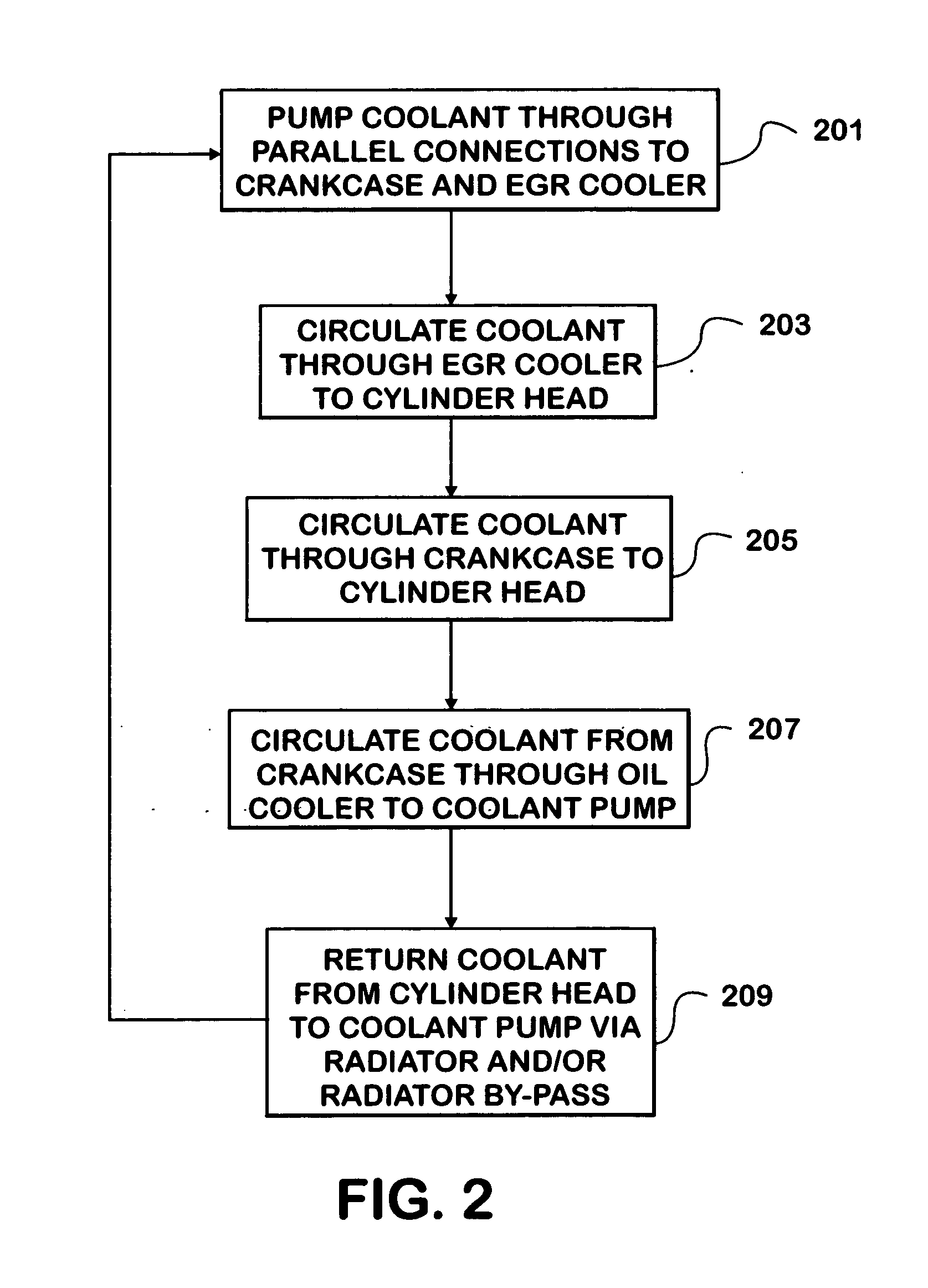
Cooling system for an internal combustion engine with exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
A cooling system pumps coolant through parallel connections to a crankcase and an EGR cooler in an internal combustion engine with exhaust gas recirculation (EGR). A crankcase supply conduit connects a coolant pump to a coolant channel formed by the crankcase. The coolant channel is connected to a coolant chamber formed by the cylinder head. An EGR cooler supply conduit connects the EGR cooler to the coolant pump. The EGR cooler is connected to the coolant chamber. Coolant flows from the coolant pump into the crankcase supply conduit and into the EGR cooler supply conduit at essentially the same time and at essentially the same temperature. The coolant circulates from the coolant pump through the coolant channel into the coolant chamber. The coolant circulates from the coolant pump through the EGR cooler into the coolant chamber. The coolant returns to the coolant pump from the coolant chamber in the cylinder head.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Gas showerhead, method for making the same and thin film growth reactor
ActiveUS9534724B2Easy to manufactureImprove utilization efficiencyValve members for heating/coolingPipe heating/coolingEngineeringCooling fluid
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FAB EQUIP INC CHINA
Belt drive system with outer rotor motor
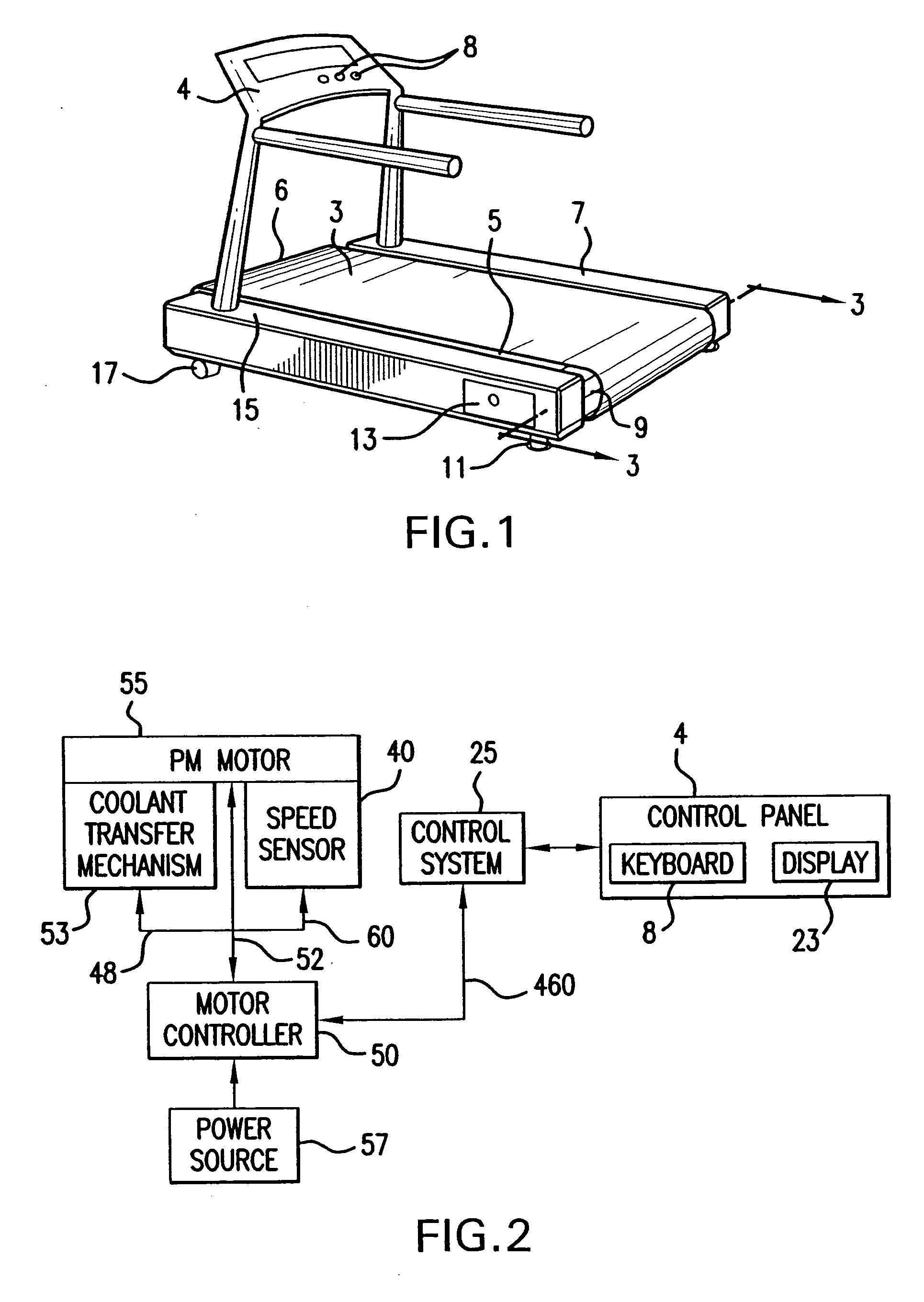
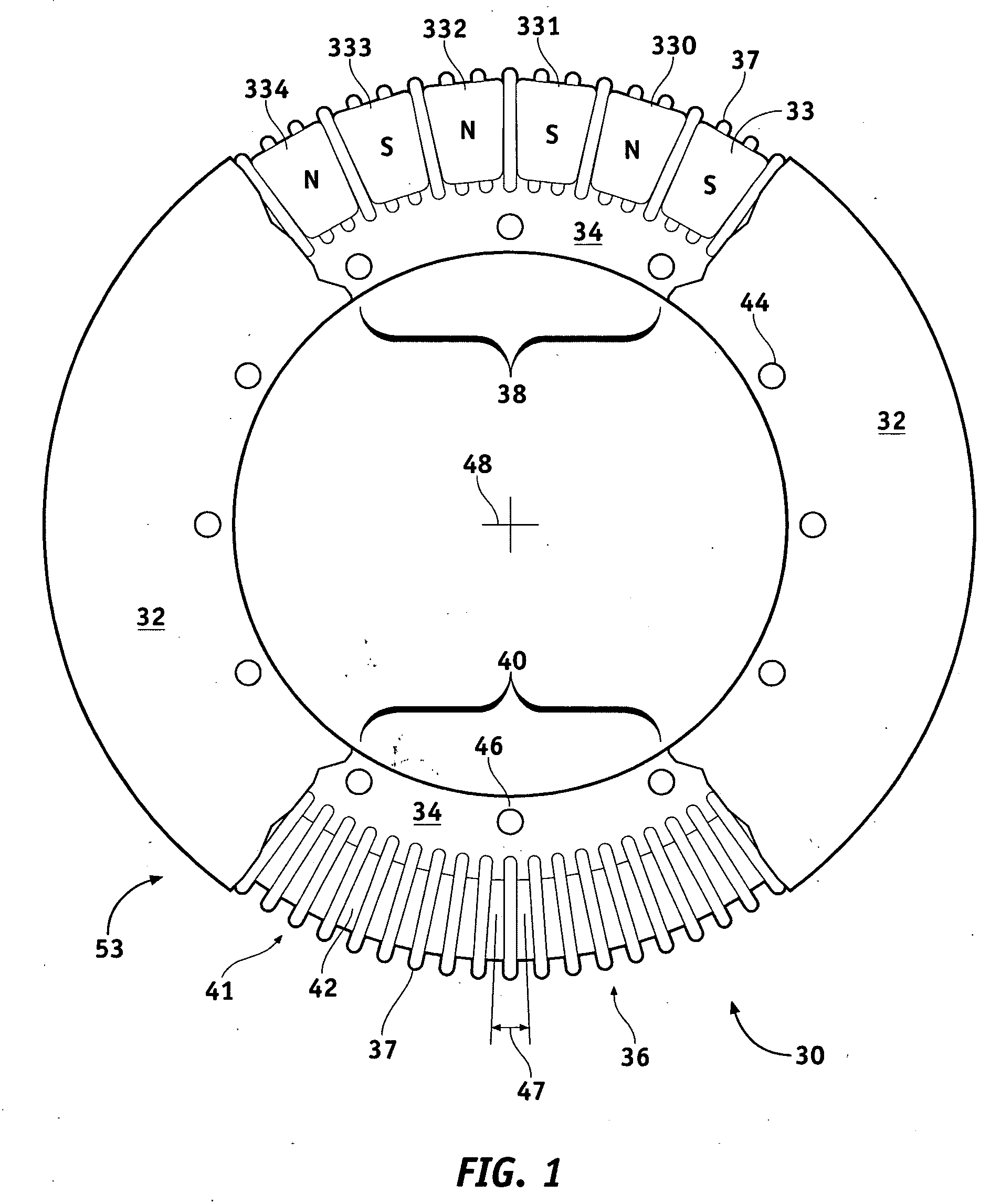
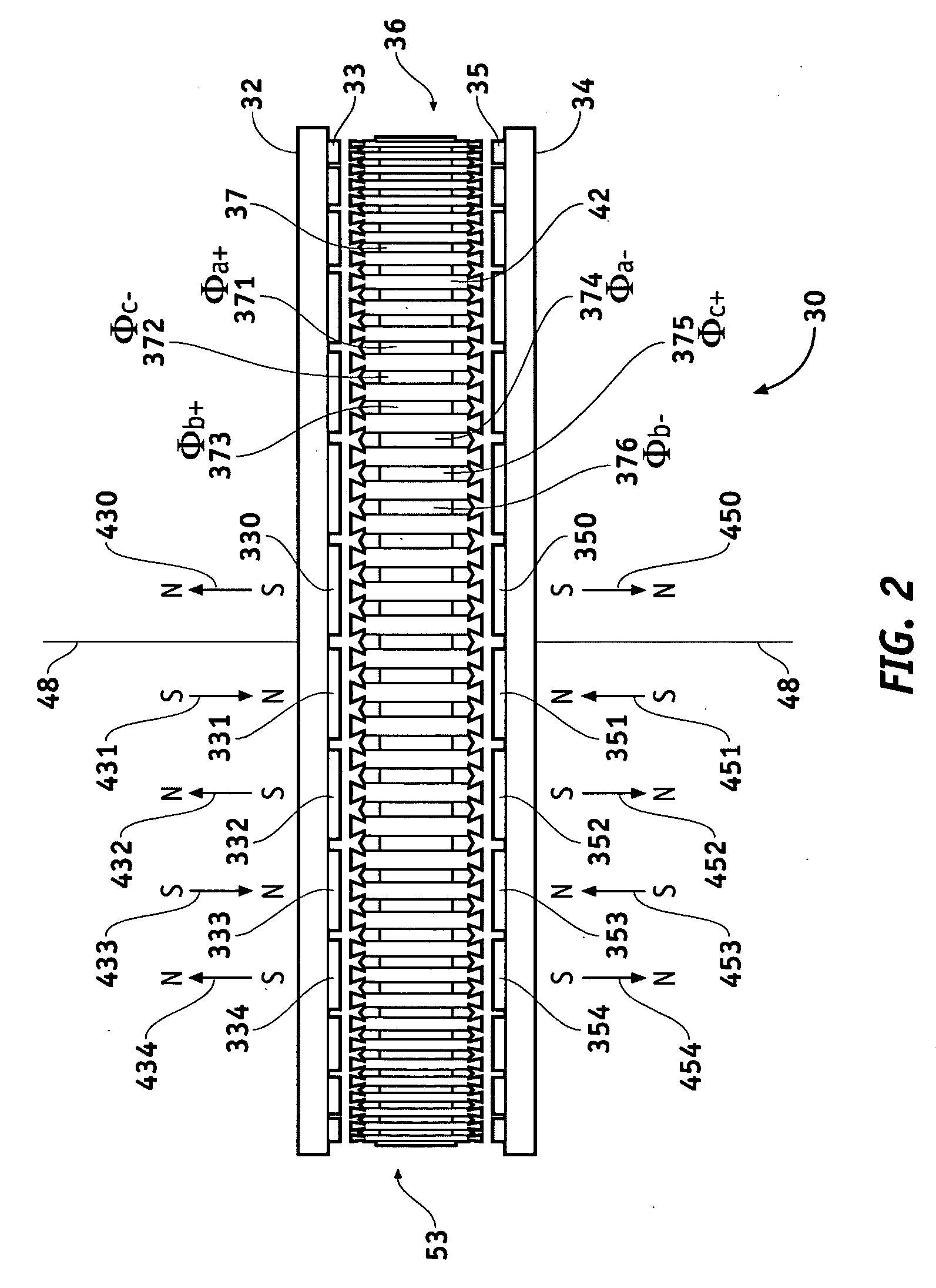
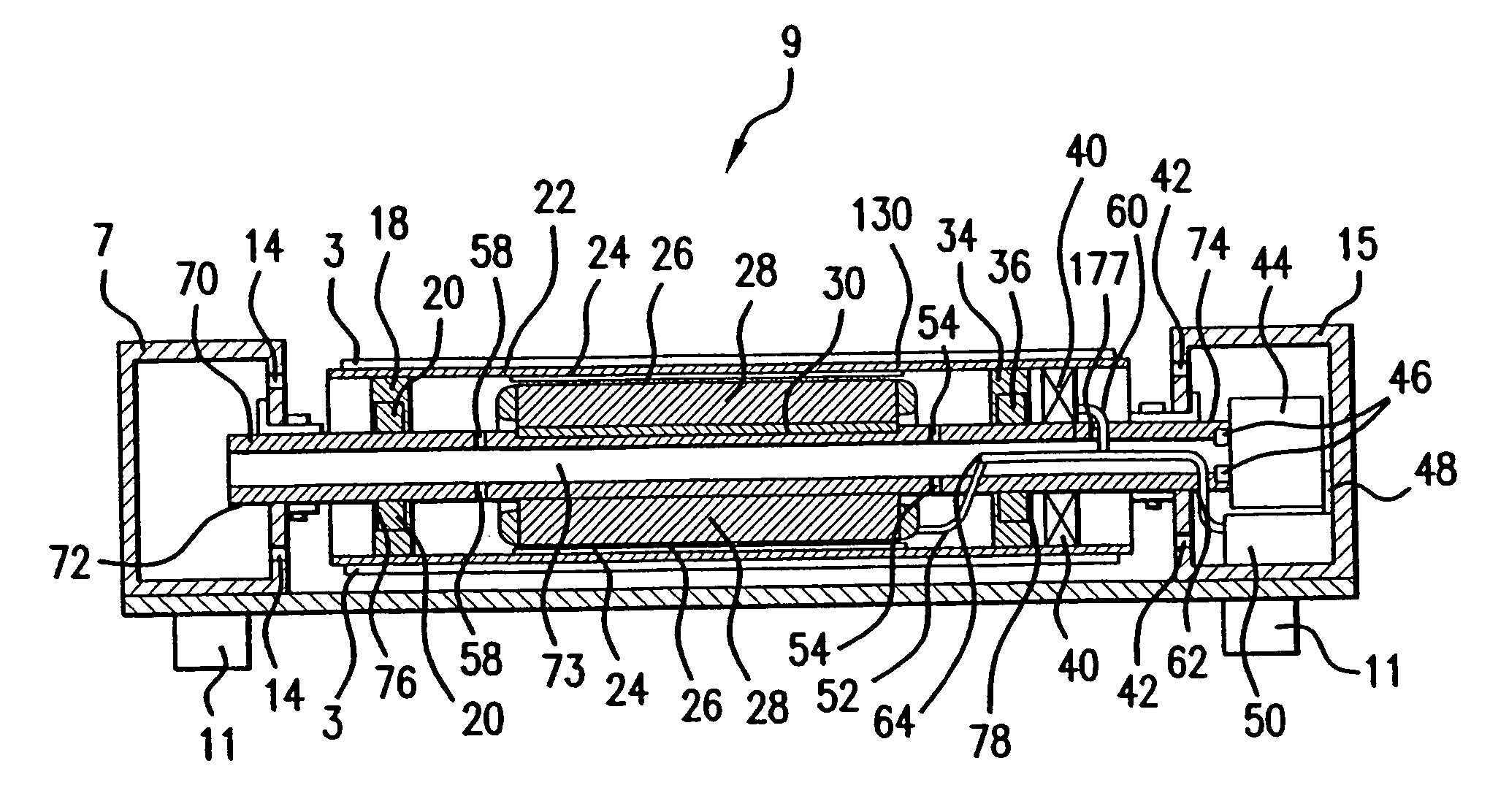
InactiveUS20060232147A1Small sizeImprove power densityVector control systemsMechanical energy handlingCooling effectCoolant channel
An outer rotor motor comprises a tubular shaft for maximum motor cooling effect. Coolant may flow through coolant channels of the shaft and the motor in various configurations to carry away the heat. A thermally conductive component may be inserted into the hollow shaft under the stator section to optimize the airflow and cooling. Physical construction of the motor and control algorithms may further enhance motor performance with appropriate sensors. A compact, smooth, and cool operating motor may thus be achieved for applications such as treadmills or other belt drive systems.
Owner:AEC MOTIONSTAR
Fuel cell fabrication using photopolymer based processes
InactiveUS20100159303A1Optimizes fuel cell durabilityReduce tooling costsElectrolyte moving arrangementsAdditive manufacturing apparatusFuel cellsPhotopolymer
A fuel cell component is provided, including a substrate disposed adjacent at least one radiation-cured flow field layer. The flow field layer is one of disposed between the substrate and a diffusion medium layer, and disposed on the diffusion medium layer opposite the substrate. The flow field layer has at least one of a plurality of reactant flow channels and a plurality of coolant channels for the fuel cell. The fuel cell component may be assembled as part of a repeating unit for a fuel cell stack. A method for fabricating the fuel cell component and the associated repeating unit for the fuel cell is also provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Coolant tray of liquid based cooling device
InactiveUS20050183848A1Limited interior spaceEfficient heat dissipationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringLiquid based
A liquid based cooling device includes a pump for driving a coolant through a coolant tray that is positionable on a heat generating device and a radiator that dissipates the heat into the surrounding. The coolant tray includes a housing on which coolant inlet and outlet are formed for receiving the coolant from the pump and discharging the coolant to the radiator. The coolant tray also forms a recess in which a thermally conductive base forming a coolant channel is received in a liquid tight manner. The pump includes a casing in which coolant inlet and outlet are formed. The inlet of the coolant tray is integrally connected to the outlet of the pump and the housing of the coolant tray and the casing of the pump are integrally formed with each other with an integrally formed conduit connected therebetween. This simplifies the manufacturing of the cooling device and reduces the overall size of the cooling device.
Owner:CHENG RUEI FU +1
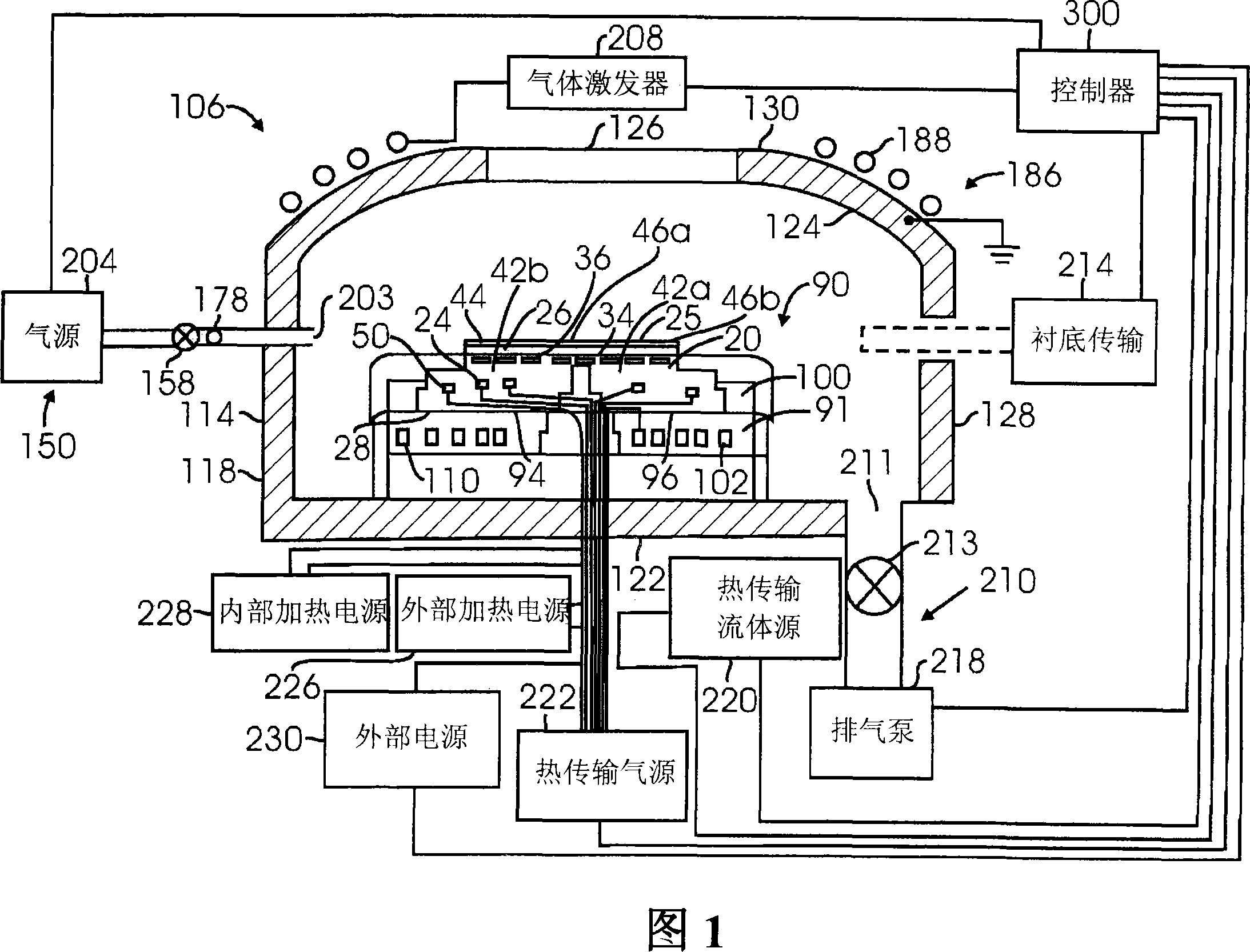
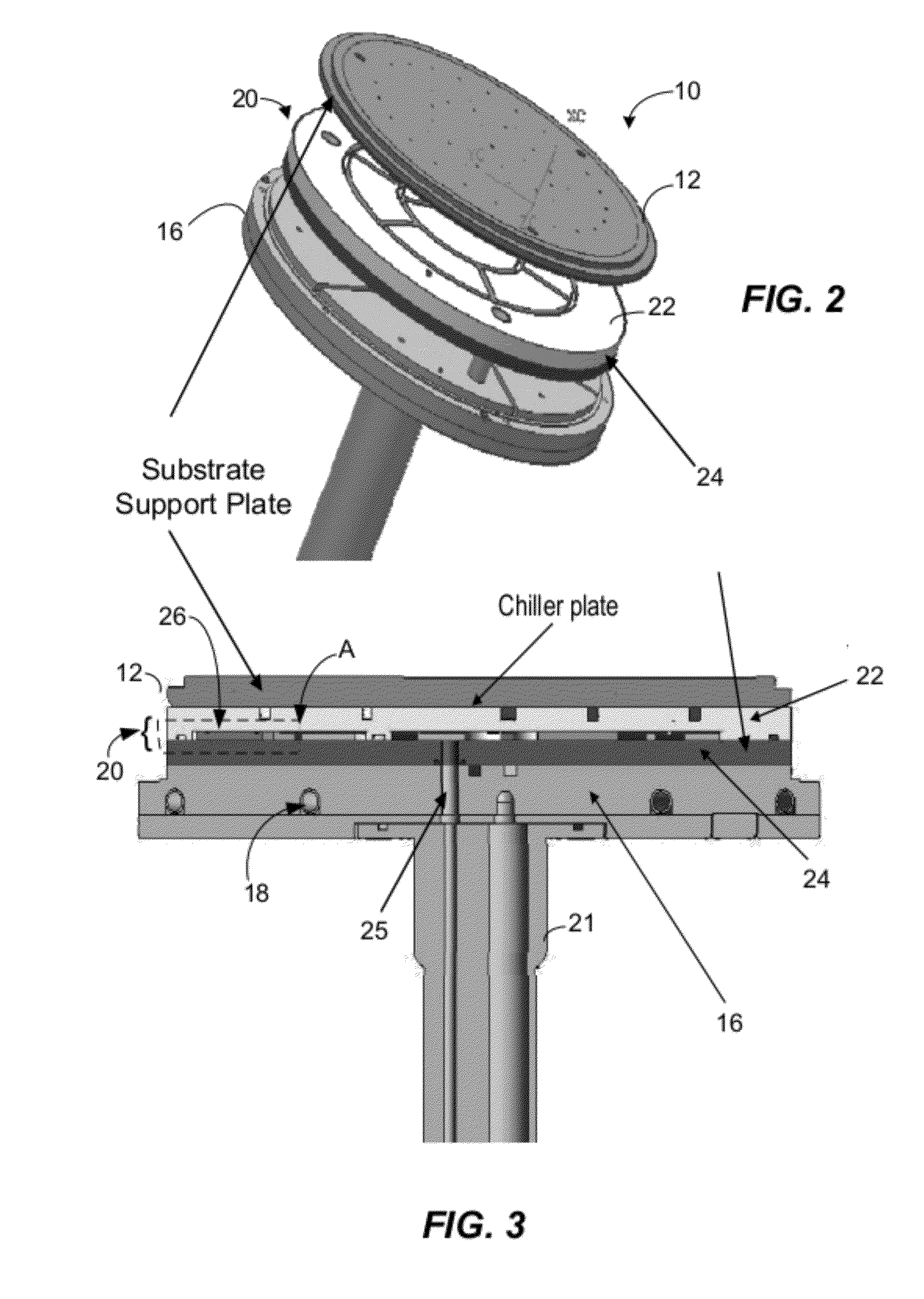
Substrate processing with rapid temperature gradient control
ActiveCN101110381AFast temperature controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTemperature controlMetallurgy
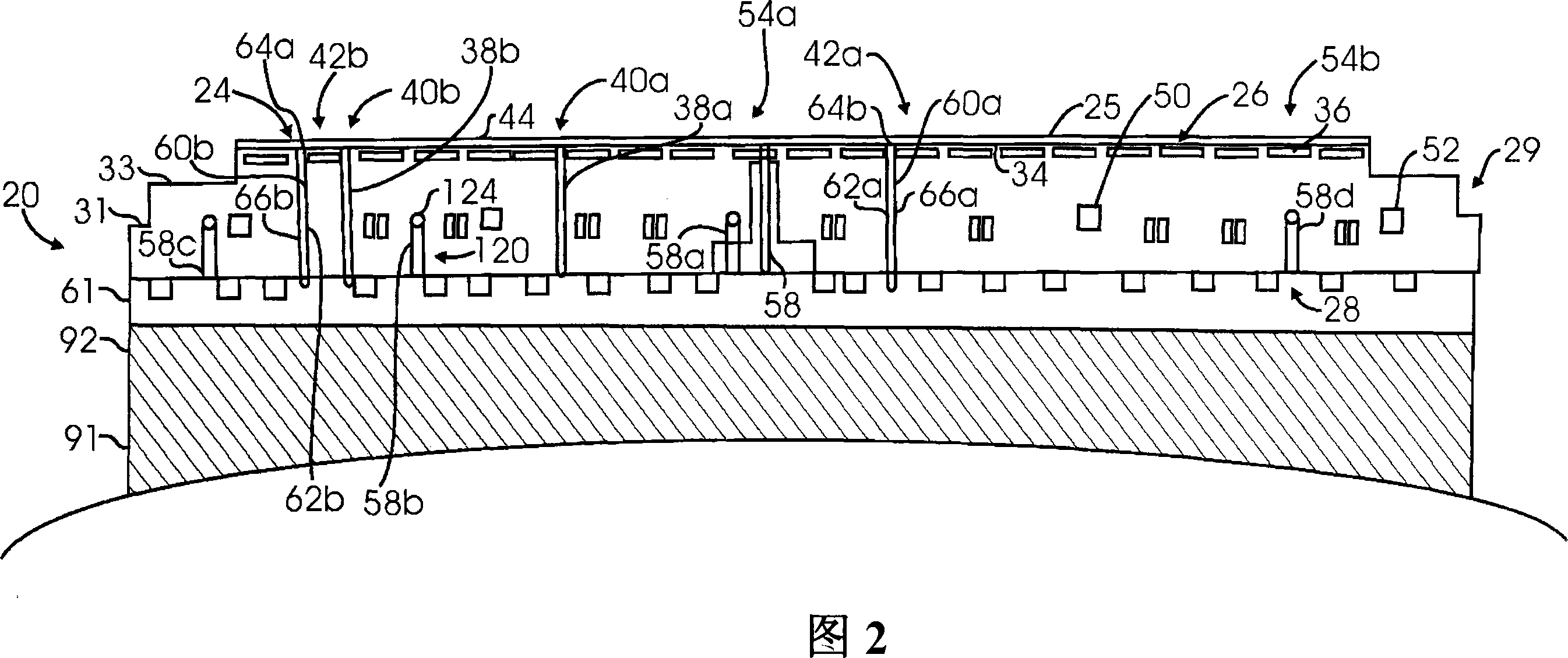
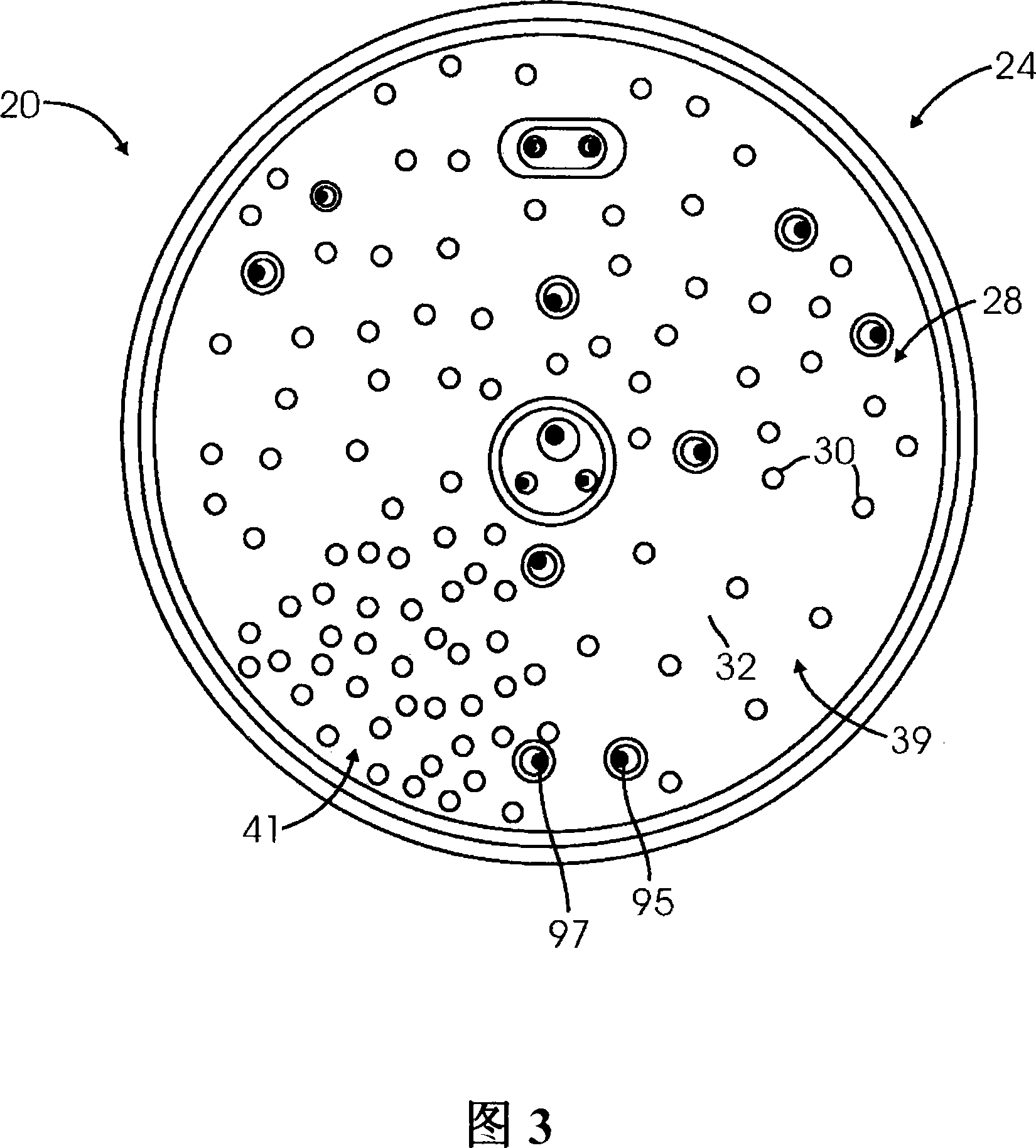
A substrate processing chamber comprises an electrostatic chuck comprising a ceramic puck having a substrate receiving surface and an opposing backside surface. In one version, the ceramic puck comprises a thickness of less than 7 mm. An electrode is embedded in the ceramic puck to generate an electrostatic force to hold a substrate, and heater coils in the ceramic puck allow independent control of temperatures at different heating zones of the puck. A chiller provides coolant to coolant channels in a base below the ceramic puck. A controller comprises temperature control instruction sets which set the coolant temperature in the chiller in relation prior to ramping up or down of the power levels applied to the heater.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Wafer profile modification through hot/cold temperature zones on pedestal for semiconductor manufacturing equipment
InactiveUS20120074126A1Precise temperature regulationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHot plates heating arrangementsEngineeringThermoelectric element
A substrate support comprising a top ceramic plate providing a substrate support surface for supporting a substrate during substrate processing, a substrate pedestal having coolant channels formed therein and a thermoelectric deck sandwiched between the top ceramic plate and substrate pedestal. The thermoelectric deck includes a plurality of embedded thermoelectric elements that can either heat or cool the substrate support surface.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Heat exchanger for the outer skin of an aircraft
ActiveUS20110186263A1Increase cooling powerImprove thermal conductivityAir-treatment apparatus arrangementsEnergy efficient board measuresPlate heat exchangerNuclear engineering
A heat exchanger for an outer skin of an aircraft comprises at least one feed line for a coolant, at least one discharge line for the coolant and at least one bundle of coolant channels through which coolant flows, wherein in the case of the heat exchanger being attached to the outer skin, the coolant channels are positioned directly on the outer skin of the aircraft, at least in areas, for dissipating heat to the surrounding environment of the aircraft. The heat exchanger may comprise cooling fins around which air flows for increasing the heat dissipation.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Cooling and handling of reaction torque for an axial flux motor
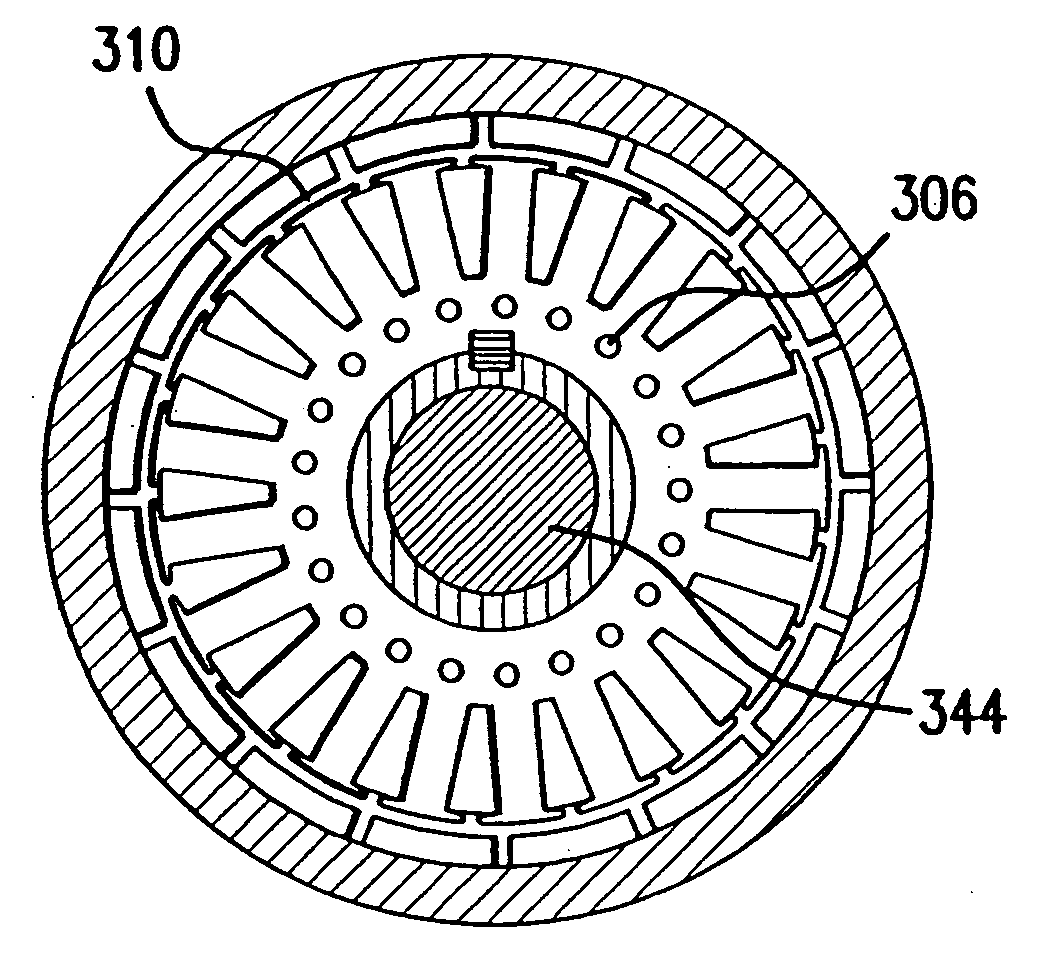
Methods and apparatus are provided for an axial electric motor. The apparatus comprises, a stator having coils thereon for producing a magnetic field, a rotor rotated by the magnetic field, an output shaft coupled to the rotor, and a ring incorporating a coolant channel circumferentially engaging the stator for absorbing heat and reaction torque from the stator. It is preferable that that the ring have inwardly extending teeth that mesh with the coils on the stator. The space between the teeth and the coils is preferably filled with a substantially solid thermally conductive material to transmit stator reaction torque to the teeth and cool the stator. The coils are preferably formed from a flat ribbon a portion of whose principal surface is perpendicular to the teeth. A supporting frame is desirably fixedly coupled to the ring and rotatably coupled to the output shaft.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Belt drive system with outer rotor motor
InactiveUS7362016B2Small sizeImprove power densityVector control systemsMechanical energy handlingCooling effectCoolant channel
An outer rotor motor having a tubular shaft for maximum motor cooling effect. Coolant may flow through coolant channels of the shaft and the motor in various configurations to carry away the heat. A thermally conductive component may be inserted into the hollow shaft under the stator section to optimize the airflow and cooling. Physical construction of the motor and control algorithms may further enhance motor performance with appropriate sensors. A compact, smooth, and cool operating motor may thus be achieved for applications such as treadmills or other belt drive systems.
Owner:AEC MOTIONSTAR
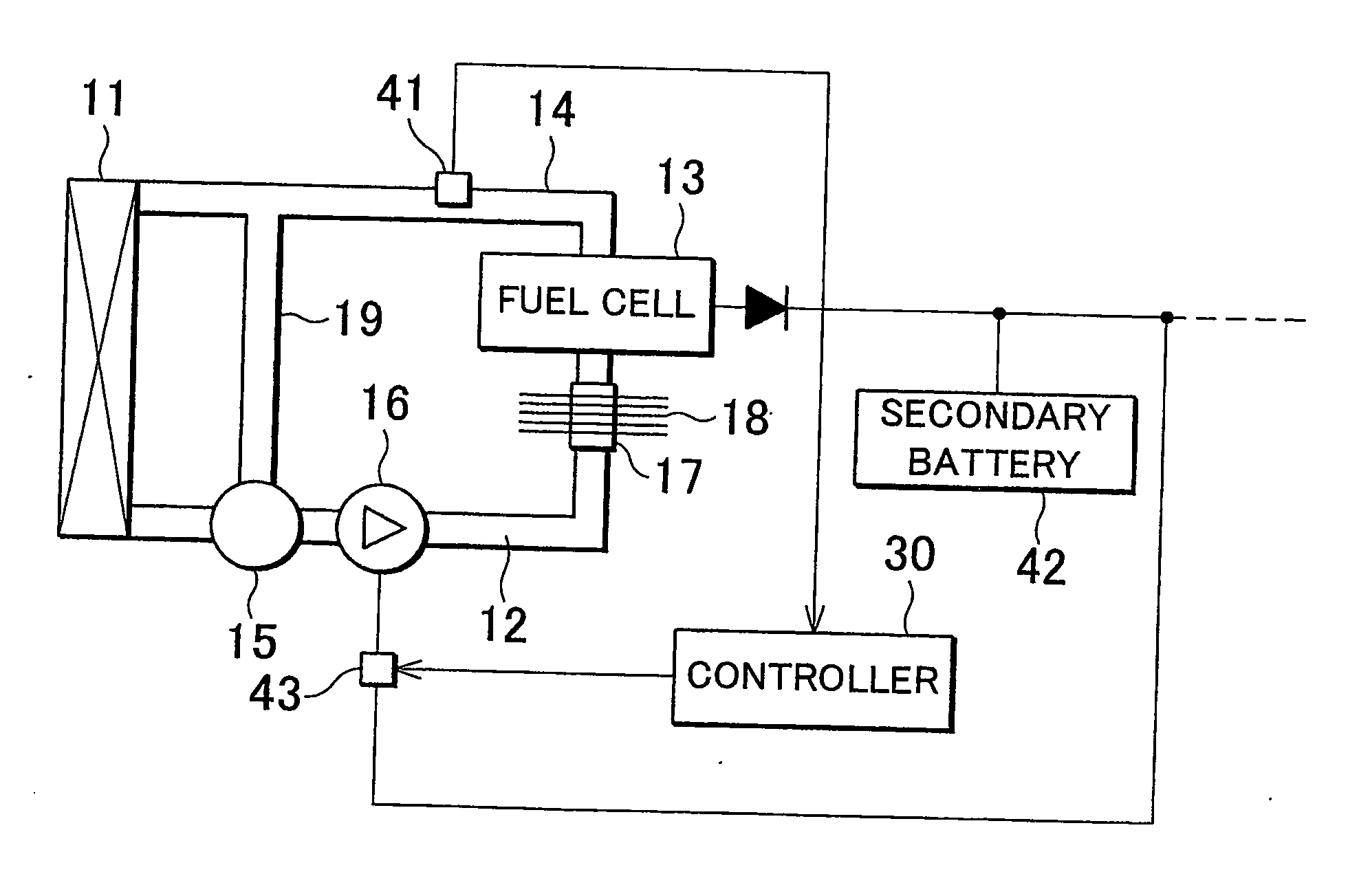
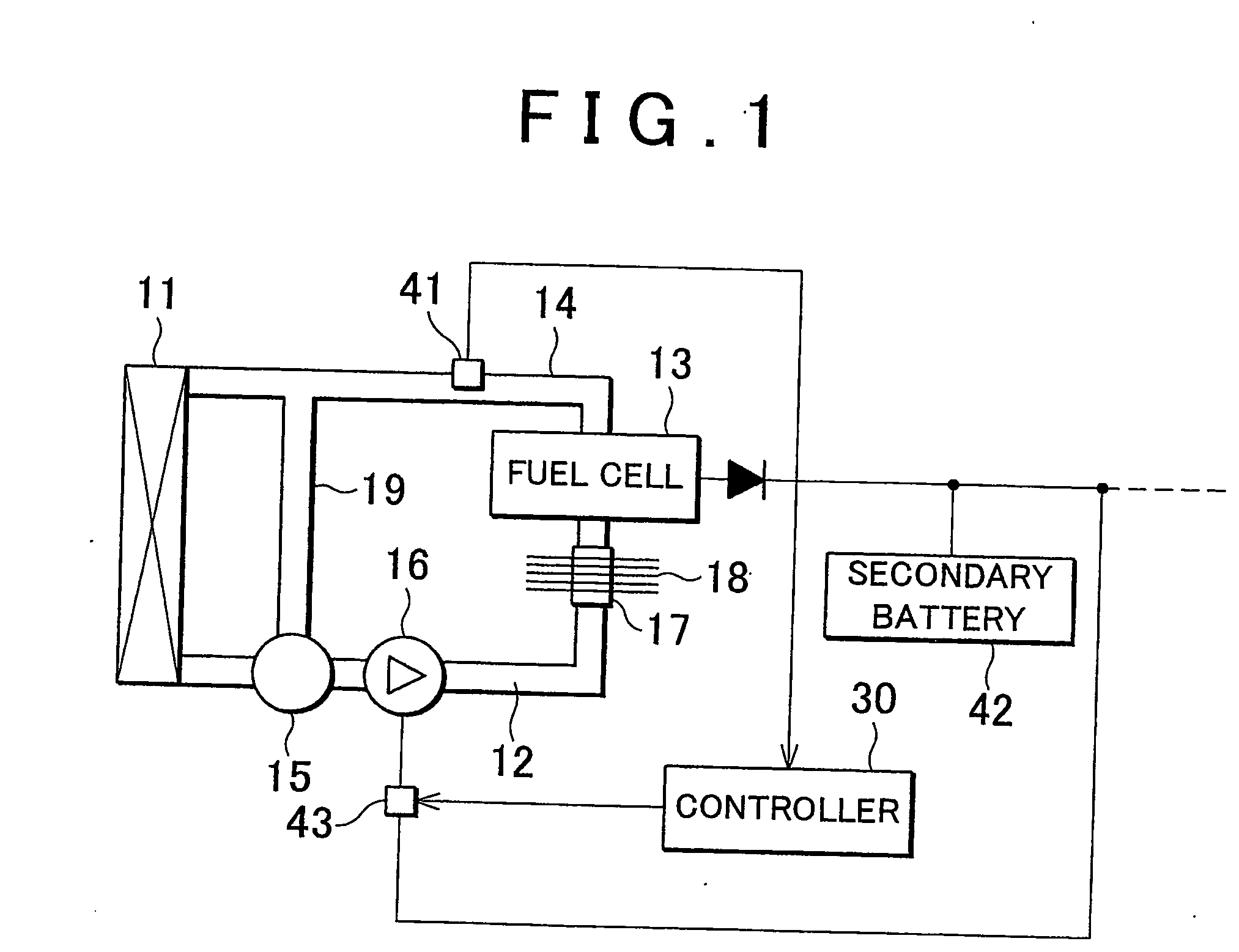
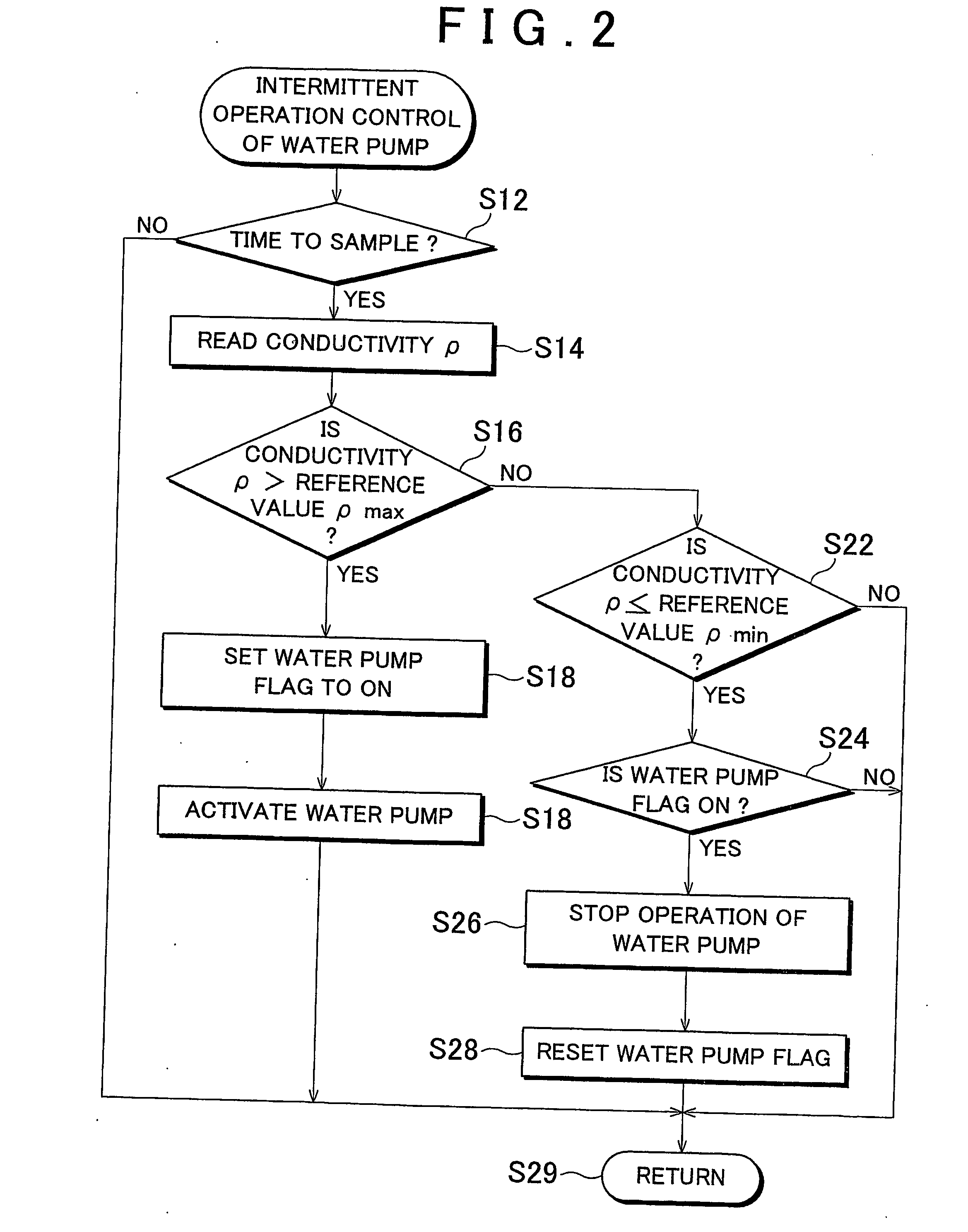
Fuel cell cooling system and method for controlling circulation of cooling liquid in fuel cell
ActiveUS20060269807A1Reduce startup timeImpurities increaseFuel cell auxillariesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cellsNuclear engineering
A cooling system for a fuel cell is provided with a cooling apparatus that regulates the temperature of the fuel cell by supplying the fuel cell with a cooling liquid via a cooling liquid passage by means of a water pump; an impurity-removing device which is provided in the cooling liquid passage and which removes impurities from within the cooling liquid; and flow generating means for causing the cooling liquid in the cooling liquid passage to flow through the impurity-removing device when the fuel cell is not operating.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Perfused core dielectrically loaded dipole microwave antenna probe
A microwave surgical ablation probe having an arrangement of coolant channels in fluid communication with a cooling chamber disposed within the distal end of the probe is disclosed. A hypotube having one or more longitudinal ribs extending radially inward from an inner surface thereof is coaxially disposed around a coaxial feedline. The longitudinal ribs of the hypotube engage an outer sheath of the feedline to define a fluid inflow channel to deliver coolant to the cooling chamber, and a fluid outflow channel to receive fluid from the cooling chamber. The cooling chamber may be formed from porous ceramic or porous metallic material that provides structural support to the probe while permitting coolant to circulate therethrough. The probe includes dielectric and choke members that are adapted to control the microwave radiation pattern (e.g., ablation shape), and which may provide improved coupling of the probe to tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
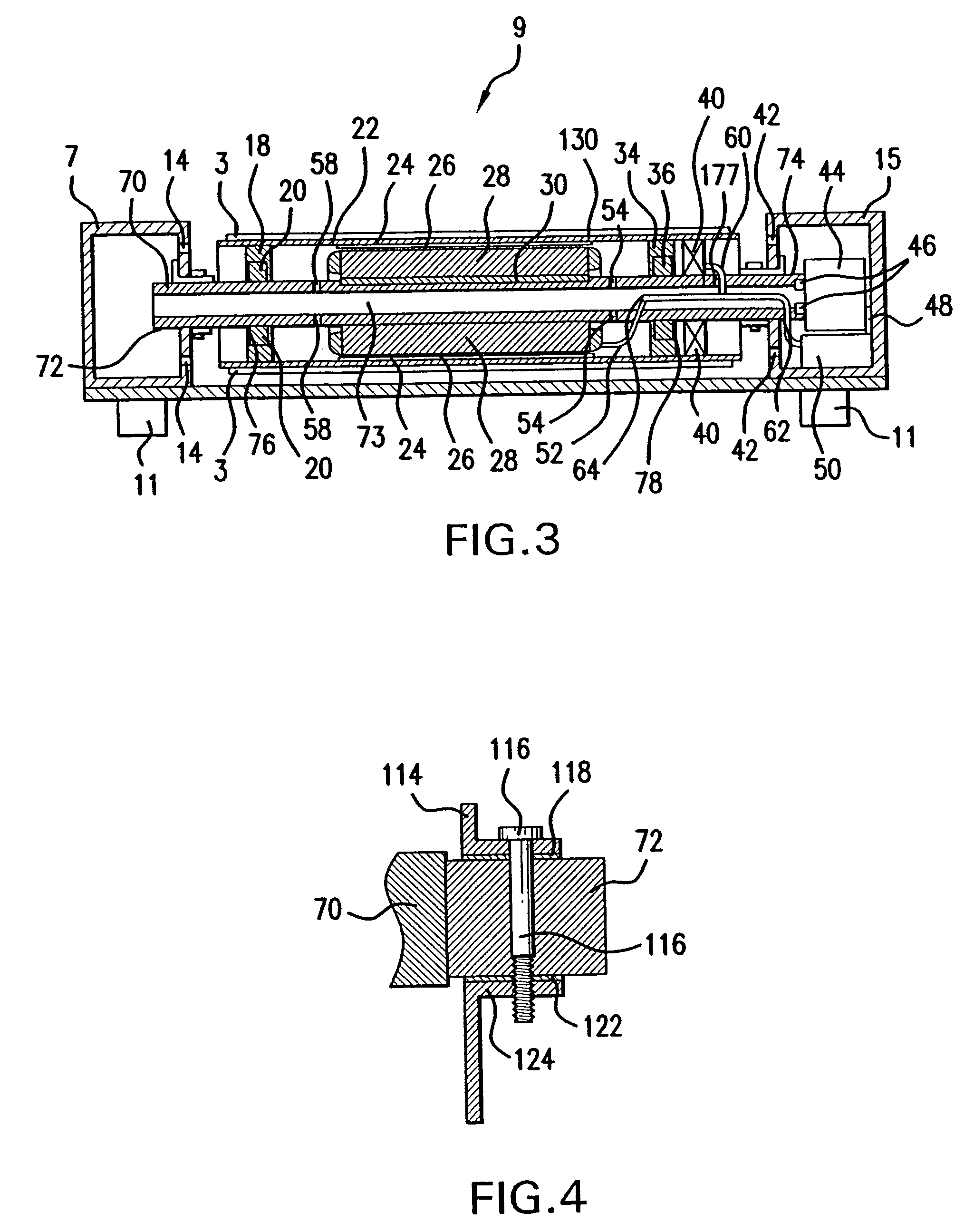
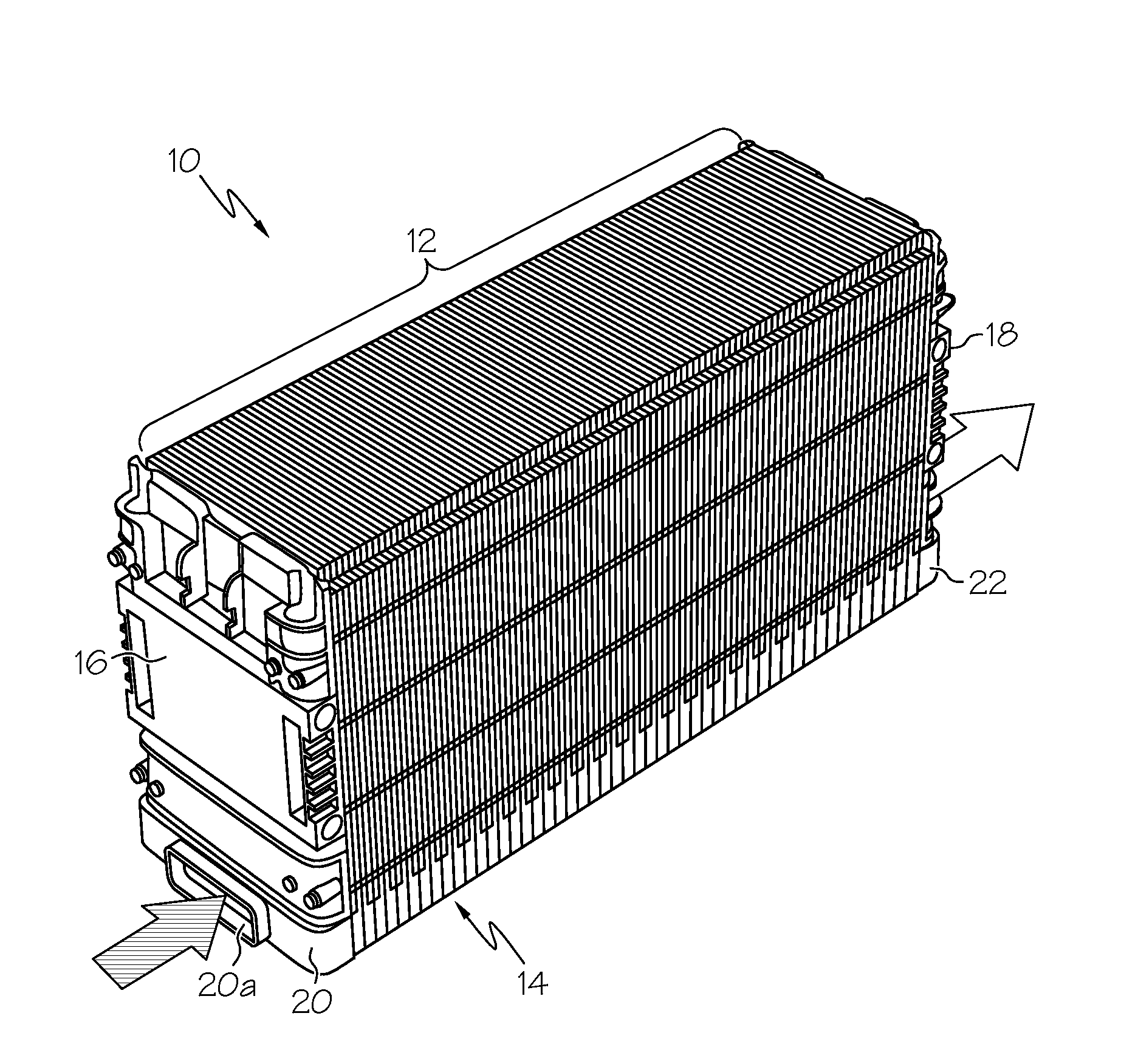
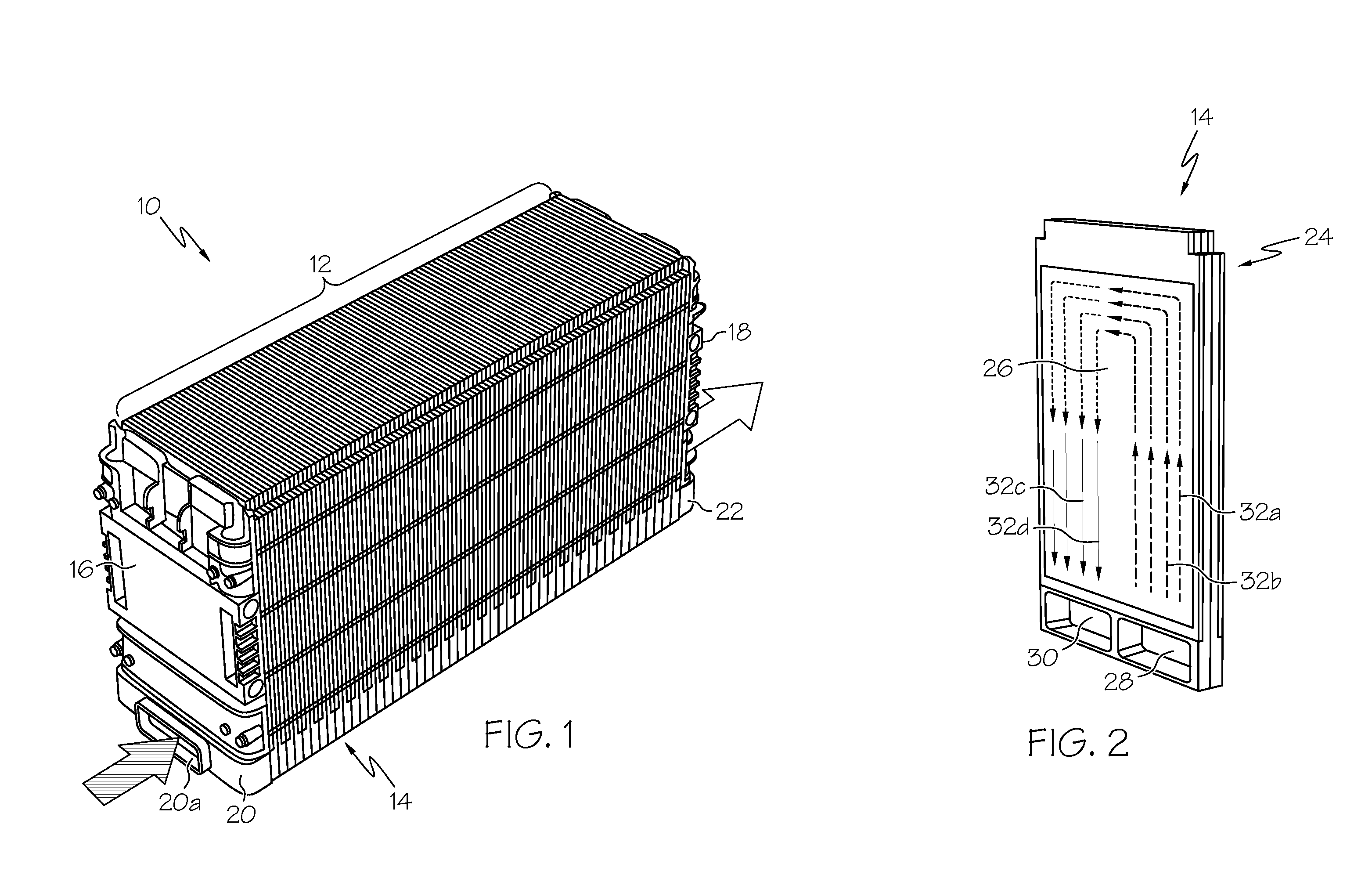
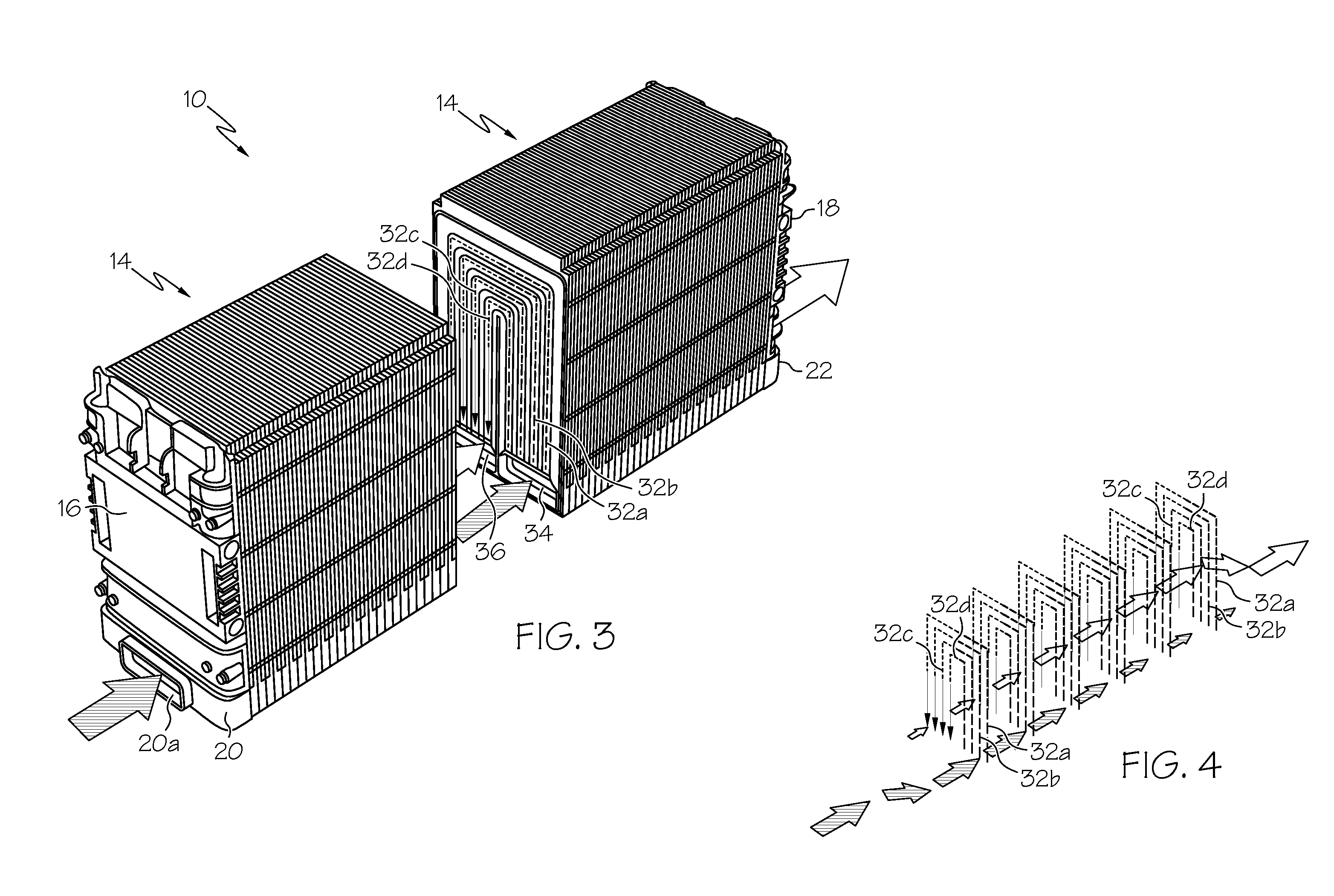
Prismatic-cell battery pack with integral coolant passages
ActiveUS20100143782A1Primary cell to battery groupingCell temperature controlCooling fluidBattery cell
A prismatic-cell battery pack is provided with integral coolant passages including an intake plenum, an exhaust plenum, and a distributed array of coolant channels coupled between the intake plenum and the exhaust plenum. Coolant medium forced into the intake plenum enters the coolant channels in parallel, draws heat away from the battery cells, and then enters the exhaust plenum for expulsion into the atmosphere. The battery pack is configured as a set of stackable interlocking battery cell modules including at least one battery cell in thermal proximity to an array of coolant channels distributed over the profile of the battery cell, and a pair of peripheral chambers joined to opposite ends of the coolant channels to form the intake and exhaust plenums when the modules are arranged and interlocked in a lineal stack.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
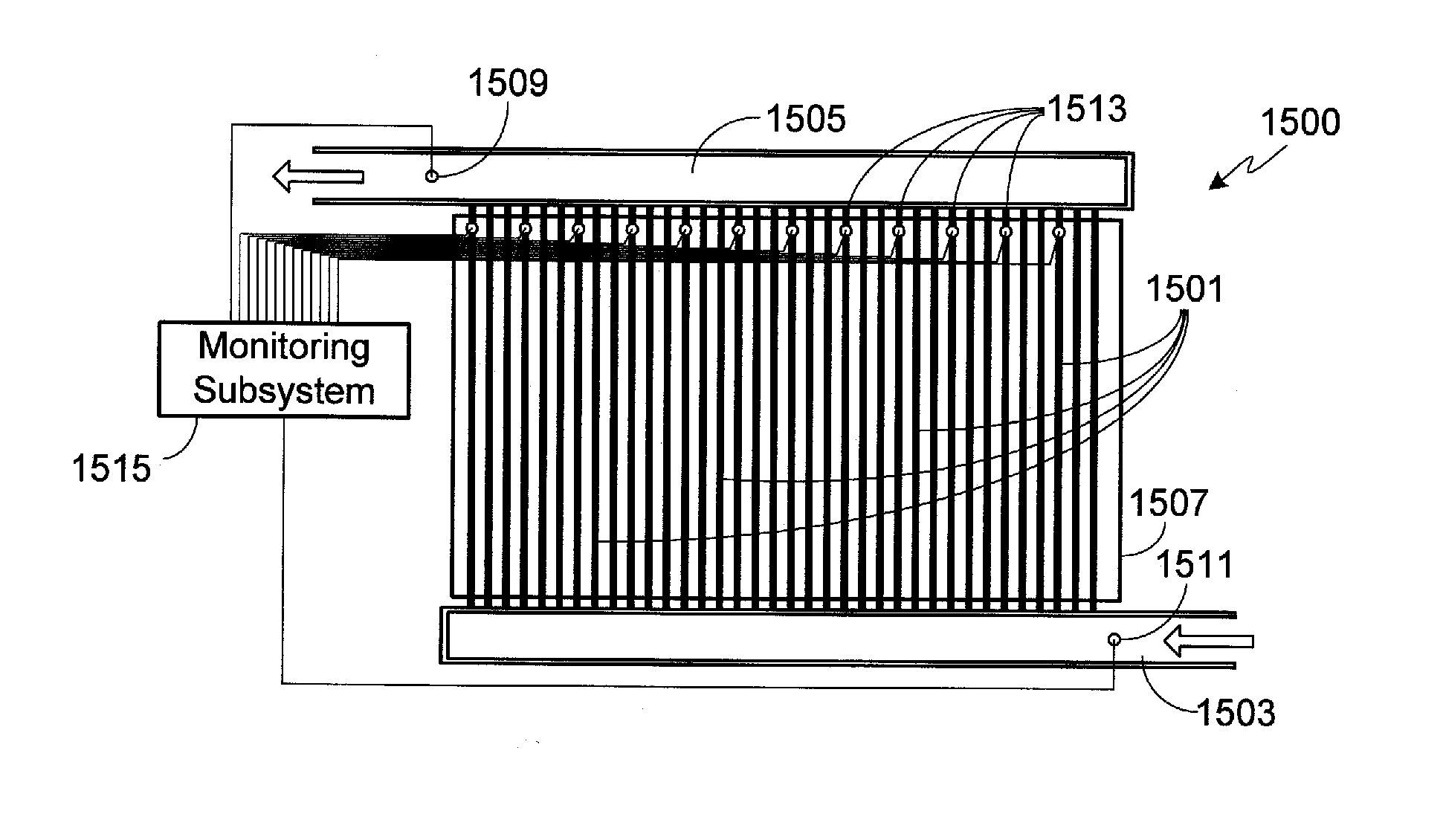
Method of Detecting Battery Pack Damage
ActiveUS20150171486A1Cell temperature controlMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRoad debrisCoolant flow
A method is provided for detecting when a vehicle mounted battery pack is damaged from an impact with a piece of road debris or other obstacle. Positioned within the battery pack is a plurality of deformable cooling conduits located between the lower surface of the batteries within the battery pack and the lower battery pack enclosure panel. One or more sensors are incorporated into the cooling conduits which monitor coolant flow rate or pressure. When the cooling conduits deform, a change in coolant flow / pressure occurs that is detected by the sensors integrated into the conduit's coolant channels. A system controller, coupled to a sensor monitoring subsystem, may provide any of a variety of responses when cooling conduit deformation is detected.
Owner:ATIEVA USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com