Methods and systems for autoinduction of protein expression
An inducible and purposeful technology, applied in the field of self-induced protein expression and system, can solve the problem of expensive preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
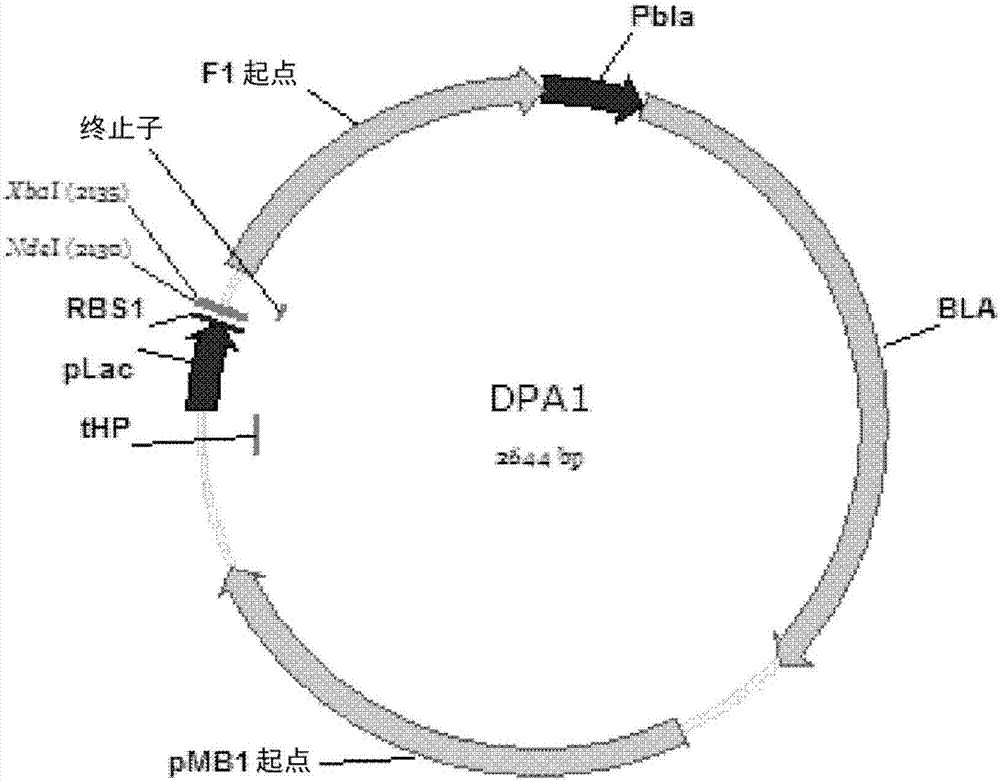
[0081] Embodiment 1: Construction of plasmid DPA1
[0082] The first plasmid, DPA1 (dual-plasmid autoinduction 1 ), was based on the multi-copy pBluscript KS(+) backbone, and the promoter used for protein expression was the lac promoter (SEQ ID NO. 3) lacking any lacI ORF sequence. The shorter lac promoter is fully functional as it is fully repressed by the lad repressor and induced by inducers such as lactose or IPTG. The target gene can be cloned into a multiple cloning site (NdeI and XbaI sites are used here as examples) downstream of the lac promoter. To reduce basal or leaky expression, the lac promoter was preceded by a strong tHP transcription terminator (SEQ ID NO. 2). In addition, a lambda terminator (SEQ ID NO. 4), another strong transcriptional terminator, was placed downstream of the target gene to further reduce leaky expression.
[0083] The DPA1 plasmid map is shown in figure 2 middle. The complete sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1.
[0084]The size of plas...
Embodiment 2
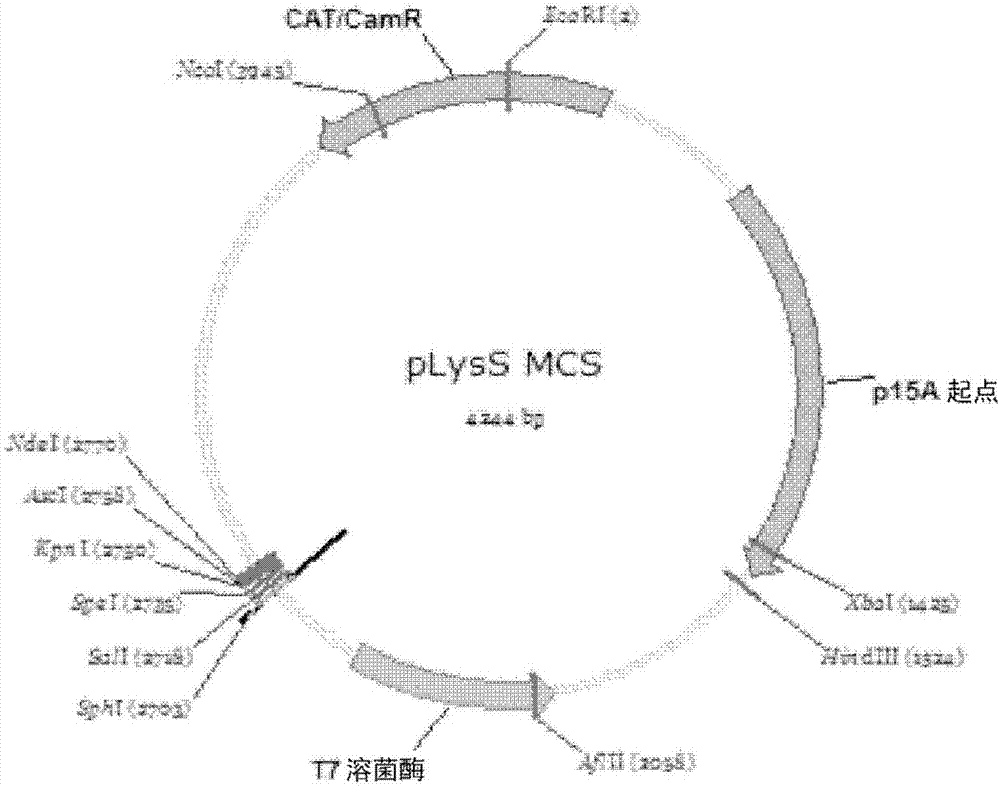
[0086] Embodiment 2: Construction of plasmid pLysS MCS
[0087] Plasmid pLysS MCS was constructed to allow insertion of multiple DNA fragments into vector pLysS. We chose the Tet ORF in the vector pLysS as the insertion site for the MCS (Multiple Cloning Site), because the Tet ORF has been disrupted by the gene encoding T7 lysozyme and the tetracycline resistance gene is no longer effective. In order to make the size of the plasmid smaller and easy to handle, we removed the DNA fragment (715bp) from the unique SphI site to the stop codon in the Tet ORF, and replaced it with a DNA fragment containing a multiple cloning site, whose DNA sequence as follows:
[0088] SEQ ID NO.5:
[0089]
[0090] The plasmid map of pLysS MCS is shown in Figure 3A middle. The sequence is SEQ ID NO.6.
Embodiment 3
[0091] Embodiment 3: Construction of DPA2
[0092] lacI q Inserted between the unique KpnI and AscI sites within the multiple cloning site of pLysS MCS to construct plasmid DPA2 ( two-plasmid autoinduction 2). lacI q The transcription of T7 lysozyme is opposite to that of T7 lysozyme. The plasmid map of DPA2 is shown in Figure 3B middle. The sequence is SEQ ID NO.7. DPA2 contains a cryptic promoter that may be constitutive. LacI q Expressed from DPA2 and is functional because in the absence of DPA2, DPA1 cannot be converted to not have lacI in the F' factor q bacterial strains (data not shown).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com