Non-mirror symmetrical two-dimensional code logo graphic verification and layout method for monocular vision positioning
A technology of monocular vision and layout method, which is applied to the recording carrier used by the machine, image analysis, image data processing, etc. It can solve the problems of positioning error, unrecognizable, low camera precision, etc., and achieve the increase of the number of bits and the layout method Simple and intuitive, convenient for manual data inspection and verification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
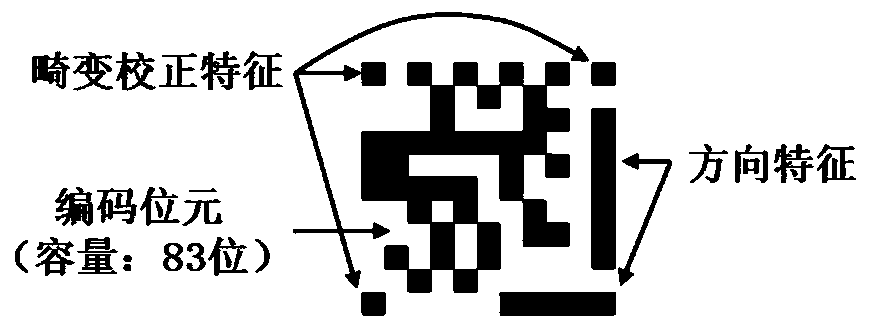
[0031] Embodiment 1: The non-mirror symmetrical two-dimensional code logo graphic verification and layout method for monocular vision positioning includes the following steps:
[0032] Step 1: Divide the two-dimensional code logo graphic into 7×7 rectangular code units, that is, divide the two-dimensional code logo graphic into 7 rows and 7 columns, a total of 49 rectangular code units, and each rectangular code unit is represented by (i, j), i represents the row number, j represents the column number, and the rectangular ring formed by the rectangular code elements of i=1, i=7, j=1 and j=7 is called the rectangular identification ring; the code elements except the rectangular identification ring form the code domain; the coding domain is made up of 25 rectangular code elements, that is, 25 coding bits; each coding bit has two states of 0 or 1, and each state is filled with a color (all states are the same color for 0, and all states are 1 has the same color, 0 and 1 have diff...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0050] Specific embodiment 2: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the code elements located at (2, 2), (2, 6) and (6, 6) and located at (6, 2) in the step 4 The different code element states are as follows:
[0051] If the symbol state at (2, 2), (2, 6) and (6, 6) is set to 1, then the symbol state at (6, 2) is 0; if the state at (2, 2 ), (2, 6) and (6, 6) are set to 0, then the code state at (6, 2) is 1; that is, at (2, 2), (2, 6) and The symbol at (6,6) is filled with a different color than the symbol at (6,2).
[0052] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0053] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one or two is: according to the code selected in step five in the described step six, the check digit is calculated, and the specific process of filling the check digit color is:
[0054] Step six one: Divide the codes selected in step five into two groups, (2,3), (2,4), (2,5), (3,6), (4,6) and (5,6) is the first group, (6,5), (6,4), (6,3), (5,2), (4,2) and (3,2) are the second group;
[0055] Step 62: arbitrarily insert 5 binary supplementary codes into the first group and the second group of codes, and lengths are respectively amplified to 11 bits; judge whether the two groups of codes amplified to 11 bits are mirror image symmetric codes, if not mirror images For symmetrical codes, perform step six and three, if it is a mirror image symmetrical code, then return to step five to reselect one of the 4096 codes;
[0056] The definition of the mirror imag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com