Remote-sensing image target recognition method based on feature tensors and support tensor machine
A technology that supports tensor machines and remote sensing images. It is applied in the field of remote sensing image target recognition. It can solve the problem of unable to maintain the spatial structure information of remote sensing images, and achieve the effect of high practical value and good real-time performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0070] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 5 Describe this embodiment, the specific process of the remote sensing image target recognition method based on feature tensor and support tensor machine of this embodiment is:
[0071] Step 1. Select the training image set on the remote sensing image, and select the slices of the target to be recognized and the background sample on the training image according to the size of the target to be recognized on the training image. The size ratio of the circumscribed rectangle is 1.1-2;
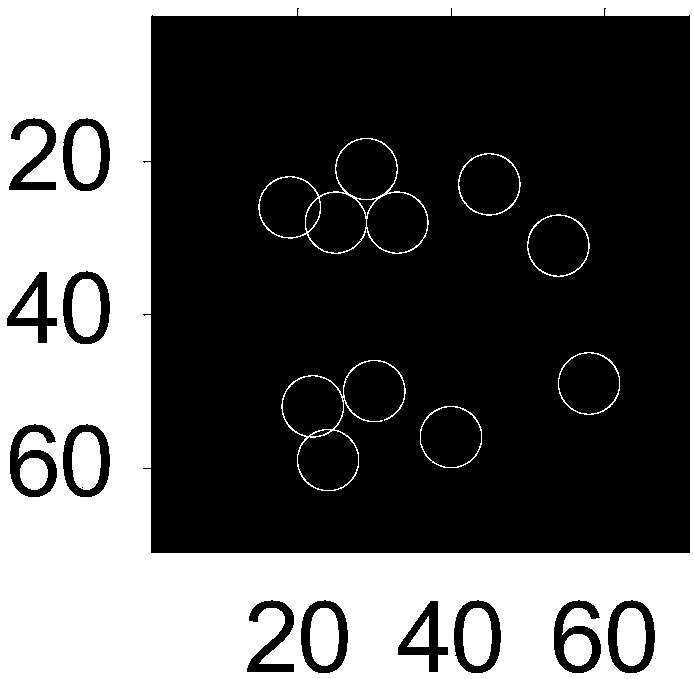
[0072] For the recognition of aircraft targets, the original training images come from the GoogleEarth data source, and the recognition target is the KC135 tanker see figure 1 , according to the size of the recognition target, set the slice size to 70 pixels × 70 pixels, see target and background slices Figure 4a , Figure 4b , Figure 4c , Figure 4d , Figure 4e , Figure 4f , Figure 4g , Figure 4h , Figure 4i , Figure 4j , ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0083] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: extract the SIFT or SURF feature of slice in the described step 2, and build feature tensor; Process is:
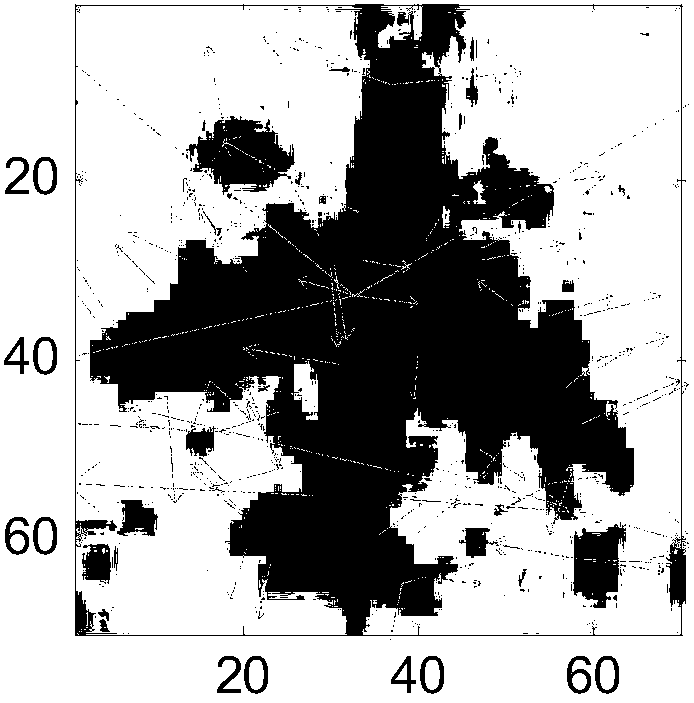
[0084] Step 21, extract the SIFT or SURF features of the slice, wherein the SIFT extraction results are shown in figure 2 , the starting point of the arrow is the feature point, which is the extracted SIFT or SURF feature. The direction of the arrow indicates the direction of the main gradient within the neighborhood of the feature point, and the longer the arrow, the larger the response of the main gradient direction. SURF feature extraction results see image 3 , the circles in the figure represent the positions of SURF feature points on the slice. In order to better maintain the spatial structure of the data, according to the SIFT or SURF features of the slice, a fifth-order feature tensor is established. The first and second order of the feature tensor represent t...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0140] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the optimization process of the objective function to be optimized in the step three is:
[0141] Step 1): Initialize the parameters of the objective function to be optimized Alpha[i]=0, i=1, 2,..., N, b 0 = 0,
[0142] Among them, Alpha is the Lagrangian multiplier that supports the optimization objective function of the tensor machine. In order to reduce the amount of calculation, the projection vector W is optimized by optimizing Alpha. iter-1 , b 0 As the offset, it supports a collection of tensor sequences
[0143] Step 2): iter=1, η iter =1 / (iter+1);
[0144] Where iter is the number of iterations, η iter is the learning rate;
[0145] Step 3): Randomly select a feature tensor from the feature tensor constructed in step 2, set its subscript as t, t represents the tth feature tensor, and the value of t is 1 to N, and X is obtained t , X t is the tth fe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com