Heat dissipation structure of high speed optical module
A heat dissipation structure and optical module technology, applied in the field of optical modules, can solve the problems of affecting the high temperature performance of the module, unfavorable rapid heat dissipation of the module, and unscientific heat dissipation paths, and achieve the effect of improving high temperature performance, reducing working power consumption, and improving heat dissipation function.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
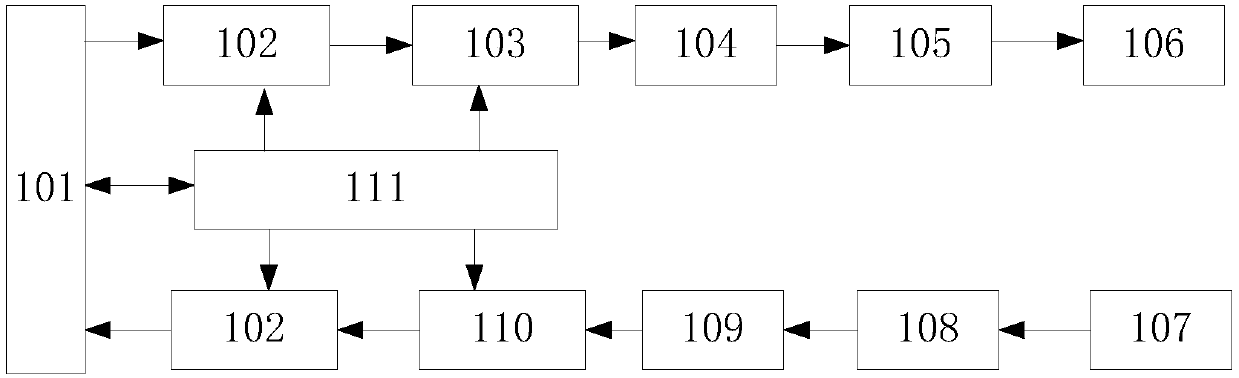
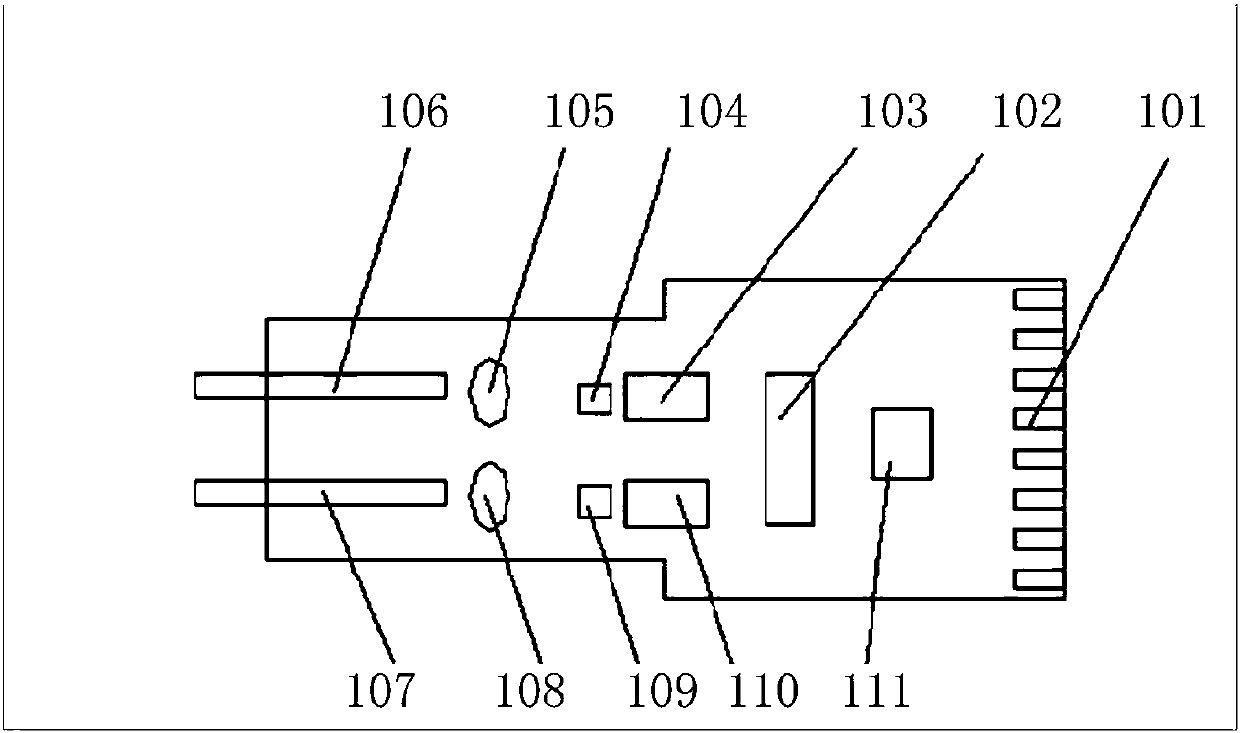
[0045] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a heat dissipation structure of a high-speed optical module, such as Image 6 with Figure 8 As shown, it includes a tube shell base 214, a cover plate 215 and a light engine. The heat dissipation structure also includes a PCB bottom plate 213, a first Z-shaped transition plate 212 and a gold finger sub-board 201, specifically:
[0046] An electrical signal connection is established between the PCB bottom plate 213 and the golden finger sub-board 201 through the first Z-shaped transition plate 212; wherein, the first Z-shaped transition plate 212 enables the PCB bottom plate 213 to be fixed to the After the package base 214, the first surface 2131 of the PCB base plate 213 is adjacent to the bottom of the package base 214, and the second surface 2132 on the PCB base plate 213 with the light engine faces the cover 215 side of the optical module;
[0047] Wherein, the length of the gold finger sub-board 201 is set according to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com