Root limiting cultivation method with films embedded in furrows between ridges for greenhouse vegetables
A technology of vegetables and soil ridges, which is applied in the field of root-restricted cultivation with embedded film in the ditch between soil ridges of facility vegetables, can solve the problems of reducing root-restricted cultivation of vegetables in summer, blank root-restricted cultivation technology, and large disturbance of soil cultivation, etc., to achieve reduction The effects of temperature, environmental pollution and risk reduction of continuous cropping obstacles, and reduction of damage to growth and development
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
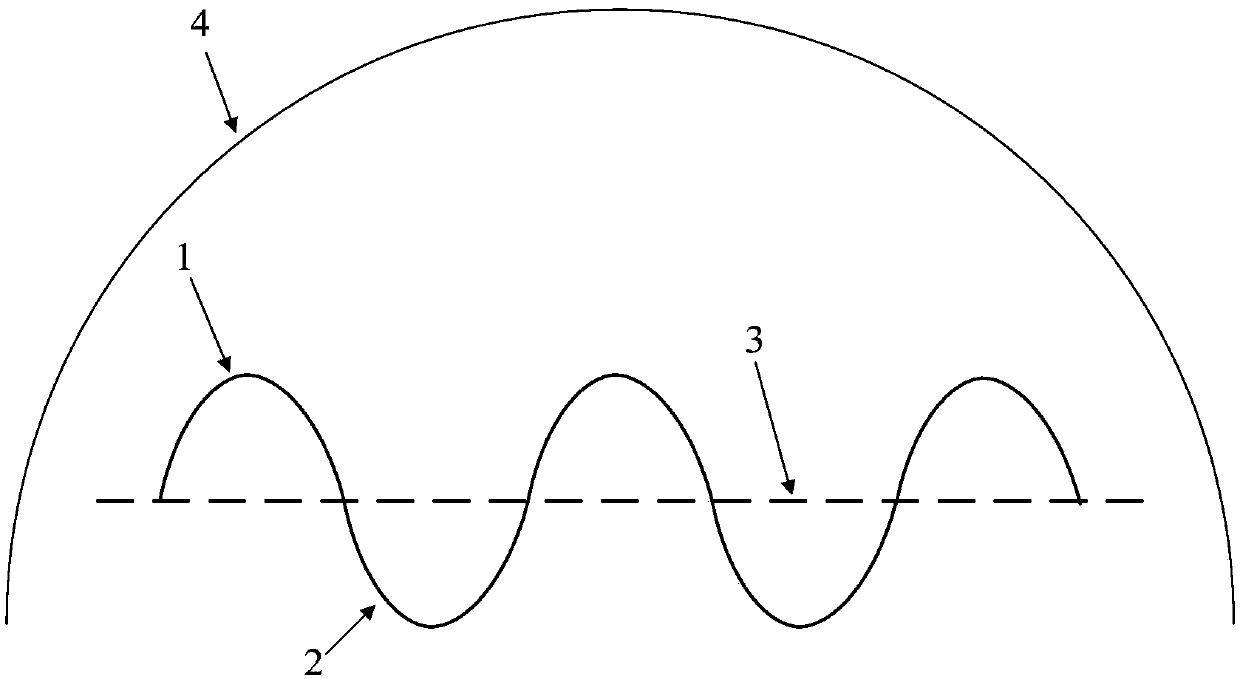
[0037] This example proposes a film-type root-limiting cultivation method in the inter-ridge ditch that is suitable for use in summer solar greenhouses and plastic greenhouses. This method forms ridges and ditches by forming ridges and ditches. Arranged wavy field soil cross-section structure, such as figure 1 As shown, wherein 1 is a ridge, 2 is a ditch, 3 is the ground, and 4 is a solar greenhouse or a plastic greenhouse. During specific implementation, the soil is excavated in a straight line in the field soil, and the soil obtained by excavation is used to form ridges on both sides of the ditch. Through calculation, the soil generated by digging the ditch is just used for the amount of ridge soil and the amount of cultivation soil, forming a certain size specification. A soil structure in which ridges and furrows are arranged alternately.
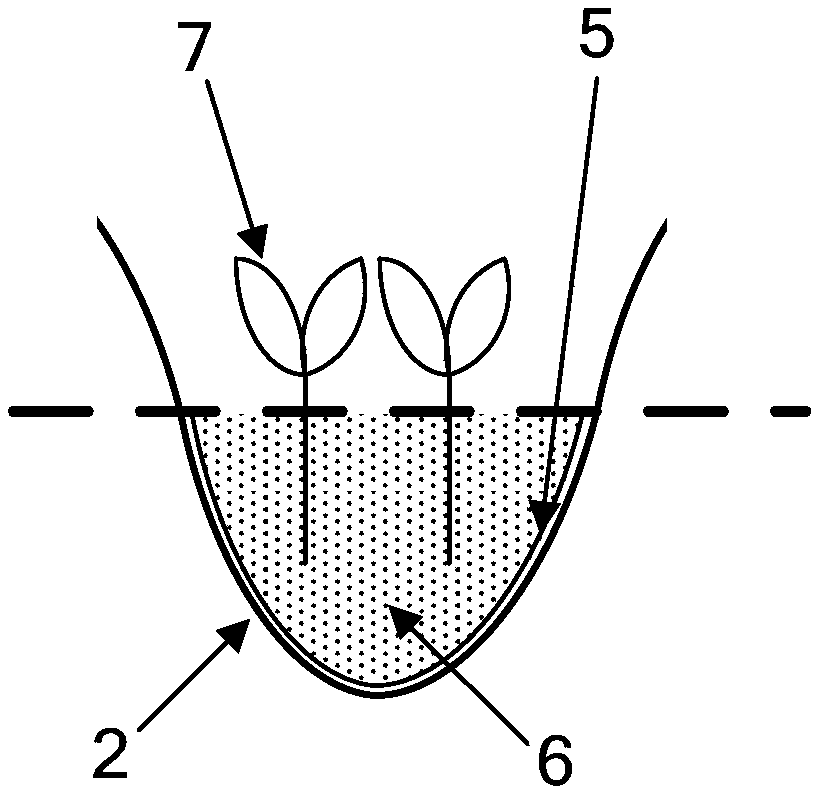
[0038] figure 2 It is the internal structure diagram of the ditch between every two ridges. In this embodiment, ditch 2 is directl...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the structure used for root-limited cultivation in the ditch is not the form of using soil to form a cultivation soil groove and pasting a flexible film, but as Figure 7 Shown, hard container 9 is set in ditch, and cultivation medium is housed in hard container 9, and the space between the outer wall of hard container 9 and the inwall of ditch fills up with soil. Similar to the flexible film, there are ventilation holes in the middle and lower part of the side wall of the rigid container. The hard container 9 can be in various shapes such as square, cylindrical, semi-spherical.
Embodiment 3
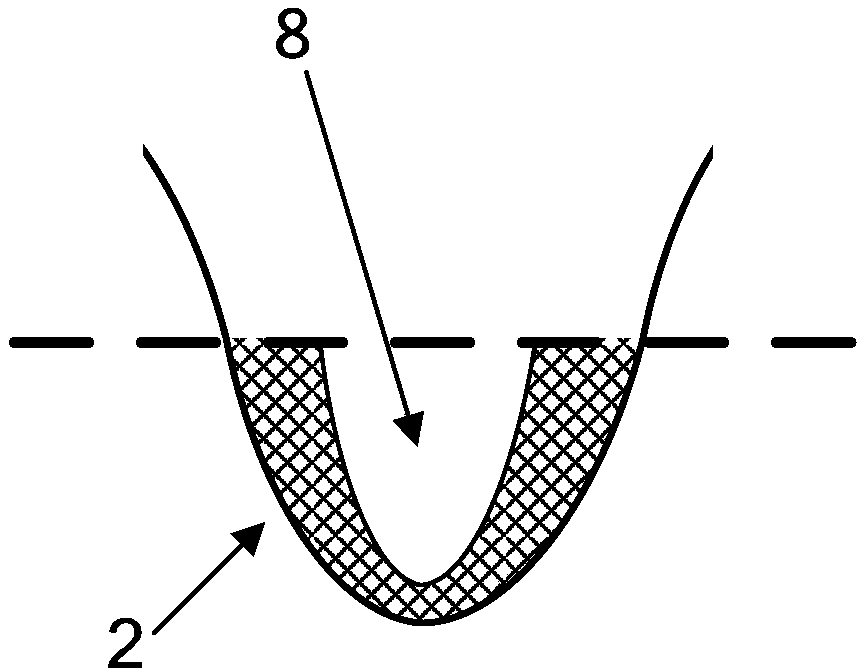
[0048] In this embodiment, on the basis of Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2, a reflective material layer 10 is covered on the surface of the groove, such as Figure 8 As shown, it is used to reflect light and reduce radiation heat transfer, which is more conducive to keeping the low temperature in the trench. The edge of this light-reflecting material layer covers part of the slope of the ridges on both sides. If the light-reflecting material layer arranged on the surface of the same ditch is composed of many small pieces of light-reflecting material layer, each small piece of light-reflecting material layer is connected with the adjacent piece of small one. The layers of reflective material are overlapped to prevent the soil on the ridge from entering the ditch, and it is also beneficial to fix the layer of reflective material.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com