Local Dynamic Path Planning Method for Mobile Robots Based on Adaptive Dynamic Window
A mobile robot and dynamic window technology, applied in the direction of instruments, non-electric variable control, two-dimensional position/channel control, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient smoothness of robot trajectory, reduced safety and comfort, and longer running time, etc. Achieve the effect of reducing the number of running steps and running time, ensuring high speed and safety, and improving overall efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] Embodiment 1: Objective function optimization
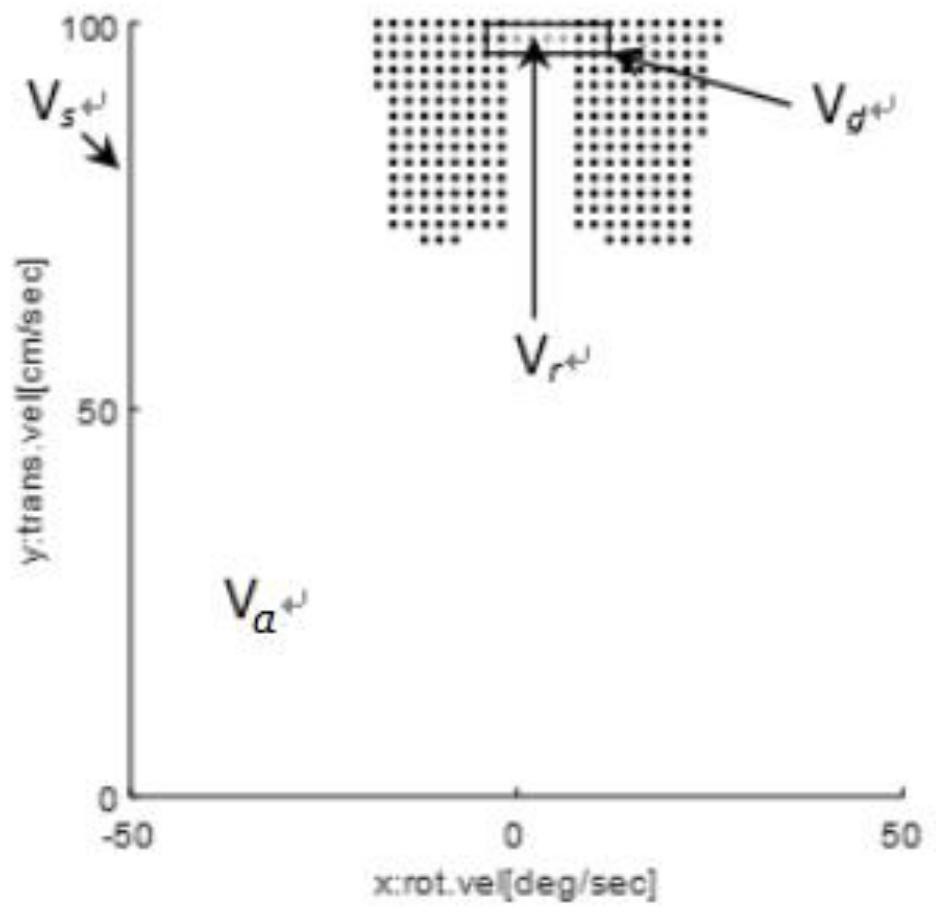
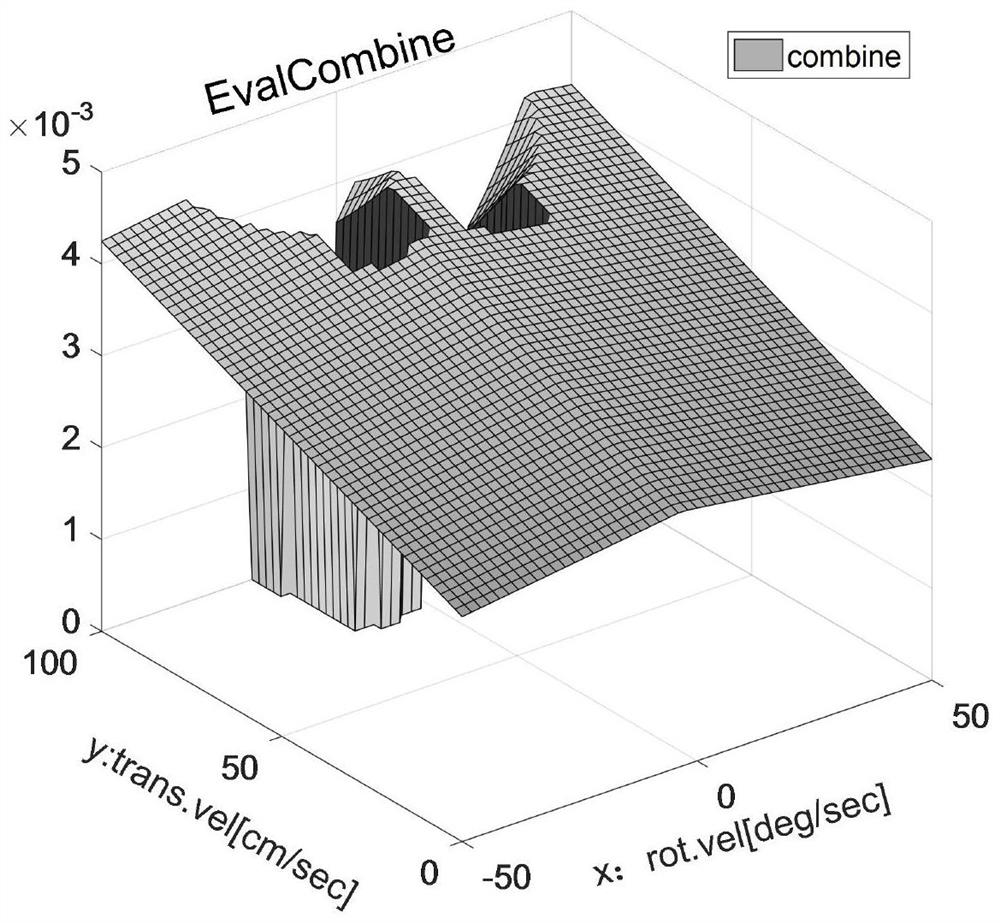
[0078] Fig. 2(a) is a schematic diagram of velocity space in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and Fig. 2(b) is a 3D diagram of the objective function when acceleration constraints are ignored in Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0079] In order to obtain the optimal speed at time t+1, firstly normalize the three inputs heading, dist, and vel respectively, and then filter out the optimal speed at time t+1 through the objective function G(v,ω).
[0080] In order to ensure the entire objective function, it is assumed that the acceleration of the mobile robot at time t can be from 0 to arbitrarily large, the linear velocity is [0, 100], and the angular velocity is [-50, 50]. In this case, we plot the acceleration at time t 3D objective function, as shown in Figure 2(b), at this time the mobile robot pose (x, y, θ) t = (4.6833, 5.7965, 0.6807), velocity (v, ω) t =(100,4). Comparing the velocity space diagram in ...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Example 2: Verify the influence of the distance between the mobile robot and the obstacle on the speed optimization when the weight of the speed item γ is a low weight
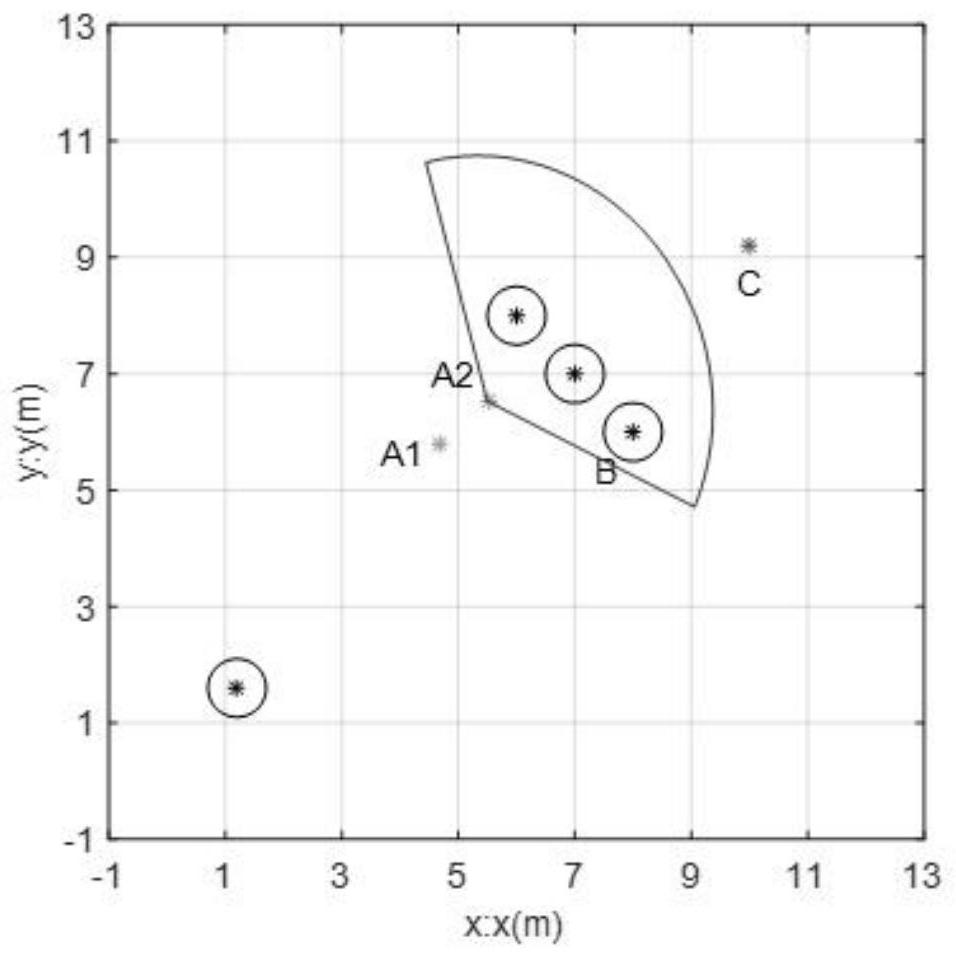
[0083] figure 1 It is the experimental simulation environment map in the embodiment of the present invention, and Fig. 3 (a) is the 3D schematic diagram of objective function when the mobile robot is far away from the obstacle in the embodiment of the present invention; Fig. 3 (b) is the implementation of the present invention The 3D diagram of the objective function when the mobile robot in the second embodiment is closer to the obstacle in the example.
[0084] Fig. 3 (a) is the 3D schematic diagram of the objective function when the mobile robot in the second embodiment of the present invention is far away from the obstacle, Fig. 3 (b) is the mobile robot in the second embodiment of the present invention is far away from the obstacle 3D plot of the near-time objective function.
[0085] When the mo...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Example 3: Speed Weight γ High Time Original DWA Optimization Experiment
[0088] Fig. 4 (a) is the 3D figure of objective function when the mobile robot in the embodiment three in the embodiment of the present invention is far away from the obstacle, Fig. 4 (b) is the mobile robot in the embodiment three in the embodiment of the present invention is far away from the obstacle 3D plot of the objective function when obstacles are close.
[0089] When the mobile robot is far away from the obstacle at time t, such as figure 1 A in 1 , γ=20, mobile robot pose (x, y, θ) t = (4.6833, 5.7965, 0.6807), velocity (v, ω) t = (100, 4), the objective function obtained by DWA is shown in Figure 4(a). The optimal speed at time t+1 after optimization is (100, 4), namely v t+1 =v t , which is also the maximum linear speed of the mobile robot. It can be concluded that when the velocity weight γ is high and the mobile robot is closer to the obstacle, the optimal linear velocity a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com