A group of genes for molecular typing of renal cell carcinoma and its application
A technology for renal cell carcinoma and molecular typing, which is applied in the fields of cancer diagnosis and molecular biology, and can solve the problem of inability to distinguish various subtypes of renal cell carcinoma.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] Collection and processing of training set samples;
[0089] The present invention analyzes a large number of clinical data of renal tumor patients and their biological sample data, including 106 cases of clear cell carcinoma, 66 cases of papillary cell carcinoma, 42 cases of chromophobe cell carcinoma, 46 cases of oncocytoma, 35 cases of non- A total of relevant clinical data and gene expression data of 295 patients in tumor tissues were used to construct a renal cell carcinoma gene expression database.
[0090] Screening of 44 specific genes;
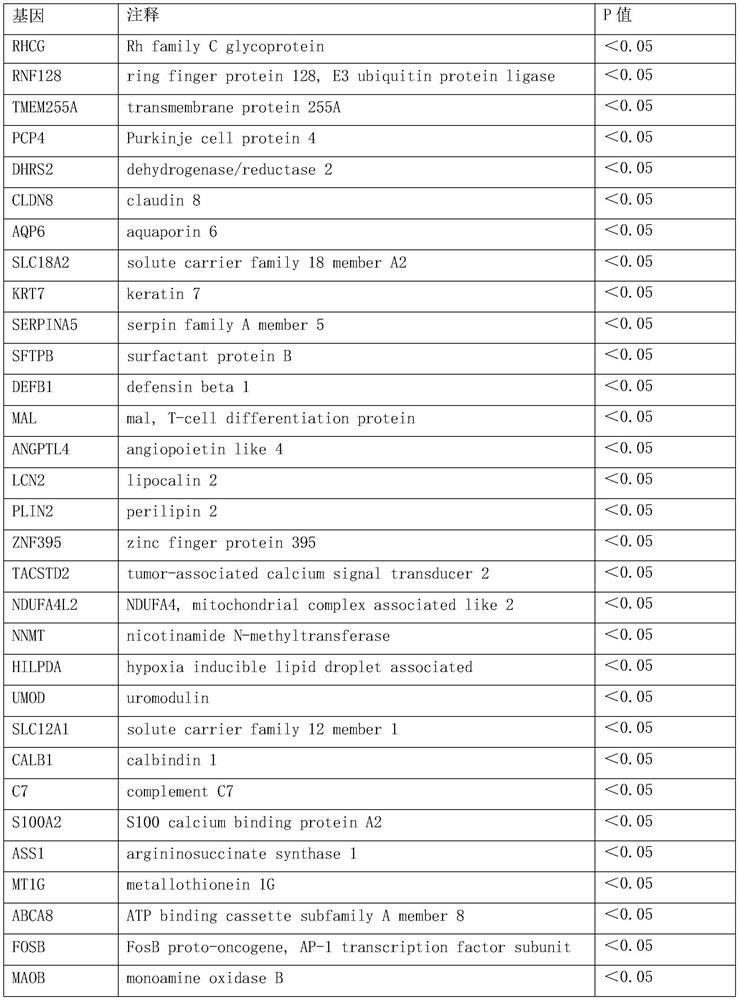
[0091] According to the measured value of gene expression abundance, the inventors used the statistical analysis method T-test to select 44 genes that are closely related to the renal cell carcinoma type from 12263 genes. These genes were differentially expressed in RCC subtypes with statistical significance, as shown in Table 1.
[0092] Table 2: 44-gene set
[0093]
[0094]
[0095] 44 genes based on the construction...
Embodiment 2
[0098] Validation set test:
[0099] In this example, the inventors analyzed the high-throughput sequencing data of 1020 cases of renal cell carcinoma, including 534 cases of clear cell carcinoma, 291 cases of papillary cell carcinoma, 66 cases of chromophobe cell carcinoma and 129 cases of non-tumor tissue. The 44-gene statistical analysis model was used to discriminate the type of each sample, and compared with the results of clinicopathological diagnosis, the accuracy rate was 93.4%. Taking clear cell carcinoma as a reference, the predicted sensitivity is 94.2%, and the specificity is 95.7%, see Table 2.
[0100] Table 3: Discrimination results of the 44-gene model in the validation set of 1020 cases
[0101]
Embodiment 3
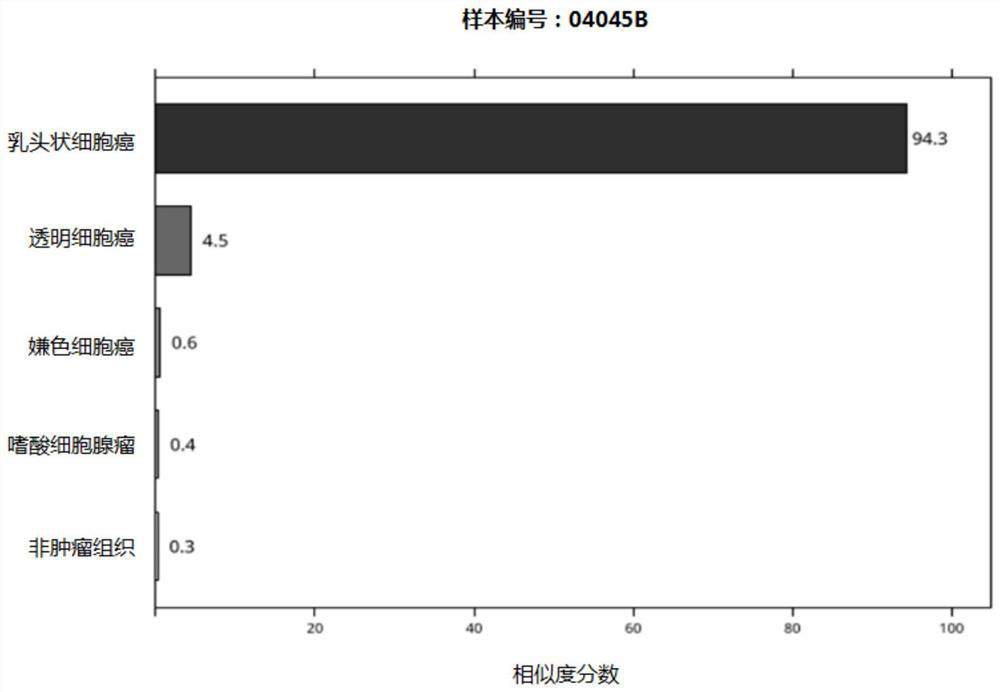
[0103] In this example, the inventors conducted molecular typing experiments on 121 cases of renal tumor samples and 8 cases of non-tumor tissue samples, including 26 cases of clear cell carcinoma, 28 cases of papillary cell carcinoma, 40 cases of chromophobe cell carcinoma and eosinophilic cell carcinoma. There were 27 cases of adenoma. The experimenters collected renal tumor-enriched areas from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue blocks by hand scraping, and extracted total RNA; treated with DNase to ensure complete removal of genomic DNA contamination; obtained after reverse transcription cDNA, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, RTQ-PCR) of 44 genes was used to detect the expression level of genes in paraffin-embedded tumor tissue, and the analysis model calculated that the sample was similar to the subtype of renal cell carcinoma degree score.
[0104] The 44-gene statistical analysis model was used to d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com