New use of inhibitor of cystine-glutamate transporter
一种转运蛋白、抑制剂的技术,应用在胱氨酸-谷氨酸转运蛋白抑制剂领域,能够解决不确定作用等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0065] Instance 1 system x c - effect on addiction
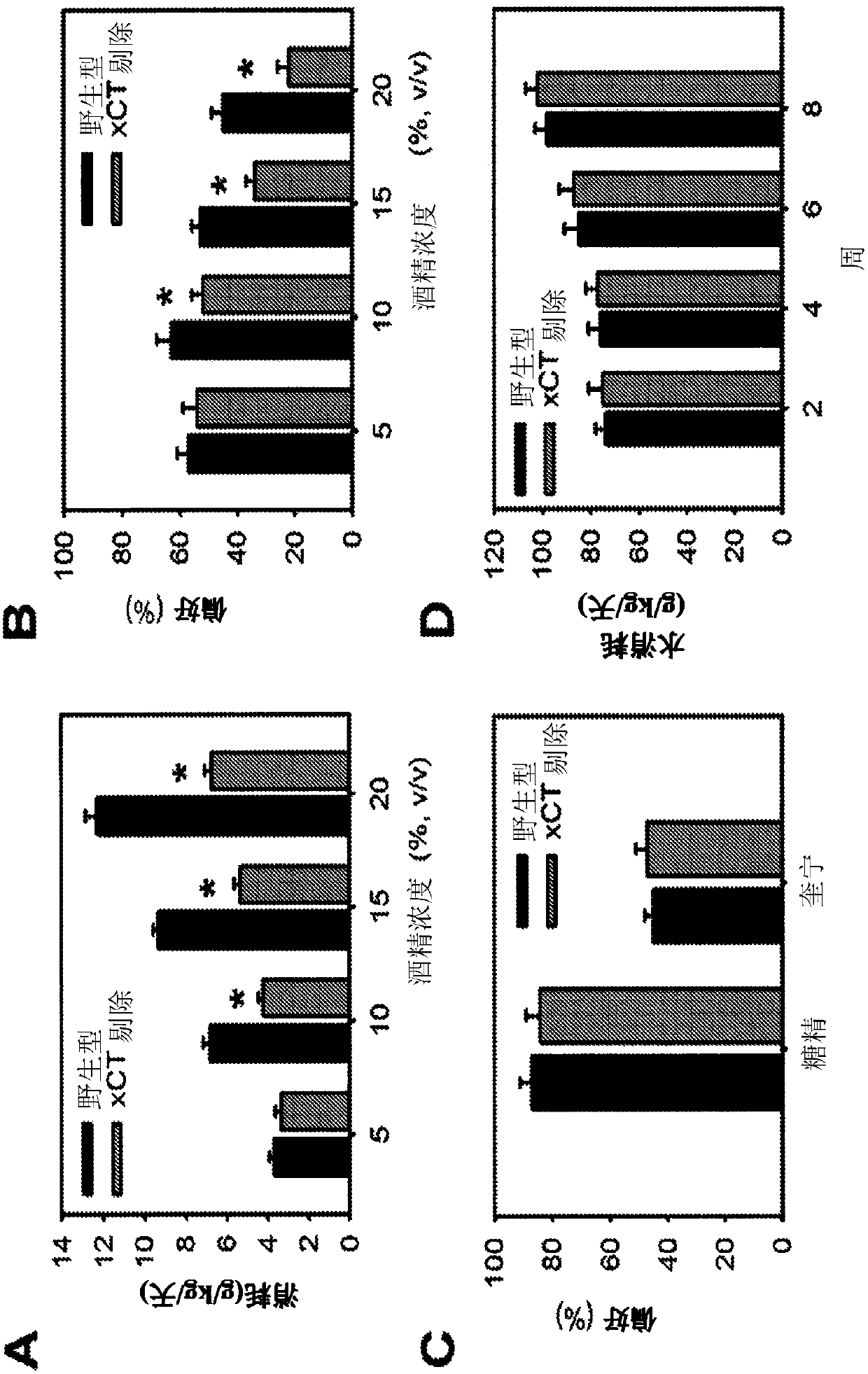
[0066] for trying to get system x c - Insights into the role of addiction, first using a free-choice two-bottle drinking behavior test to measure alcohol self-administration and preference. xCT knockout (KO) mice consumed much less alcohol than wild-type (WT) mice ( figure 1 A). Furthermore, alcohol preference in xCT KO mice was much lower than in WT mice ( figure 1 B). There was no significant difference in saccharin or quinine preference between xCT KO mice and WT mice ( figure 1 C), which indicates that alcohol avoidance in xCT KO mice does not stem from taste neophobia. The water consumption of the two genotypes was not significantly different throughout the experiment ( figure 1 D). To induce alcohol-dependent mice, xCT KO mice and WT mice were subjected to long-term alcohol exposure by feeding an alcoholic liquid diet for 14 days and then presented during the alcohol acquisition period using 2 vials (one cont...
example 2
[0067] System x in Example 2 Alcohol Dependence c - The therapeutic potential of manipulation
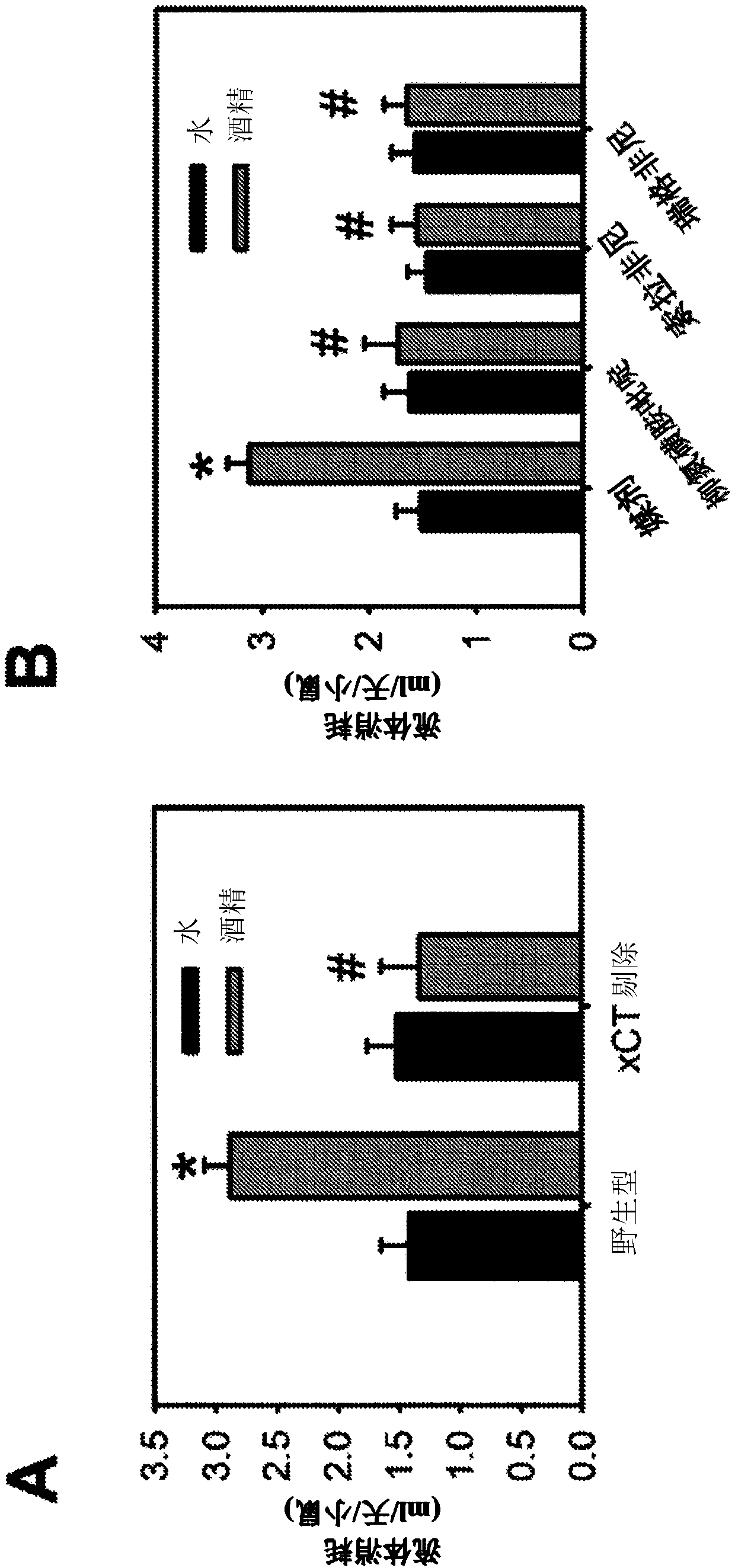
[0068] Research Systemx c - Therapeutic Potential of Manipulation in Alcohol Dependence, Using the Blocking System x c - Sulfasalazine, sorafenib and regorafenib (Buckingham S.C. et al., Glutamate release-induced epilepsy activity in primary brain tumors. Nature Medicine, 2011.17(10): pp. 1269-74 ; Zhong W.J. (Chung, W.J.) et al. Inhibition of cystine uptake disrupts the growth of primary brain tumors. Journal of Neuroscience, 2005.25 (31: No. 7101-10 pp) to treat alcohol-dependent mice. Compared with the control vehicle, sulfasalazine, sorafenib and regorafenib significantly reduced daily alcohol consumption (DMSO) during free choice drinking ( figure 2 B). These results show that the system x c - Alcohol addiction can be ameliorated by pharmacological inhibition of its inhibitors (ie, sorafenib, regorafenib, and sulfasalazine).
example 3
[0069] Example 3 Improved Analysis of Cocaine Addiction and Alcohol Addiction
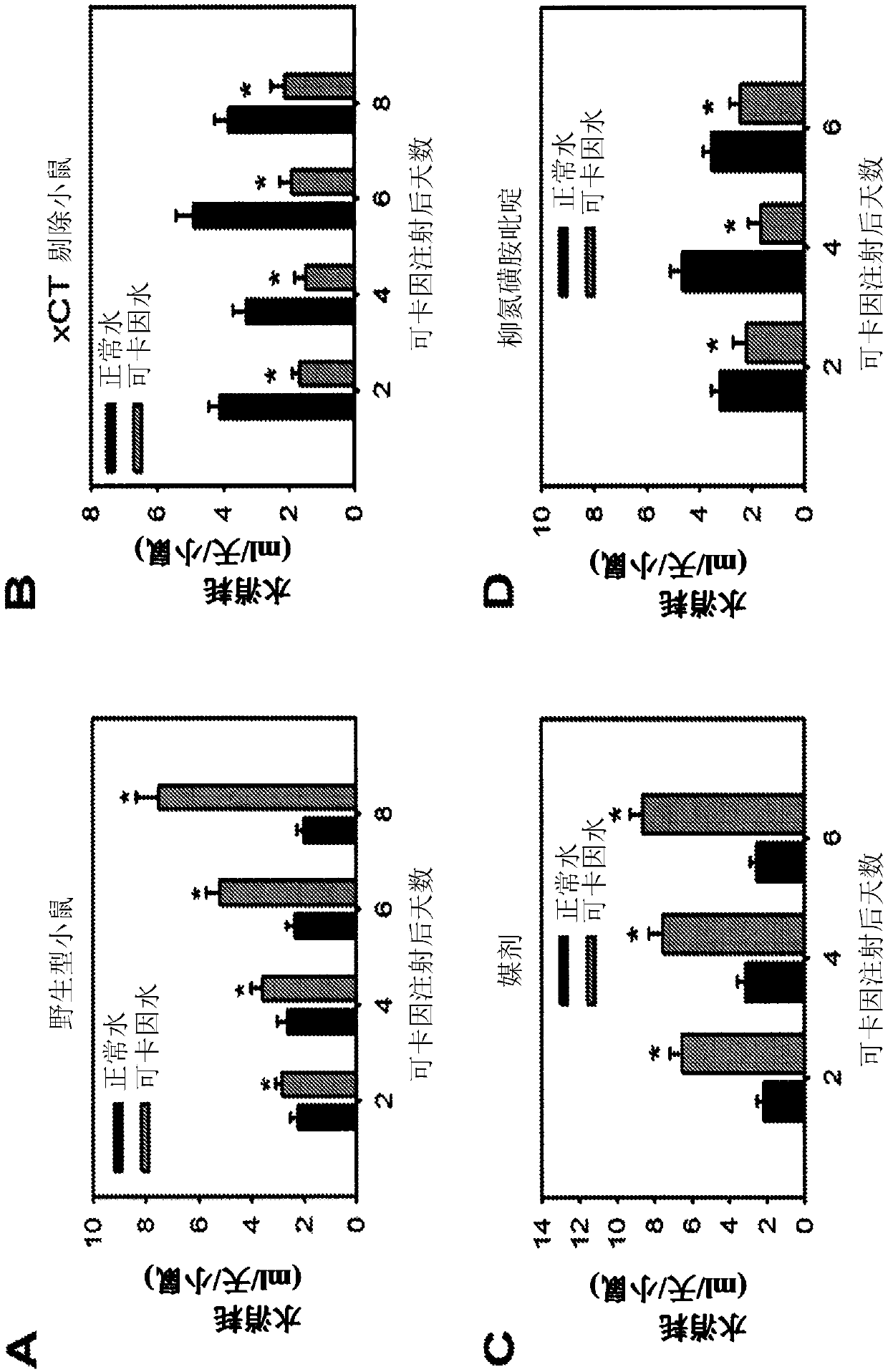
[0070] for test system x c - Whether to play the same role in other substance use disorders, xCT KO mice and WT mice were forced to receive intraperitoneal injection of cocaine for 7 days and then transferred to use 2 vials (one containing diluted cocaine and the other containing normal water) for 8 days in a free-choice drinking model. Like alcohol-dependent mice, WT mice had cocaine-preferring behavior and displayed craving behavior after chronic cocaine exposure ( image 3 A). However, xCT KO mice attempted to drink normal water, thus indicating systemic x c - A genetic defect suppresses cocaine addiction. Additionally, cocaine-dependent WT mice were treated daily with sulfasalazine or vehicle following chronic cocaine exposure. Surprisingly, compared with vehicle treatment, sulfasalazine treatment completely suppressed cocaine preference and craving behavior ( image 3 B). These result...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com