Magnetic resonance imaging method and device
A magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance imaging technology, applied in medical imaging, medical science, sensors, etc., can solve the problems of increased radio frequency pulse energy deposition, too large time interval setting, insufficient blood flow suppression, etc., to avoid blood vessel pulsation Artifacts, reduced number of applications, effects of suppressing interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
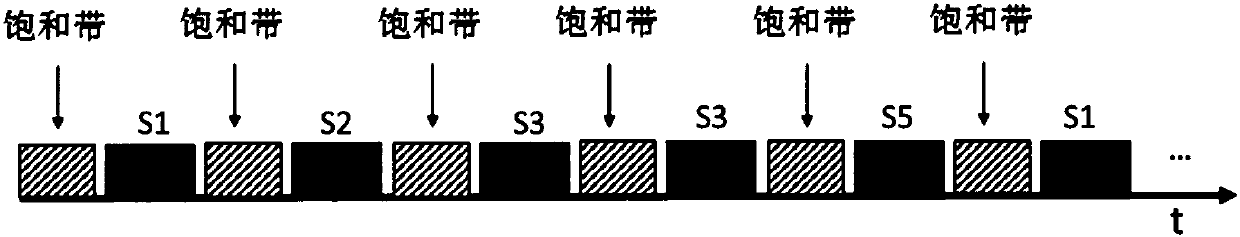
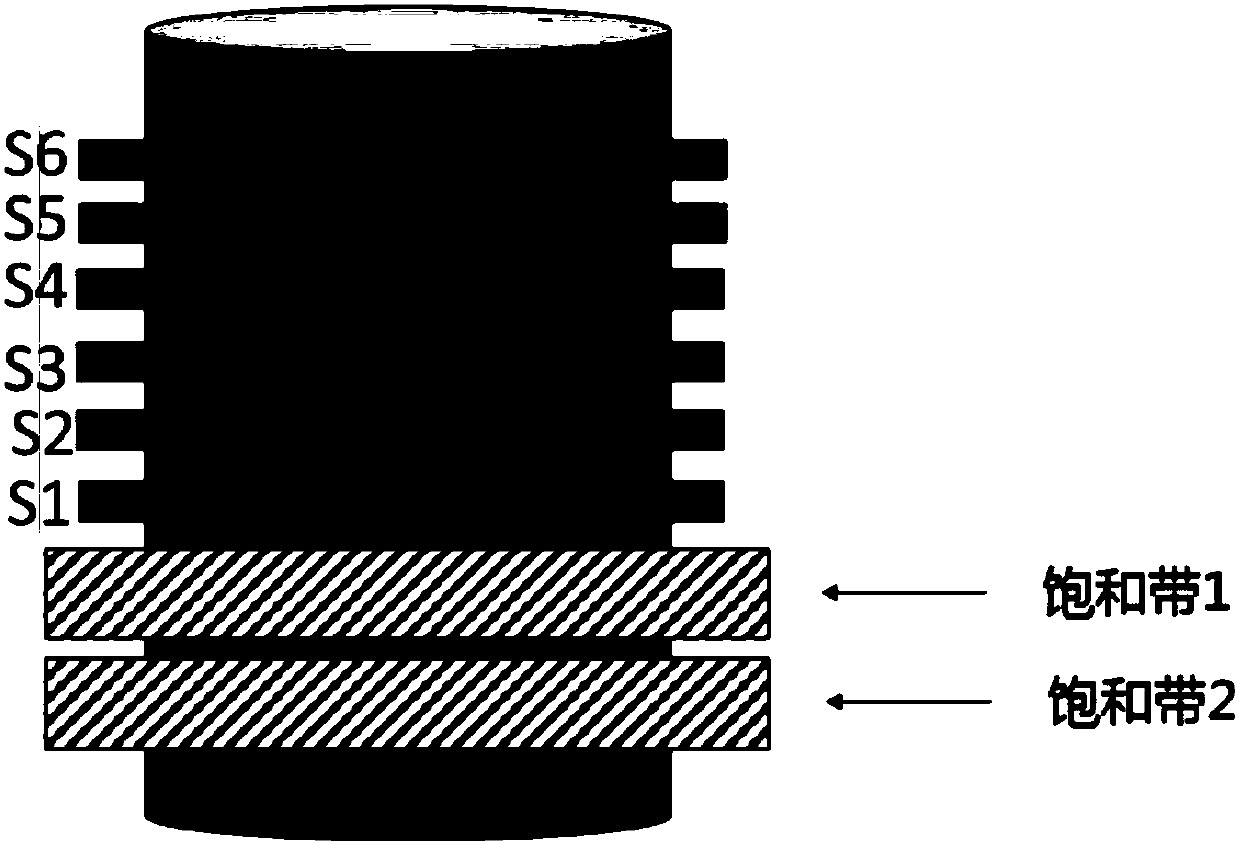
[0052] The scanning sequence may include two saturation pulses and a set of excitation radio frequency pulses, and the two saturation pulses are applied simultaneously before the set of excitation radio frequency pulses. Such as figure 2 As shown, the target area of the subject is divided into six consecutive layers S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6 in spatial position, and the saturation zone 1 and saturation zone 2 are set on the same side of the target area (a side), and the direction in which the saturation pulse is applied to the two saturation bands is along the direction of blood flow. Multiple (two) saturation pulses (sequences) can be applied to the two saturation zones, and each level is correspondingly excited by an excitation radio frequency pulse, and the excitation radio frequency pulse can excite six levels of the target area, and then the corresponding K-space data is collected. According to the preset distance threshold of the scan, the saturation band 1 and the ...
Embodiment 2
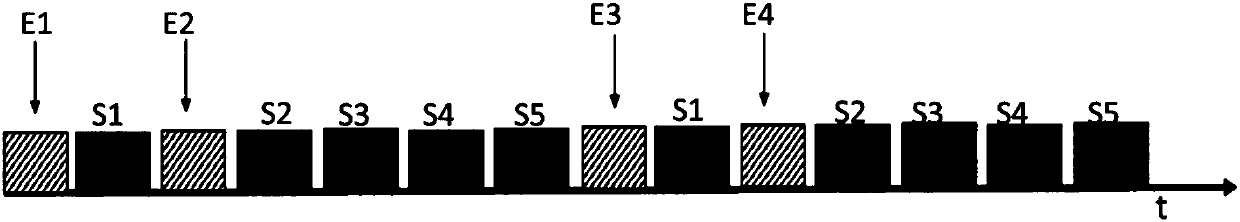
[0056] saturation band such as figure 2As shown, it is set on the same side of the target area (not shown), and the number of saturation bands is two. The difference from Embodiment 1 lies in the number of slices and the number of scans. The scan includes the first saturation pulse (sequence) E1, the second saturation pulse (sequence) E2 and a group of excitation radio frequency pulses (sequence), wherein a group of excitation radio frequency pulses includes the first excitation radio frequency pulse (sequence), the second excitation radio frequency pulse (sequence) and the third excitation RF pulse (sequence), the first saturation pulse E1 is applied before the first excitation RF pulse, and the second saturation pulse E2 is applied before the second excitation RF pulse. Furthermore, the target area can be divided into multiple groups of layers, the saturation pulse includes a first saturation pulse and a second saturation pulse, and the number of excitation radiofrequency p...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the target area of the subject is divided into six consecutive layers S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6 in spatial position, and two saturation bands (saturation band 1 and saturation band 2) are respectively set in the target area On both sides, the direction of the saturation pulse applied on the saturation band is the same or opposite, which can be determined according to the direction of the blood flow to be suppressed or the direction of the chemical shift of the fat signal generated by the radio frequency pulse. A set of excitation radio frequency pulses in the scanning sequence includes multiple pulse sequences, and each layer corresponds to excitation radio frequency pulses, and the excitation radio frequency pulses can excite six layers of the target area, and then collect the corresponding K-space data. According to the preset distance threshold, the saturation bands 1 and 2 are respectively set on both sides (ends) of the target area. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com