Managing external interference in a wireless network
An external interference, wireless network technology, applied in wireless communications, data exchange networks, diversity/multi-antenna systems, etc., can solve the problems of interference, lack, and inability to quickly solve problems such as rapid spatial and temporal interference pattern changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
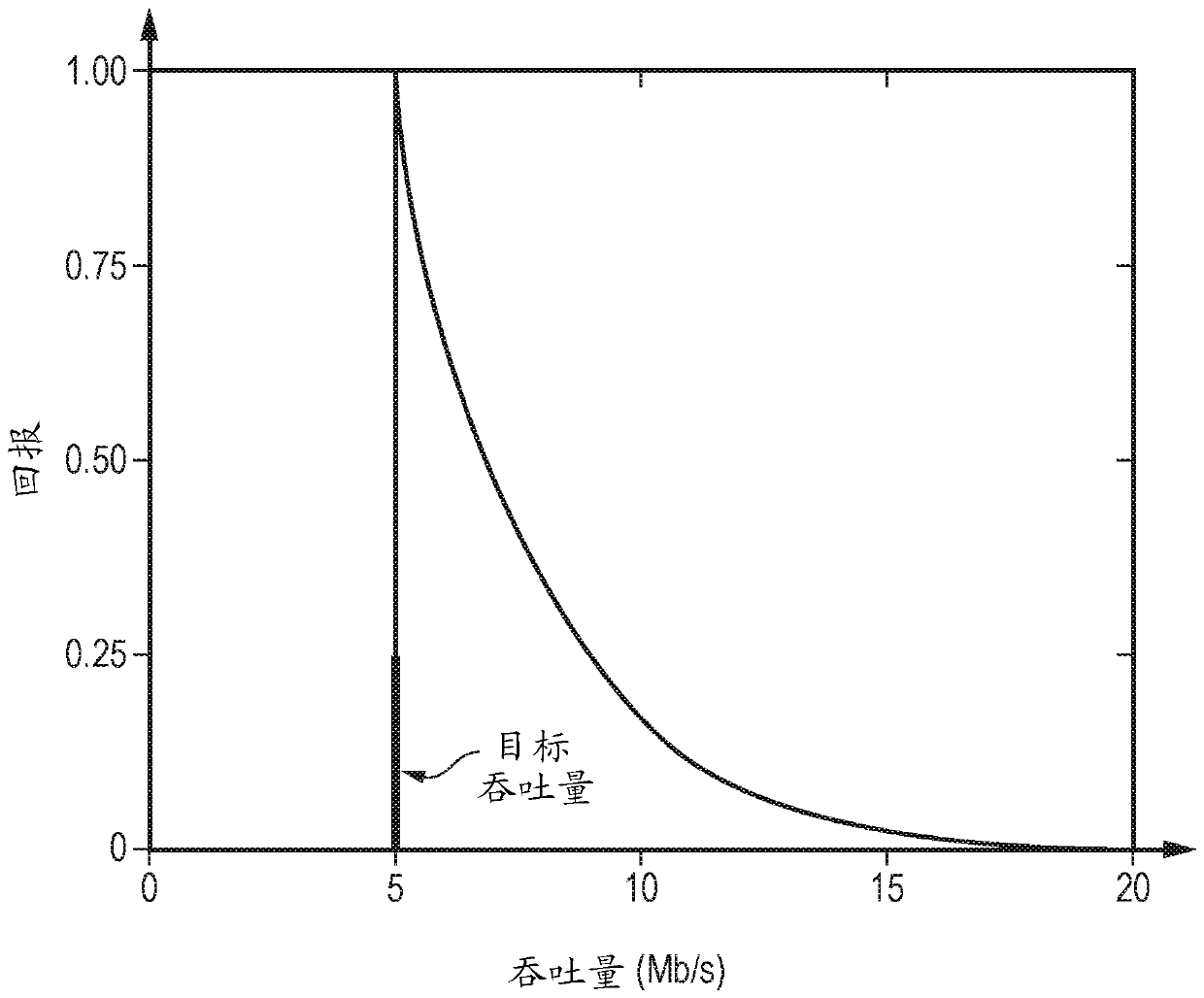
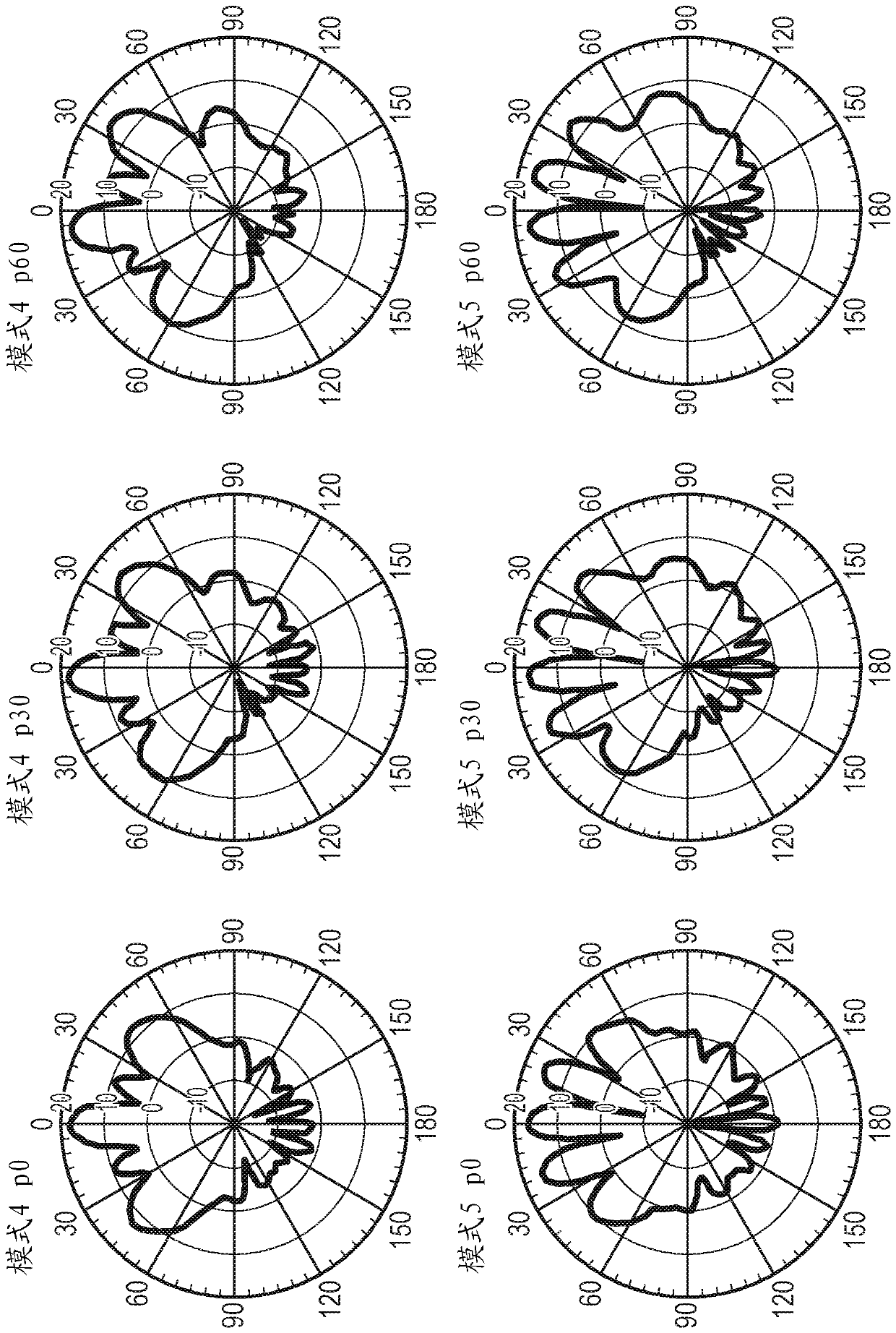
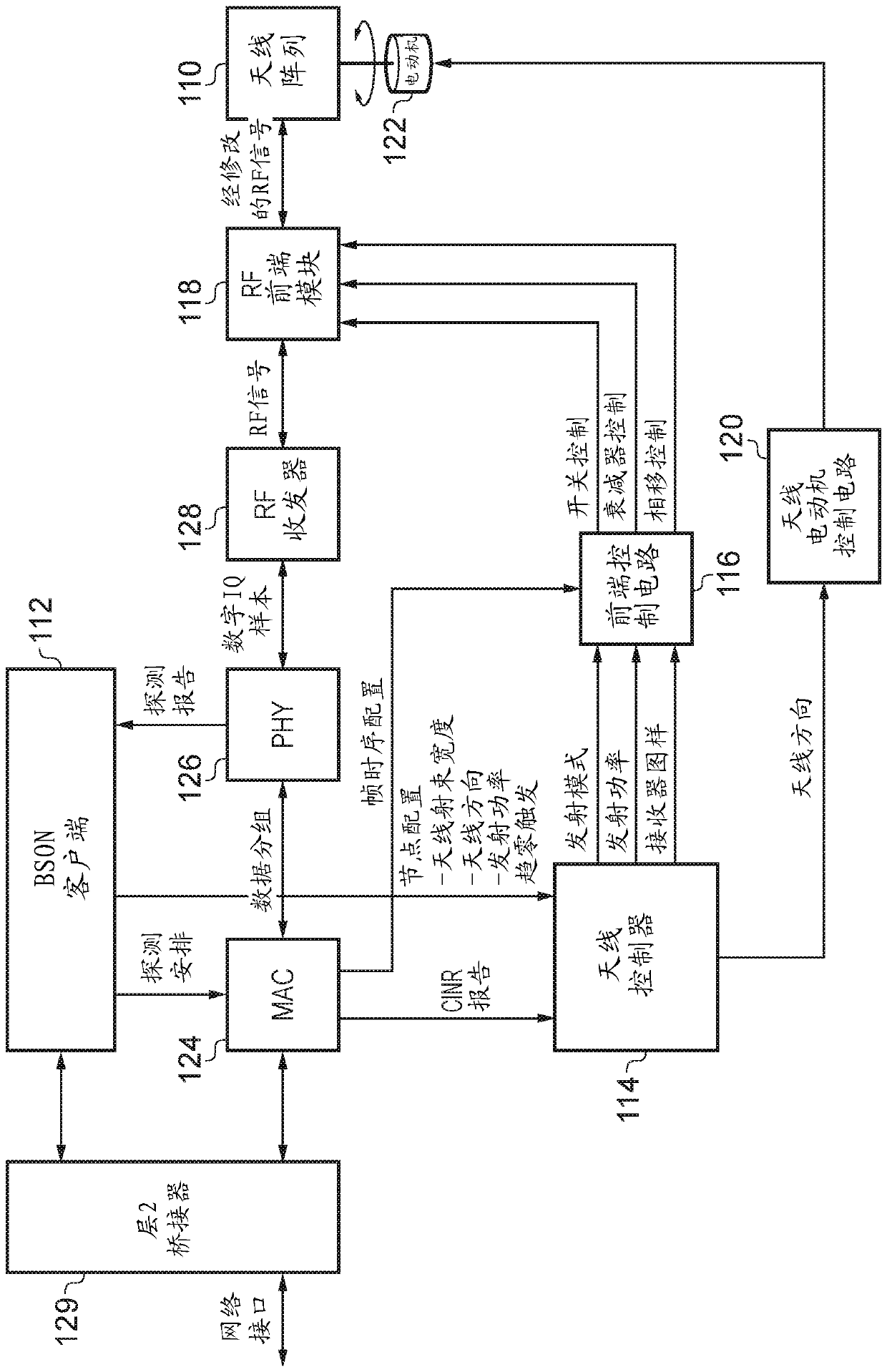
[0059] Some specific embodiments are now described with reference to the figures. figure 1 A multi-component network providing user equipment (UE) connectivity to a communication network such as the Internet is schematically illustrated. The item of user equipment 10-15 of this example communicates wirelessly with an LTE base station (enhanced Node B (eNB)). pay attention, figure 1 The LTE air interfaces shown in are examples only and the techniques are equally applicable to other suitable non-LTE air interfaces. Furthermore, although each access base station is shown communicating with a single item of end-user equipment for simplicity, it will be appreciated that such an access base station that actually forms a point-to-multipoint device enables many Items are able to communicate with individual access base stations. These eNB access sites then either have a direct wired connection (via IP protocol) to the communication infrastructure 20 in the case of 21 and 22 or to th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com