Method for producing mixed powder for powder metallurgy, method for producing sintered compact, and sintered compact
A mixed powder and powder metallurgy technology, which is applied in metal processing equipment, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of reduced strength of sintered body, difficulty in increasing compacted powder density, solid solution hardening of steel powder, etc., and achieves high fluidity and easy operation Excellent efficiency and the effect of improving fluidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
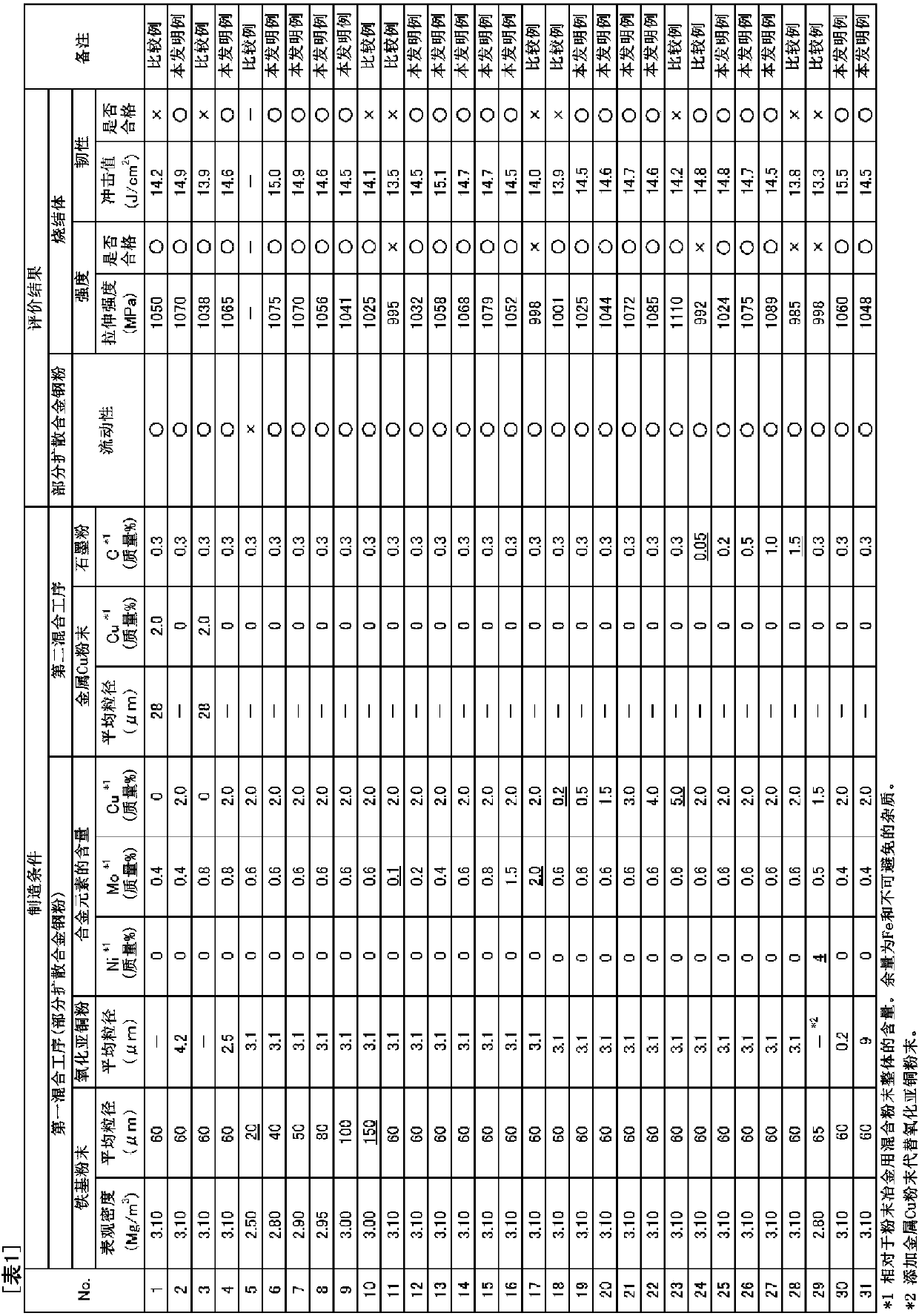
[0110] Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail based on examples, but the present invention is not limited to the following examples.
[0111] Mixed powder for powder metallurgy was produced by the following procedure.
[0112] (first mixing process)
[0113] The raw material mixed powder is obtained by mixing the Mo-containing powder and the Cu-containing powder in the iron-based powder. As the above-mentioned iron-based powder, atomized raw powder having an apparent density shown in Table 1 was used. The specific surface area of the iron-based powder is 0.39m 2 / g. Mo oxide powder having an average particle diameter of 10 μm was used as the Mo-containing powder. As the Cu-containing powder, cuprous oxide powder having an average particle diameter shown in Table 1 was used. The above mixing was performed for 15 minutes using a V-type mixer. In addition, the compounding quantity of each powder was adjusted so that content of Mo and Cu in the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com