LED packaging structure
A technology of LED packaging and heat dissipation substrate, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient concentration of light source lighting, affecting light transmission efficiency, reducing light intensity, etc., to suppress total reflection effect, reduce costs, The effect of increasing the cooling effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
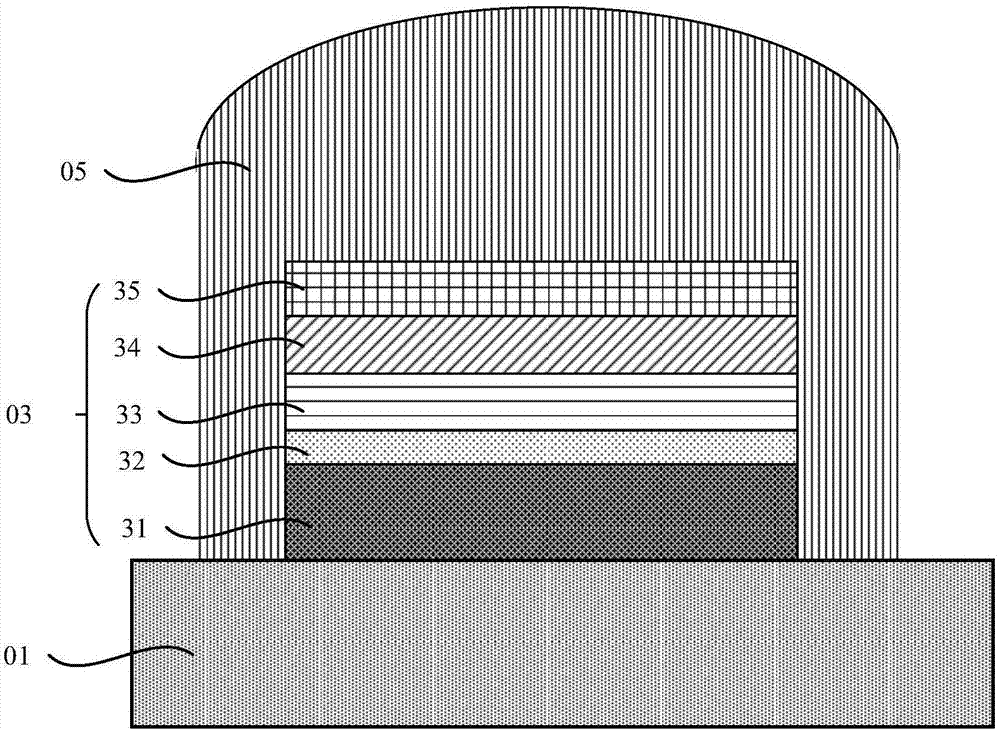
[0043] See figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of an LED package structure provided by an embodiment of the present invention. The structure includes:
[0044] heat dissipation substrate 01;
[0045] The ultraviolet lamp wick 03 is arranged on the upper surface of the heat dissipation substrate;
[0046] The silica gel layer 05 is disposed on the heat dissipation substrate and the upper surface of the ultraviolet lamp wick.
[0047] Wherein, the material of the heat dissipation substrate 01 is copper.
[0048] Further, the outer side of the heat dissipation substrate 01 is provided with circular grooves along the width direction and parallel to the plane of the heat dissipation substrate; wherein, the diameter of the circular grooves is 0.3-2 mm, and the spacing between the circular grooves is 0.5-10 mm.
[0049] Wherein, the ultraviolet lamp wick 03 includes an n-AlGaN layer 32, an MQW layer 33, a p-AlGaN layer 34, and a p-GaN layer 35 sequentially disposed on ...
Embodiment 2
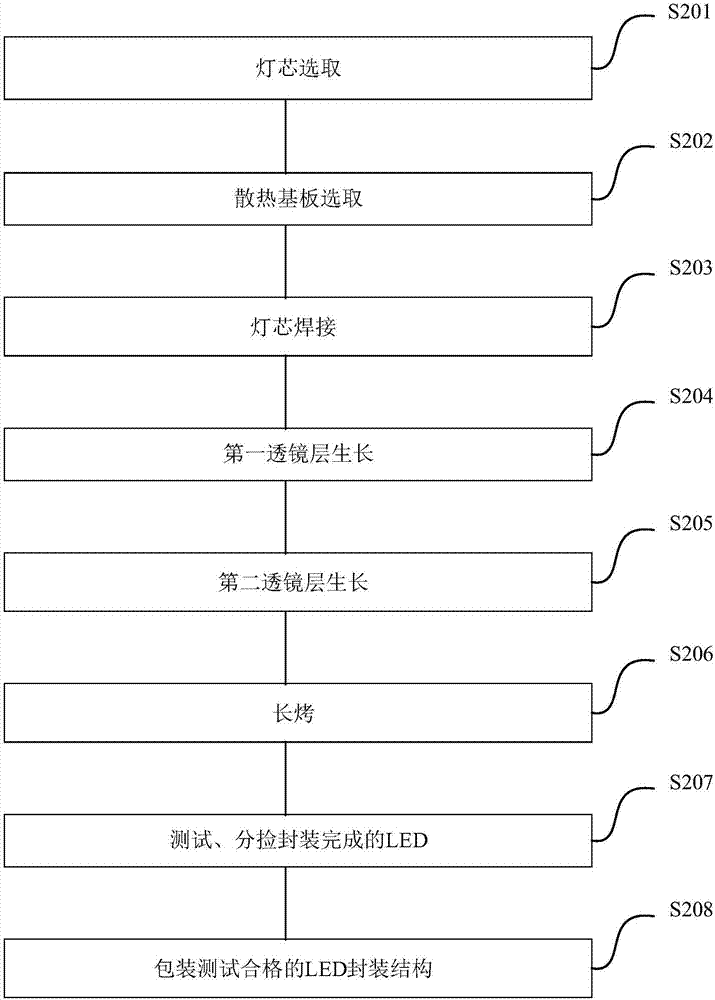
[0066] See figure 2 , figure 2 This is a flow chart of a method for packaging a double-lens layer LED according to an embodiment of the present invention. On the basis of the above embodiments, this embodiment will introduce the process flow of the double-lens layer LED package proposed by the present invention in more detail. The method includes:
[0067] S201, wick selection
[0068] The UV wick was chosen as the wick of the LED.
[0069] S202, heat dissipation substrate selection
[0070] Only a part of the LED input power is converted into light energy, and the rest is converted into heat energy. Therefore, for LED chips, especially LED chips with high power density, how to control their thermal energy is an important problem that LED manufacturing and lamps should focus on. The heat of high-power diodes, high-power triodes, IGBTs, and MOSFETs can be dissipated through an external radiator with almost unlimited size installed on the chassis of the instrument, or a ...
Embodiment 3
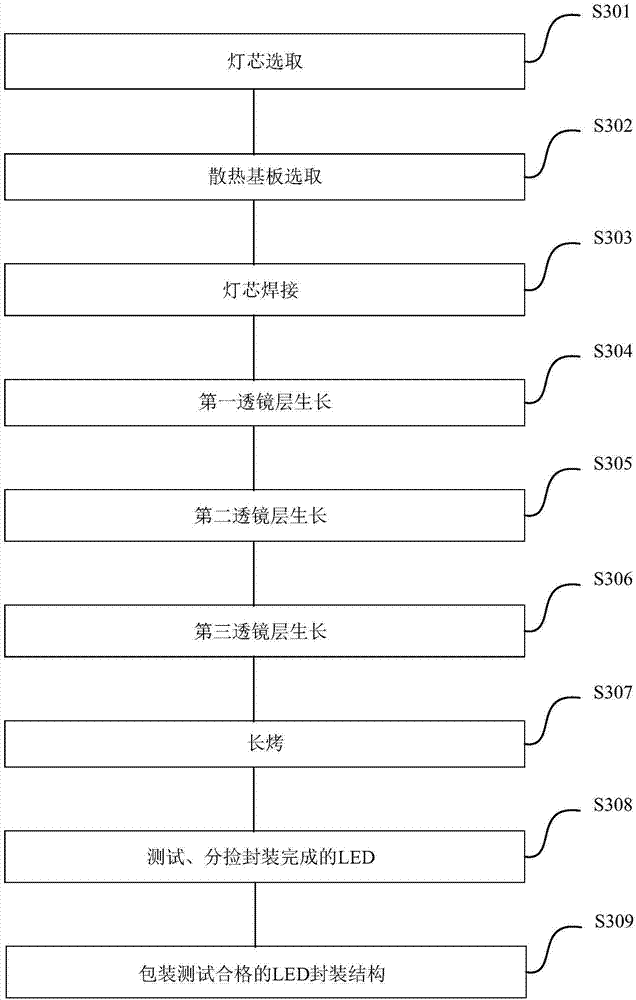
[0115] See image 3 , image 3 A flow chart of a three-layer lens layer LED packaging method provided in an embodiment of the present invention. On the basis of the above embodiments, this embodiment will introduce the process flow of the three-layer lens layer LED packaging proposed by the present invention in more detail. include:
[0116] S301, wick selection
[0117] The UV wick was chosen as the wick of the LED.
[0118] S302, heat dissipation substrate selection
[0119] S3021, bracket / cooling substrate preparation
[0120] Metal copper is selected as the material of the heat dissipation substrate, and the thickness of the heat dissipation substrate is 0.5-10 mm. The outer side of the heat dissipation substrate is provided with a circular groove along the width direction and parallel to the plane of the heat dissipation substrate; wherein the diameter of the circular groove is 0.3-2 mm, and the distance between the circular grooves is 0.5-10 mm. The circular groov...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com