Rotating electric machine
A technology for rotating electrical machines and rotors, applied in the field of rotating electrical machines, can solve the problems of difficult winding operations, deterioration of manufacturability, and lengthening of the stator axis, and achieve the effects of improving the space factor, improving the manufacturability, and shortening the length.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
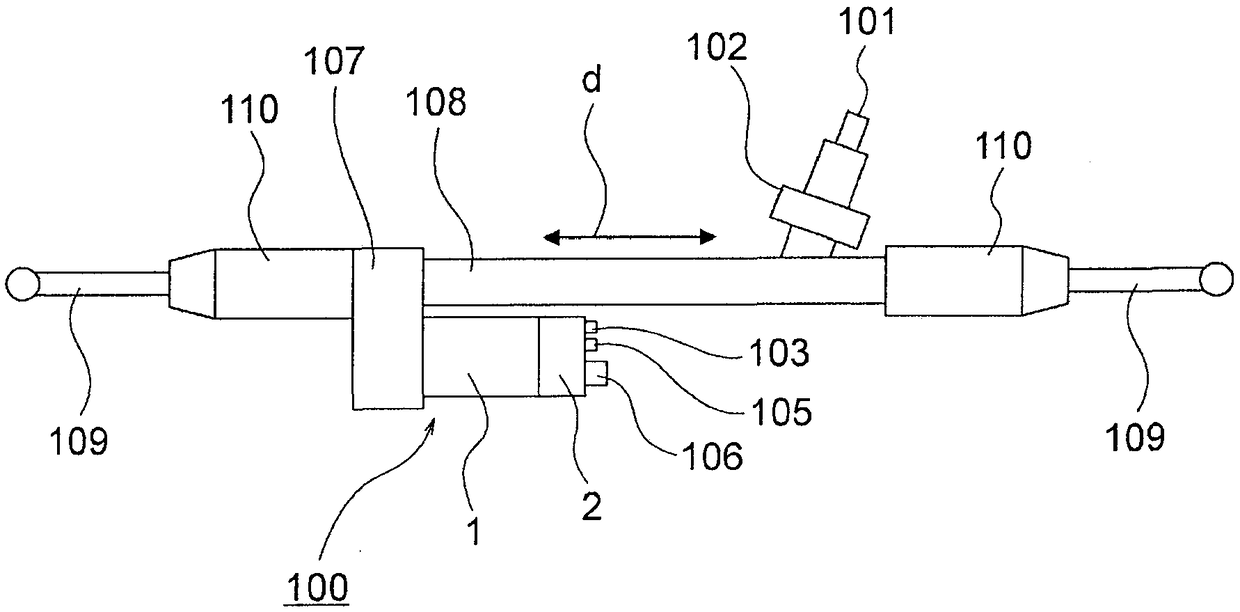
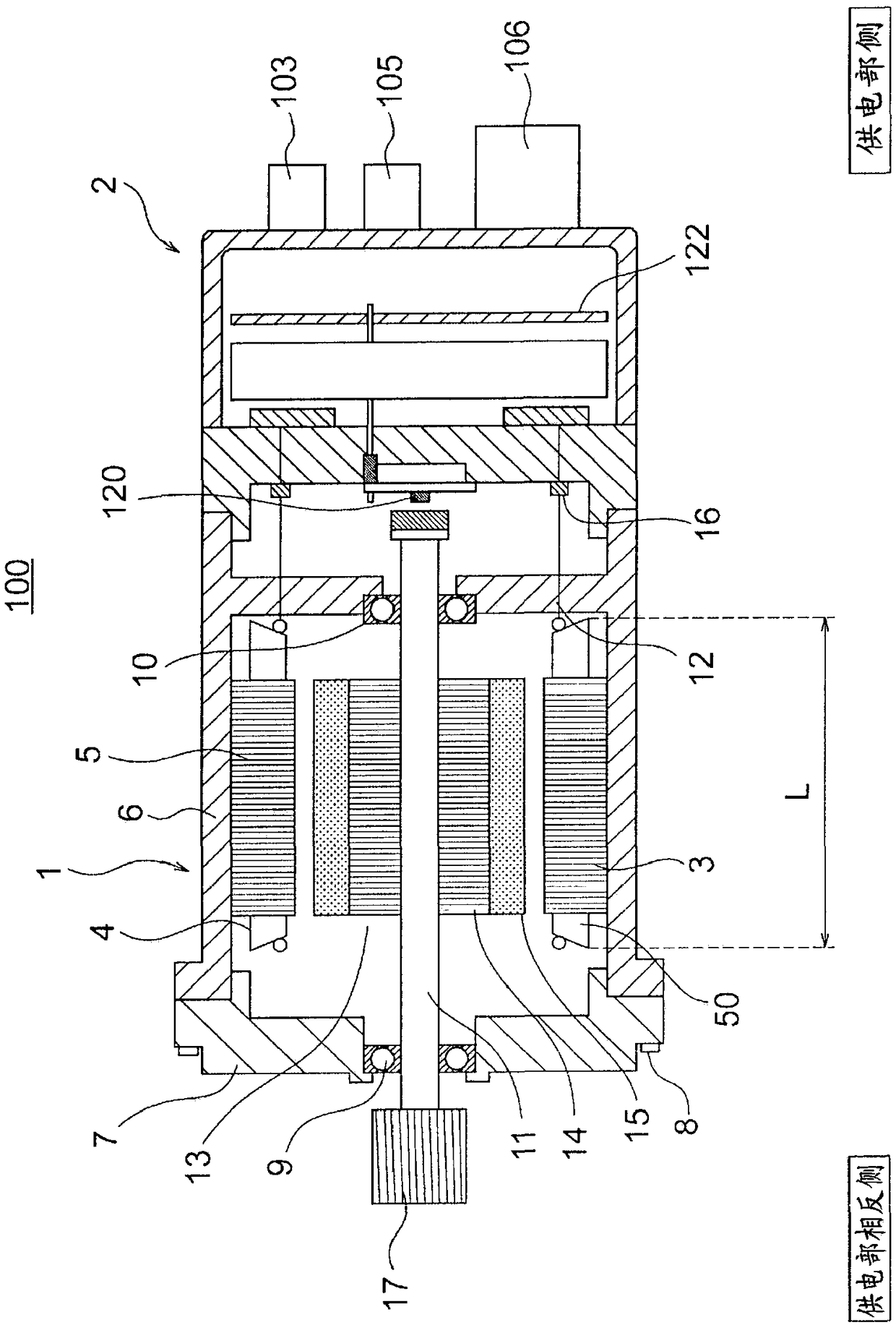
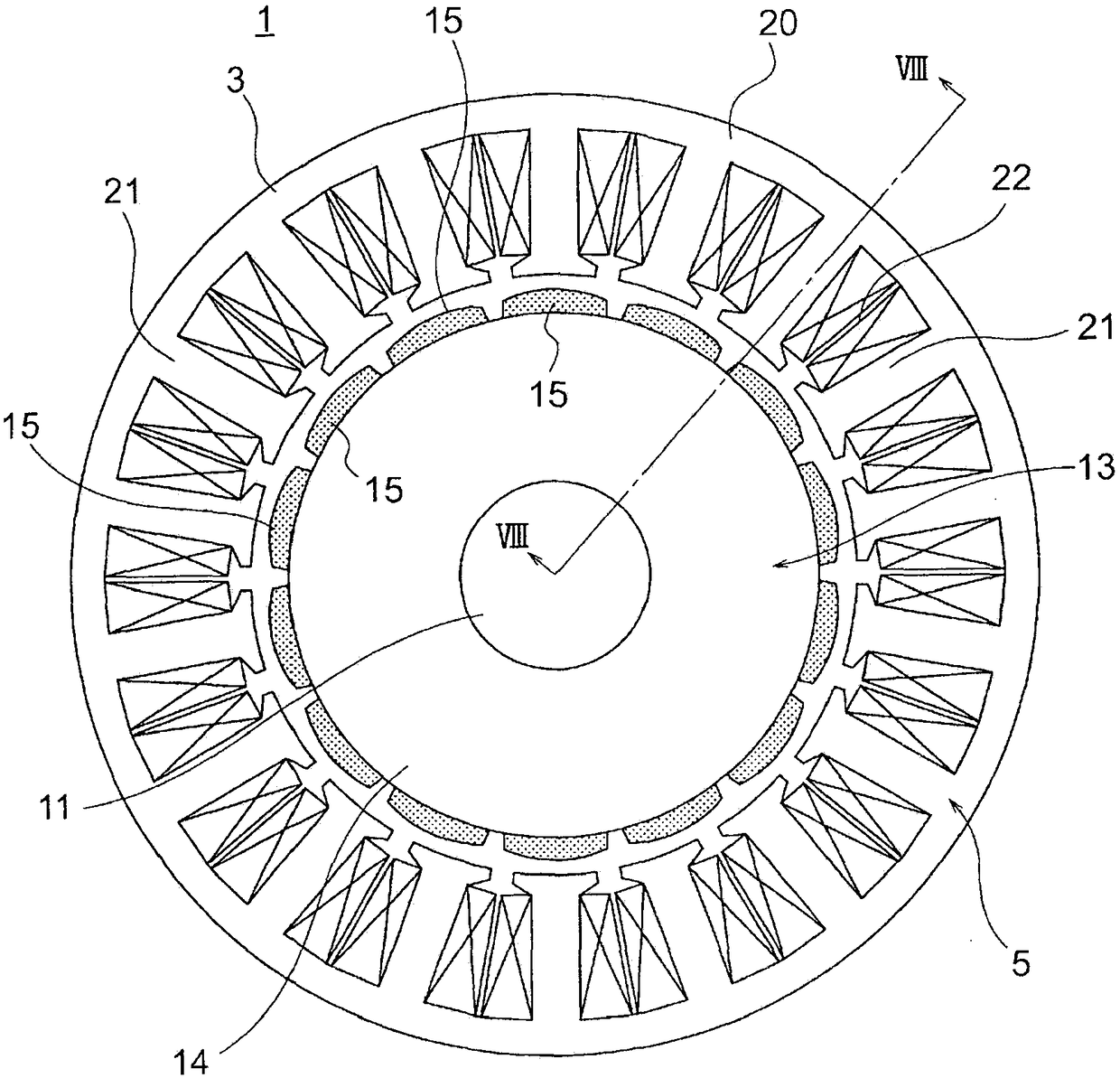
[0049] figure 1 It is a block diagram showing the electric power steering apparatus of the automobile in which the electric motor 1 according to the first embodiment of the present invention is mounted, figure 2 is shown figure 1 The cross-sectional view of the electric drive device 100, image 3 is shown figure 2 The main sectional view of the motor 1, Figure 4 is shown image 3 The main cross-sectional view of the stator 5.
[0050] The electric power steering apparatus includes an electric drive device 100 including an electric motor 1 as a rotating electrical machine, and an ECU 2 (Electric Control Unit) 2 .
[0051] In this electric power steering apparatus, a driver steers a steering wheel (not shown), and the torque thereof is transmitted to the shaft 101 via a steering shaft (not shown). At this time, the torque detected by the torque sensor 102 is converted into an electric signal and transmitted to the ECU 2 via the first connector 103 through a cable (not s...
Embodiment approach 2
[0129] Figure 10 It is a longitudinal cross-sectional view which shows the electric motor 1 which concerns on Embodiment 2 of this invention.
[0130] In this electric motor 1, the number of poles of the rotor 13 is 28, and the number of the teeth 21 of the stator core 3 is 36.
[0131] The rotor 13 is provided with a shaft 11 and a rotor core 14 provided outside the shaft 11 , and 28 permanent magnets 15 are attached to the outer peripheral surface of the rotor core 14 at equal intervals in the circumferential direction.
[0132] Furthermore, although in Figure 10 Although omitted here, in order to protect the permanent magnets 15 and prevent scattering of the permanent magnets 15 , the outer side of the permanent magnets 15 may be covered with a cover made of a non-magnetic material such as stainless steel or aluminum in a cylindrical shape.
[0133] The stator 5 includes a stator core 3 and an armature winding 4 wound around the stator core 3 .
[0134] The stator core...
Embodiment approach 3
[0163] Figure 12 It is a longitudinal cross-sectional view which shows the electric motor 1 which concerns on Embodiment 3 of this invention.
[0164] The number of poles of the rotor 13 of this motor is ten, and the number of the teeth 21 of the stator core 3 is twelve.
[0165] The rotor 13 includes a shaft 11 , a rotor core 14 provided outside the shaft 11 , and ten permanent magnets 15 affixed to the outer peripheral surface of the rotor core 14 at equal intervals in the circumferential direction.
[0166] Furthermore, although in Figure 12 Although omitted here, in order to protect the permanent magnet 15 and prevent the permanent magnet 15 from scattering, the outer side of the permanent magnet 15 may be covered with a cover made of a non-magnetic material such as stainless steel or aluminum in a cylindrical shape.
[0167] The stator 5 includes a stator core 3 and an armature winding 4 wound around the stator core 3 .
[0168] The stator core 3 has an annular core ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com