Polybutylene succinate composite material and preparation method thereof
A technology of polybutylene succinate and polybutylene succinate is applied in the field of biodegradable polymer materials to achieve the effects of improving mechanical properties, excellent mechanical properties and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
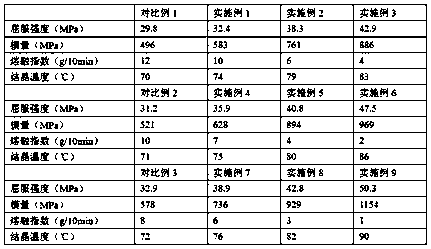
[0024] Add 100 parts by weight of polybutylene succinate with a weight-average molecular weight of 50,000 and 3 parts by weight of poly-L-lactic acid with a weight-average molecular weight of 100,000 into an internal mixer, at 165 ° C, 80 rpm Mix for 10 minutes under the same conditions, then add 7 parts by weight of D-lactic acid with a weight average molecular weight of 100,000 and mix for 20 minutes under the same conditions, and cool to room temperature after blending, which is polybutylene succinate reinforced by stereocomplex polylactic acid. Glycol ester composites. The composite materials were tested by tensile mechanics, melt index and DSC. The results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0026] 100 parts by weight of polybutylene succinate with a weight-average molecular weight of 50,000 and 14 parts by weight of poly-L-lactic acid with a weight-average molecular weight of 20,000 were added to the internal mixer at 165°C and 80 rpm. Mix for 15 minutes under the same conditions, then add 6 parts by weight of D-lactic acid with a weight average molecular weight of 20,000 under the same conditions and mix for 15 minutes. Glycol ester composites. The composite materials were tested by tensile mechanics, melt index and DSC. The results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Add 100 parts by weight of polybutylene succinate with a weight-average molecular weight of 50,000 and 24 parts by weight of poly-L-lactic acid with a weight-average molecular weight of 200,000 into an internal mixer at 165°C and 80 rpm. Mix for 12 minutes under the same conditions, then add 16 parts by weight of D-lactic acid with a weight average molecular weight of 50,000 and mix for 18 minutes under the same conditions, and cool to room temperature after blending, which is polybutylene succinate reinforced by stereocomplex polylactic acid. Glycol ester composites. The composite materials were tested by tensile mechanics, melt index and DSC. The results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com