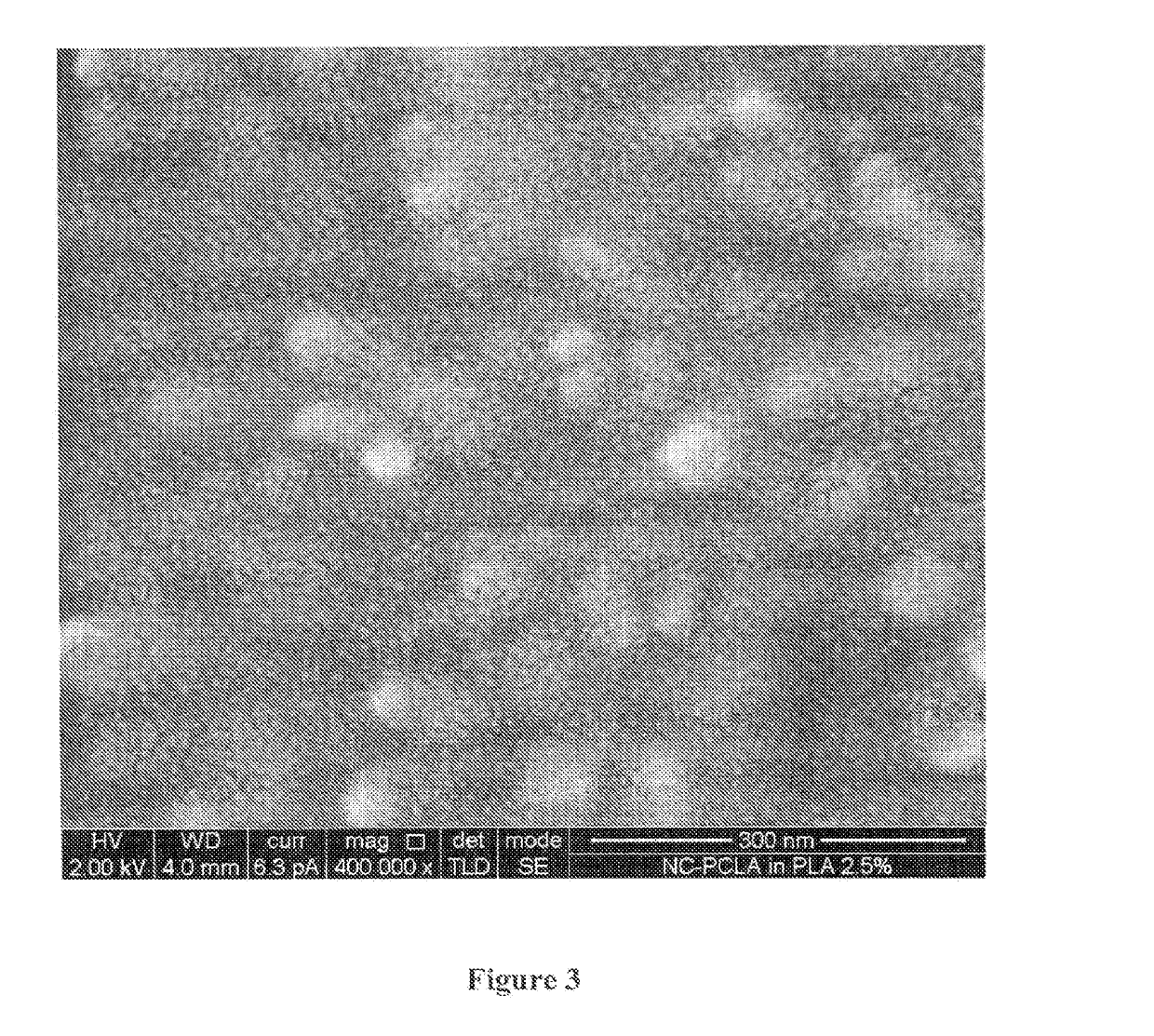
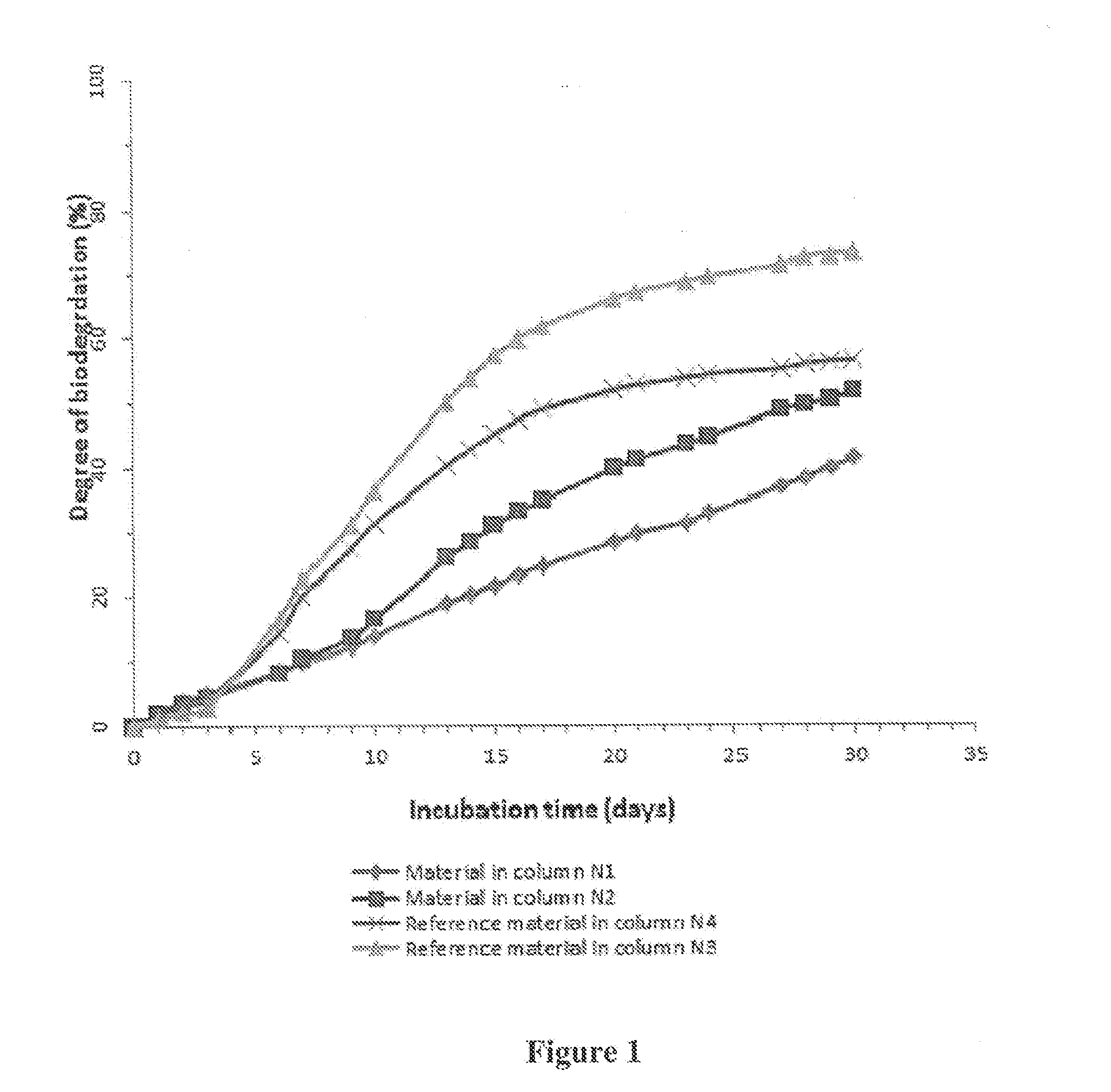
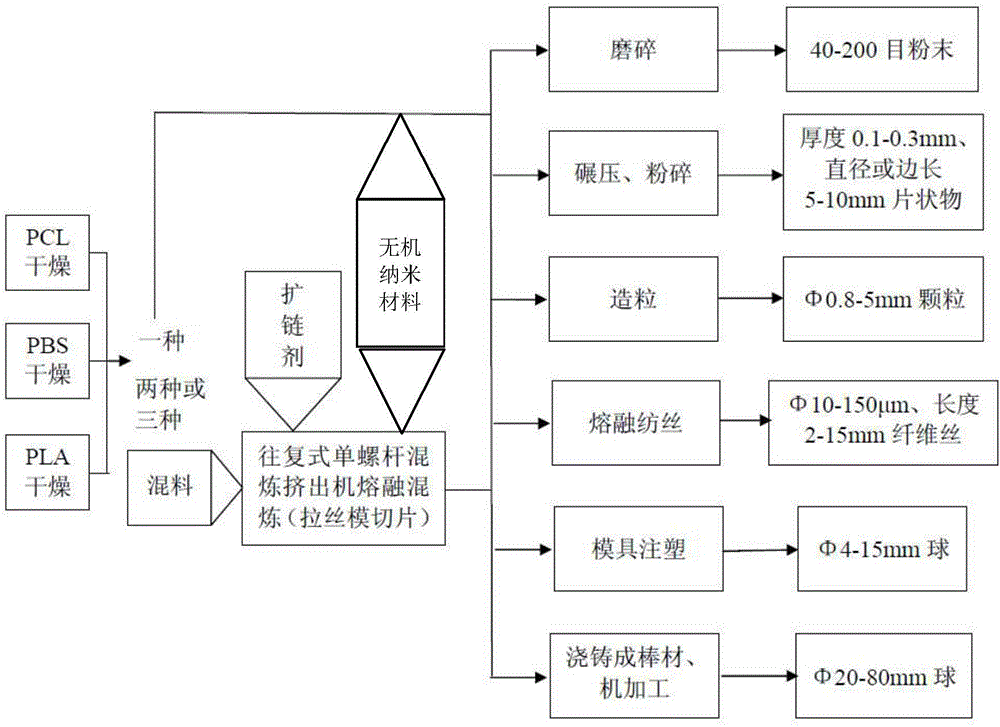
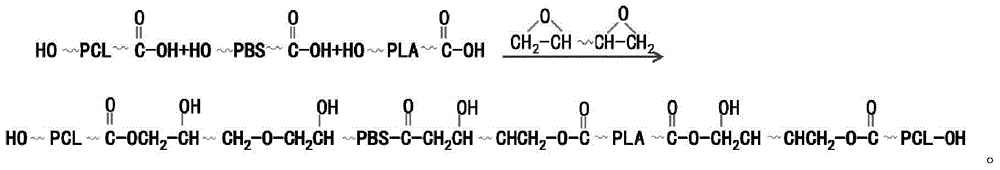
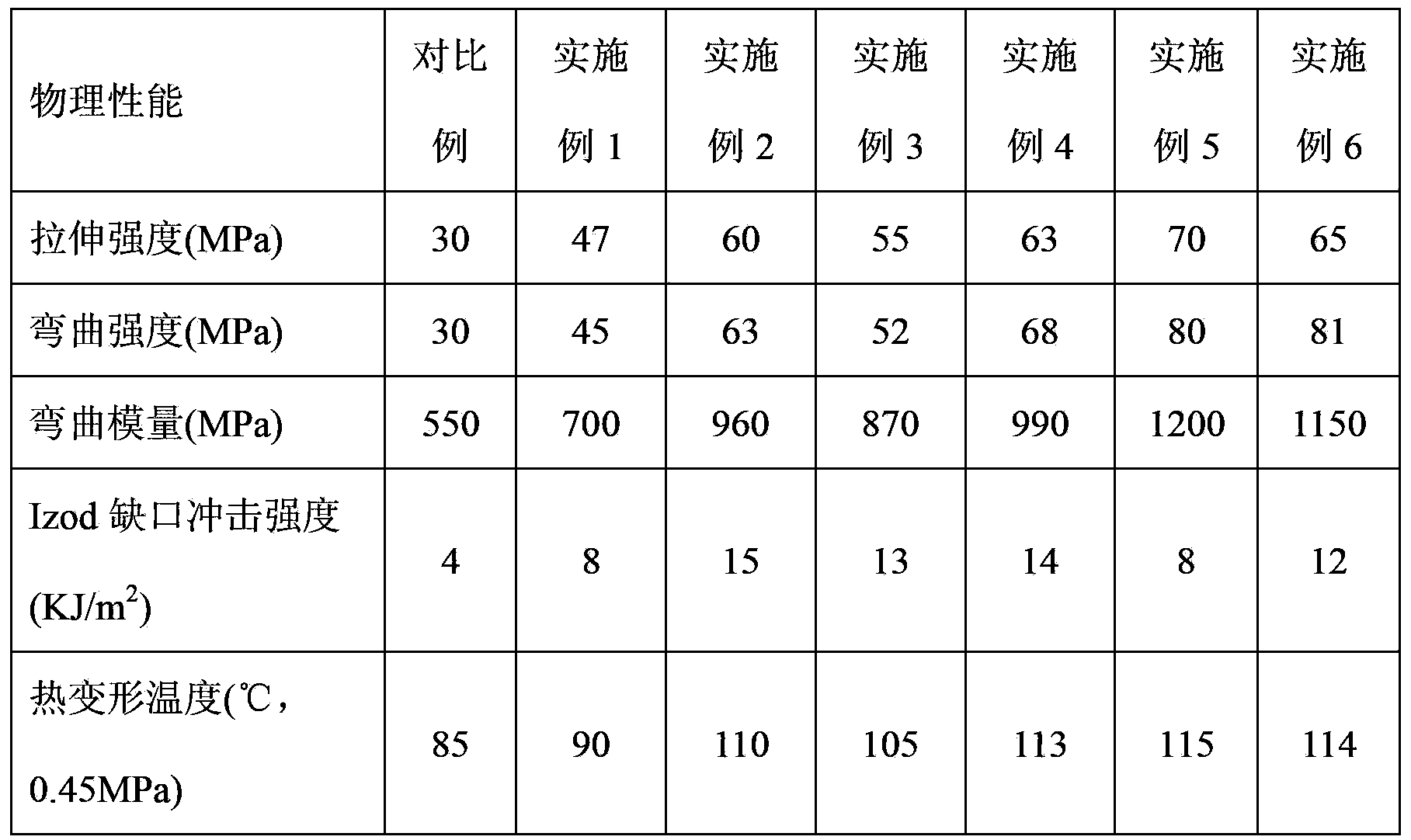
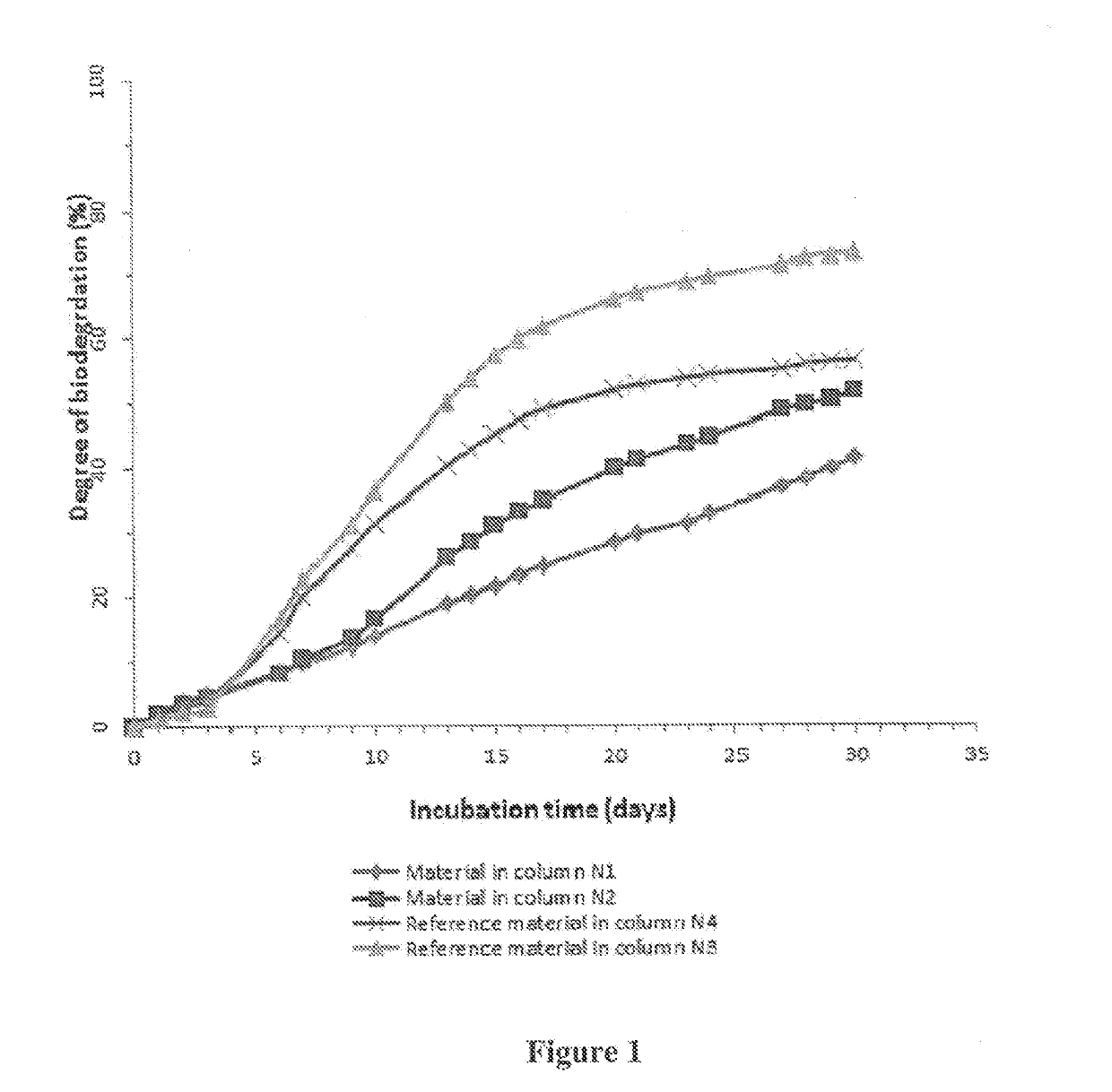
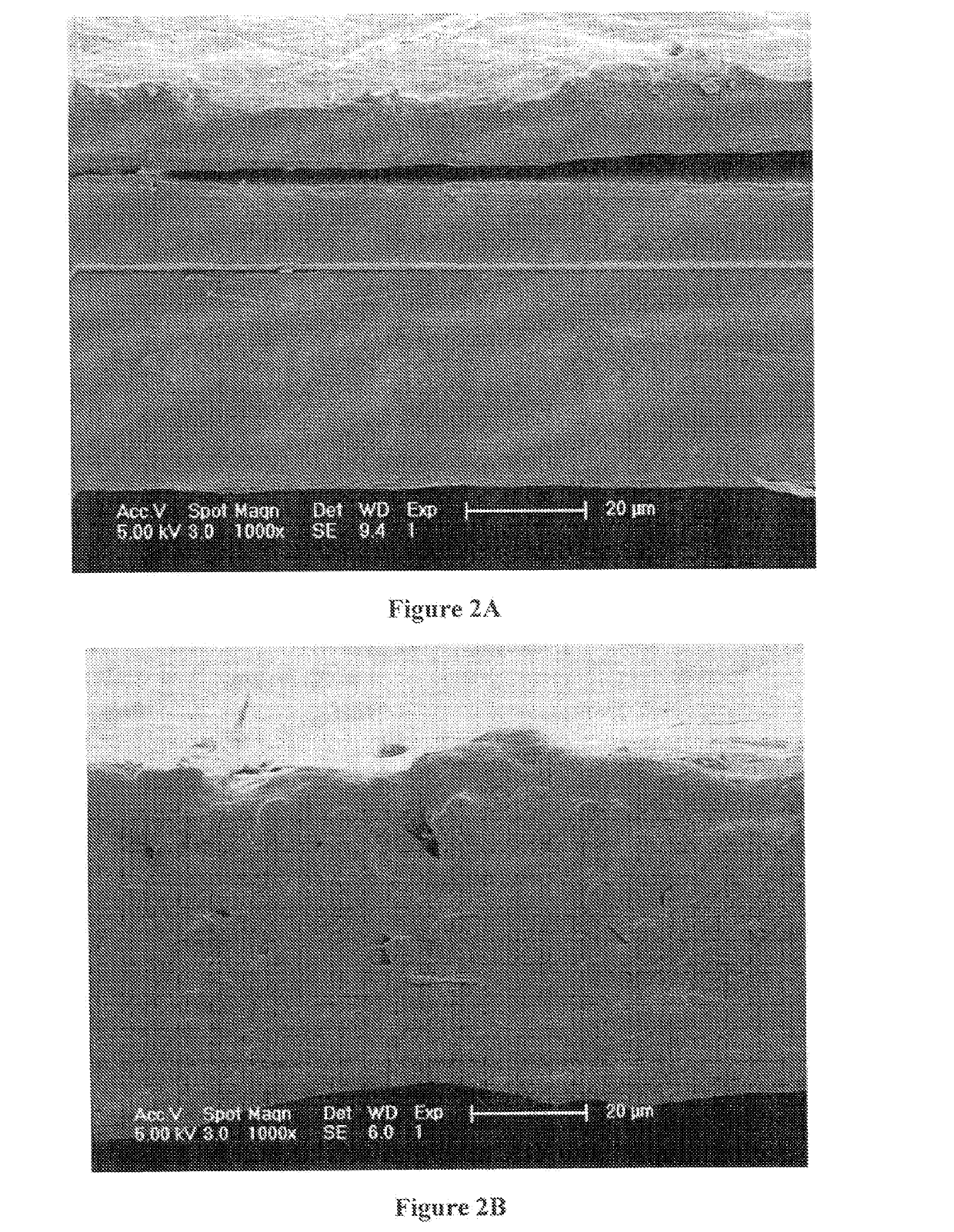
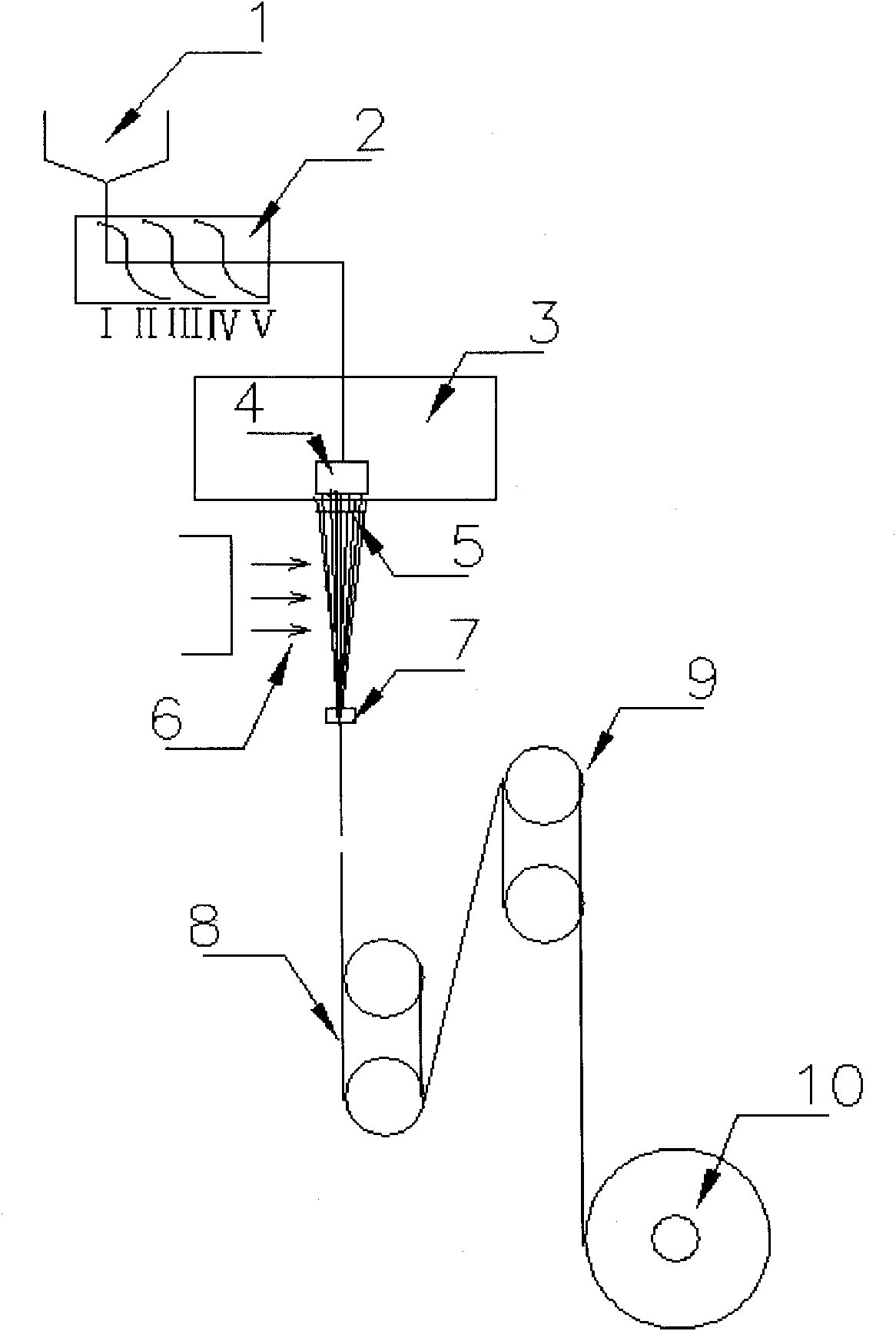
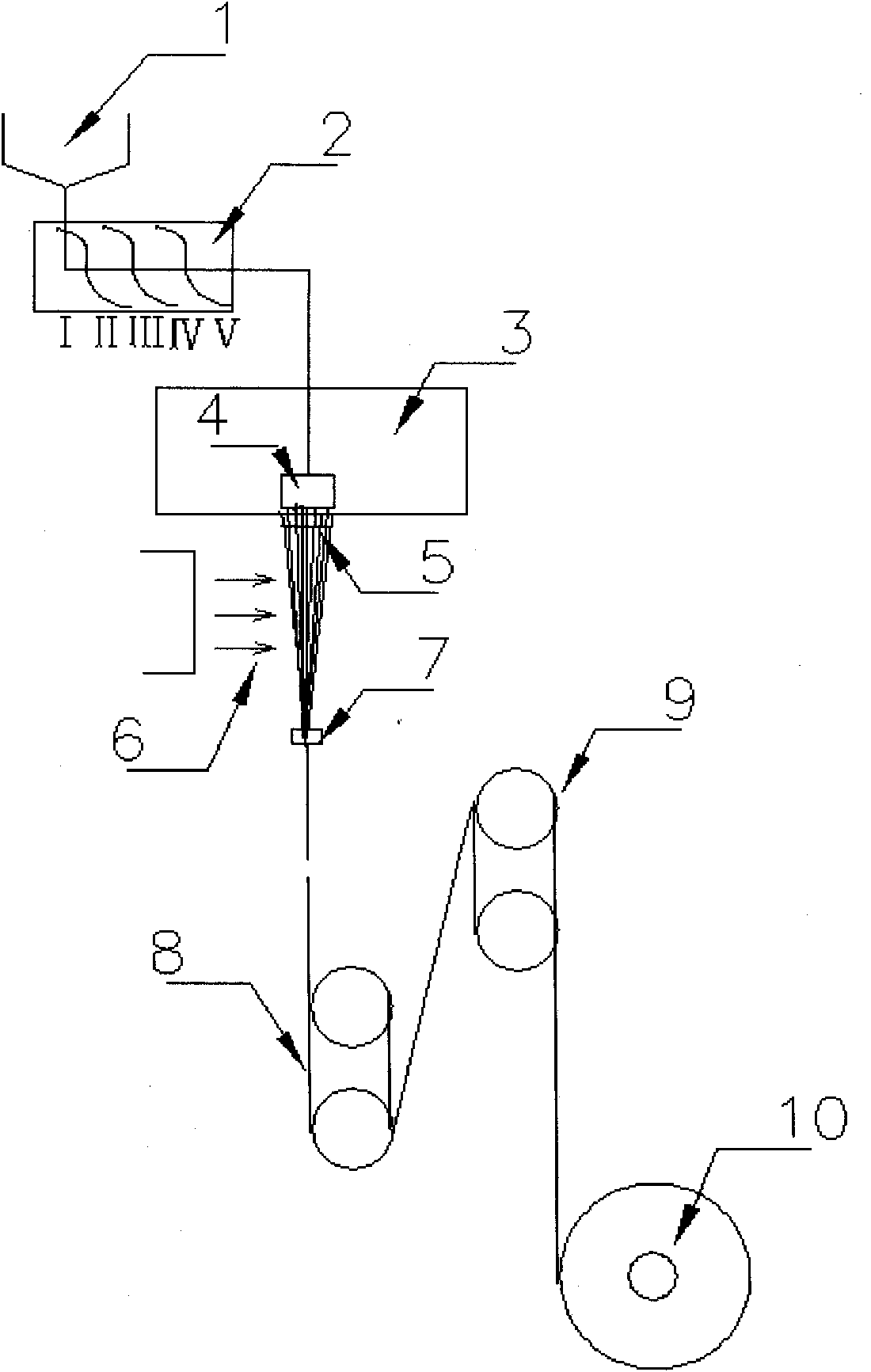
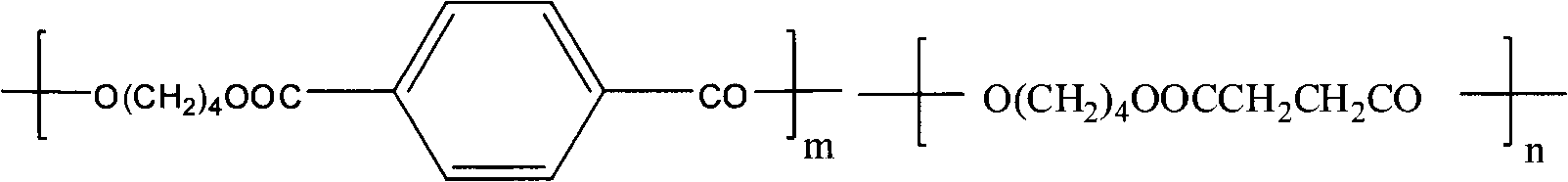Patents
Literature
535 results about "Polybutylene succinate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polybutylene succinate (PBS) (sometimes written polytetramethylene succinate) is a thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family. PBS is a biodegradable aliphatic polyester with properties that are comparable to polypropylene.
Biodegradable bicomponent fibers with improved thermal-dimensional stability
InactiveUS6953622B2Improve wettabilityImprove bindingConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsYarnFiberPolyester
A biodegradable hydrophilic binder fiber. These fibers may be produced by co-spinning an aliphatic polyester material in a side-by-side configuration with a polylactide polymer to obtain a fiber with improved material attributes. A multicarboxylic acid may be incorporated into either or both components of the fiber. The aliphatic polyester polymer may be selected from a polybutylene succinate polymer, a polybutylene succinate-co-adipate polymer, or a blend of these polymers. The biodegradable bicomponent fiber exhibits substantial biodegradable properties, yet has improved thermal stability and has significantly reduced shrinkage. The bicomponent fiber may be used in a disposable absorbent product intended for the absorption of fluids such as body fluids.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Material capable of completely biodegrading and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a material capable of completely biodegrading, containing the following parts by weight:100 of polyester resin, 5-100 of polylactic resin and the multipolymer thereof, 10-80 of compounding converted starch, 10-60 of inorganic fillers and 0.1-0.9 of resin acceptor, wherein the polyester resin is at least one of polybutylene succinate resin, polybutylene adipate resin and the multipolymer thereof. The invention also provides a preparation method of the material. The material capable of completely biodegrading can combine the advantages of each component and has high intensity, modules, elongation at break and toughness, good heat resistance, and the like, thereby meeting the property requirements of a plurality of plastic products in the market and in particular products, such as non-returnable containers, mess kits, agricultural films, and the like, which cause serious white pollution, retaining the complete biodegradability of the material and reducing the production cost under the precondition of no influence on the property requirement.
Owner:深圳市未名北科环境材料有限公司 +1
Degradable film containing starch and preparation method of degradable film
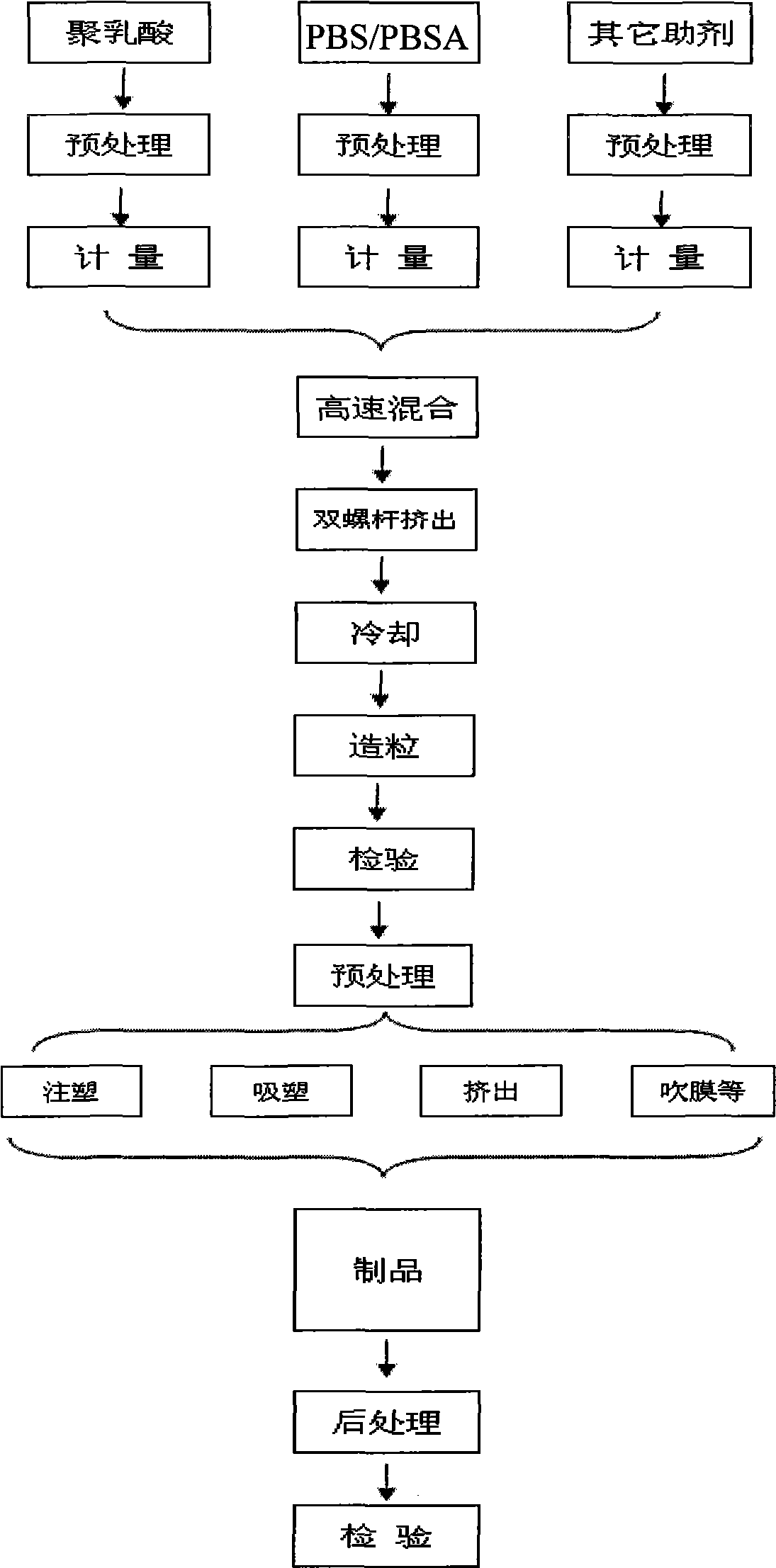
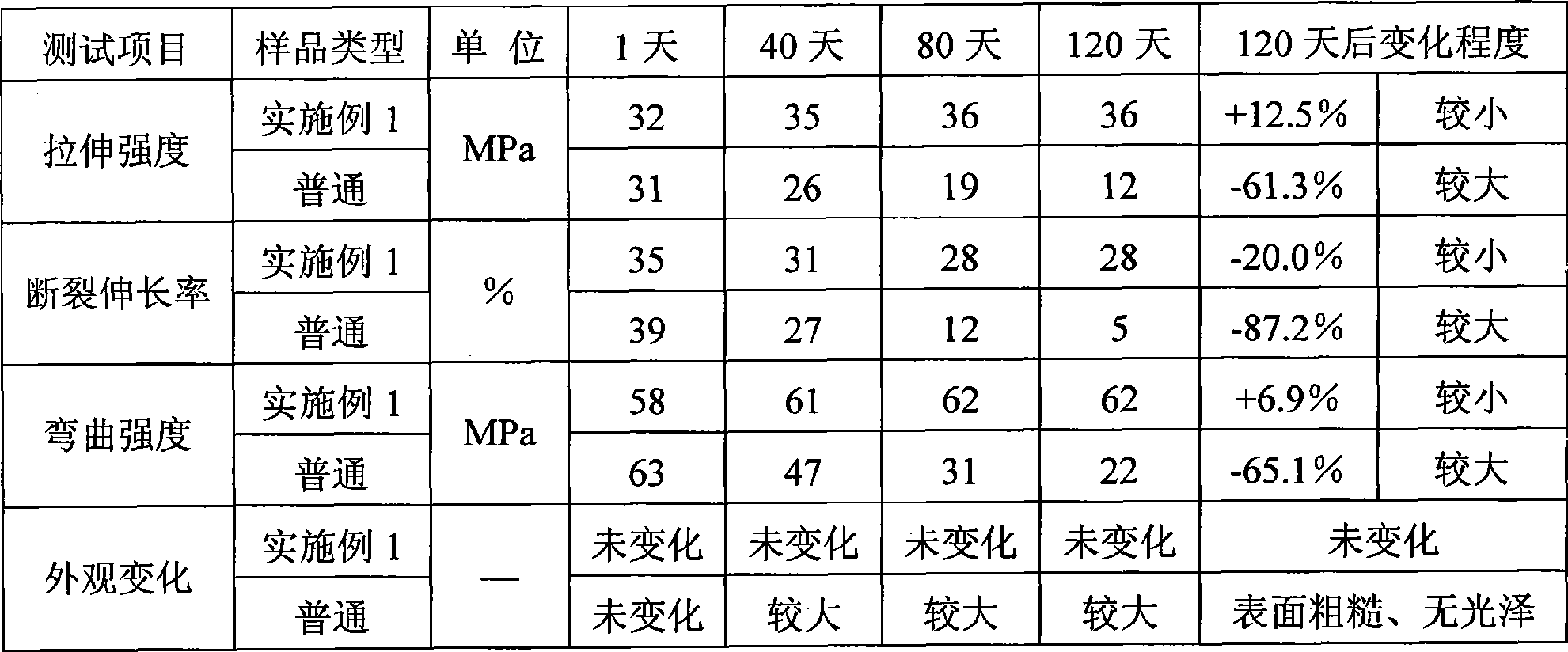
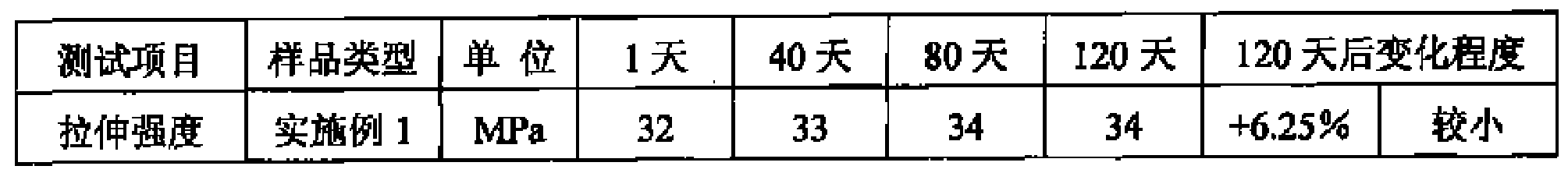
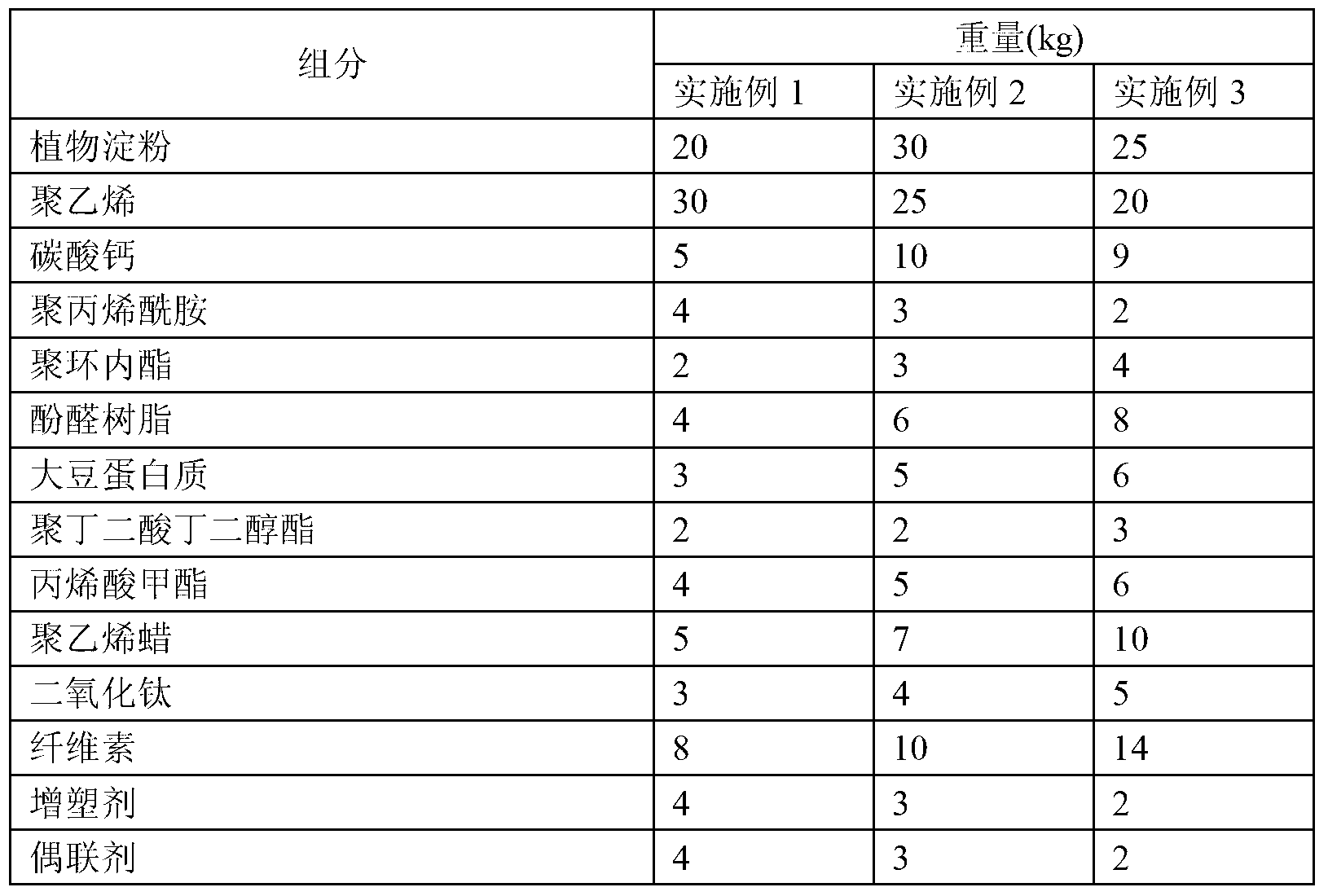
The invention provides an agricultural film material and particularly relates to a degradable film material containing starch serving as a raw material, belonging to the technical field of high molecular materials. The degradable film comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20-30 parts of plant starch, 20-30 parts of polyethylene, 5-10 parts of calcium carbonate, 2-4 parts of polyacrylamide, 2-4 parts of poly cyclic lactone, 4-8 parts of phenol aldehyde resin, 3-6 parts of soybean protein, 2-3 parts of polybutylene succinate, 4-6 parts of methyl acrylate, 5-10 parts of polyethylene wax, 3-5 parts of titanium dioxide, 8-14 parts of cellulose, 2-4 parts of plasticizer and 2-4 parts of coupling agent. The degradable film provided by the invention has excellent strength, the tensile strength of the degradable film can be higher than 16MPa, the light transmittance can be higher than 88%, and the degradable film can be generally degraded within 4-6 months.
Owner:SUZHOU FUTONG NEW MATERIALS & HIGH TECH
Biologic degradable copolyester and preparation process thereof
A biodegradable copolyester (butanediester polysuccinate for example) is prepared from butanedioic acid, butanediol, copolydiol and copolydiacid through copolymerizing to obtain atactic linear copolyester, and condensation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Starch-based biodegradable material composition
ActiveUS20090075346A1Overcomes drawbackSugar derivativesHydrolasesCopolyesterPoly(butylene succinate)
A starch-based biodegradable material composition includes: an enzyme-hydrolyzed starch; and a biodegradable polyester selected from at least one of an aliphatic polyester of polybutylene succinate and an aliphatic-aromatic copolyester. The enzyme-hydrolyzed starch is prepared by hydrolyzing a native starch using a starch-hydrolyzing enzyme. The starch-hydrolyzing enzyme has an activity unit ranging from 15000 to 40000.
Owner:GRACE BIOTECH CORP
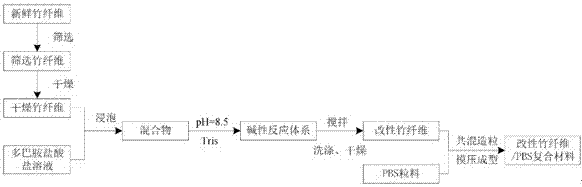
Technique for improving interfacial compatibility of bamboo fiber and polybutylene succinate based on polydopamine bionic interfacial modification modifier
InactiveCN107459830ALow priceGood dimensional stabilityBiocompatibility TestingPoly(butylene succinate)
The invention discloses a method for preparing a bionic modified bamboo fiber reinforced polybutylene succinate (PBS) composite material. The method comprises the following steps: (1) screening a bamboo fiber, keeping the length less than 380mu m, and performing soaking treatment with a dopamine hydrochloride solution; 2) putting trismetyl aminomethane (Tris) into the soaked mixed system to adjust the pH value to alkalescence, stirring at normal temperature and normal pressure, filtering, and drying so as to obtain a polydopamine modified bamboo fiber of which the water content is less than 1%; and 3) uniformly mixing the modified bamboo fiber with PBS granules in a mass ratio of 1:1 in a high-speed mixing machine, pelletizing in a double-screw extruder, performing compression molding on mixed granules in a hot press, naturally cooling in a cold press, and demolding, thereby obtaining a modified bamboo fiber / PBS composite material. According to the method disclosed by the invention, dopamine has biocompatibility, the fiber is slightly damaged, no complex container is needed in the modification process, the production method is simple and convenient and safe and environmentally friendly, and the mechanical properties of the composite material are remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Catalyst for preparing polybutylene succinate and copolyesters thereof and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a catalyst for preparing polybutylene succinate and copolyesters thereof and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) adding titanium alkoxides, silica-alkoxides, dibastic alcohol and a metal cocatalyst into solution for reaction at a temperature of between 80 and 180DEG C, and separating and removing unreacted substances and micromolecular products in a reaction system; and (2) adding a complexing agent for continuous reaction and collecting the catalyst in reaction products. Or the preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) adding titanium alkoxides, dibastic alcohol and a metal cocatalyst into solution for reaction at a temperature of between 80 and 180DEG C, and separating and removing unreacted substancesand micromolecular products in a reaction system; and (2) adding silica-alkoxides and a complexing agent for continuous reaction and collecting the catalyst in reaction products. The catalyst has high catalytic activity, low addition volume, good product quality, no reaction when meeting water at normal temperature, easy long-term storage and good industrial application prospect and value.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAMING HI TECH GRP
Biodegradable coated carbamide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101723751AReduce releaseReduce rateUrea compound fertilisersFertilizer mixturesCoated ureaNitrification inhibitors
The invention relates to coated carbamide, in particular to a totally biodegradable coated carbamide and a preparation method thereof. The coated carbamide consists of a coated layer and a carbamide core. The main body of the coated layer is polylactic acid and / or polybutylene succinate. The coating process adopts fluidized bed spraying-coated technology, and comprises the following steps: dissolving polylactic acid and / or polybutylene succinate in trichloromethane, adding carboxymethylcellulose, organic and / or inorganic conditioner, urease and / or nitrification inhibitor in the solution, spraying and coating the surfaces of the fluidized carbamide after uniformly mixing the mixture under the stirring of a stirrer to form the uniform and complete organic polymeric membrane layer. The process has the advantages of easy implementation, and capacity of effectively slowing down the release of the nutrient to the outside and the conversion rate of nitrogen in soils, effectively controlling the release of the nitrogen nutrient in soils, and reducing the pressure on environment caused by the rapid release of nutrient. The coated material can be totally biodegradable, and the degradation products have no secondary pollution to the environment.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low Glass Transition Polyhydroxyalkanoates for Modification of Biodegradable Polymers
ActiveUS20150147929A1Improve propertiesHigh strengthWoven fabricsNon-woven fabricsPolytetramethylene terephthalateVitrification
Compositions of biobased polymer blends of polymers of polybutylene succinate (PBS) or polybutylene-adipate-terephthalate (PBAT) and a polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer are described. In certain embodiments, the copolymer is a multiphase copolymer blend having one phase a glass transition temperature of about −5° C. to about −50° C. Methods of making the compositions of the invention are also described. The invention also includes articles, films and laminates comprising the compositions.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
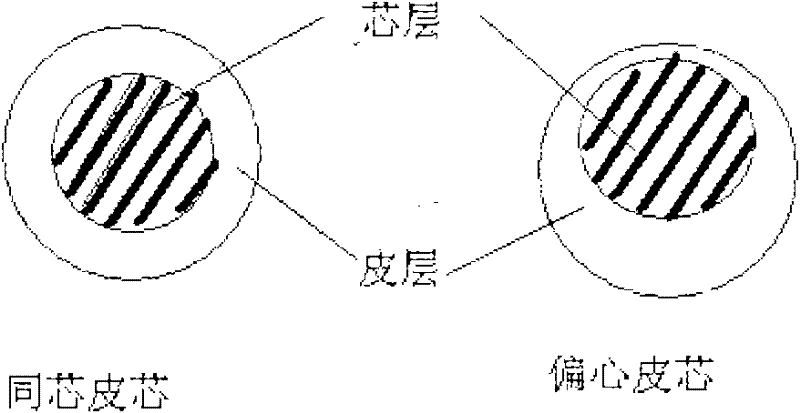
Biodegradable two-component low-melting point composite fiber
The invention provides a biodegradable two-component low-melting point composite fiber. The material of the biodegradable two-component low-melting point composite fiber comprises poly (butylene succinate) (PBS) and another biodegradable polymer; and the cross section of a fiber made of the two materials has a sheath and core structure. In particular, in the biodegradable two-component low-melting point composite fiber, the PBS is used as a sheath layer of the composite fiber; and polylactic acid esters (PLA) is used as a core layer of the composite fiber. An additive is added into the sheath layer PBS; and the additive is grafted by the sheath layer PBS and maleic anhydride or other unsaturated anhydride. The composite short fiber has complete biodegradability, can be well bonded to other fibers, in particular the fibers with cellulose as main constitutions; and the manufactured non-woven cloth has biodegradability and bio-decomposability.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF IND TECH
Full-biodegradation high-tenacity heat-resistant type polylactic resin and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101824211AGood mechanical propertiesImprove heat resistanceGlycidyl methacrylatePoly(butylene succinate)
The invention discloses full-biodegradation high-tenacity heat-resistant type polylactic resin and a preparation method thereof. The polylactic resin comprises polylactic resin, polybutylene succinate, dicumyl peroxide and glycidyl methacrylate; and the weight-average molecular weight of the polylactic resin is 8-13 ten thousand, and the weight-average molecular weight of the polybutylene succinate is 7-11 ten thousand. In parts by weight, the total amount of the polylactic resin and the polybutylene succinate is 100 parts, wherein the polylactic resin accounts for 70-90 parts, the polybutylene succinate accounts for 10-30 parts, the dicumyl peroxide accounts for 0.1-1 part, and the glycidyl methacrylate accounts for 1-10 parts. Compared with the prior art, the full-biodegradation high-tenacity heat-resistant type polylactic resin has good biodegradation property, mechanical property and heat-resisting property; and the preparation method has simple technique process, excellent processing performance and low cost, and can realize large-scale industrial production.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Biodegradable multilayer co-extrusion material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107031153APromote degradationWith natural propertiesSynthetic resin layered productsFlat articlesPolybutyleneMedical product
The invention provides a biodegradable multilayer co-extrusion material. The material is characterized by comprising two surface functional layers and a middle layer located between the two surface functional layers, components of the surface functional layers and the middle layer include biodegradable materials, and the biodegradable materials refer to one or more of polybutylene succinate, polylactic acid, polyhydroxyalkanoate and polybutylene adipate-polybutylene terephthalate. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the material. The biodegradablity of four selected master batches of the multilayer co-extrusion material is good, and adopted inorganic minerals are natural, so that the co-extrusion material has completely biodegradable properties and can be widely used in various types of food packages, medical products, environmental protection labels, advertisements and all kinds of environmental-protection products.
Owner:齐庆德
Resin Composition, Molded Product From Resin Composition and Method for Preparing Resin Composition
InactiveUS20070270527A1Eliminate the problemImprove flame retardant performanceConductive materialOrganic conductorsCellulosePolybutylene
Disclosed is a biodegradable resin composition containing at least one biodegradable organic high molecular compound, a flame retardant additive containing a phosphorus-containing compound, and a hydrolysis suppressing agent suppressing the hydrolysis of the at least one biodegradable organic high molecular compound. An aliphatic polyester resin is polylactic acid, polycaprolactone, polyhydroxy lactic acid, polyhydroxy valeric acid, polyethylene succinate, polybutylene succinate, polybutylene adipate, polymalic acid, polyesters synthesized by fermentation, or a copolymer containing at least one of them. A polysaccharide is cellulose, starch, chitin, chitosan, dextrane, a derivative of at least one of them, or a copolymer containing at least one of them.
Owner:LERNER DAVID LITTENBERG KRUMHOLZ & MENTLIK LLP
Polyphenol cross-linking agent and application thereof to preparation of anti-calcification biovalve
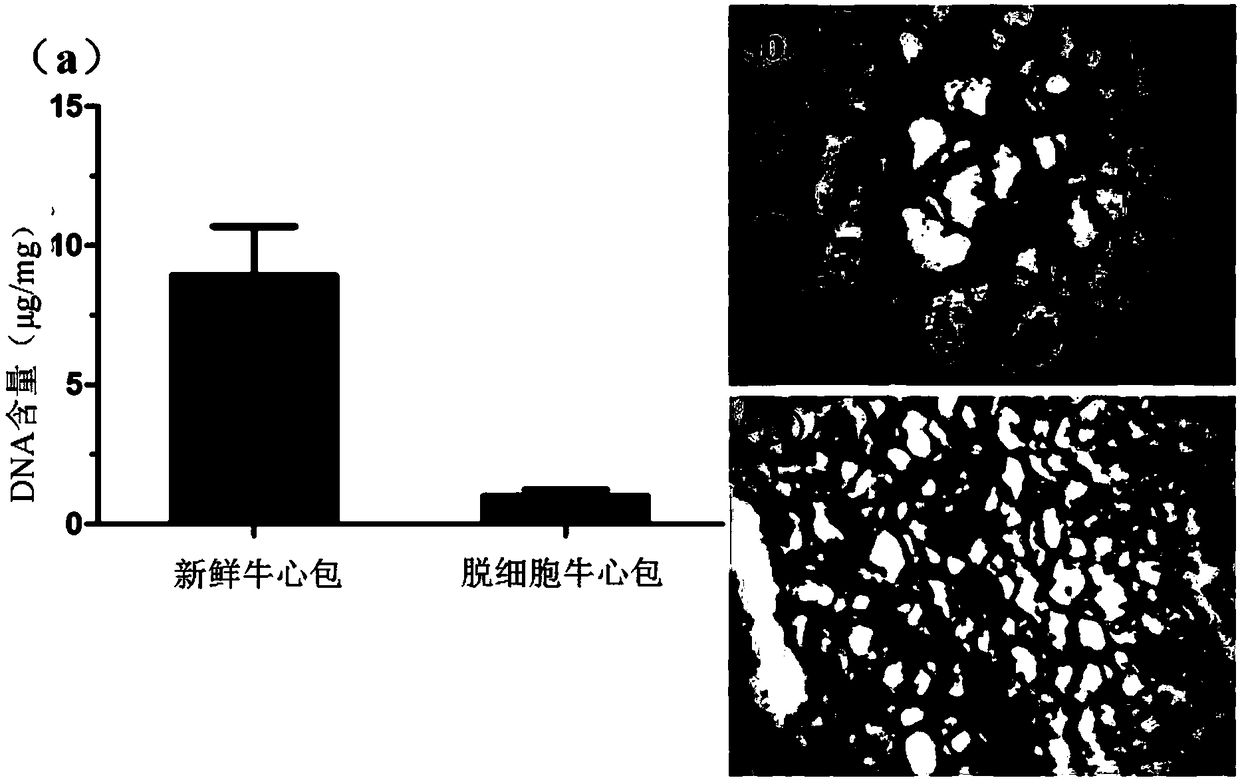
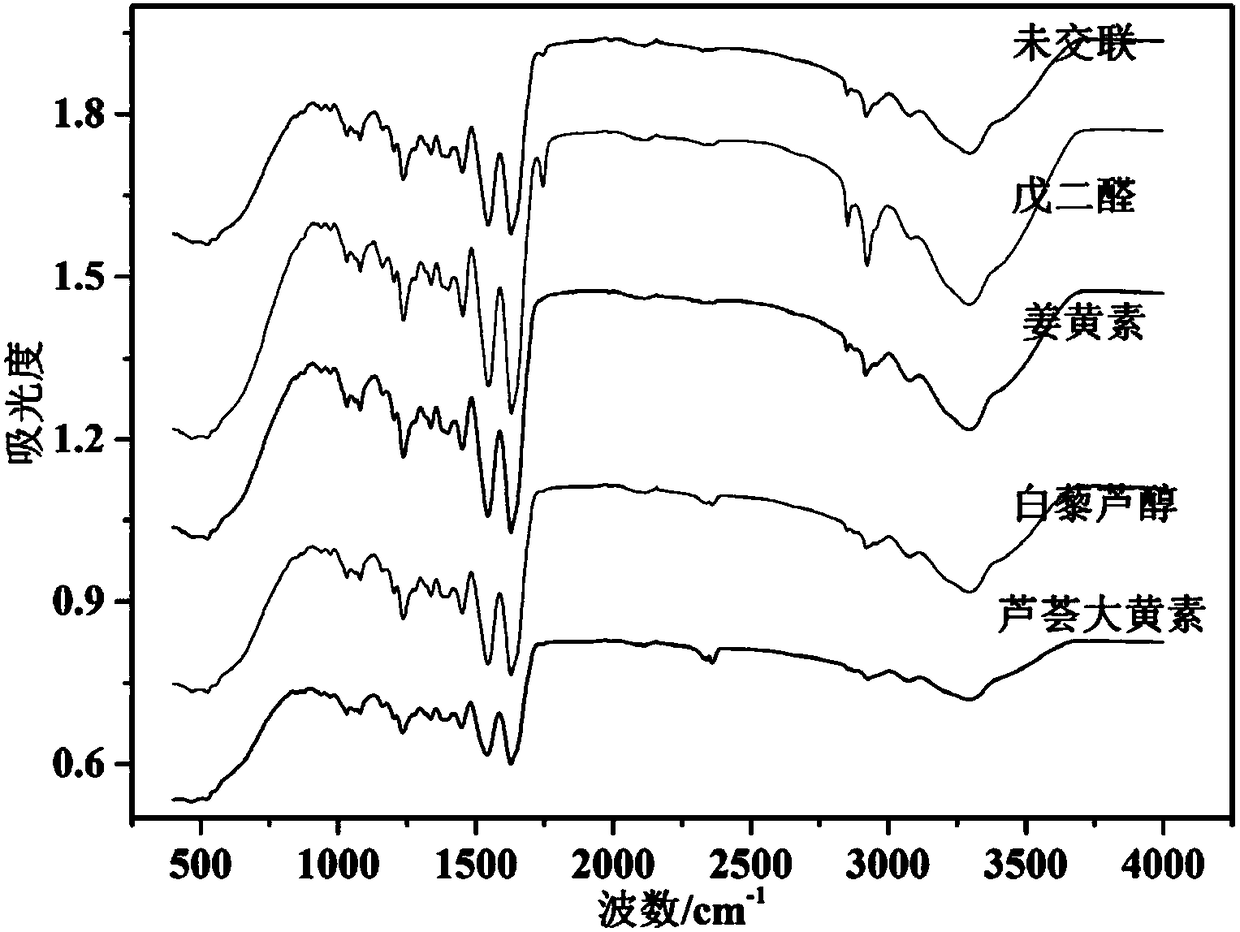
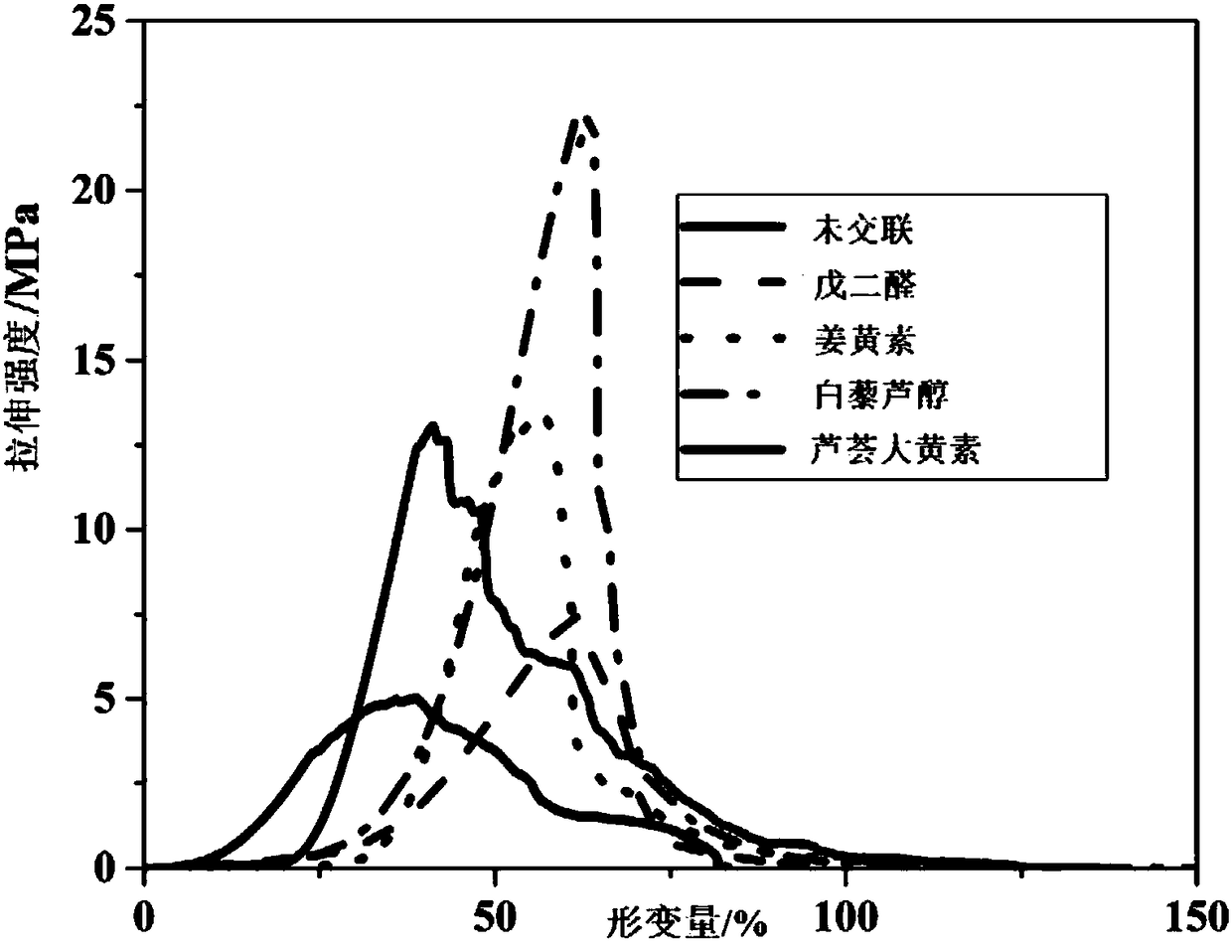
The invention relates to a polyphenol cross-linking agent and application thereof to preparation of an anti-calcification biovalve. The polyphenol cross-linking agent is prepared in a way that polyphenol compound is dissolved in organic solvent, and then, buffer solution is adopted for dilution, wherein the polyphenol compound is selected from one or multiple of procyanidine, curcumin, resveratrol, puerarin, aloin and aloe-emodin. The preparation method for the anti-calcification biovalve comprises the following steps: dipping a bio-based material which completely removes cells into the polyphenol cross-linking agent to be subjected to cross-linking, and fully cleaning after ending; dipping in PBS (polybutylene succinate) solution and / or D-Hanks solution to be subjected to post-processingto obtain the anti-calcification biovalve. The anti-calcification biovalve provided by the invention has better mechanical property and stability, tissue calcification, inflammation and thrombus can be obviously reduced, biotoxicity is lowered, service life is greatly prolonged, and the defects of serious calcification, short service life and the like of biological cardiac valve materials processed with a traditional glutaraldehyde crosslinking method are overcome.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Preparation method of polybutylene succinate
InactiveCN101880377AImprove thermal performanceImprove mechanical propertiesReaction temperatureNitrogen atmosphere
The invention discloses a preparation method of polybutylene succinate, which comprises the steps of: carrying out ring-opening polymerization on polymer monomer succinic anhydride, butanediol and catalyst under the nitrogen atmosphere, and controlling the reaction temperature to be 160-200 DEG C and the reaction time to be 1-4h; then, carrying out condensation polymerization reaction under the vacuum condition, and controlling the vacuum degree to be absolute pressure of 30-300 Pa, the reaction temperature to be 200-280 DEG C and the reaction time to be 1-6h; and finally, obtaining the target product polybutylene succinate. The detection proves that the polybutylene succinate has the weight-average molecular weight Mw reaching up to more than 100 thousand and the molecular weight distribution Mw / Mn of 1.8-2.2. Compared with the prior art, the invention reduces the byproduct water molecules by half, improves the product yield, avoids binary acid being taken as polymerization monomer, and reduces the corrosion for equipment, thus reducing the investment and maintenance cost for the fixed equipment, and being more beneficial to industrialized production.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI GRP CO
Biodegradable sheet
Disclosed is a biodegradable sheet comprising at least one layer which is a direct contact layer, intended to successfully contact materials, such as liquids, while maintaining the mechanical properties of the sheet and to extend the biodegradable sheet shelf life. The direct contact layer may comprise a hydrophobic polymer selected from poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (PCL) polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), Polydioxanone (PDO) polyglycolic acid (PGA), polybutylene succinate (PBS), polybutylene succinate adipate (PBS A), poly lactic acid (PL A), polybutylene adipate terphtalate (PBAT), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), such as polyhydroxybutyrates (PHB), polyhydroxyvalerates (PHV), and polyhydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate copolymers (PHBV) or any mixture thereof. The biodegradable sheet may further comprise surface treated nanoclay particles, PVOH grafted with a crosslinker and PBS or PBS A The biodegradable sheet may further include at least one metalized, biodegradable, laminate layer.
Owner:TIPA CORP
Food container having an inner protecting layer
A food container includes: a container body made of paper, and having an inner surface defining a receiving space therein, and an outer surface opposite to the inner surface; and an inner protecting layer coated on the inner surface and made from a biodegradable coating composition including polybutylene succinate as a major component. The biodegradable coating composition further includes a minor component selected from polybutylene adipate / terephthalate, polylactic acid, and combinations thereof.
Owner:HUANG CHIEN MING
Completely-biodegradable copolymerized extruded sheet raw material and production process of product
The invention discloses a completely-biodegradable copolymerized extruded sheet raw material. The material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 13-17 parts of polylactic acid (PLA), 14-16 parts of poly(butylene adipate terephthalate) (PBAT), 13-17 parts of polybutylene succinate (PBS), 27-33 parts of plant starch, 8-12 parts of straw cellulose, 14-16 parts of a filler, 0.5-2 parts of a plasticizer and 0.2-1 part of an antioxidant. According to the completely-biodegradable copolymerized extruded sheet raw material provided by the invention, the material has a good degradation effect, simultaneously the product after degradation does not cause secondary pollution, and moreover, the biodegradable material provided by the invention can resist to high temperature and low temperature.
Owner:谢子栋
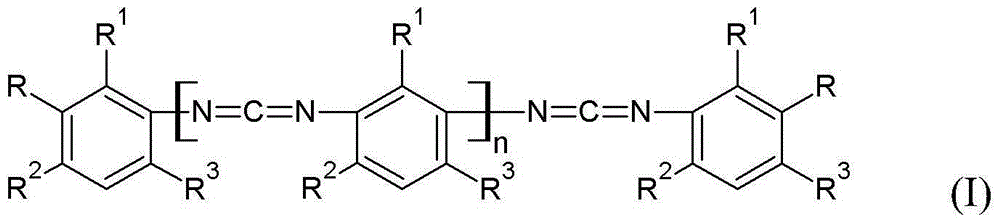
New carbodiimides having terminal urea and/or urethane groups, methods for producing said carbodiimides, and use of said carbodiimides
ActiveCN105228980AUrea derivatives preparationCarbamic acid derivatives preparationCarbamatePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
Owner:LANXESS DEUTDCHLAND GMBH
Degradable resin nano-composite material for oil and gas field operation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104962052ANew mechanical propertiesChange mechanical propertiesConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsAcid fracturingFiltration
The invention provides a degradable resin nano-composite material for oil and gas field operation and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the composite material comprises the steps of using two or three polymers of polycaprolactone, polybutylenes succinate and polylactic acid as raw materials, adding inorganic nano-materials and chain extender, performing melt-mixing reaction to prepare resin nano-alloy, i.e., the degradable resin nano-composite material for oil and gas field operation. The composite material is prepared by adopting the method, can be prepared into sheets, powder, particles, spheres and the like, or can be prepared into sheets, powder, particles, spheres and the like by using mixture of one of polycaprolactone, polybutylenes succinate and polylactic acid and the inorganic nano-materials, is used for temporary plugging and filtration reduction to protect reservoirs and temporary plugging of blast holes and constructed layer sections and the like during various construction operations (drilling, well completion, well repair and acid fracturing) in oil and gas fields, and has the advantages of complete degradability and zero harm to formations.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING) +1
Polybutylene succinate resin composition and its preparation method
The invention discloses a high strength and toughening polybutylene succinate resin composition and its preparation method, as well as a product containing the polybutylene succinate resin composition. Due to adding of an elastomer, glassfiber and other components into polybutylene succinate, high impact performance can be obtained, and at the same time, the mechanical properties and thermal resistance of the obtained resin composition product can be improved. The obtained polybutylene succinate resin composition has the prominent advantages of good mechanical properties, good fluidity, good heat resistance, easy processing molding, biodegradability and the like, and is suitable for the field of mobile phone shells, laptop shells and other electronic products. The preparation method of the polybutylene succinate resin composition has the characteristics of simple and continuous process and high production efficiency, and the prepared product has stable quality.
Owner:BEIJING RISUN TECH CO LTD
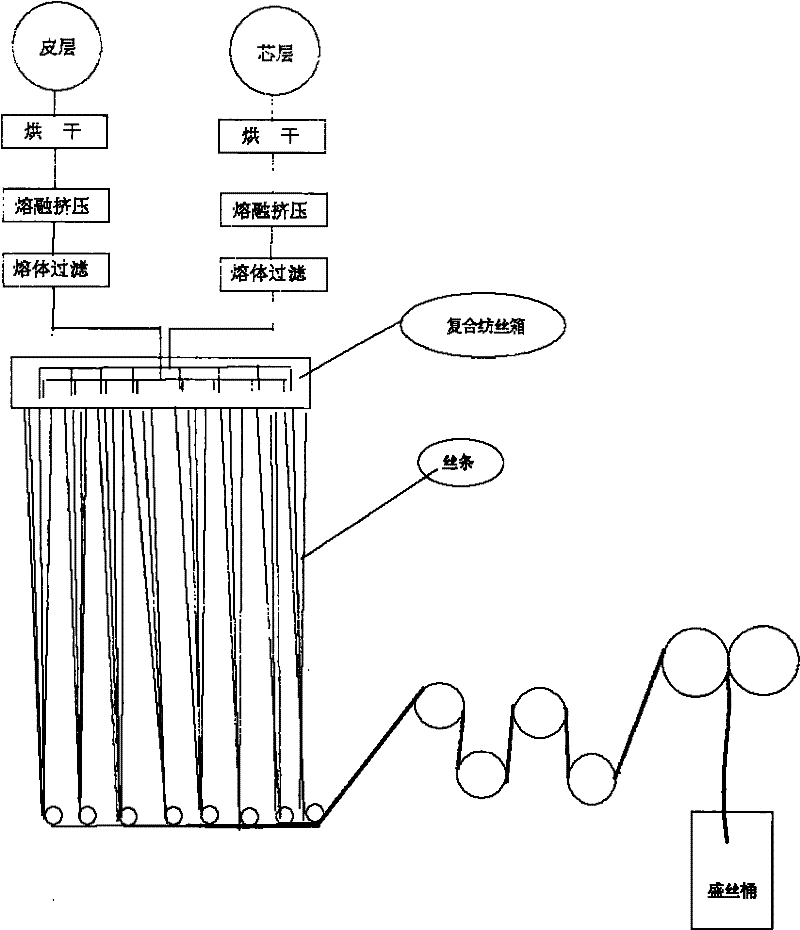
Preparation method of polybutylene succinate fiber
InactiveCN101597815ANo pollution in the processNo need to recycleMelt spinning methodsMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentMass ratioPoly(butylene succinate)
A preparation method of polybutylene succinate fiber belongs to the technical field of preparation of functional synthetic fiber by melt spinning. Vacuum drying is carried out on spinning material of polybutylene succinate; matching mixing is carried out on the spinning material of polybutylene succinate and spinning material phase transition material of microcapsule according to mass ratio of (88-100):(12-0) as well as on spinning processing additive and the total mass between polybutylene succinate and phase transition material of microcapsule according to mass ratio of (0.1-0.5):100; melt spinning is carried out at the spinning speed of 500-800m / min; drafting and heat setting are carried out to obtain the polybutylene succinate fiber. The invention has simple device and process, and saves production cost and energy. The polybutylene succinate phase transition thermo-regulated fiber can provide people with garment and products with cosy sensation and thermo-regulating function, and has the characteristics of environmental friendliness and environmental protection simultaneously, thus having wide application range and prospect.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CLOTHING TECH
Biodegradable sheet
Disclosed is a biodegradable sheet comprising at least one layer which is a direct contact layer, intended to successfully contact materials, such as liquids, while maintaining the mechanical properties of the sheet and to extend the biodegradable sheet shelf life. The direct contact layer may comprise a hydrophobic polymer selected from poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (PCL) polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), Polydioxanone (PDO) polyglycolic acid (PGA), polybutylene succinate (PBS), polybutylene succinate adipate (PBSA), poly lactic acid (PLA), polybutylene adipate terphtalate (PBAT), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), such as polyhydroxybutyrates (PHB), polyhydroxyvalerates (PHV), and polyhydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate copolymers (PHBV) or any mixture thereof. The biodegradable sheet may further comprise surface treated nanoclay particles, PVOH grafted with a crosslinker and PBS or PBSA The biodegradable sheet may further include at least one metalized, biodegradable, laminate layer.
Owner:TIPA CORP
Method for preparing biodegradable copolyester fully-drawn yarns in one step
InactiveCN101781805AImprove spinning stabilityImprove evennessFilament manufactureMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentYarnEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of the melt-spinning manufacturing functional synthetic fibers, and provides a method for preparing biodegradable copolyester fully-drawn yarns in one step, which is specifically used for preparing the biodegradable polybutylene terephthalate-co-polybutylene succinate fully-drawn yarns by taking biodegradable polybutylene terephthalate-co-polybutylene succinate slices as raw materials and adopting a one-step melt-spinning process. The method has the advantages of high spinning stability, no broken filament, high yarn levelness, good winding property and high spinning speed; and by the method, the strength of the fully-drawn yarn is enhanced and production efficiency is improved.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Synthetic board with a film
InactiveUS20080026235A1Reduce the burden onSimplify workSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsCelluloseAdhesive
A transparent or colored film is placed on a preform that is fabricated by mixing lignocellulose-based material with polybutylene succinate-based resin or polylactic-based resin as adhesive, and the film and the preform are heated and pressed.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORP
Catalyst for producing polybutylene succinate or copolyester thereof, and preparing mehtods of the catalyst
InactiveUS20110162205A1High activityQuality improvementTitanium compoundsHollow articlesAlcoholSilicon alkoxide
The present invention provides a catalyst used in the production of PBS or its copolyesters and the preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding titanium alkoxide, silicon alkoxide, dihydric alcohol and metal co-catalyst into the solvent and conducting the reaction at a temperature of about 80° C. to 180° C., then removing the unreacted materials and small molecular products in the reaction system; (2) adding complexing agent into the reaction system, then collecting catalyst from the products obtained in this step. Moreover, the method may comprises steps of: (1) adding titanium alkoxide, dihydric alcohol and metal co-catalyst into the solvent and conducting the reaction at a temperature of about 80° C. to 180° C., then removing the unreacted materials and small molecular products in the reaction system; (2) adding silicon alkoxide and complexing agent into the reaction system, then collecting catalyst from the products obtained in this step. The catalyst in the present invention has higher activity and thus the catalyst additional amount is reduced which will improve the quality of the products. Moreover, the catalyst in the present invention could be used alone in the production of PBS or its copolyester without the need for other materials and it won't react with water and thus could be stored for a long time. In sum, the catalyst in the present invention has a broad prospect in industrial application.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAMING HI TECH GRP
Preparation method of polybutylene succinate
The invention provides a preparation method of polybutylene succinate. The preparation method of the polybutylene succinate takes mono-methyl succinate and 1, 4-butanediol as monomers, adopts an efficient compound catalyst system and comprises the following steps: reacting to obtain a PBS (polybutylene succinate) oligomer first and then performing polycondensation reaction to obtain a PBS polymer with a high molecular weight and good color and luster. Through the adoption of the preparation method, on one hand, the problems that in the conventional technology that succinic acid and the 1, 4-butanediol are taken as monomers to prepare the PBS, the speed rate of esterification reaction is low, the succinic acid cannot react completely, and the amount of a generated byproduct tetrahydrofuran is high can be solved; on the other hand, the acidicity of the mono-methyl succinate is less than that of the succinic acid, so that corrosion to equipment is reduced, and thus the maintenance cost of the equipment is reduced and greater contribution is made to industrial production; in addition, a chain extender is not used, the application range of PBS degradable plastic in the field of food packaging can be further expanded.
Owner:TANGSHAN XUYANG CHEM IND CO LTD
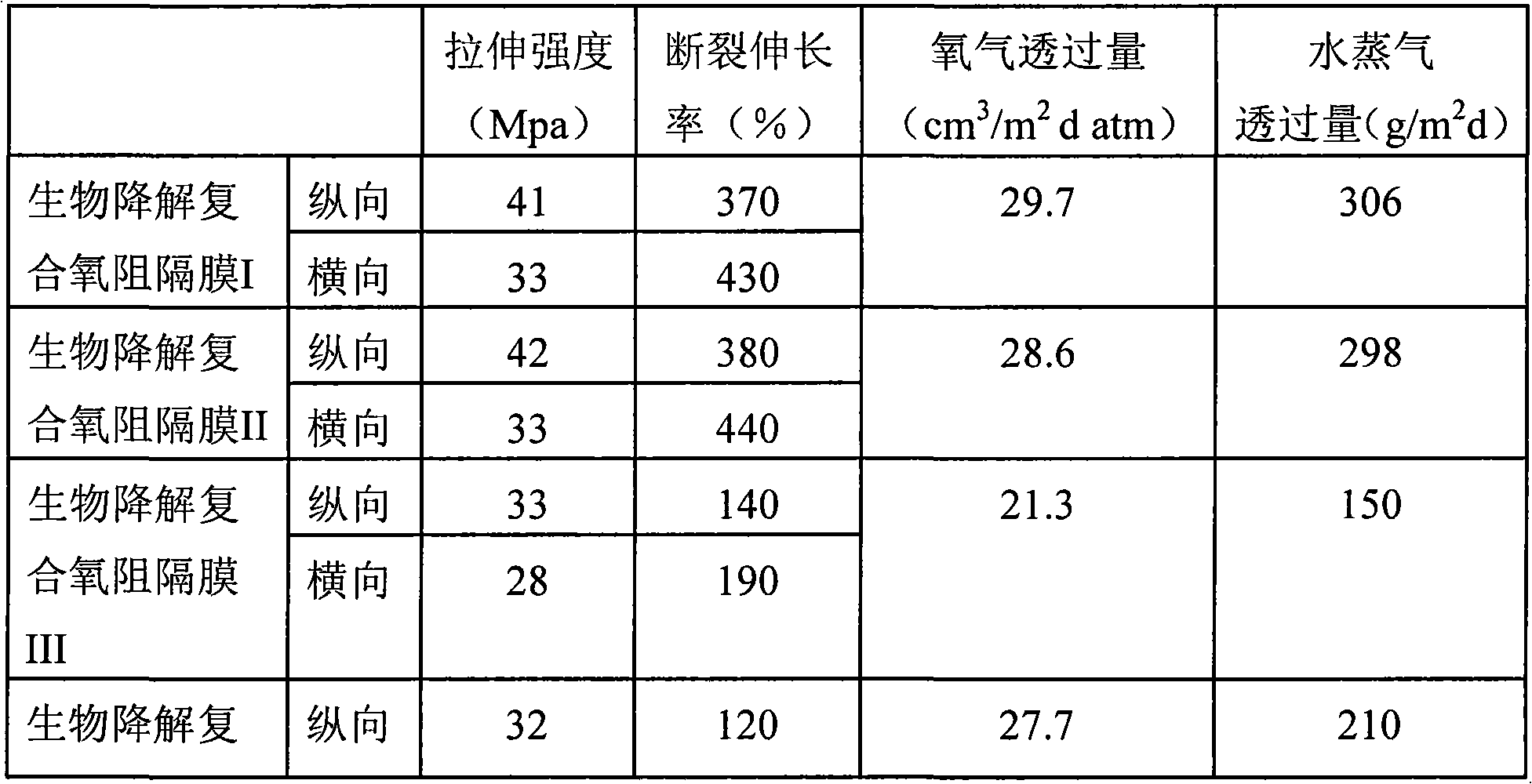
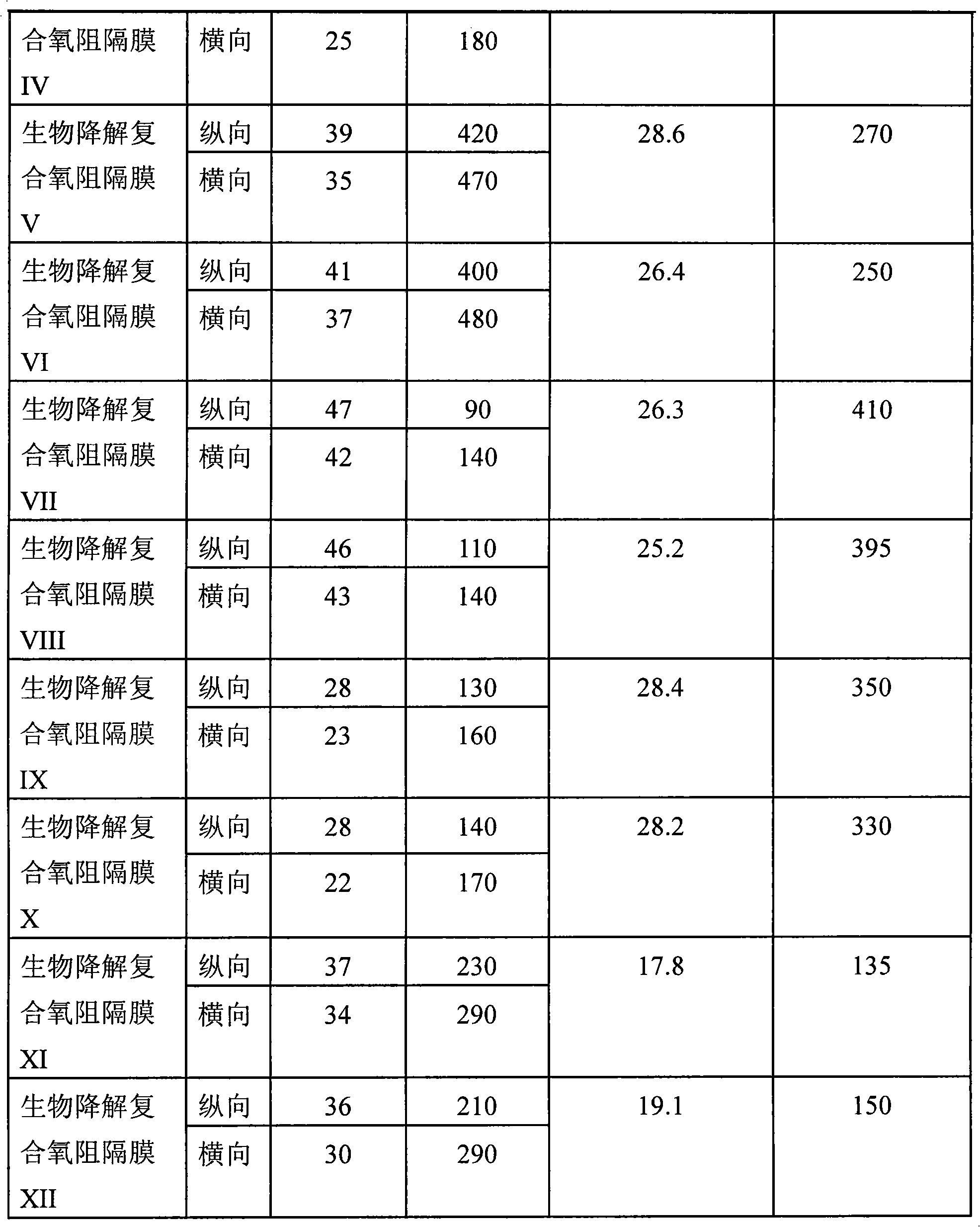
Biodegradable composite oxygen-barrier film and use thereof
ActiveCN102007001AExtended shelf lifeExtend your lifeFlexible coversWrappersEngineeringPoly(butylene succinate)
The invention discloses a biodegradable composite oxygen-barrier film and its preparation method and use. The biodegradable composite oxygen-barrier film is composed of at least two support layers and barrier layer which is located in each of the two support layers. Said support layer is selected from at least one of the following materials: polylactic acid, polybutylene succinate, polycaprolactone, poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate), poly(beta-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(beta-hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate); said barrier layers located in each of the two support layers are same or different, and the barrier layer is selected from poly(1,2-propylene carbonate) and nano-montmorillonite modified poly(1,2-propylene carbonate). The biodegradable composite oxygen-barrier film can be used as food or medicine package, and it will help to prolong shelf-life of food and medicine and the like; it can also prevent white-pollution.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +3
Maleic anhydride graft polybutylene succinate (PBS) alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a maleic anhydride graft polybutylene succinate (PBS) alloy, comprising the following ingredients in terms of the weight ratios: 100 parts of PBS, 20-30 parts of polylactic resin, 1.0-2.0 parts of maleic anhydride monomer, 0.02-0.05 part of initiator and 0.4-1.0 part of acetone. The degradable materials formed by the maleic anhydride monomer graft PBS and polylactic acid having excellent mechanical property, tensile strength and elongation at break; each material system has better compatibility. The invention also relates to a method for preparing the alloy material.
Owner:深圳市未名北科环境材料有限公司 +1
Bicomponent fiber additive delivery composition
InactiveUS20180223454A1Physical treatmentFilament/thread formingLow-density polyethylenePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The biocomponent fiber functions as a carrier or vehicle for delivering additives to a polymer composition. The bicomponent fiber may be “splittable segmented pie” or “island-in-the-sea” construction with the sea being the low melt temperature component and the island being the high melt temperature component. The low melt temperature polymer may be selected from the group consisting of low density polyethylene (LDPE), high density polyethylene (HDPE), polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkenoate (PHA), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), polyvinylidene fluoride, polybutylene succinate (PBS), low melt temperature polyethylene terephthalate, polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) and low melt temperature nylons. The high melt temperature component polymer is selected from the group consisting of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), co-polyester, polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), polyether ether ketones (PEEK), polyphenylene sulfides (PPS), high melt temperature nylon, polylactic acid (PLA), including stereocomplex PLA, namely 100% PDLA, 100% PLLA or a 50 / 50 blend of 100% PDLA and 100% PLLA.
Owner:EARTH RENEWABLE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com