Dynamic equivalence method for double-fed wind turbines on basis of equivalent power angle co-modulation
A double-fed wind turbine, dynamic equivalent technology, applied in the field of value, can solve the problems of large difference in dynamic characteristics, no inertia, no consensus, etc., to reduce the scale and simplify the external area.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
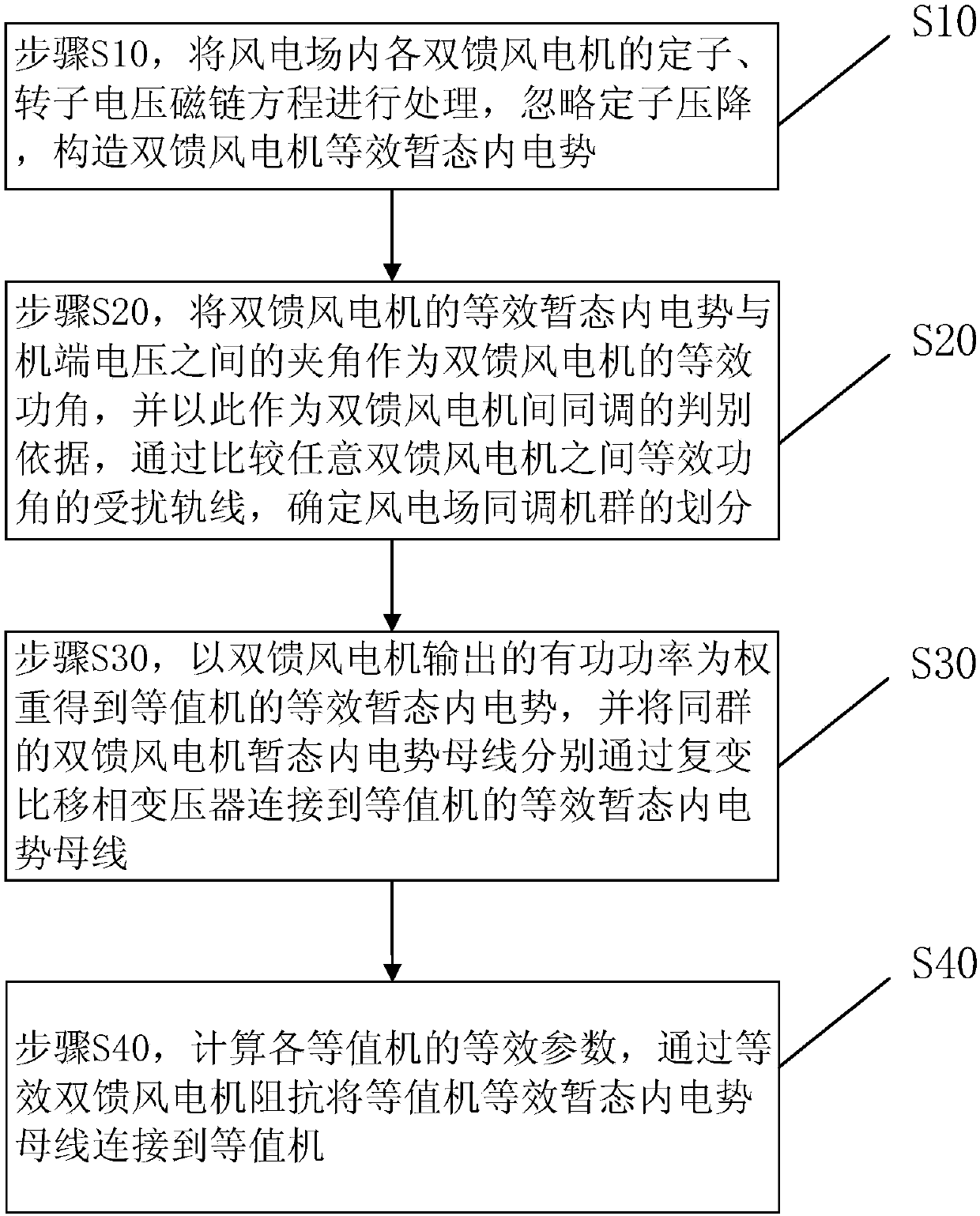
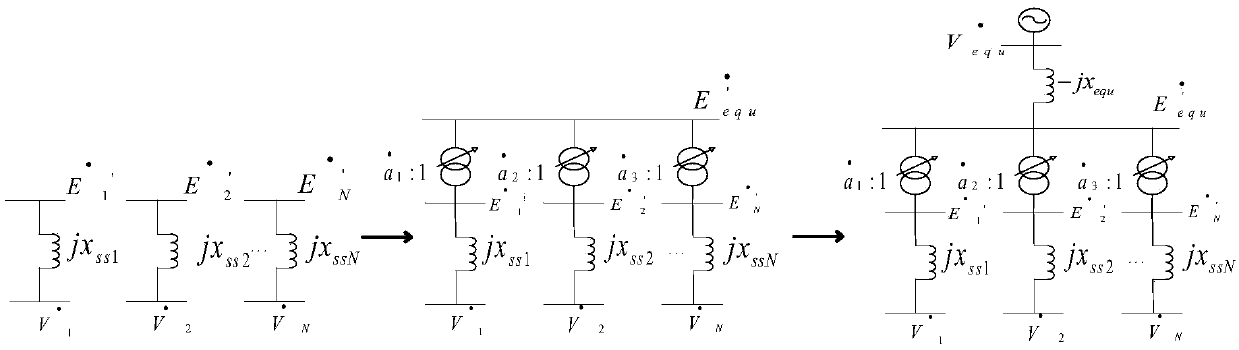
[0042] This embodiment provides a dynamic equivalence method for DFIG based on equivalent power angle coherence, the flow chart of the method is as followsfigure 1 shown, including the following steps:
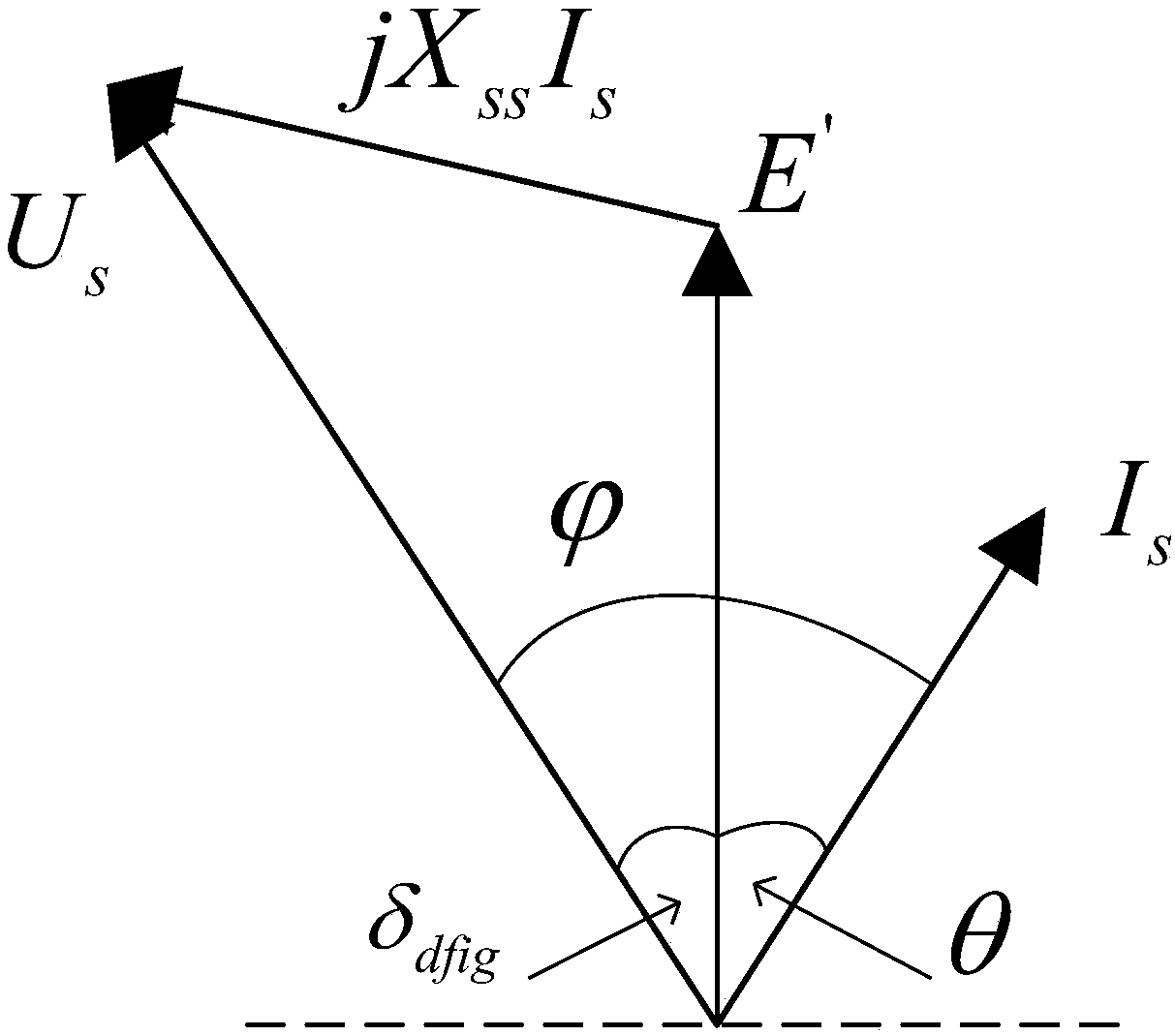
[0043] Step S10, process the stator and rotor voltage flux equations of each DFIG in the wind farm, ignore the stator voltage drop, and construct the equivalent transient internal potential of the DFIG; the specific process is:
[0044] A. Under the premise of ignoring the influence of magnetic saturation, the voltage and flux linkage per unit value equations of the double-fed wind turbine in the d-q synchronous rotating coordinate system are obtained as shown in equations (1) and (2):
[0045]
[0046]
[0047] Among them, u, i, and ψ respectively represent the voltage, current and flux linkage of the DFIG; R and L represent the resistance and inductance of the DFIG respectively; s and r in the subscript represent the stator of the DFIG respectively , rotor; d and q in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com