ESD (electrostatic discharge) device structure
An ESD device and asymmetric structure technology, applied in the semiconductor field, can solve problems such as large latchup risk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
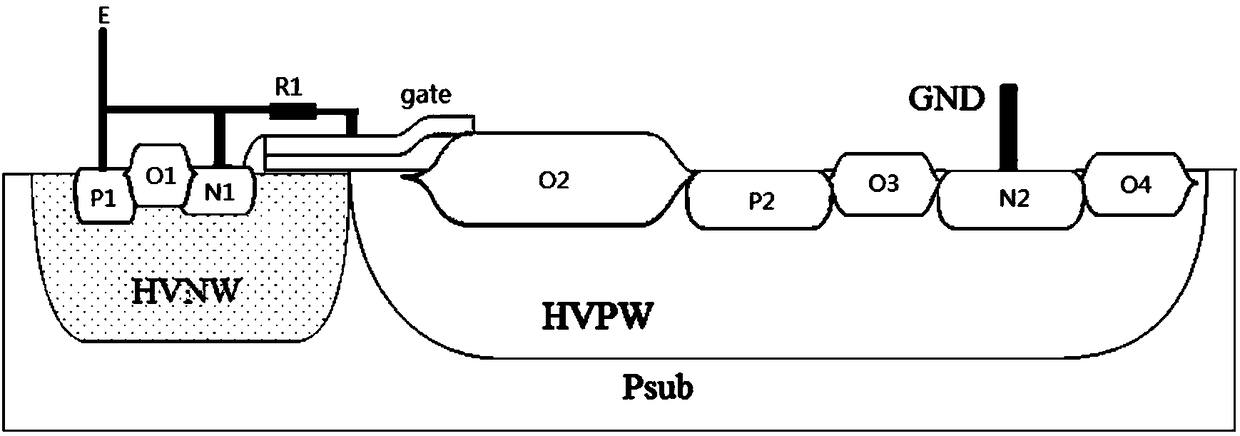
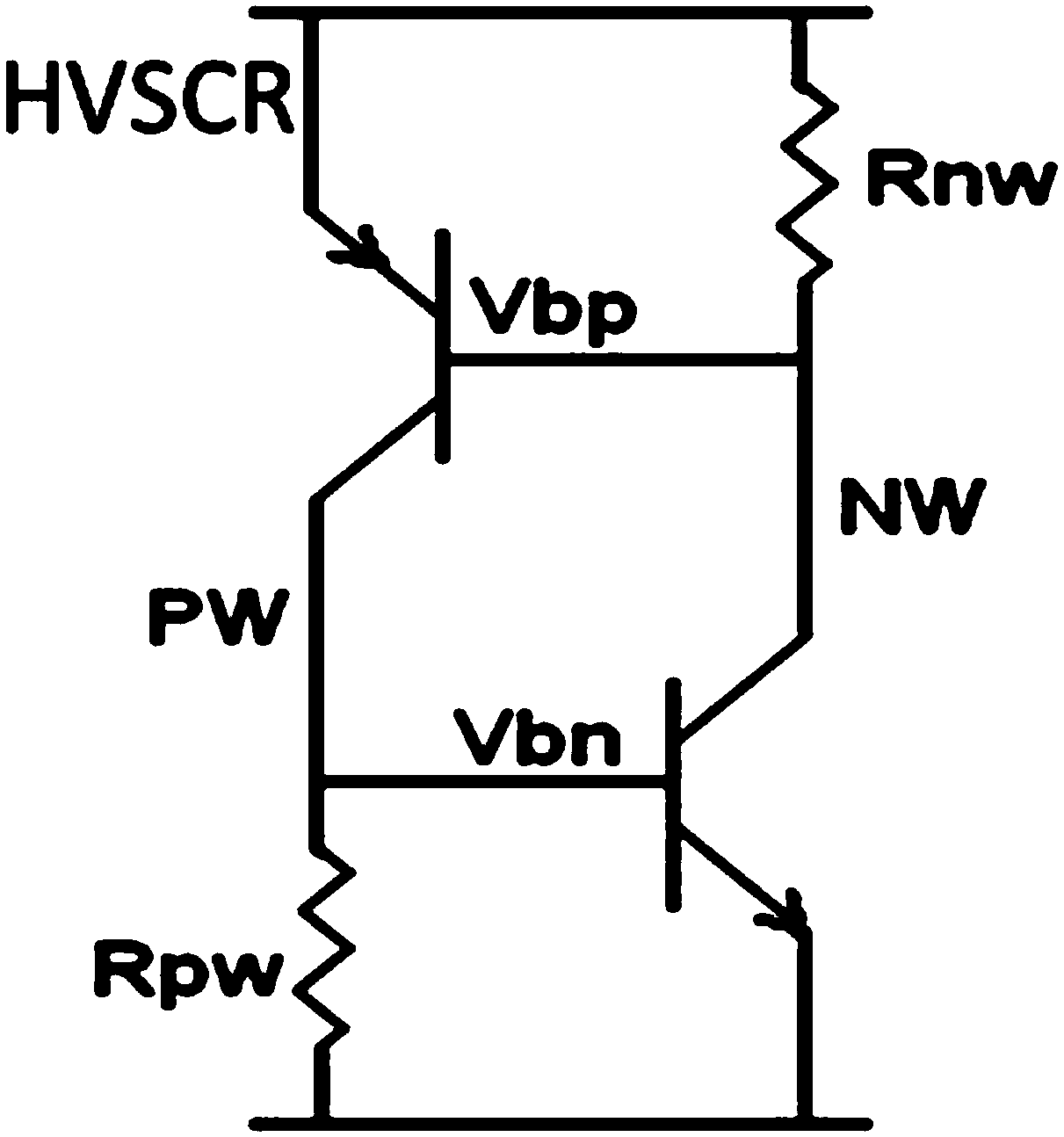
[0043] The ESD device structure of the present invention includes: a first LDMOS, a second LDMOS and a parasitic SCR;
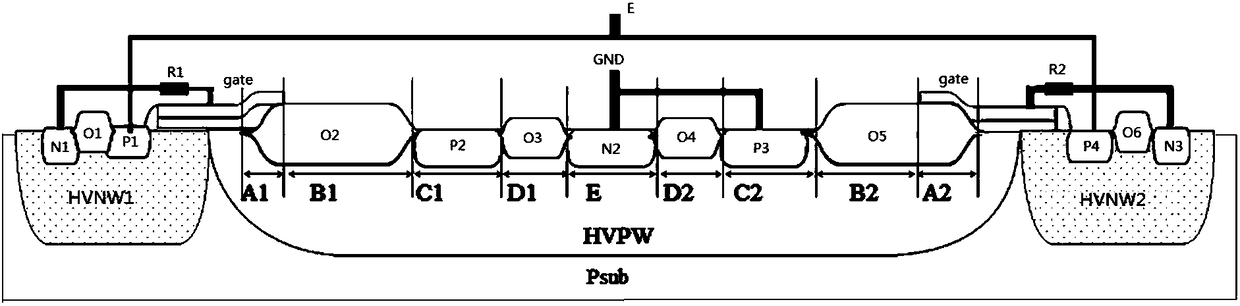
[0044] The first PLDMOS and the second LDMOS are P-LDMOS with the same structure and layout sharing a high-voltage P well (HVPW), and the high-voltage P well (HVPW) between the first P-LDMOS drain and the second P-LDMOS drain The parasitic SCR formed by the N+ region is arranged in the middle, and the first P-LDMOS and the second P-LDMOS form a left-right asymmetric structure centering on the N+ region of the parasitic SCR. The width (A1+B1) of the field oxygen region between the first LDMOS gate and the drain is greater than the width (A2+B2) of the field oxygen region between the second LDMOS gate and the drain, so that the structure can be reduced Turn on the voltage.
[0045] like image 3 As shown, a specific embodiment of the ESD of the present invention includes: a P-type substrate Psub, a first high-voltage N well HVNW1, a second high-voltage N well...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com