High-temperature superconductive current-sharing cable and current sharing realizing method
A high-temperature superconducting and cable technology, applied in the usage of superconducting elements, superconducting magnets/coils, superconducting devices, etc., can solve the problems of many factors affecting contact resistance, no current in the strip, and excessive current.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
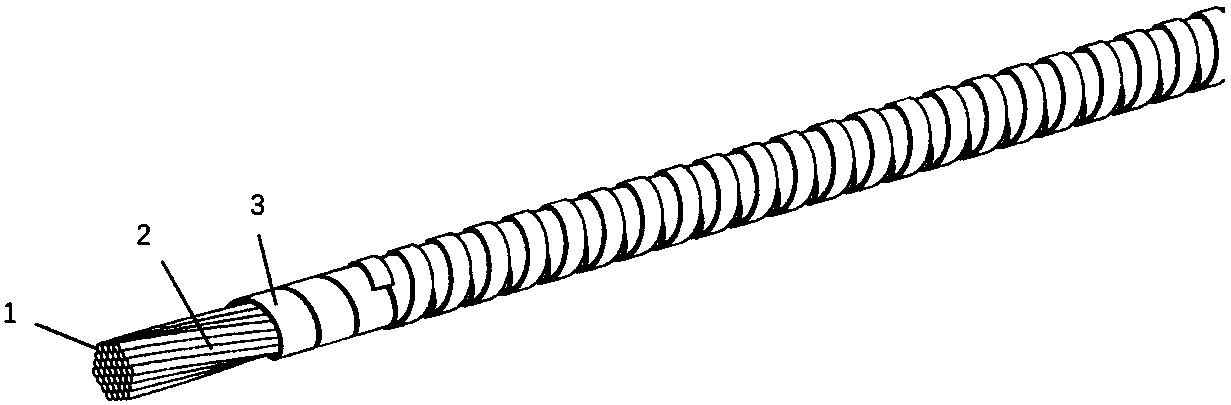
[0024] Such as figure 1 The schematic diagram of the structure of the superconducting cable is shown, in which the innermost layer uses bundled multi-core copper wires 1 to form a cluster skeleton 2. 15mm, a thin copper strip 3 is spirally wound around the skeleton as a transition layer to smooth local unevenness; the first layer of superconducting strip 4 is wound outside the transition layer of the thin copper strip, and the superconducting strip 4 is YBCO with a thickness of 0.15mm and a width of 4mm Strip;
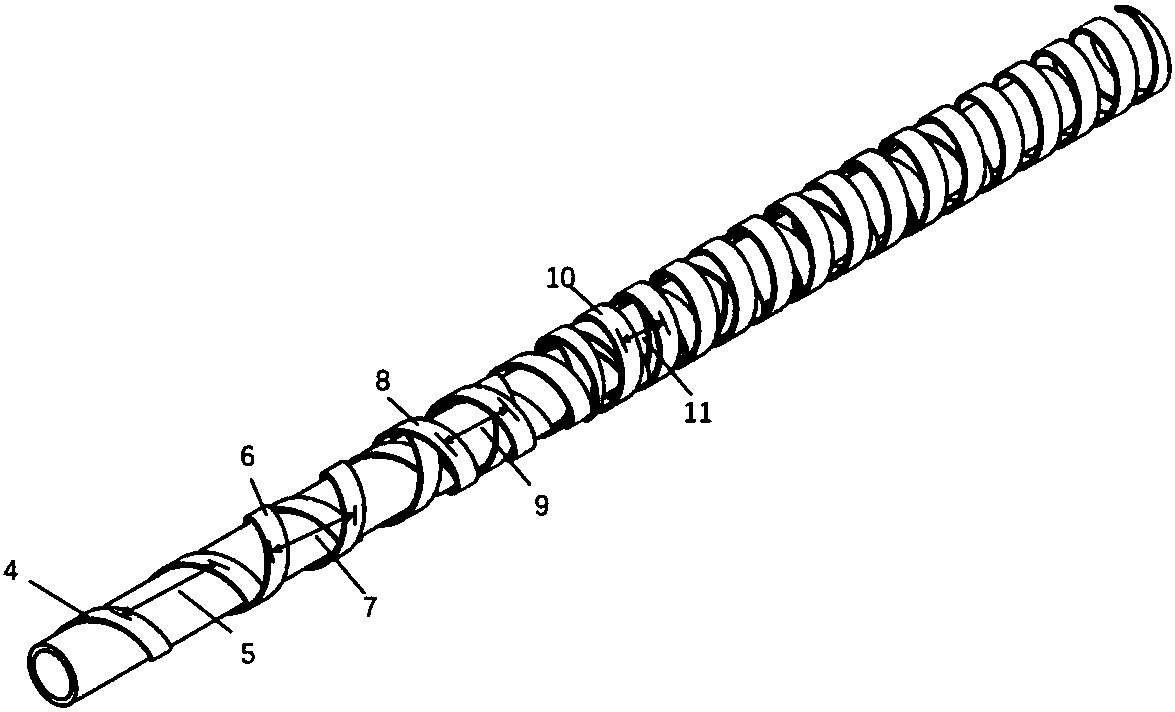
[0025] Such as figure 2 As shown, the first layer of superconducting tape 4 is wound clockwise according to the right-hand rule, the pitch 5 of the first layer of superconducting tape is 14mm, and whether the initial layer is clockwise or counterclockwise is not strictly regulated; The first layer of superconducting tape 6 is wound counterclockwise, the pitch 7 of the second layer is 12mm; the third layer of superconducting tape 8 is wound clockwise, and the pitch 9...
Embodiment 2
[0028] In embodiment 1, using strips of the same width to balance the inductance between different layers by changing the pitch to achieve current sharing; in embodiment 2, using strips of different widths to achieve inductance balance, such as Figure 4 As shown, the first layer of superconducting tape 4 is wound clockwise by YBCO tape with a thickness of 0.15 mm and a width of 12 mm. The superconducting tape 6 is wound in a counterclockwise manner by YBCO tape with a thickness of 0.15 mm and a width of 10 mm, and the winding pitch is arranged in a close manner; the third layer of superconducting tape 8 is wound in a clockwise manner with a YBCO tape with a thickness of 0.15 mm and a width of 8 mm. The winding pitches are closely arranged; the fourth layer of superconducting tape 8 is wound counterclockwise by 0.15mm and 6mm wide YBCO strips, and the winding pitches are arranged in a close manner, and the pitch is 0 when closely arranged.
[0029] In actual use, the pitch of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com