Human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) virus-like particles (VLPS) based vaccine
A syncytial virus, virus-like technology, applied in the direction of viruses, viral peptides, antiviral agents, etc., can solve problems such as ineffective vaccines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0152] Embodiment 1: the production of pneumonia virus VLP
[0153] Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a major cause of severe respiratory disease in infants and children and represents a significant health burden in the elderly and the globally immunocompromised. Despite decades of research effort, there is still no licensed vaccine available for RSV.
[0154] We developed a virus-like particle (VLP)-based RSV vaccine, which consists of human metapneumovirus matrix protein (hMPV M) as the structural backbone and RSV fusion glycoprotein (F) in a pre- or post-fusion conformation as its main surface immunogen Assembled. The vaccine consists of the prefusion F protein, the postfusion F protein, or a combination of these two conformations, and is adjuvanted with a squalene-based oil emulsion. Immunization with these VLP vaccines provided comprehensive protection against RSV infection, preventing detectable viral replication in the lungs of mice following challenge. Analysis o...
Embodiment 2
[0183] Example 2: Development of Recombinant RSV F Showing Fusion and Prefusion Conformations
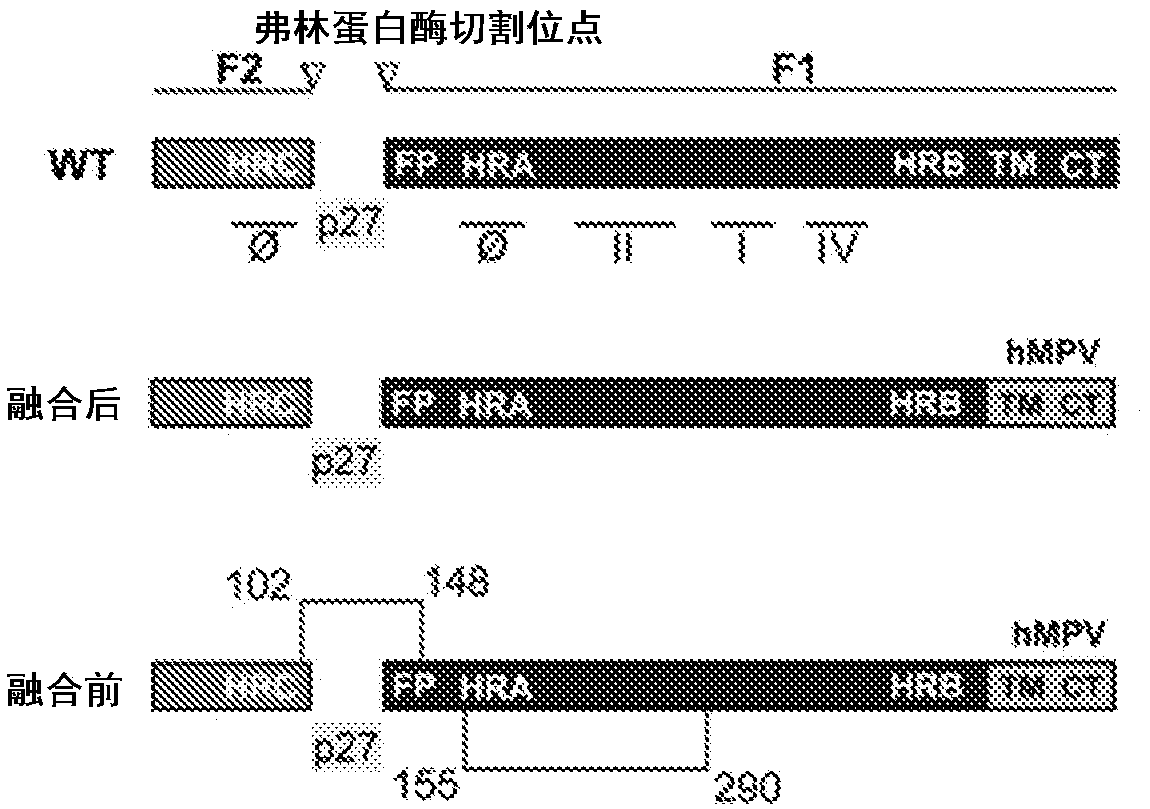
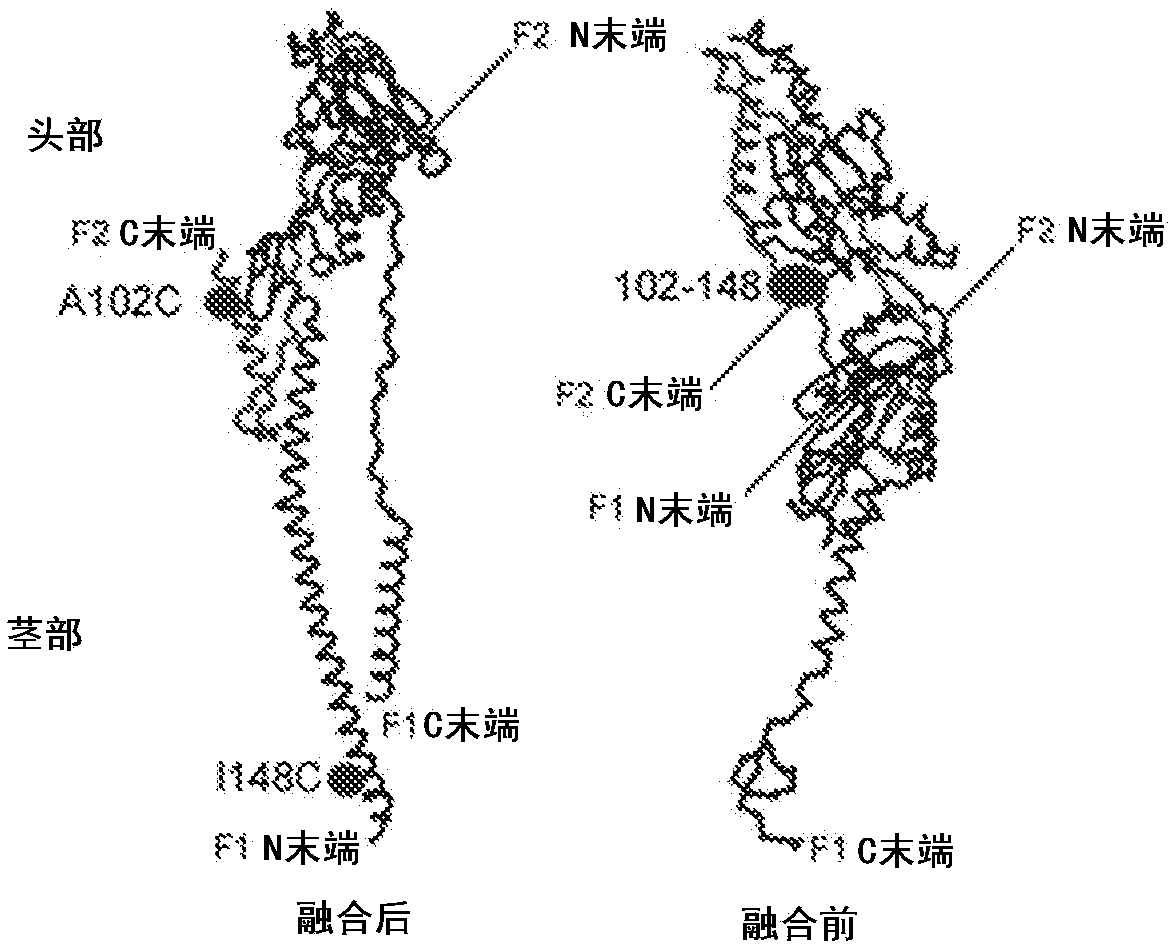
[0184] Structural analysis of the fused F protein showed that the C-terminus of F2 was located in the relative direction of and away from the N-terminus of F1 ( Figure 1B ), whereas in the prefusion conformation these domains are adjacent (9, 13). We identified several neighboring amino acids within this domain that are less than 10 Angstroms apart. Based on this analysis, we generated nine recombinant constructs with different disulfide bonds between these domains to stabilize the F protein in its prefusion conformation, as well as constructs with mutations in the furin cleavage site (Fig. 7 ).
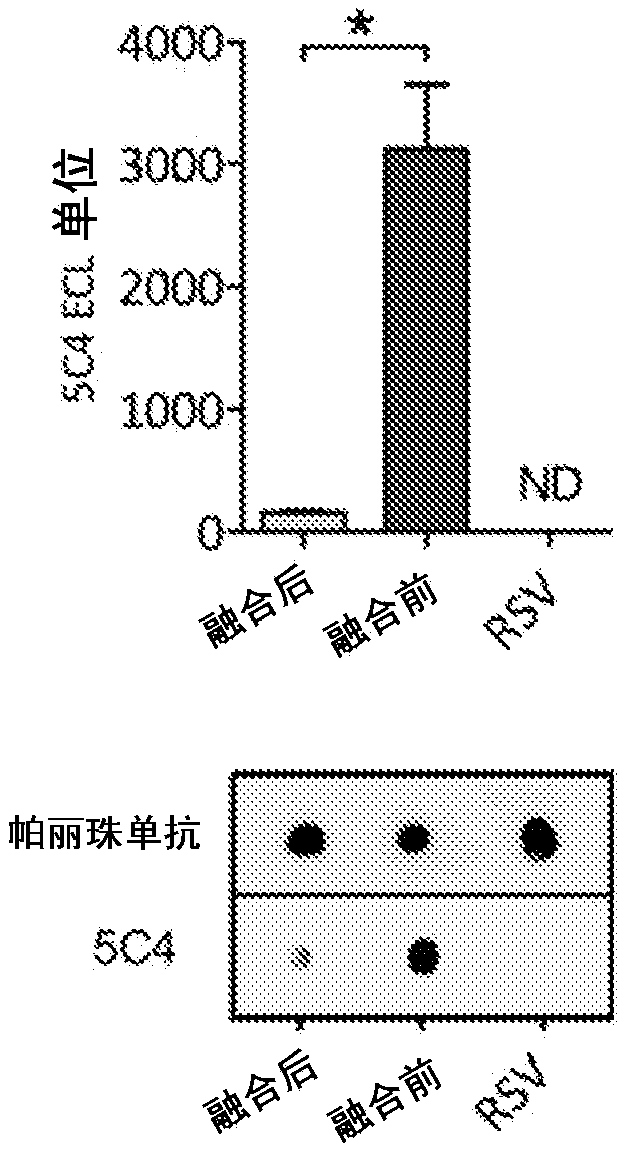
[0185] Prefusion F VLPs were produced in mammalian cells and analyzed by dot blot analysis with Palivizumab (antigenic site II) to determine F protein expression and dot blot analysis with 5C4 mAb to determine the antigenic site presence and stability (Figure 7). We assessed the post...
Embodiment 3
[0187] Embodiment 3: display the VLP of RSV F fusion post or fusion pre-conformation
[0188] The RSV envelope displays three virus-encoded membrane-anchored proteins, the F, G and SH proteins (19). Matrix (M) proteins beneath the envelope multimerize during morphogenesis and delineate virion assembly and budding (20). To assemble VLPs, we employed pre- or post-fusion RSV F and as a backbone human metapneumovirus (hMPV) matrix protein (M), which we found to be more efficient than RSV M in VLP formation. To optimize the interaction of RSV F and hMPV M, we replaced the cytoplasmic tail of the RSV F protein with an analogous domain of the hMPV F protein, based on the recruitment of RSV F and incorporation into VLPs confirmed by yield analysis compared to unmodified F surface enhancements ( Figure 1C ).
[0189] Analysis of purified VLPs by Western blot revealed that RSV F hybrids co-purify with hMPV M ( Figure 2B ), and replacing the cytoplasmic tail facilitated the incorpo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com