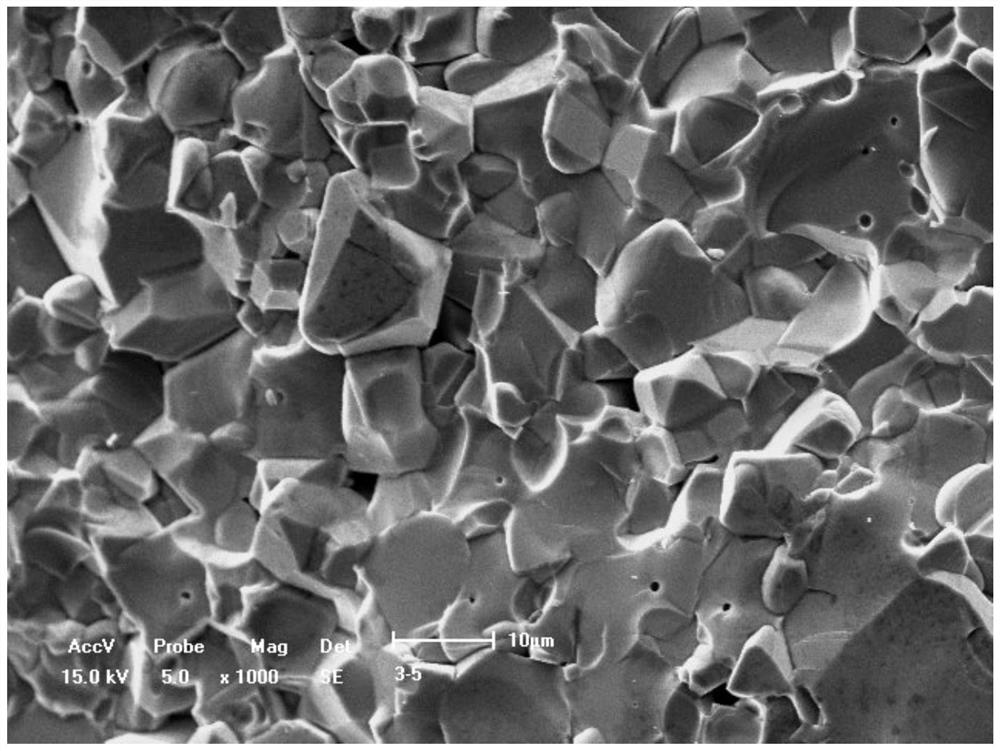
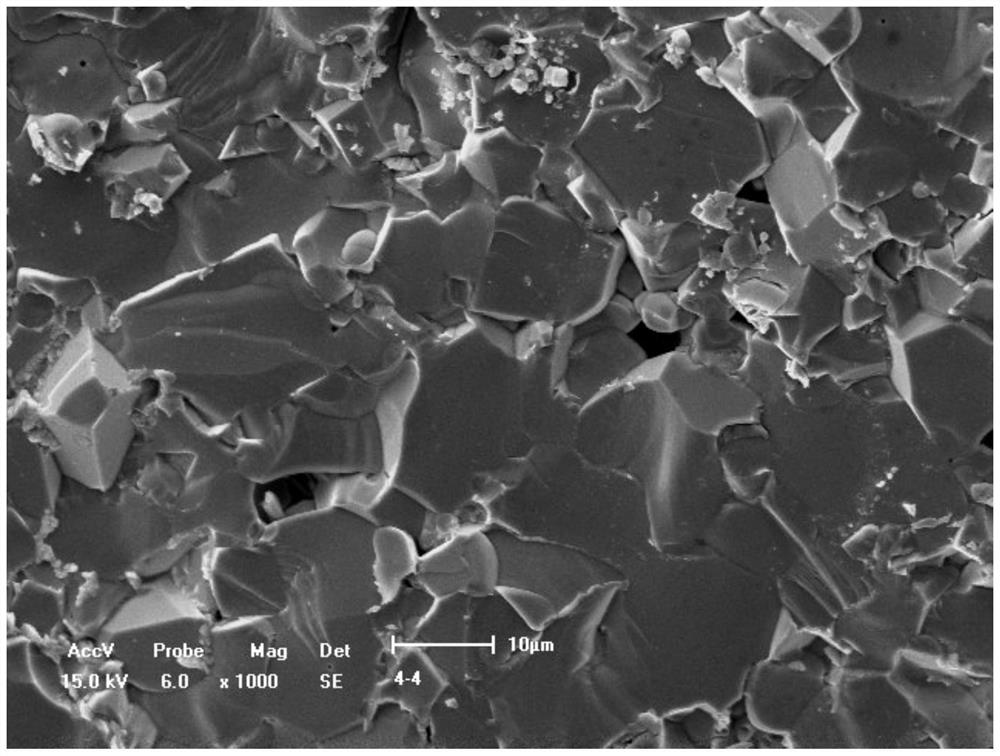
A nickel ferrite-based ceramic inert anode material for aluminum electrolysis and its preparation method
An inert anode, nickel ferrite-based technology, which is applied in the field of aluminum electrolysis technology and ceramic matrix composite materials, can solve the problem that the conductivity and corrosion resistance of the base metal ceramic inert anode cannot be balanced, and overcome the conductivity and corrosion resistance. Unable to take into account the effects of ensuring purity and reducing manufacturing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
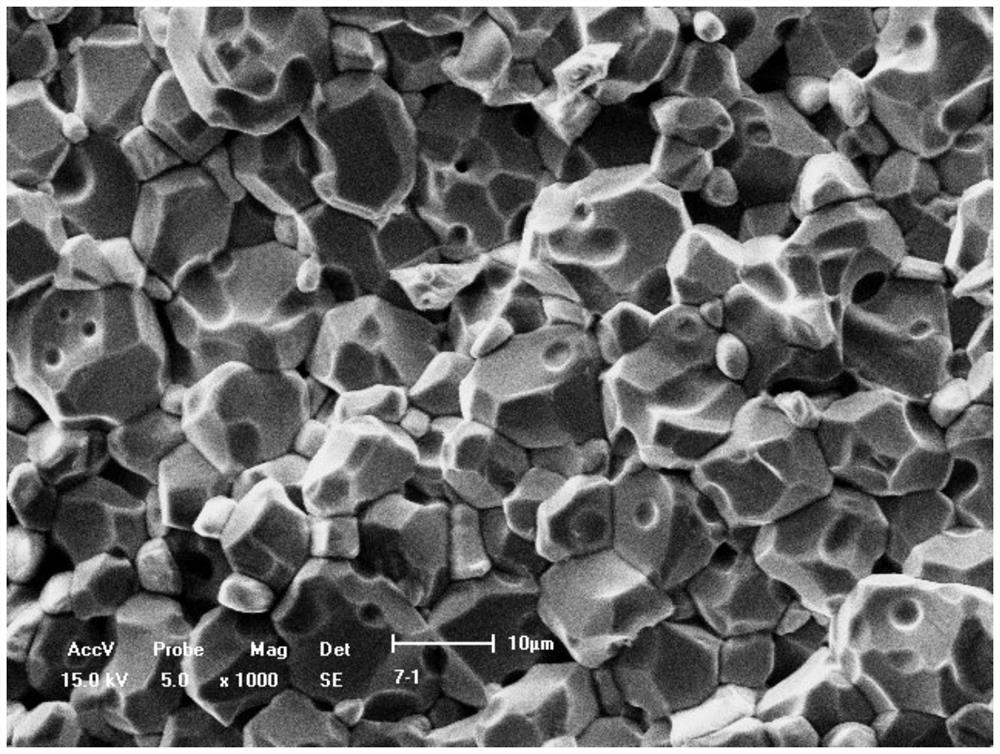
Embodiment 1
[0030] Weigh the raw material Fe respectively according to the mass ratio required by the design 2 o 3 powder, NiO powder, MnO 2 Powder and V 2 o 5 Powder, mass ratio according to Fe 2 o 3 All react with NiO to form NiFe 2 o 4 spinel, the rest with a mass fraction of 17% NiO, MnO 2 The mass fraction is 1%, V 2 o 5 The mass fraction of Fe is 1.5%; where Fe 2 o 3 Powder particle size≤1μm, NiO powder particle size≤10μm, MnO 2 Powder particle size≤5μm, V 2 o 5 Powder particle size ≤100μm;
[0031] Put all the raw materials into a ball mill tank, add deionized water to wet mill and mix for 6 hours, and then dry the mixed material at 100±2°C;
[0032] Add polyvinyl alcohol solution with an organic binder mass fraction of 8% to the dried mixed material, the organic binder accounts for 2% of the total mass of the dried mixed material, then mix evenly, and then sieve out the particle size The part of ≤250μm is used as a primary bonding material;
[0033] The primary bo...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Weigh the raw material Fe respectively according to the mass ratio required by the design 2 o 3 powder, NiO powder, MnO 2 Powder and V 2 o 5 Powder, mass ratio according to Fe 2 o 3 All react with NiO to form NiFe 2 o 4 spinel, the rest with a mass fraction of 11% NiO, MnO 2 The mass fraction is 2%, V 2 o 5 The mass fraction of Fe is 1%; where Fe 2 o 3 Powder particle size≤1μm, NiO powder particle size≤10μm, MnO 2 Powder particle size≤5μm, V 2 o 5 Powder particle size ≤100μm;
[0042] Put all the raw materials into a ball mill tank, add deionized water to wet mill and mix for 4 hours, and then dry the mixed material at 100±2°C;
[0043] Add a polyvinyl alcohol solution with a mass fraction of 5% of the organic binder to the dried mixed material, the organic binder accounts for 4% of the total mass of the dried mixed material, then mix evenly, and then sieve out the particle size The part of ≤250μm is used as a primary bonding material;
[0044] The prim...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Weigh the raw material Fe respectively according to the mass ratio required by the design 2 o 3 powder, NiO powder, MnO 2 Powder and V 2 o 5 Powder, mass ratio according to Fe 2 o 3 All react with NiO to form NiFe 2 o 4 spinel, the rest with a mass fraction of 5% NiO, MnO 2 The mass fraction is 3%, V 2 o 5 The mass fraction of Fe is 0.5%; where Fe 2 o 3 Powder particle size≤1μm, NiO powder particle size≤10μm, MnO 2 Powder particle size≤5μm, V 2 o 5 Powder particle size ≤100μm;
[0053] Put all the raw materials into a ball mill tank, add deionized water to wet mill and mix for 8 hours, and then dry the mixed material at 100±2°C;
[0054] Add polyvinyl alcohol solution with an organic binder mass fraction of 2% to the dried mixed material, the organic binder accounts for 6% of the total mass of the dried mixed material, then mix evenly, and then sieve out the particle size The part of ≤250μm is used as a primary bonding material;
[0055] The primary bon...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| corrosion rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| corrosion rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com