Gray level and binary image expansion corrosion processing method based on FPGA
A binary image and corrosion processing technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as performance limited memory bandwidth, and achieve the effect of reducing the number of visits and speeding up computing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
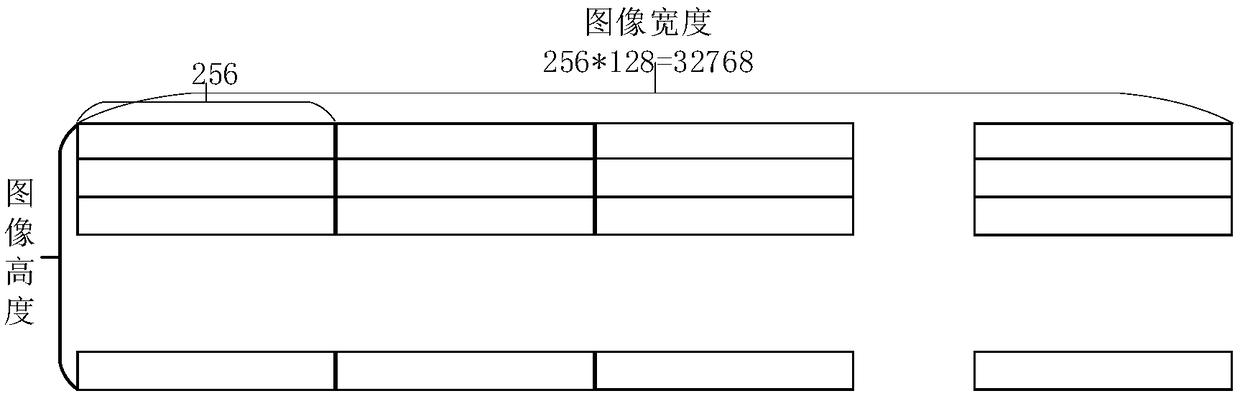
[0033] Select the grayscale image with a structural element window size of 3×3, a grayscale of 2, and a width of 32768 as the first embodiment, such as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 , Figure 6 and Figure 7 As shown, the process steps are described as follows:
[0034] Step 1: Set dilation or erosion, and determine the calculation method, which is used to specify the intra-row calculation and inter-row calculation methods.
[0035] Step 2: Copy the boundary pixels according to the window size of the structural element. The size of the structural window is 3×3, so the number of copied boundary pixels is 1; the boundary copy is realized by buffering the 2-shot register cache. The schematic diagram of the boundary copy is as follows Figure 4 shown. When copying border pixels, the first and last border pixels copy their own border pixels, and the middle border pixels copy adjacent border pixels.
[0036] Step 3: Perform in-line calculation on th...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Select the binary image with a structural element window size of 3×3 and a width of 32768 as the second embodiment, such as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 8 , Figure 9 and Figure 10 As shown, the process steps are described as follows:
[0041] Step 1: Set dilation or erosion, and determine the calculation method, which is used to specify the intra-row calculation and inter-row calculation methods.
[0042] Step 2: Copy the boundary pixels according to the structuring element window size. Embodiment 2 The size of the structural window is 3×3, so the number of copied boundary pixels is 1. Embodiment 2 Realize boundary copy by caching 2 beat register cache, the schematic diagram of boundary copy is as follows Figure 8 shown. When copying border pixels, the first and last border pixels copy their own border pixels, and the middle border pixels copy adjacent border pixels.
[0043] Step 3: Perform in-row calculation on the data after copying the bound...
Embodiment 1
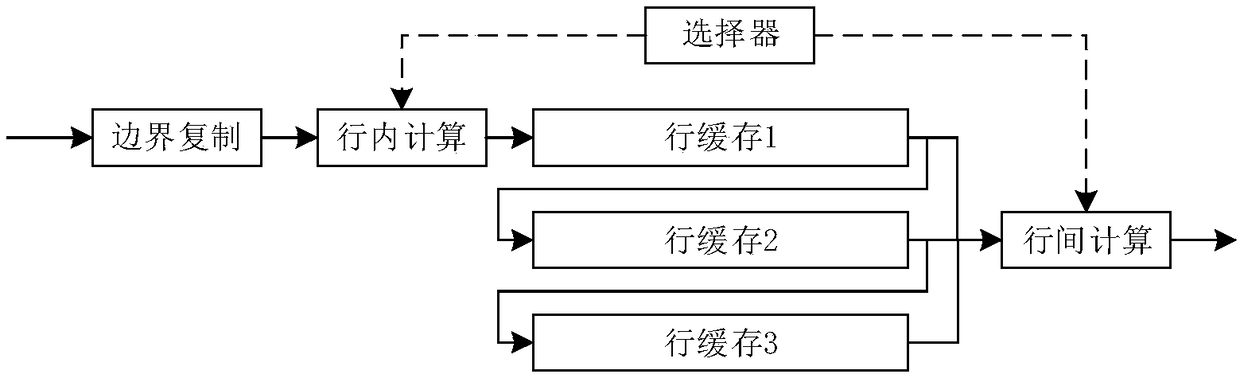
[0046] Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 have the same implementation block diagram. The implementation block diagram adopts a pipeline structure, and the data enters the boundary copy, intra-row calculation, row cache and inter-row calculation unit components in turn, and the selector controls the intra-row calculation and inter-row calculation units respectively. The size of the structural element window is optional, and the present invention takes the window size of 3*3 as an example for illustration, which can be reflected in figure 2 The number of middle row caches is 3, Figure 6 The number of instantiated RAM is 3, Figure 4 and Figure 8 The number of border pixels assigned in the middle is 1, that is (3-1) / 2, Figure 5 , Figure 7 , Figure 9 and Figure 10 3 pixels are used as the calculation unit, but the structural element window is not drawn separately.
[0047] In summary, the present invention duplicates the left and right borders, and the width of the image...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com