Semiconductor device
A semiconductor, N-type semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, transistors, etc., can solve the problems of semiconductor switch opening, voltage division, reaching or exceeding, etc., to achieve the effect of preventing opening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0074] First, refer to Figure 1 ~ Figure 4 , the semiconductor device according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described.
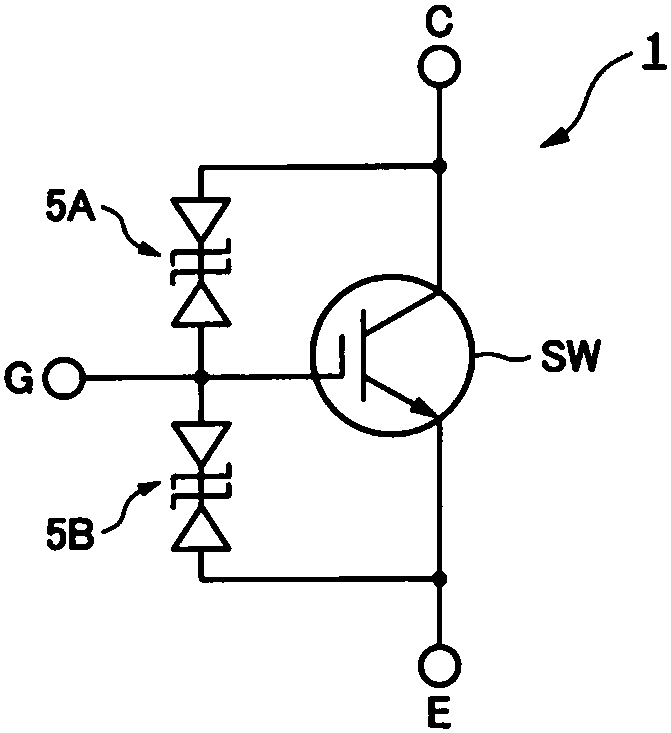
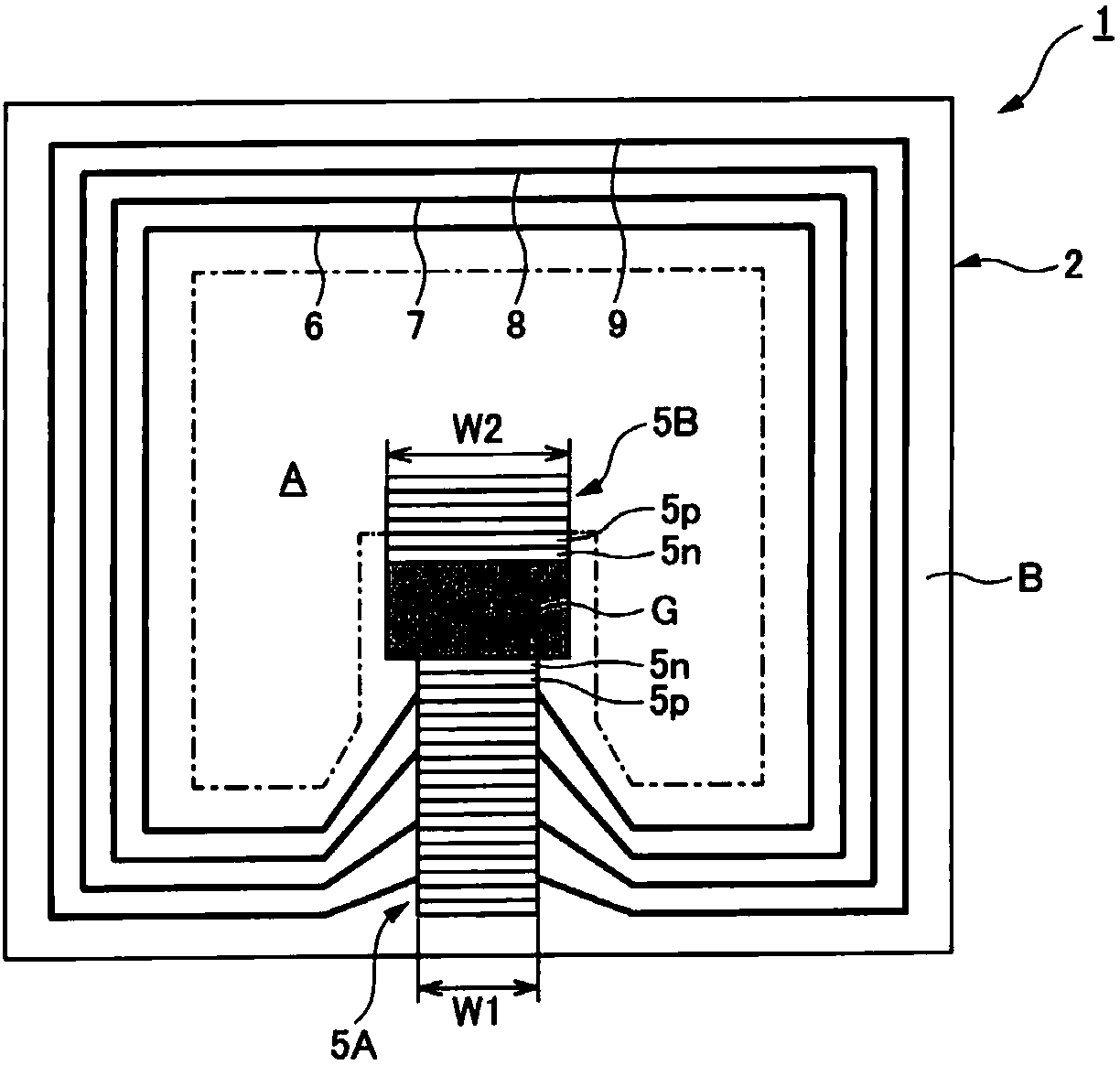
[0075] The semiconductor device 1 according to the first embodiment is, for example, figure 1 As shown, it includes: a semiconductor switch SW; a Zener diode 5A (first Zener diode); and a Zener diode 5B (second Zener diode).
[0076] The semiconductor switch SW has a first main electrode connected to a high potential, a second main electrode connected to a low potential, and a control electrode. The semiconductor switch SW has a MOS structure, and it is an insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) in the present embodiment. The first main electrode is the collector electrode C, the second main electrode is the emitter electrode E, and the control electrode is the gate electrode G. The collector C is connected to a high potential (for example, 400V), and the emitter E is connected to a low potential (for example, ground). The ...
no. 2 approach
[0099] Next, we will refer to Figure 5 , the semiconductor device according to the second embodiment of the present invention will be described. In the second embodiment, the Zener diode 5B between the gate emitters is regarded as a bipolar transistor, and the leakage current between the gate emitters is increased by increasing the current amplification factor of the transistor to suppress the gate voltage. rise. Next, the second embodiment will be described focusing on points of difference from the first embodiment.
[0100] Like the semiconductor device 1 according to the first embodiment, the semiconductor device according to the second embodiment includes: a semiconductor switch SW; a Zener diode 5A; and a Zener diode 5B.
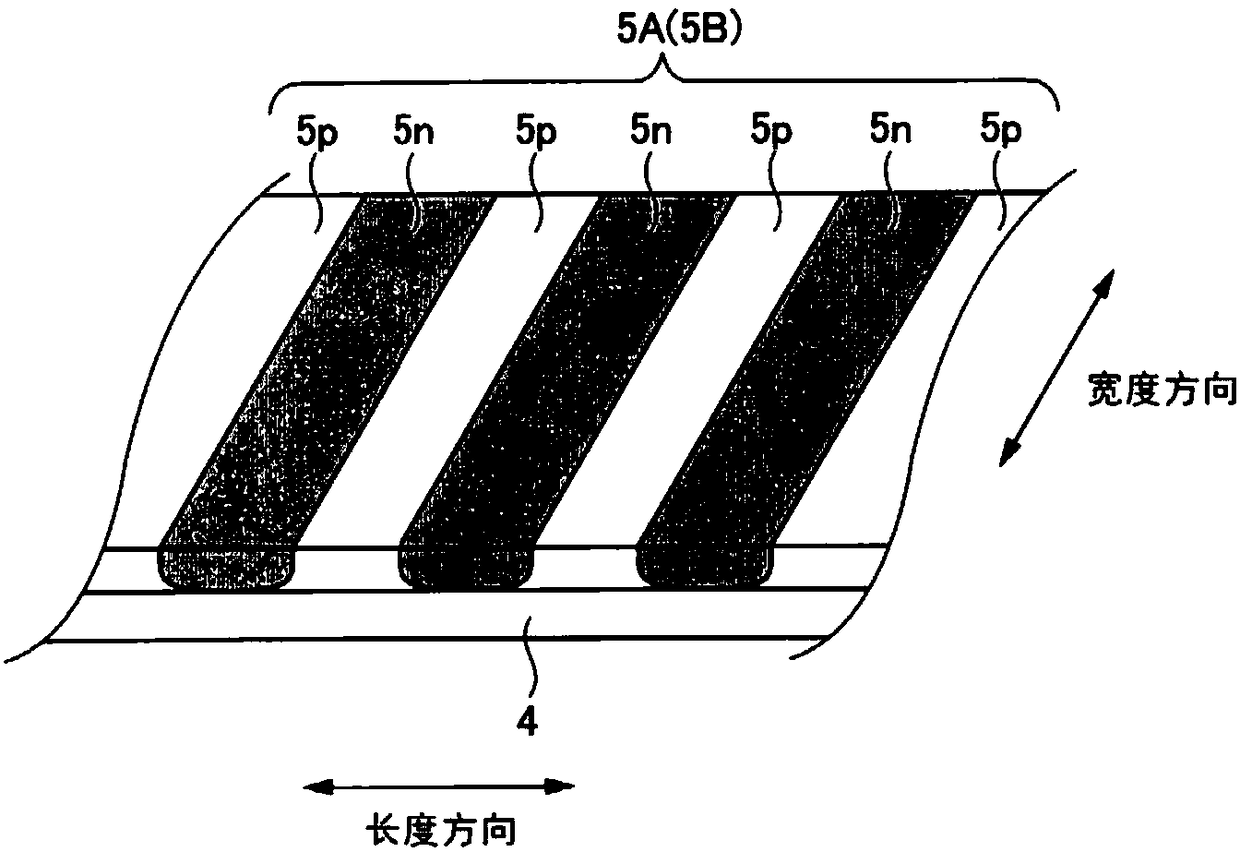
[0101] As described above, the concentration of the P-type dopant in the P-type semiconductor layer 5p constituting the Zener diodes 5A, 5B is lower than the concentration of the N-type dopant in the N-type semiconductor layer 5n. Therefore, if Fi...
no. 3 approach
[0108] Next, we will refer to Figure 6 ~ Figure 15 , the semiconductor device according to the third embodiment of the present invention will be described. In the third embodiment, by providing an integrated resistor connected in parallel with the Zener diode 5B, the leakage current between the gate and emitter electrodes is increased to suppress a rise in the gate voltage.
[0109] A semiconductor device 1A according to the third embodiment is, for example, Image 6 As shown, it includes: a semiconductor switch SW; a Zener diode 5A; a Zener diode 5B; and an integrated resistor R connected in parallel with the Zener diode 5B. The integrated resistor R is connected in parallel to the Zener diode 5B as described later, and is integrated (integrated) together with the Zener diode 5B. In other words, the integrated resistor R is not an external resistor.
[0110] In the present embodiment, among the plurality of N-type semiconductor layers 5n constituting the Zener diode 5B, t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com