Fault riding-through method and device and photovoltaic power generation system
A photovoltaic power generation system and fault ride-through technology, applied in photovoltaic power generation, circuit devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the injected power of DC-DC converters and slow response speed of DC bus voltage control, so as to reduce fluctuations, Realize the effect of fault ride-through
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
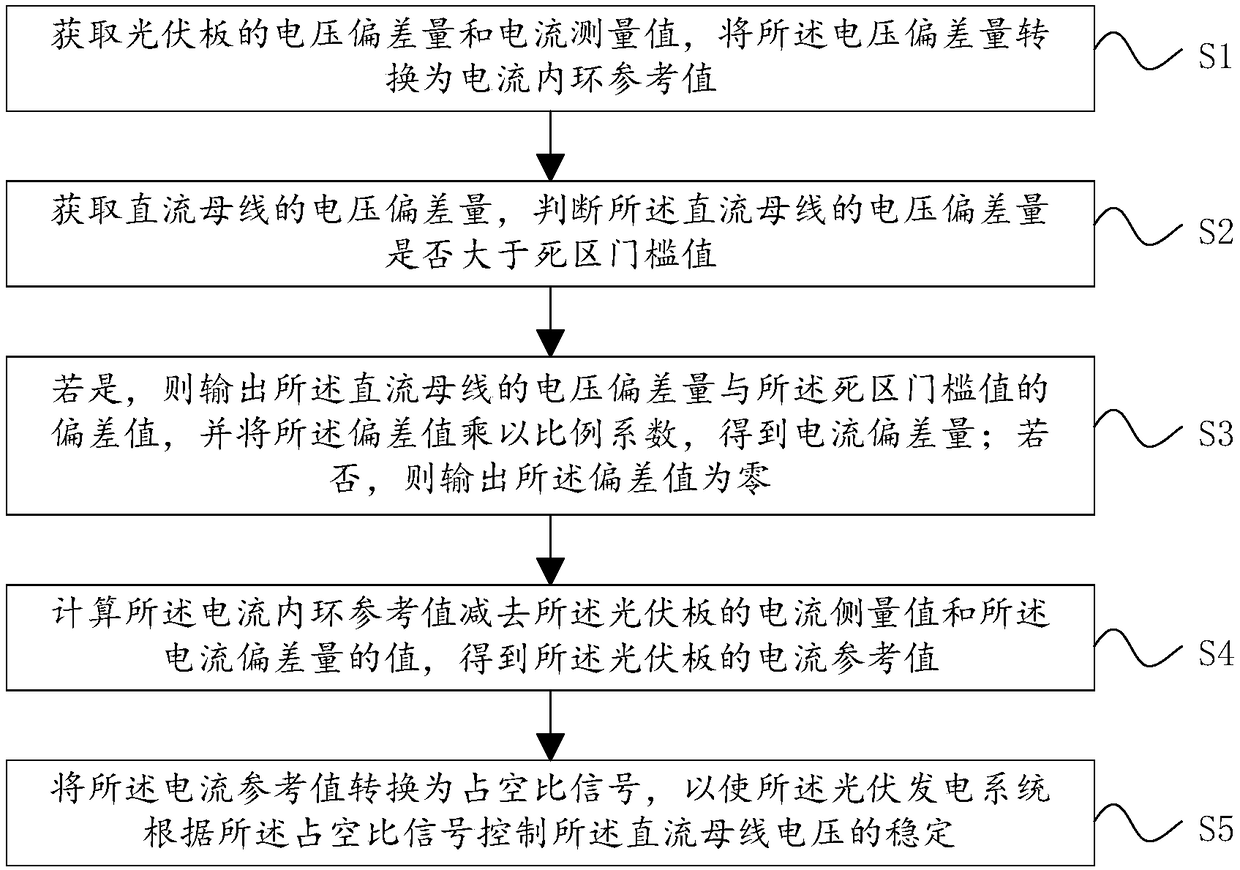
[0044] see figure 1 , figure 1 It is a flow chart of a fault ride-through method provided by an embodiment of the present invention; including:
[0045] S1. Obtain the voltage deviation and current measurement value of the photovoltaic panel, and convert the voltage deviation into a current inner loop reference value;
[0046] S2. Acquiring the voltage deviation of the DC bus, and judging whether the voltage deviation of the DC bus is greater than a dead zone threshold;
[0047] S3. If yes, then output the deviation between the voltage deviation of the DC bus and the dead zone threshold, and multiply the deviation by a proportional coefficient to obtain the current deviation; if not, output the deviation is zero;
[0048] S4. Calculate the value of the current inner loop reference value minus the current measurement value of the photovoltaic panel and the current deviation to obtain the current reference value of the photovoltaic panel;
[0049] S5. Convert the current ref...
Embodiment 2
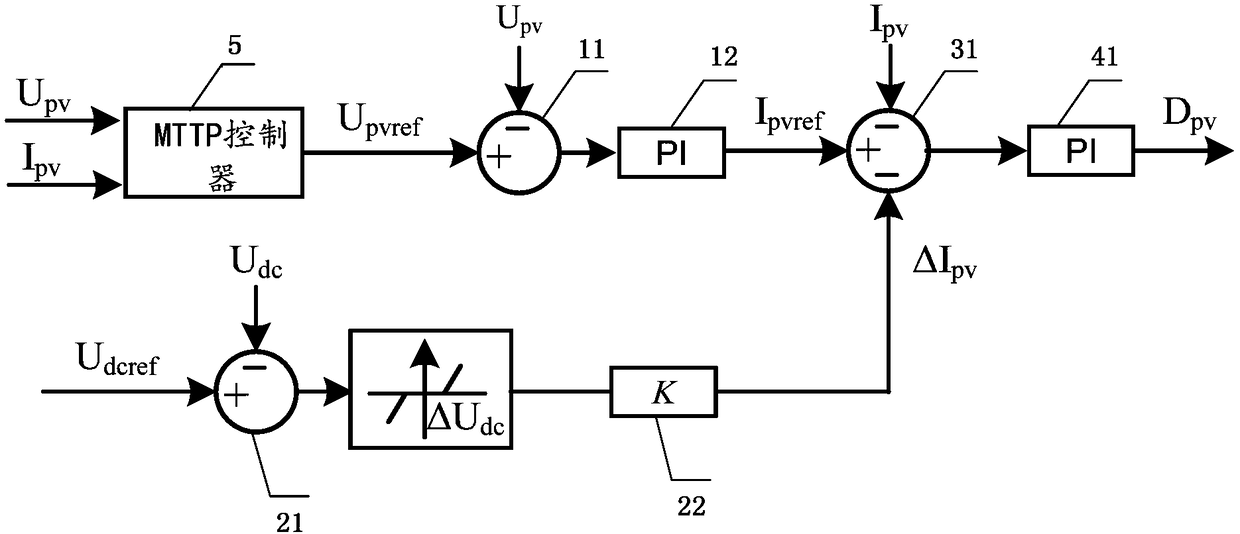
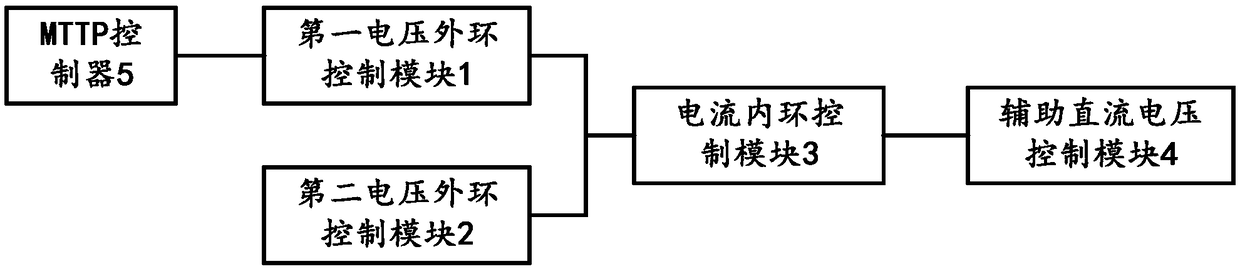
[0057] see image 3 , image 3 It is a schematic structural diagram of a fault ride-through device provided by an embodiment of the present invention; it includes:
[0058] The first voltage outer loop control module 1 is used to obtain the voltage deviation of the photovoltaic panel, and convert the voltage deviation into a current inner loop reference value;
[0059] The second voltage outer loop control module 2 is used to obtain the voltage deviation of the DC bus, and judge whether the voltage deviation of the DC bus is greater than the dead zone threshold; if so, then output the voltage deviation of the DC bus and the The deviation value of the dead zone threshold value, and multiply the deviation value by the proportional coefficient to obtain the current deviation amount; if not, then output the deviation value as zero;
[0060] The current inner loop control module 3 is used to obtain the current measurement value of the photovoltaic panel, and is also used to calcu...
Embodiment 3
[0072] see Figure 4 , Figure 4 It is a structural schematic diagram of a photovoltaic power generation system provided by an embodiment of the present invention; including:
[0073] Photovoltaic panel 101, DC boost converter 102, DC-AC converter 103, DC-AC controller 107, transformer 104, AC power grid 105, and the fault ride-through device 106 described in the second embodiment; wherein,
[0074] The photovoltaic panel 101 is used to convert light energy into a DC voltage, and transfer the DC voltage into a DC bus, and the DC bus is used to connect the photovoltaic panel 101 and the DC boost converter 102; The DC boost converter 102 is used to boost the DC voltage; the DC-AC converter 103 is used to convert the boosted DC voltage into an AC voltage; the transformer 104 is used to convert the DC voltage to the AC voltage. The voltage is boosted, so that the boosted AC voltage is input into the AC grid 105; the DC-AC controller 107 is used to control the operation of the DC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com