Path planning method based on Q-learning algorithm
A learning algorithm and path planning technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, vehicle position/route/altitude control, instruments and other directions, can solve the problems of Q-learning algorithm staying in simulation, lack of combination of practical problems, etc. Efficiency improvement, fast speed, fast convergence effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
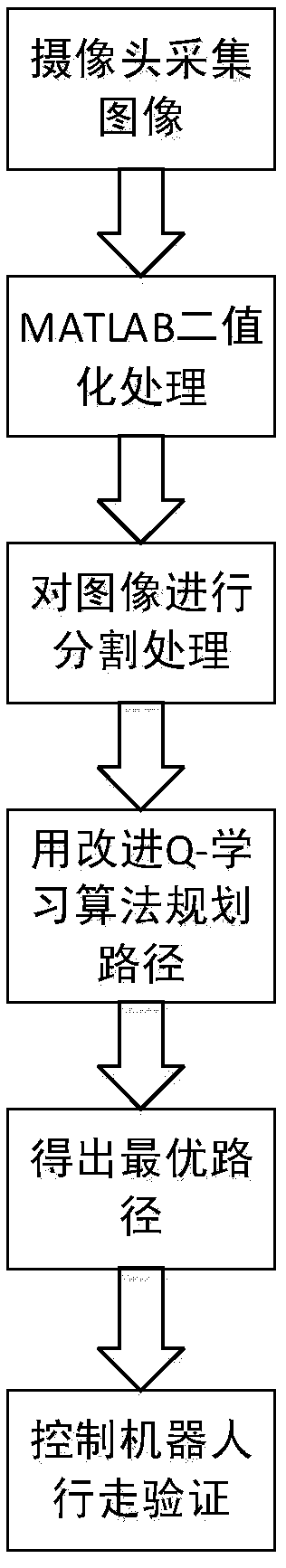
[0030] see Figure 1 to Figure 6 Shown:
[0031] The path planning method based on Q-learning algorithm provided by the present invention, its method is as follows:
[0032] Step 1: Use ordinary cameras to collect images of our actual environment to obtain basic information;
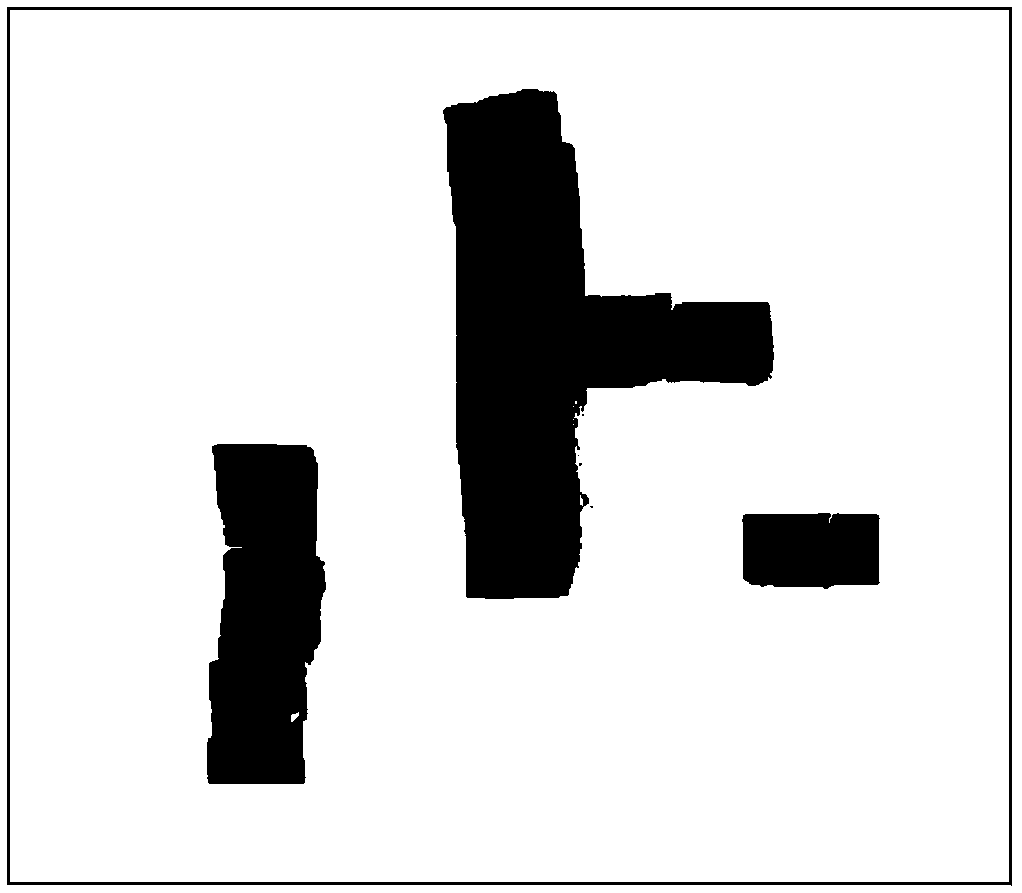
[0033] Step 2: MATLAB reads the image information collected by the camera, and performs binary processing on the image to determine the coordinates of obstacles in the image;
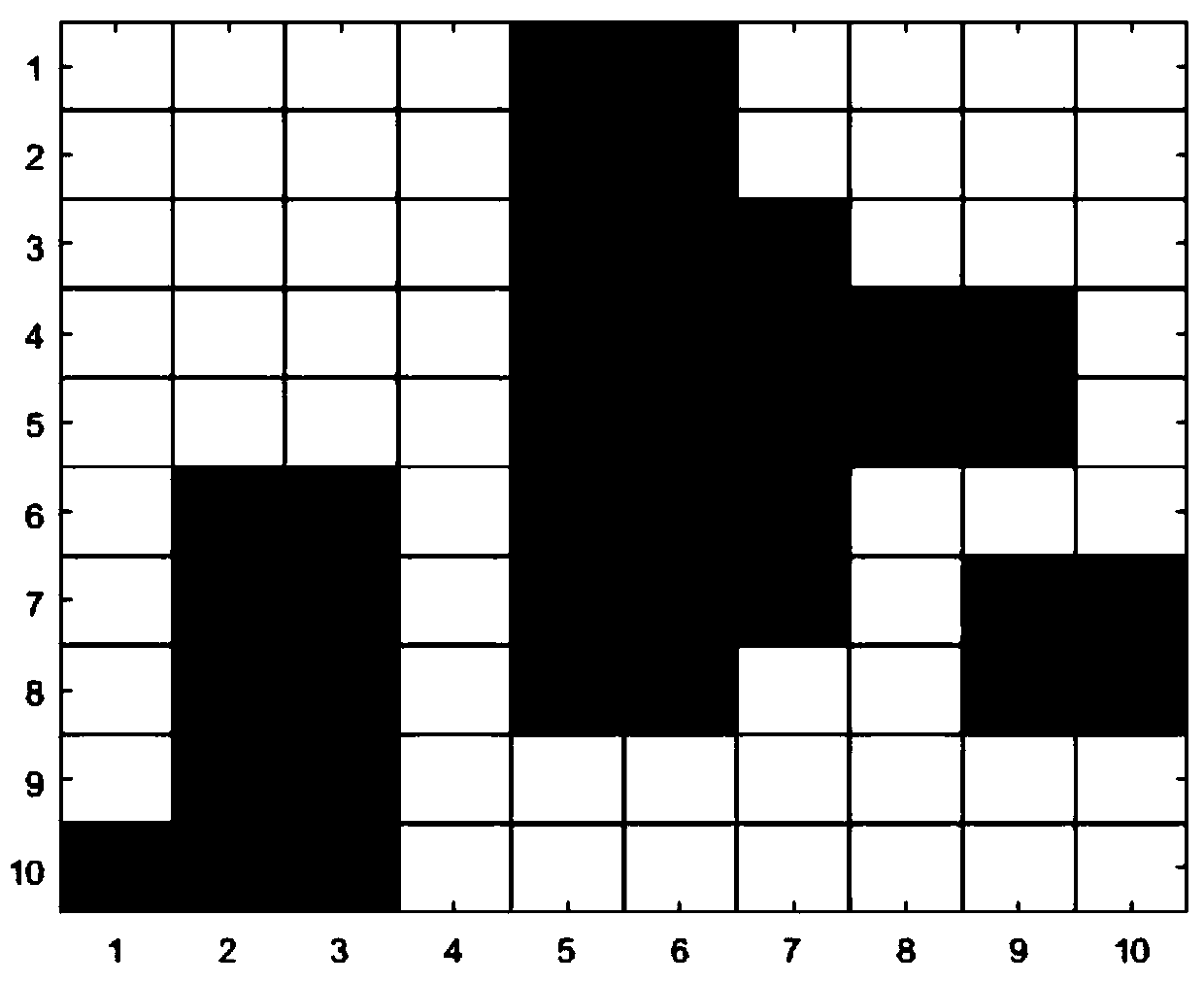
[0034] Step 3: Segment the graphics. In order to simplify the learning process, we use the grid method to build the environment model. We divide the picture in the previous step into 10×10 grids, and judge in the program. If there is an obstacle, the grid is defined as a grid with obstacles, and the robot cannot pass through it; other grids are defined as grids without obstacles, and the robot can pass through;
[0035] The fourth step: use the improved Q-learning algorithm to plan the path, first define the starting point and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com