Display screen energy saving method
A technology of display screen and local variance, applied in data processing power supply, instrument, electrical digital data processing and other directions, can solve the problems of loss of information in dark areas, dark areas of images, and images that do not conform to human visual perception.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
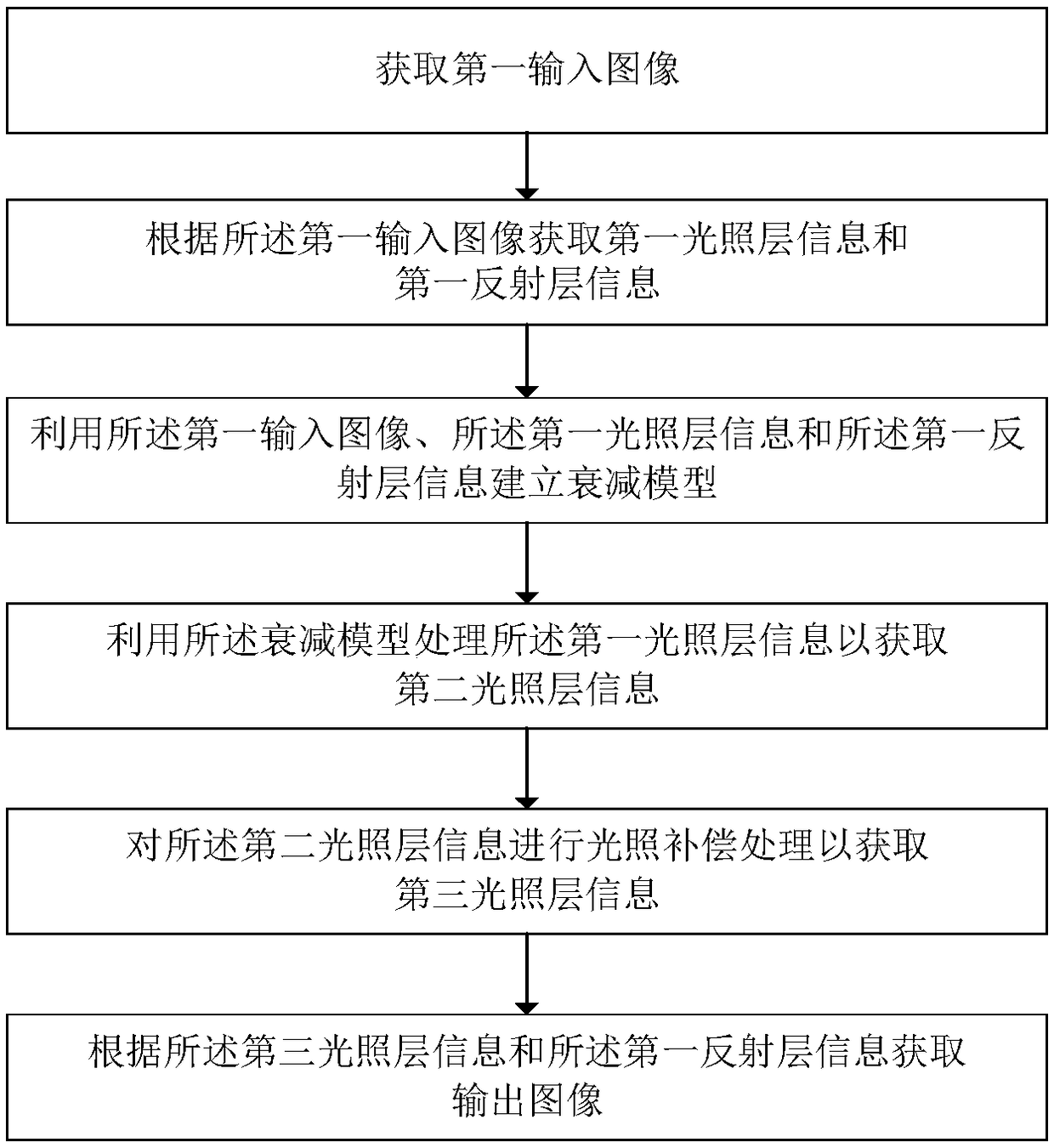
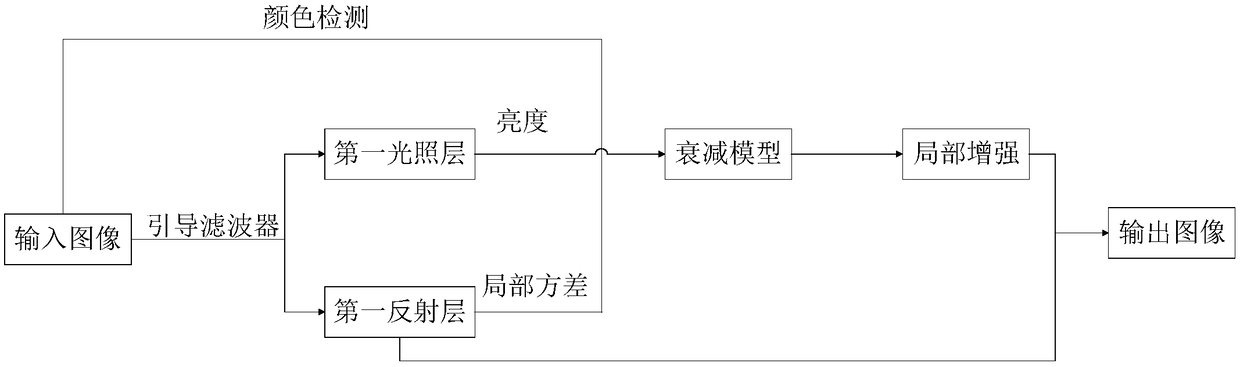
[0057] See figure 1 and figure 2 , figure 1 It is a schematic flow chart of an OLED display energy-saving method provided by an embodiment of the present invention, figure 2 It is a flow chart of a method for saving energy on an OLED display screen based on image content provided by an embodiment of the present invention. like figure 1 As shown, the energy saving method includes:
[0058] Step 1, obtaining the first input image;
[0059] Step 2. Obtain first illumination layer information and first reflection layer information according to the first input image;
[0060] Step 3, using the first input image, the first illumination layer information and the first reflection layer information to establish an attenuation model;
[0061] Step 4, using the attenuation model to process the first illumination layer information to obtain second illumination layer information;
[0062] Step 5. Perform illumination compensation processing on the second illumination layer informa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com