Artificial field source frequency domain electromagnetic apparent resistivity measuring method
A technology of apparent resistivity and artificial field source, which is applied in the field of artificial field source frequency domain electromagnetic apparent resistivity measurement, can solve problems affecting the accuracy and efficiency of apparent resistivity calculation, reduce the scope of application of CSAMT, and increase the cost of field exploration. Achieve the effects of reducing field exploration costs, avoiding poor calculation accuracy, and improving solution efficiency and accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The following is a further description of the present invention in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments
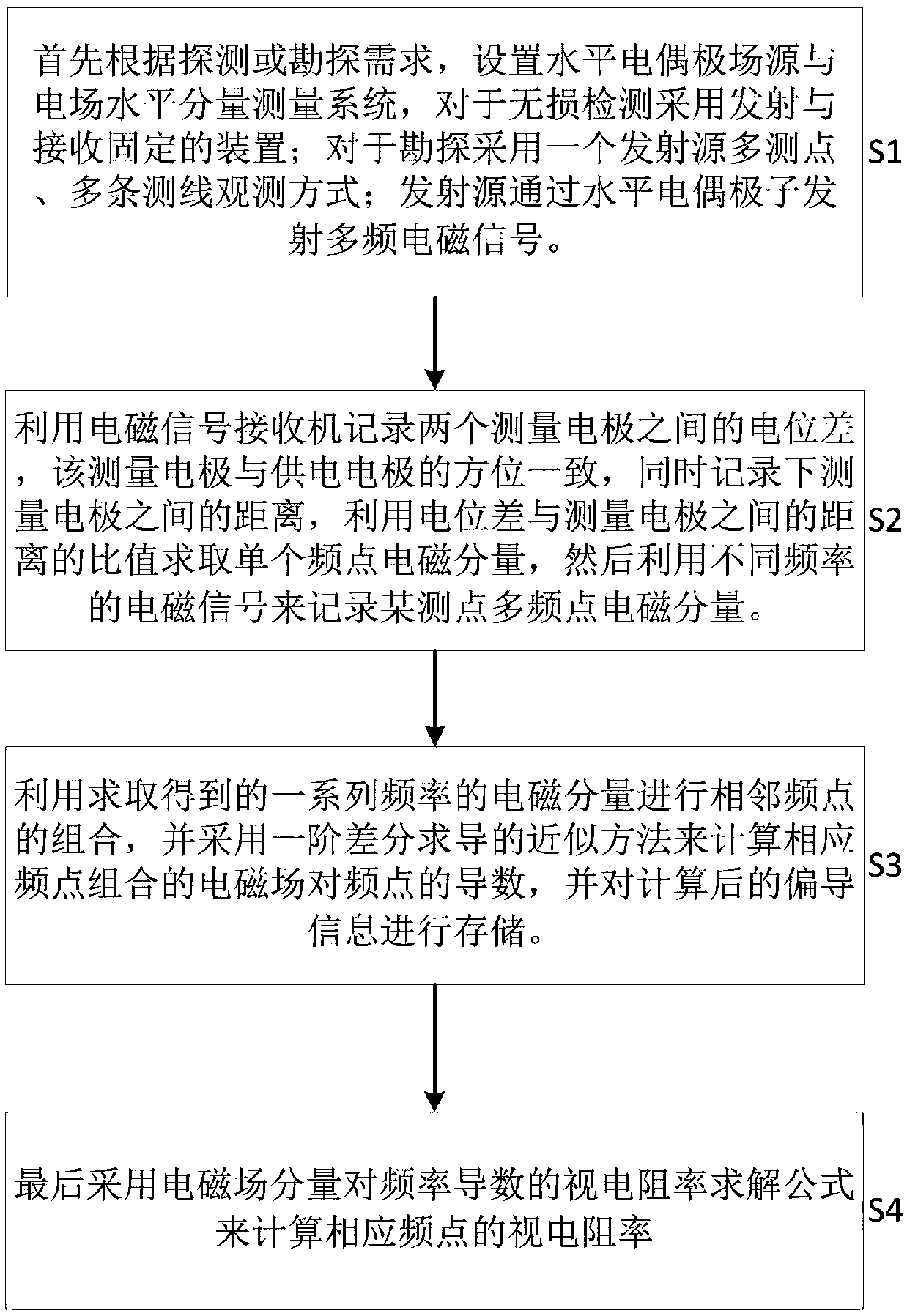
[0044] See figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides an artificial field source frequency domain electromagnetic apparent resistivity measurement method, which comprises the following steps:
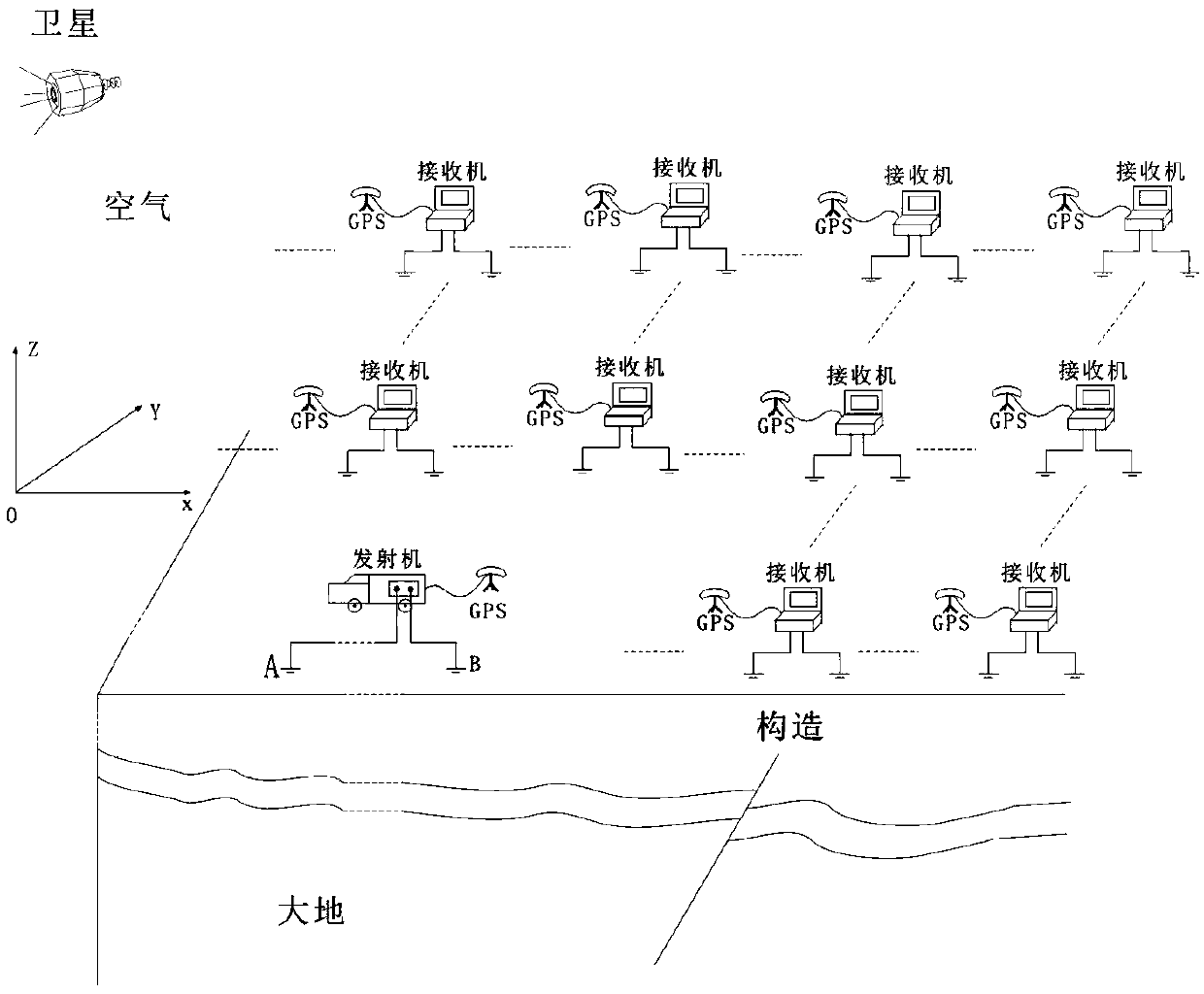
[0045] Step S1: First, according to the exploration needs, set the appropriate field source position, and lay out a number of survey lines and corresponding observation points in the exploration area, place an electromagnetic signal receiver at the observation point, and place the signal transmitter at the field source position for the exploration. The area transmits electromagnetic signals of multiple frequencies;
[0046] Step S2: Use the electromagnetic signal receiver to record the potential difference V between the two measuring electrodes, the measuring electrodes are in the same orientation as the power supply electrodes, and reco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com