Method for computer to simulate human brain in learning knowledge, logic theory machine and brain-like artificial intelligence service platform
A computer and knowledge technology, applied in logical reasoning machines and brain-like artificial intelligence service platforms, simulating the field of human brain learning knowledge, can solve problems such as learning and working of artificial intelligence without a computer, complete and systematic solution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
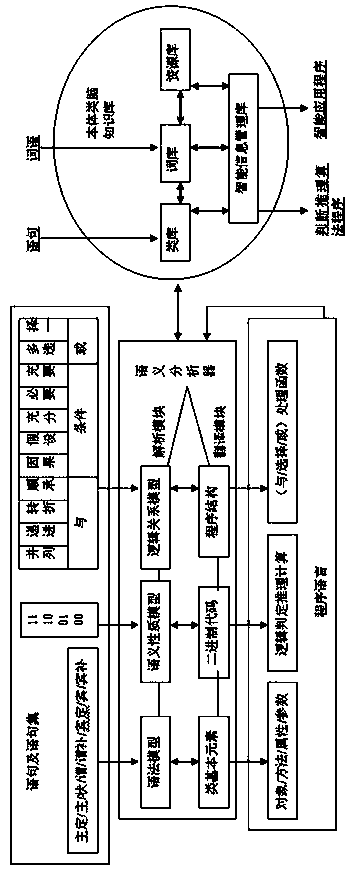
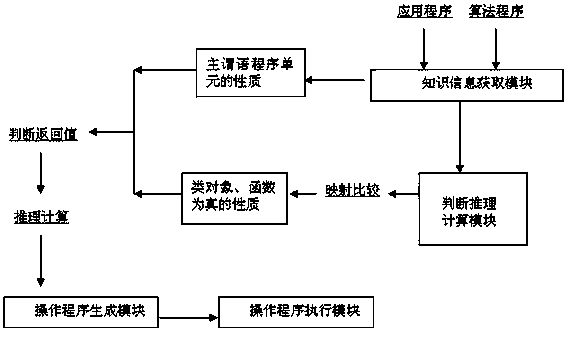
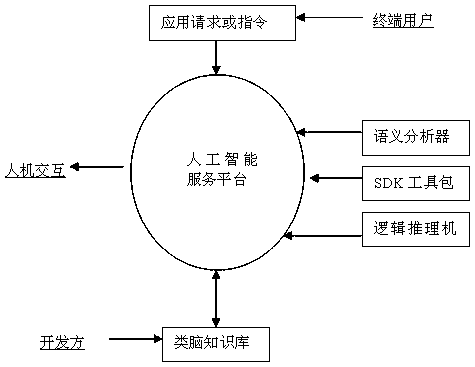
[0077] Because there are only the above five kinds of logical relations in the reasoning thinking of the human brain, through the above-mentioned axiomatic rules, an analytical reasoning program can be established for any problem-solving problem, and reliable logical conclusions can be obtained through judgment and calculation. By programming and digitizing analysis and reasoning, computers can learn and work in an intelligent way of brain-like judgment and reasoning. Through the above-mentioned executable programs, the machine can obtain human-computer interaction results that meet the application requirements, ensuring the logical correctness of the output. Specific examples are as follows:
[0078] Judgment example 1: Trump is an American.
[0079] String say="Trump is an American.";
[0080] listener.MatchListener(say); / / JH platform monitoring;
[0081] JHAction jha = new JHAction();
[0082] Semanteme semanteme = jha. JHSemanteme(say);
[0083] / / Receive the grammati...
example 2
[0091] Judgment example 2: Trump is Chinese.
[0092] String say="Trump is Chinese.";
[0093] listener.MatchListener(say); / / JH platform monitoring;
[0094] JHAction jha = new JHAction();
[0095] Semanteme semanteme = jha. JHSemanteme(say);
[0096] / / Receive the grammatical components of the sentence;
[0097] int zlj=semanteme.getZlj(); / / Get the logical value of the subject in the composition,
[0098] Here the value is 1;
[0099] int wlj=semanteme.getWlj(); / / Get the logical value of the predicate in the component,
[0100] Here the value is 1;
[0101] Int[] RLV= jha.getComparison(say); / / Get the actual comparison logic value, where the value is the actual main logic value 1, and the actual predicate logic value is 0
[0102] Boolean fal=LanguagComparisonEreality(zlj,wlj,RLV);
[0103] / / Obtain the comparison value of language and scene to get the truth value of this sentence, that is, the return value is 0. Here, after the nature of the predicate has changed: i...
example 3
[0116] Reasoning example 3 (necessary and sufficient conditions): the diameter of the cup is 5 cm, which is equal to (if and only) when the cup is qualified.
[0117] String say="The diameter of the cup is 5 cm, which is equal to the qualified cup.";
[0118] JHAction jha = new JHAction();
[0119] Semanteme semanteme=jha. JHSemanteme(say);
[0120] String JudgeConditions=semanteme.getqj(); / / Get the judgment condition of the former item in the composition "the caliber of the cup is 5 cm";
[0121] Through examples 1 and 2, when we process the cup to obtain the actual caliber of the cup, it is uncertain, it may be equal to 5 cm or may not be equal to 5 cm, so the actual caliber and the standard caliber we get are uncertain, then here There are two possible return values, one for 1 and one for 0. When the return value is 1, the correct conclusion introduced here is: the cup is qualified. That is, if the antecedent of the necessary and sufficient condition is true, the conseq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com