A thermally driven micropump experimental device and method based on microfluidic technology
A microfluidic technology and experimental device technology, applied in the field of microelectromechanical systems, can solve the problems of large flow pulsation, low flow efficiency, low driving voltage, etc., and achieve the effects of improving flow efficiency, fast response speed, and improving conversion efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
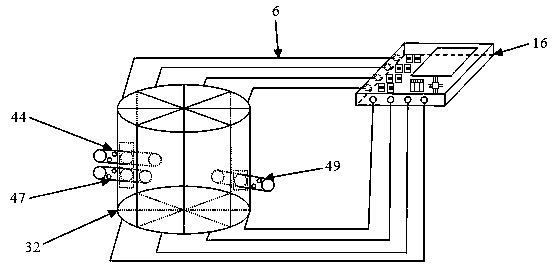
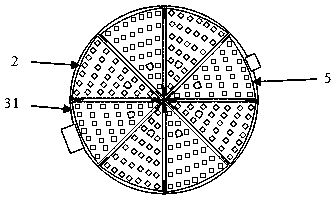
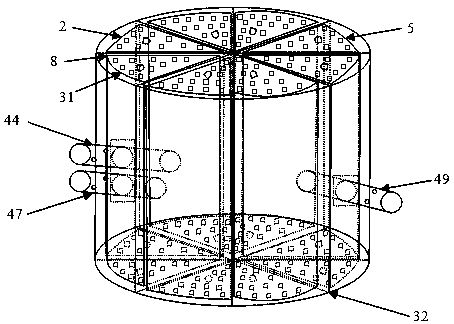
[0045] See figure 1 The thermally driven micropump experimental device based on the microfluidic technology of the present invention is composed of two modules, the thermally driven micropump 32 and the microcontroller module 16. The thermally driven micropump 32 and the microcontroller module 16 are independent modules that can be freely placed on a horizontal surface, and the two modules are connected by multiple wires 6. There are two liquid inlet pipes and one liquid outlet pipe 49 on the side wall of the thermally driven micropump 32. The two liquid inlet pipes are respectively a first liquid inlet pipe 44 and a second liquid inlet pipe 47 with the same structure. The pipe 44 and the second liquid inlet pipe 47 are arranged up and down for adding two different types of liquid to the inside of the thermally driven micropump 32 respectively. The liquid outlet pipe 49 is opposite to the two liquid inlet pipes and is used to flow out the liquid after being uniformly mixed by t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com