Optimized depth extraction and passive ranging based on monocular vision
A deep extraction and passive ranging technology, applied in image data processing, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve the problems of poor versatility, non-linear distortion correction of the image to be tested, and low accuracy of target measurement and ranging. To achieve the effect of avoiding errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
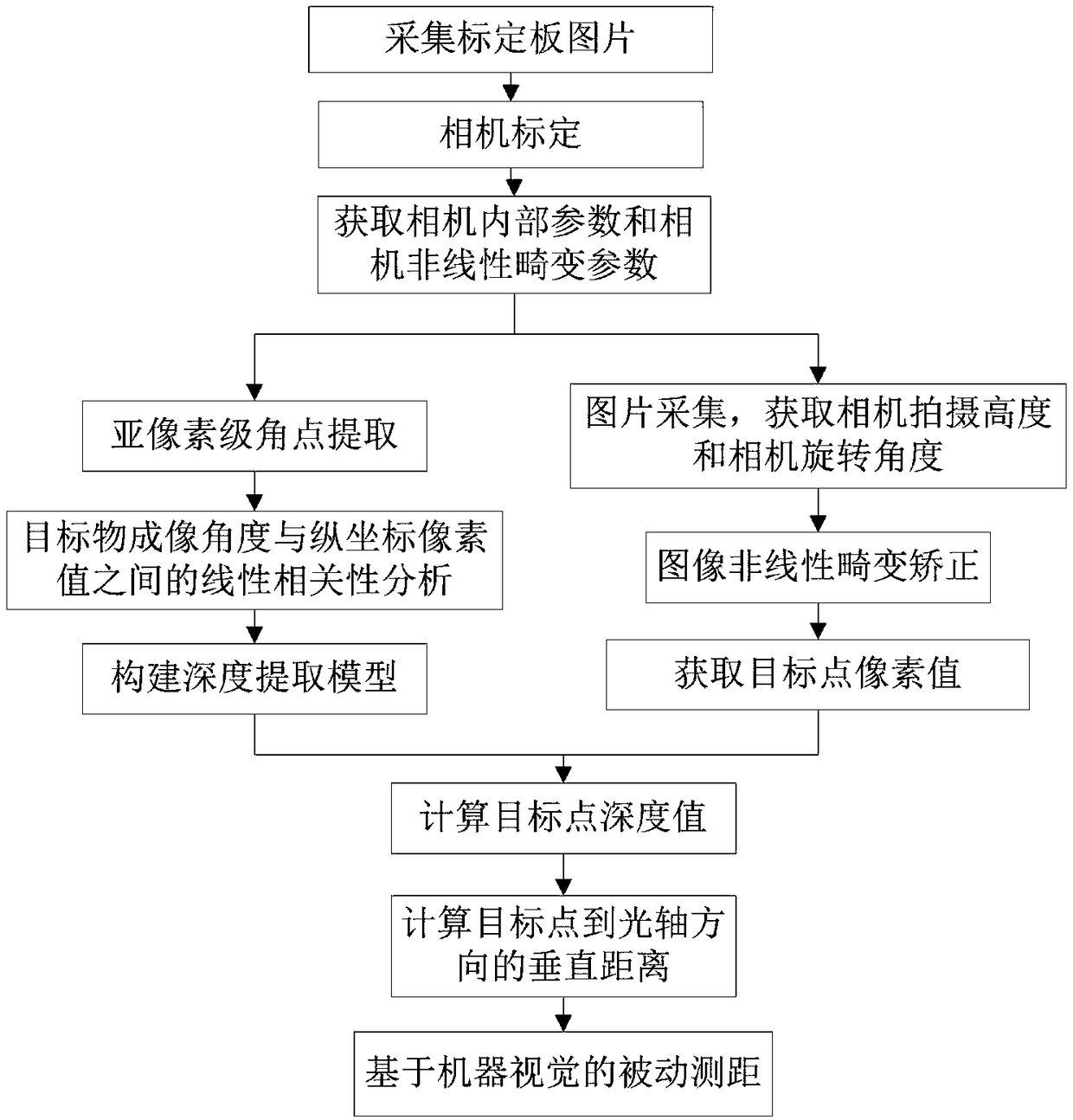
[0158] Taking Xiaomi 3 (MI 3) mobile phone as an example, the optimized depth extraction and passive ranging method based on monocular vision of the present invention will be described in detail below.
[0159] 1. Calibrate the mobile phone camera to obtain the internal parameters of the camera and image resolution
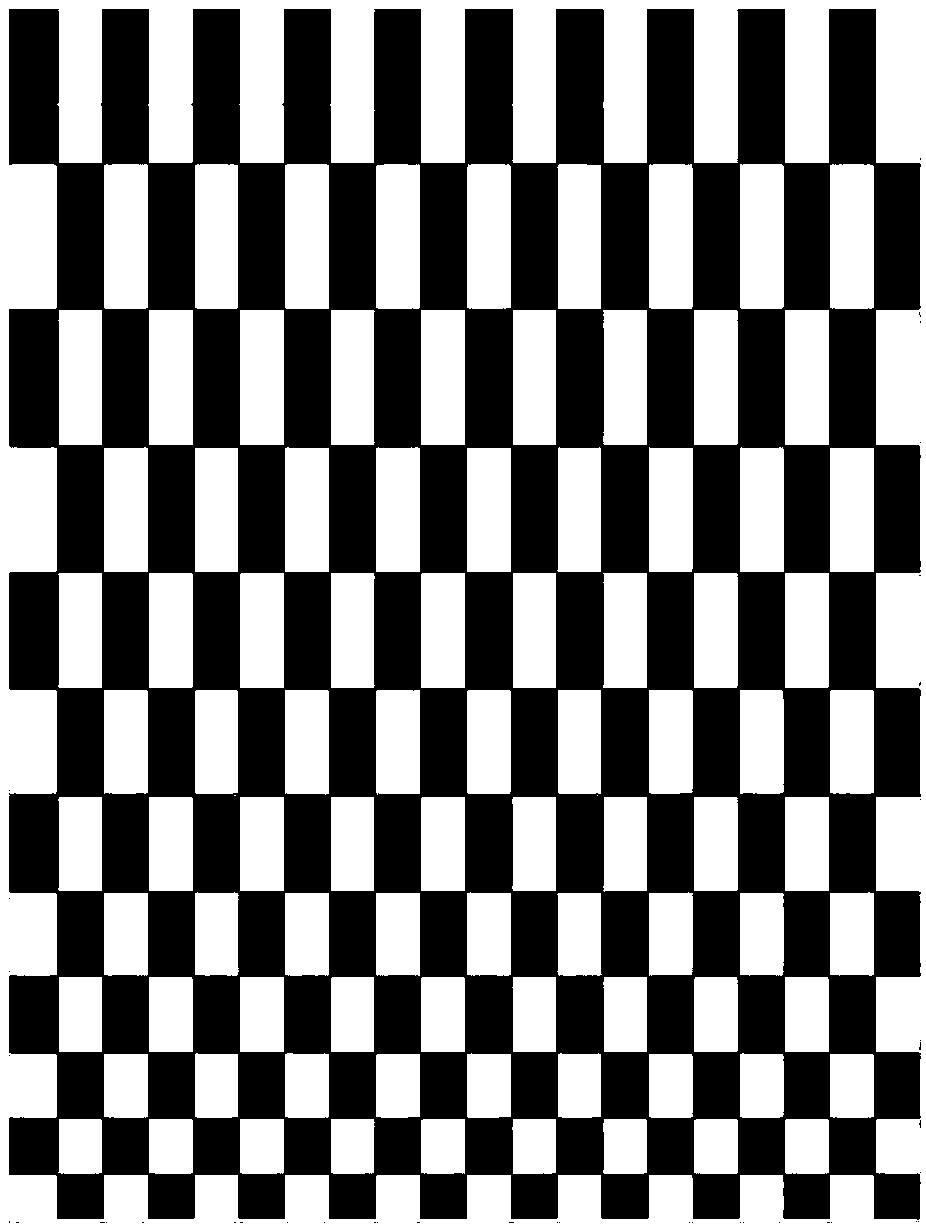
[0160] Use a checkerboard calibration board with a number of rows and columns of 8*9 and a size of 20*20 as the experimental material for camera calibration, collect 20 calibration board pictures from different angles through the camera of the Mi 3 mobile phone, and use OpenCV to improve the non-linear The camera calibration model of the distortion item is used to calibrate the Xiaomi 3 (MI 3) mobile phone camera,
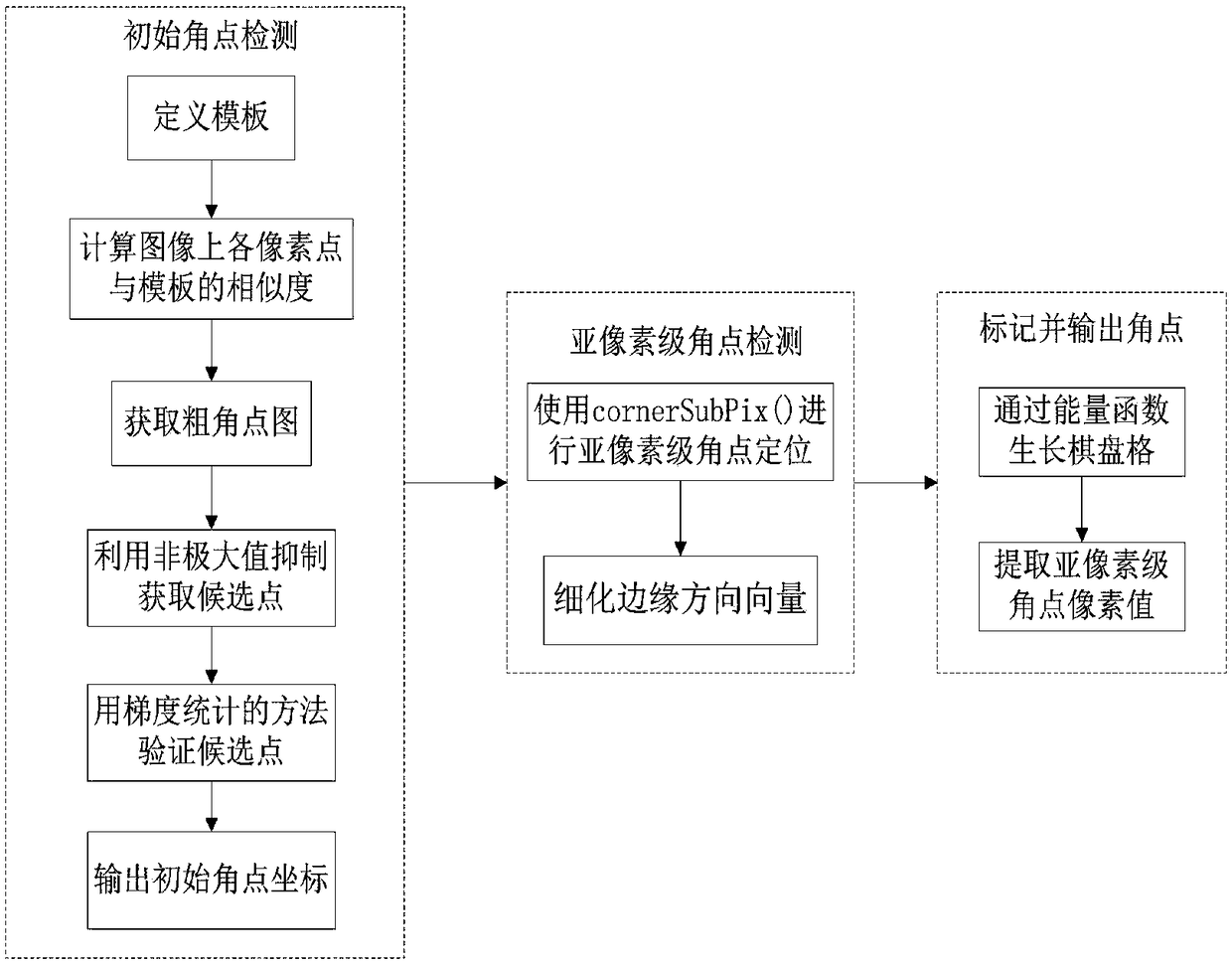
[0161] First use the fin() function to read the calibration board picture, and obtain the image resolution of the first picture through .cols and .rows; then use the find4QuadCornerSubpix() function to extract the sub-pixel corners in the calibration b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com