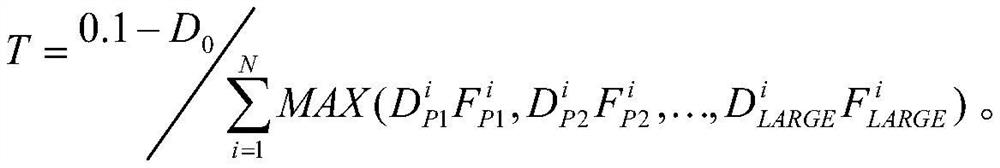A Method Applicable to Dose Risk Control of High-Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor Nuclear Power Plant Clusters
A high-temperature gas-cooled reactor, risk control technology, applied in data processing applications, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve problems such as no dose risk control, risk management, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments.
[0024] The method of the present invention applicable to the dose risk control of high temperature gas-cooled reactor nuclear power plant groups comprises the following steps:
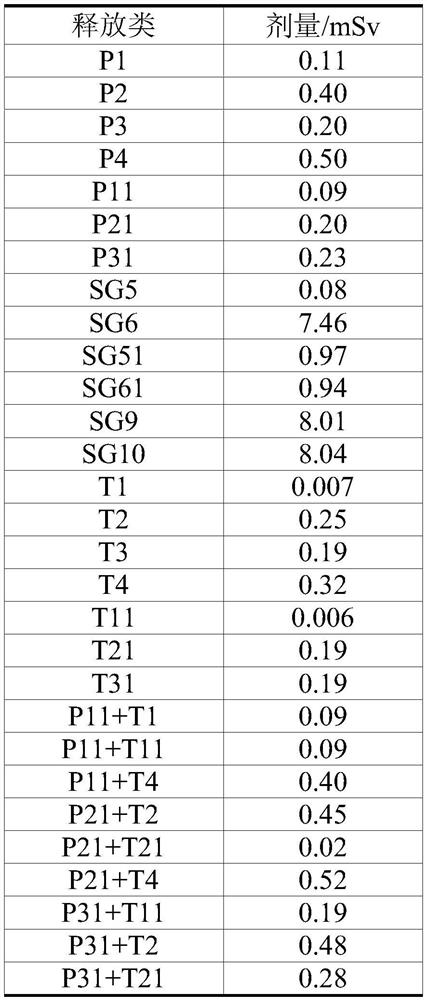
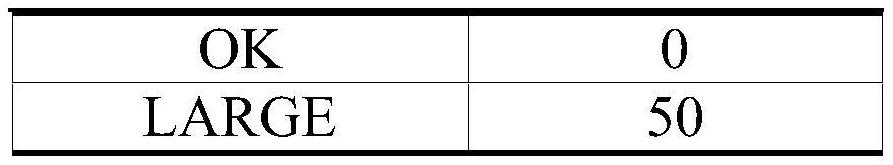
[0025] Step 1: Assuming that there are N reactors in the high temperature gas-cooled reactor nuclear power plant, and the i-th reactor needs to be temporarily changed, by running the PSA model and data, calculate the release frequency of various release types under the i-th reactor’s proposed configuration change , where configuration refers to the specific state of the unit composed of the specific conditions of the various systems and equipment of the nuclear power plant, which includes elements such as: unit operating mode, equipment standby / running status, unavailable equipment, tests, and external factors (such as high temperature weather, typhoon), etc. When the system configuration or equi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com