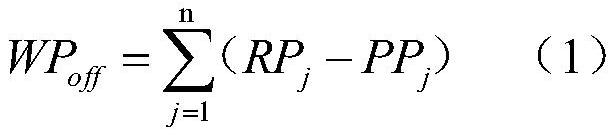A Method for Automatic Power Flow Control of Regional Power Grid Lines
A technology for regional power grids and lines, applied in circuit devices, AC network circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in meeting the requirements of power grid intelligence, improve automation capabilities, enhance safety, and reduce the possibility of misoperation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
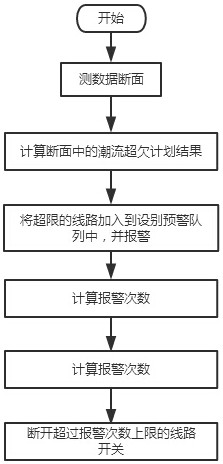
[0046] The present invention is realized through the following technical solutions, as Figure 1-Figure 2 As shown, a method for automatic power flow control of regional power grid lines specifically includes the following steps:
[0047] Step F1: get cyc SCADA measurement section data of the power grid and planned power flow data of each line and main transformer of the power grid with a period of one second, and calculation of the power flow over and under plan results of the entire network and each line;
[0048] Step F2: Add the lines whose power flow overrun plan value exceeds the set percentage to the equipment early warning queue list and give an alarm prompt, and calculate the accumulated alarm times of the lines in the equipment early warning queue list according to the set time interval;
[0049] Step F3: When the accumulative number of alarms of a certain line in the equipment early warning queue list exceeds the set upper limit of the number of early warnings, the...
Embodiment 2
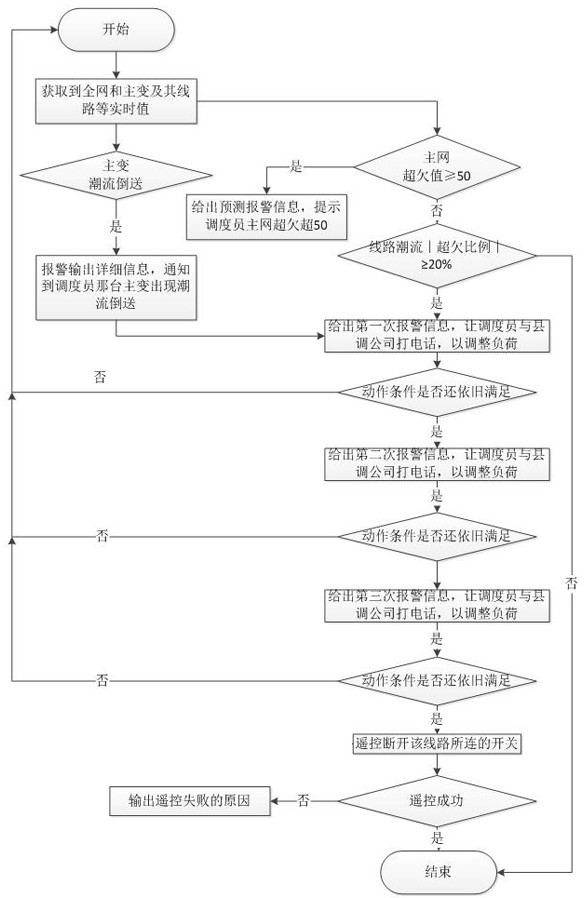
[0054] This embodiment is further optimized on the basis of the above embodiments, such as Figure 1-Figure 2 As shown, the step F1 specifically includes the following steps:
[0055] Step F11: Obtain t from grid SCADA cyc The measurement section data with a period of one second; the t cyc Set by the user, the default value is 10s;
[0056] Step F12: Calculating the power flow overrun plan value WP of the whole network in the section off ;
[0057]
[0058] In formula (1), RP j Indicates the active power measurement value of the gateway line or main transformer; PP j Indicates the active power planning value of the grid gateway line or main transformer, which is obtained from the grid active power planning function module; n indicates the total number of grid gateway lines and main transformers; j indicates each gateway line and main transformer;
[0059] Step F13: When the power flow of the whole network exceeds the planned value WP off Greater than the upper limit ...
Embodiment 3
[0072] This embodiment is further optimized on the basis of the above embodiments, such as Figure 1-Figure 2 As shown, the step F2 specifically includes the following steps:
[0073] Step F21: When the power flow of any line exceeds the percentage of planned value | LP off-k |≥LP max , then add the line to the equipment warning queue; LP max is the upper limit of the line power flow exceeding the planned value percentage; the LP max Set by the user, the default is 20%;
[0074] Step F21-1: When any line described in step F21 does not exist in the equipment early warning queue, add the line to the equipment early warning queue; set the continuous overtime time CT of the line off-k =0, cumulative alarm times CA off-k = 0;
[0075] Step F21-2: If any of the lines described in step F21 already exists in the equipment warning queue, then correct the line’s continuous time of exceeding the plan and the cumulative number of alarms of the line;
[0076] Step F21-2-1: In step F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com