A Classification Method of Human Brain Functional Network Based on Convolutional Neural Network
A convolutional neural network and functional network technology, applied in biological neural network models, neural architectures, instruments, etc., can solve the problems that convolutional neural network models cannot make full use of brain network topology information and affect the diagnosis of brain diseases. Achieve accurate brain disease diagnosis, reduce the risk of overfitting, and the method is reasonable and reliable
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
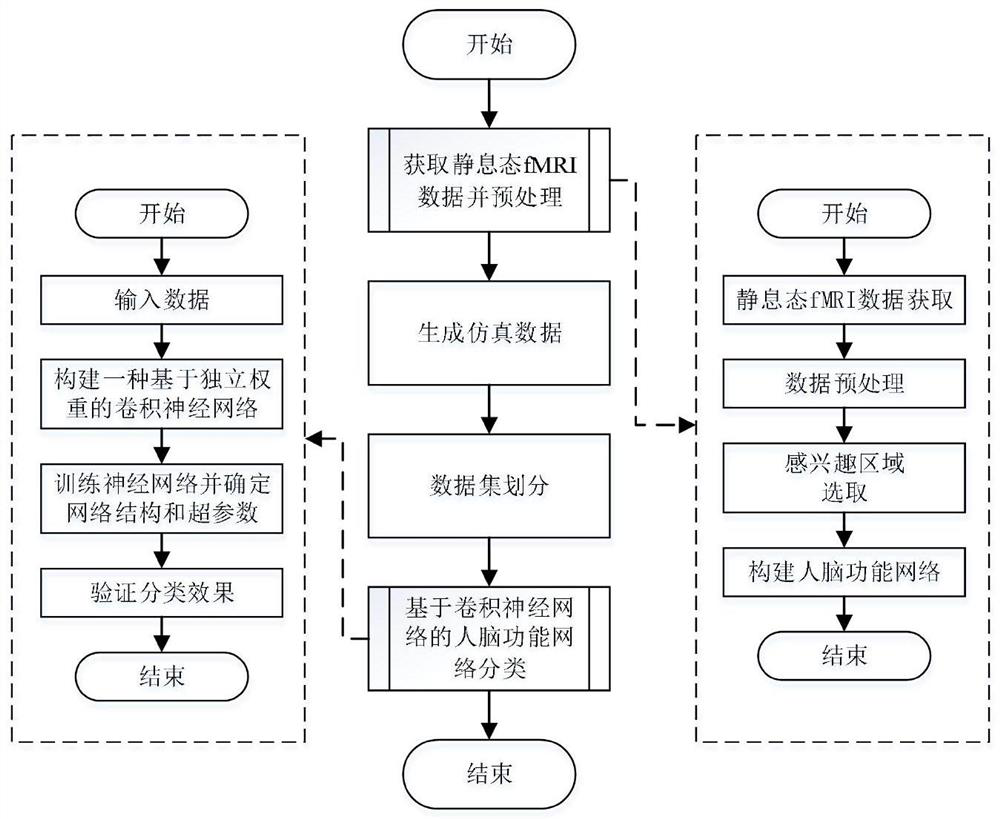
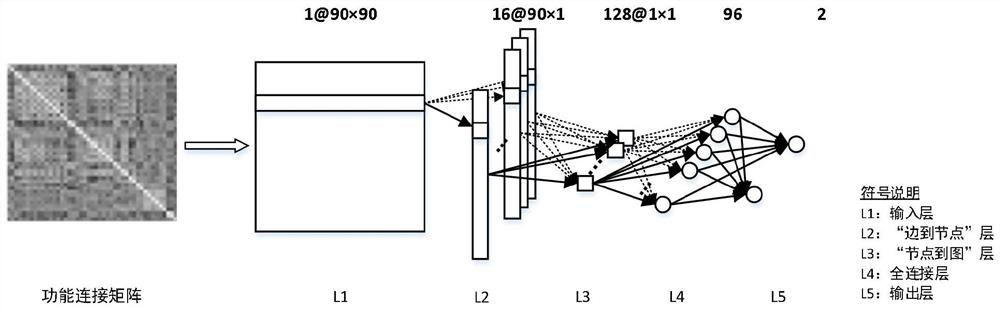
[0045] Take the simulation data set and the real fMRI data set as examples below to illustrate the specific implementation steps of the present invention: Step (1) obtain the resting state fMRI data and preprocess:
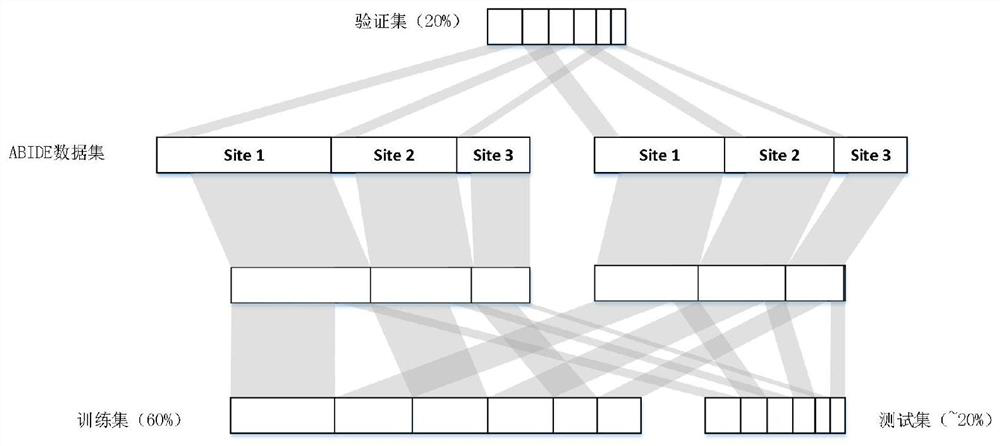
[0046] Step (1.1) Resting-state fMRI data acquisition: We obtained autism (Autismspectrum disorder, ASD) data from ABIDE (Autism Brain Imaging DataExchange, http: / / fcon_1000.projects.nitrc.org / indi / abide / ) for analysis , including the resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) data of 1112 subjects.
[0047] Step (1.2) Data preprocessing: In order to be able to easily reproduce and extend the method, all preprocessed data were obtained from the Preprocessed Connectomes Project (PCP, http: / / preprocessed-connectomes-project.org / abide / ). The PCP project publicly released and shared the preprocessed data of each site in ABIDE by four different preprocessing processes. The data used in the present invention are preprocessed by Data Processing Assist...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com