Application of NOD1 to preparation of products for inhibiting tumor SRC signal path
A signal pathway and product technology, applied in the direction of antineoplastic drugs, medical preparations containing active ingredients, pharmaceutical formulations, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example 1 Effect of NOD1 expression on liver cancer
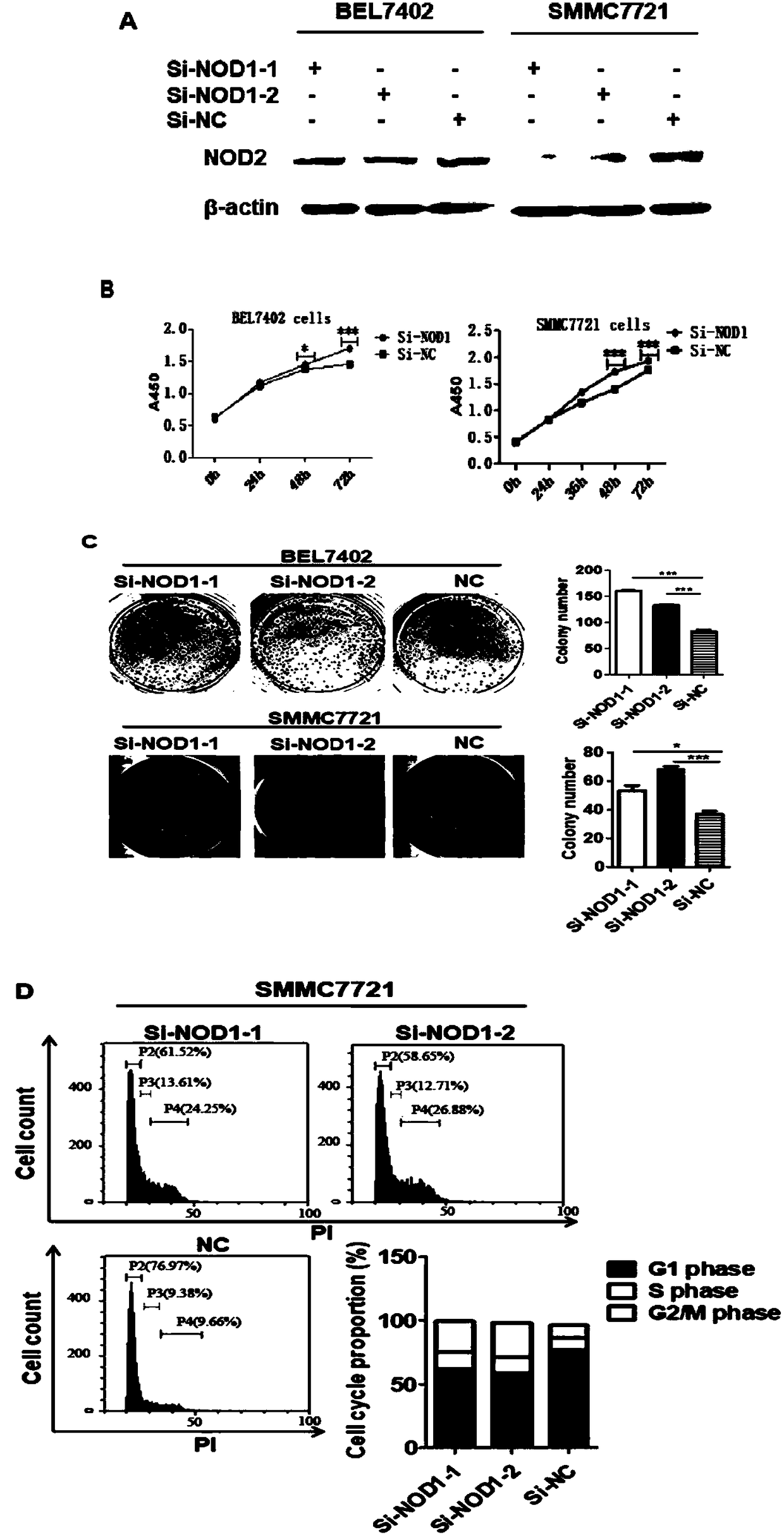
[0057] (1) SMMC7721 and BEL7402 liver cancer cells were treated with 3x10 5 Inoculate in a 6-well plate at a density of / ml, add 2ml of cell suspension to each well, and culture overnight. When the cell density was 60%-80%, the liver cancer cells were transfected with Si-NOD1, and the Si-NC transfection group was used as a control, and a blank control group was also set up. Si-NOD1 sequence: Sense: 5'-CCAGCUCGUUCAGAGCAAATT-3', as shown in SEQ ID NO.2; Anti-sense: 5'-UUUGCUCUGAACGAGCUGGTT-3', as shown in SEQ ID NO.3. Si-NC sequence: Sense: 5'-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT, as shown in SEQ ID NO.4; Anti-sense: ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT, as shown in SEQ ID NO.5.
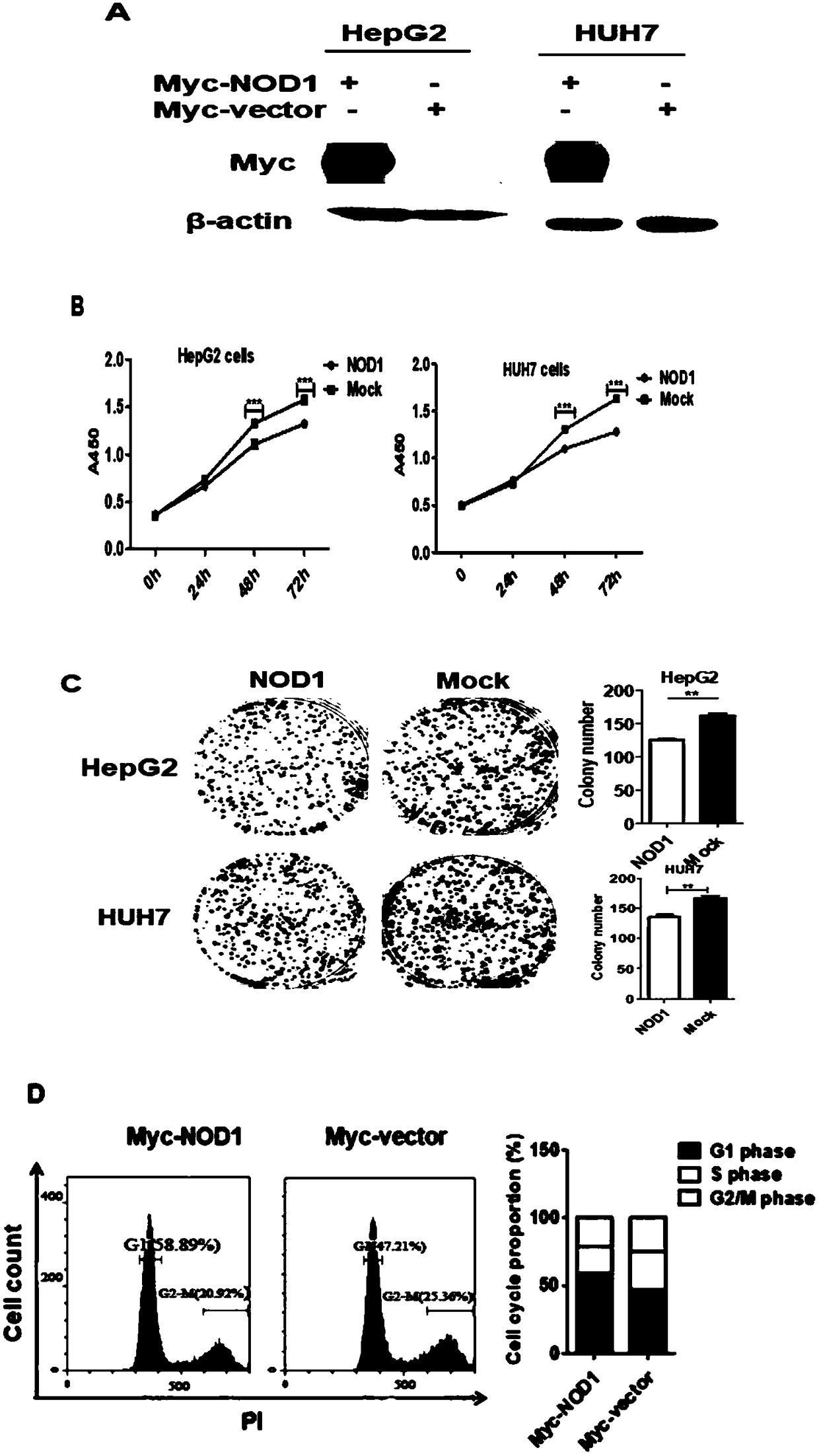
[0058] Successfully interfered with the expression of NOD1 in the liver cancer cell lines BEL7402 and SMMC7721 ( figure 1 A), CCK-8 method detects that the proliferation activity of liver cancer cells is significantly improved ( figure 1 B); After inhibiting the expre...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Example 2 NOD1 inhibits MAPK signaling pathway
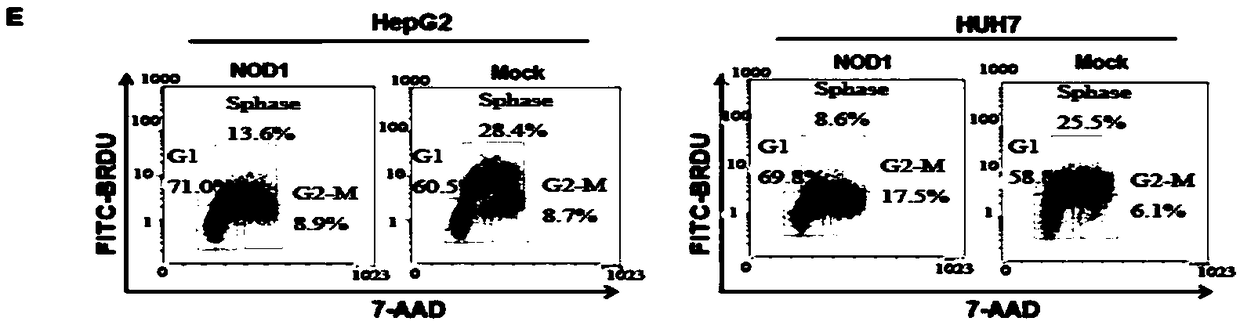
[0063] After interfering with NOD1 expression in liver cancer cell lines BEL7402 and SMMC7721, it was detected that the expression of cell cycle negative regulator protein P21 was significantly inhibited, while the expression levels of cell cycle activation proteins p-CyclinD, p-CyclinE and p-CDC2 were significantly up-regulated; Conversely, in the liver cancer cell lines HUH7 and HepG2, exogenous overexpression of NOD1 can significantly increase the expression of P21, while the expression levels of cell cycle activation proteins p-CylinD and p-CyclinE are significantly down-regulated; the above results further clarified that NOD1 can Negatively regulate the cell cycle of liver cancer cells. The further study of the present invention found that interfering with the expression of NOD1 in liver cancer cell lines can significantly activate the MAPK signaling pathway, on the contrary, overexpressing NOD1 can significantly inh...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3 Screening of molecular targets for NOD1 to exert tumor suppressor effect in liver cancer cells
[0065] Co-immunoprecipitation method detected the endogenous and exogenous combination of NOD1 and SRC ( Figure 4 A-B). Immunofluorescence staining proved that NOD1 and SRC co-localized in the cytoplasm ( Figure 4 C) In vitro protein translation and co-immunoprecipitation methods prove that there is a direct binding effect between NOD1 and SRC ( Figure 4 D). In the further study, the present invention constructed the truncated mutants of NOD1 and SRC respectively, and proved that NOD1 combined with the SH3 domain of SRC through its CARD domain through co-immunoprecipitation method.
[0066] In the present invention, by interfering with the expression of NOD1 in liver cancer cells BEL7402, it is detected that inhibiting the expression of NOD1 can significantly increase the expression level of p-SRC without affecting the expression of SRC ( Figure 5 A); Conve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com