Black hole attack detection and tracking method based on doubtful degree accumulation
A black hole attack and suspicion technology, applied in the field of mobile ad hoc network routing security, can solve the problems of no technical means for detection, misjudgment, and no consideration of intense channel conditions for topology changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
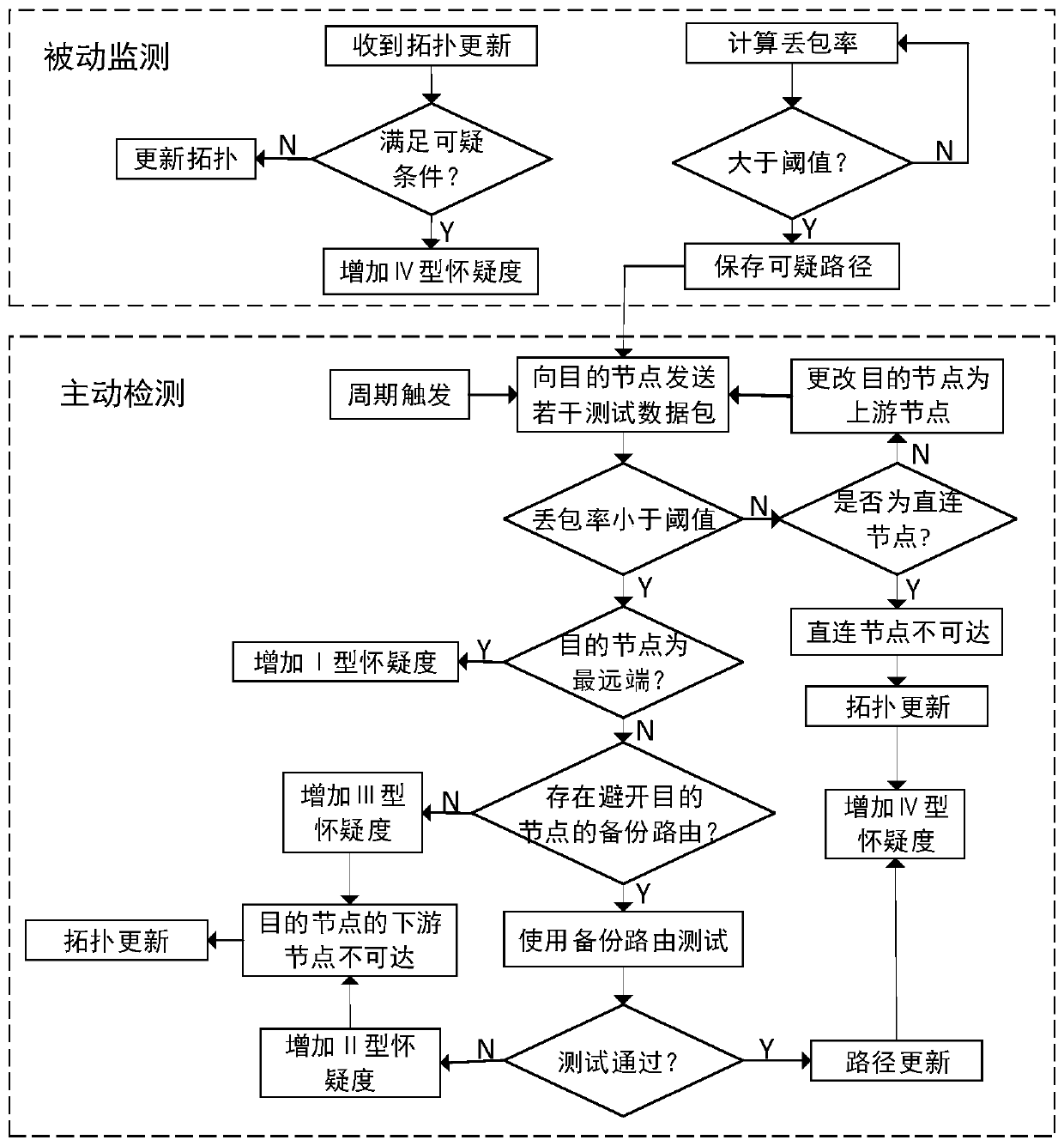
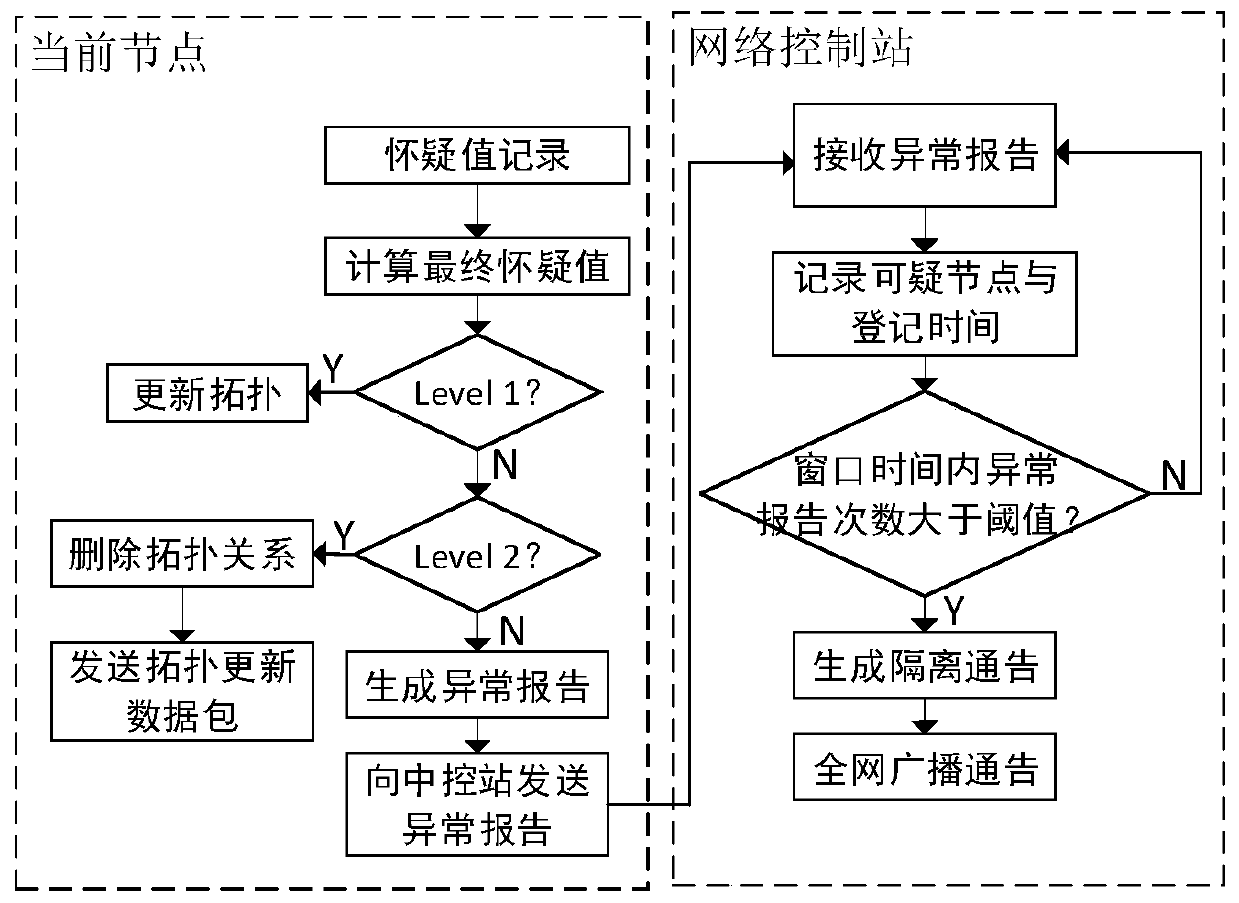
[0058] In this embodiment, the BADTOAC algorithm is divided into four parts: active detection, passive monitoring, suspicious value recording and abnormal reporting. The present invention uses the global topology record method, each node not only records the shortest path from the current node to the destination node through the sparse tree algorithm when exchanging topology updates, but also maintains a global topology data according to the topology update data surface. A(G) is the adjacency matrix about the current node, and the node m obtains the sparse tree route between m point and each destination node through A(G) and the sparse tree algorithm.
[0059] a. Active detection
[0060] The present invention uses an end-to-end confirmation mechanism to track malicious nodes. The source node sends several test messages to the destination node. When the destination node receives the test messages, the destination node will reply to the source node with a confirmation message....
Embodiment 2
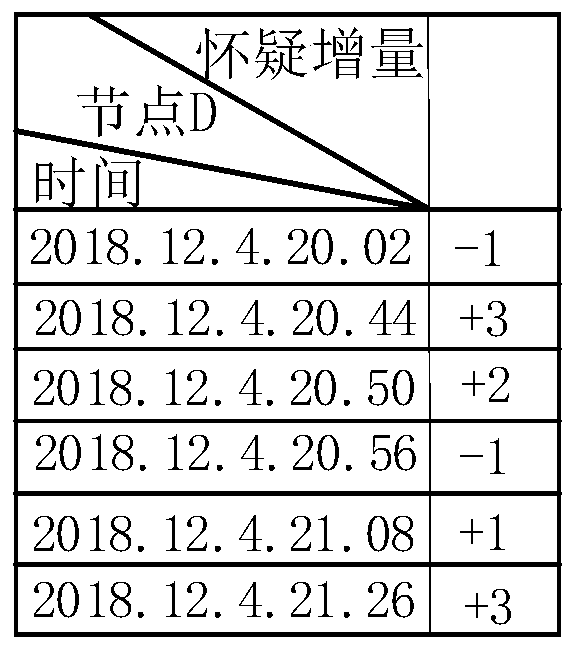
[0090] This embodiment mainly describes the passive monitoring process. The network topology of the embodiment is as follows Figure 5 As shown, the source node A sends data to the destination node D through the routing path A-B-M2-D, the malicious nodes M1 and M2 are in two different stages of the black hole attack, the M1 node is in the initial stage of the black hole attack, and the M2 node is in the obtained Trust stage of source node A.
[0091] In order to reduce the delay and network load as much as possible in the process of data transmission, nodes use UDP transmission services in large quantities, and a small part of data that requires high information accuracy uses TCP transmission services. It is impossible for the source node to calculate its end-to-end packet loss rate during the UDP service process using multi-hop relays, so the BADTOAC algorithm introduces active detection to make up for the lack of passive monitoring. The packet loss rate calculation in passiv...
Embodiment 3
[0115] This embodiment mainly describes the active detection process. The routing path for node A to send data to destination node D is A-B-M2-D, and the reputation registration table of the current node D is stored in node A, such as Figure 4 As shown, the specific steps that node A performs to node D are as follows:
[0116] S1. Node A determines that the remote destination node and the destination node are D;
[0117] S2. Node A sends 20 test messages that require end-to-end confirmation to node D;
[0118] S3. Node A starts a reply confirmation timer after sending each test message, and waits for node D to reply;
[0119] S4. After the countdown of the last reply confirmation timer of node A ends, it is calculated that the packet loss rate on the A-B-M2-D path is greater than 10%. Node A determines that there may be malicious nodes in this path, and suspicious nodes need to be detected. track;
[0120] S5. Node A changes the destination node to the upstream node M2 o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com