Resource allocation method and device for a fog wireless access network
A technology of wireless access network and resource allocation, which is applied in the field of resource allocation of fog wireless access network, and can solve problems such as storage, computing and processing capabilities without considering resource limitations, waste of resources, and inability to guarantee the transmission rate of user UEs. , to achieve the effect of saving average deployment time and improving spectrum efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
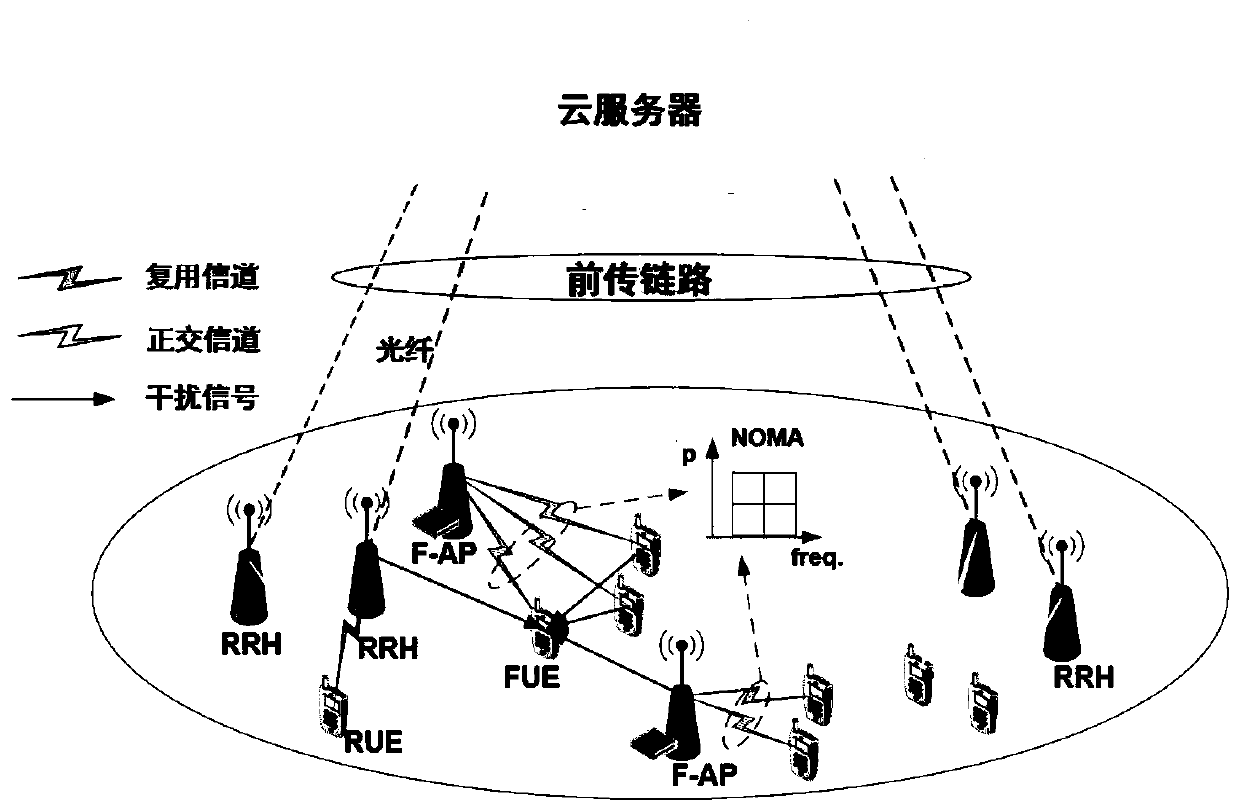
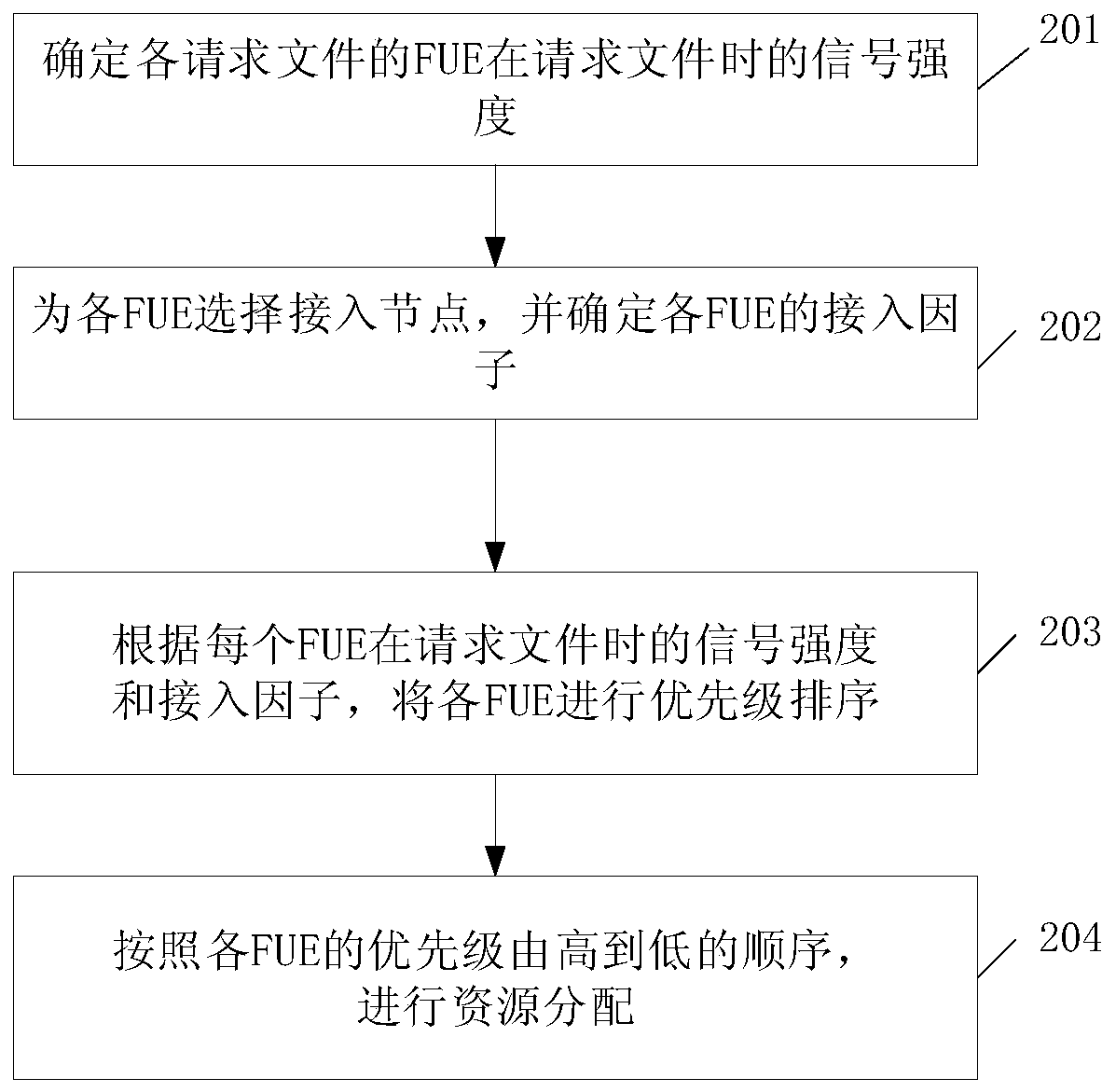
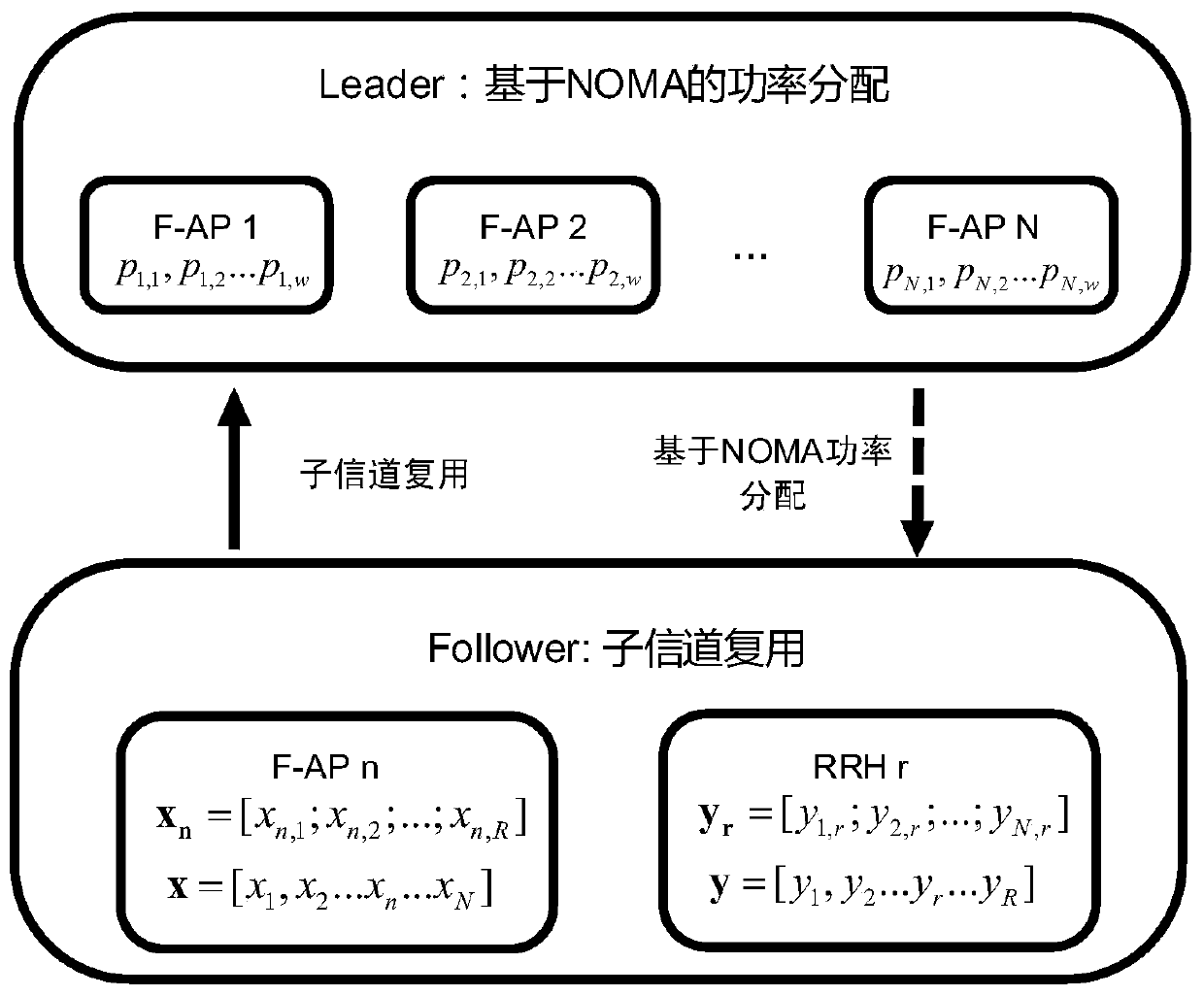
[0074] Step 401: Calculate the signal strength of each FUE in the scheduling queue of the current access subframe when requesting a file, and select an access node for the FUE. It is assumed that all file services requested by the FUE entering the coverage of the F-AP are cached in the adjacent F-AP. Obtain the historical CSI of the FUE to calculate the service rate R obtained when the FUE accesses the desired F-AP, and compare it with μ times the required service rate R>μR, then it can be determined that the FUE can directly access the F-AP. If R<μR, then the user FUE needs to search for the second nearest node F-AP, and perform access judgment in the same way. If R=μR, adhering to the principle of saving resources and minimizing time, the nearest node is selected for access.
[0075] Step 402: Calculate the service impact factor as e according to the selected access node x ; Calculate the access mode selection factor according to the signal strength and service impact fact...
example 2
[0079] Step 501: Calculate the signal strength of each FUE in the scheduling queue of the current access subframe when requesting a file, and select an access node for the FUE. Obtain the historical CSI of the user's FUE to calculate the service rate obtained when the FUE accesses the desired F-AP, and compare it with μ times the required service rate. The comparison method is as in 401, which will not be repeated here. It is assumed that some of the file services requested by the FUE that currently enter the coverage of the F-AP are not cached in the neighboring F-AP, that is, some users that enter the coverage of the F-AP cannot access the F-AP node and can only Select the F-AP node with the second closest access distance.
[0080] Step 502: Calculate the service impact factor as e according to the selected access node x ; Calculate the access mode selection factor of each FUE in the scheduling queue of the access subframe according to the signal strength and service impact...
example 3
[0084] Step 601: Calculate the signal strength of each FUE in the scheduling queue of the current access subframe when requesting a file, and select an access node for the FUE. Obtain the historical CSI of the user's FUE to calculate the service rate obtained when the FUE accesses the desired F-AP, and compare it with μ times the required service rate. The comparison method is as in 401, which will not be repeated here. The file service requested by the user FUE entering the coverage of the F-AP is cached in the F-AP.
[0085] Step 602: According to the selected access node, obtain the service impact factor of the user's FUE as e x .
[0086] Step 603: Use the calculated access mode selection factor to determine the priority of each FUE, and sort all the FUEs according to the priority, that is, sort according to the access mode selection value of each FUE, and establish a scheduling queue for the current access subframe.
[0087] Step 604: According to the priority ordering ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com