Connection mechanism with three rotational degrees of freedom, robot, robot arm, and robot hand
A technology of connection mechanism and degrees of freedom, applied in the directions of manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, joints, etc., can solve problems such as joint enlargement, and achieve the effect of simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
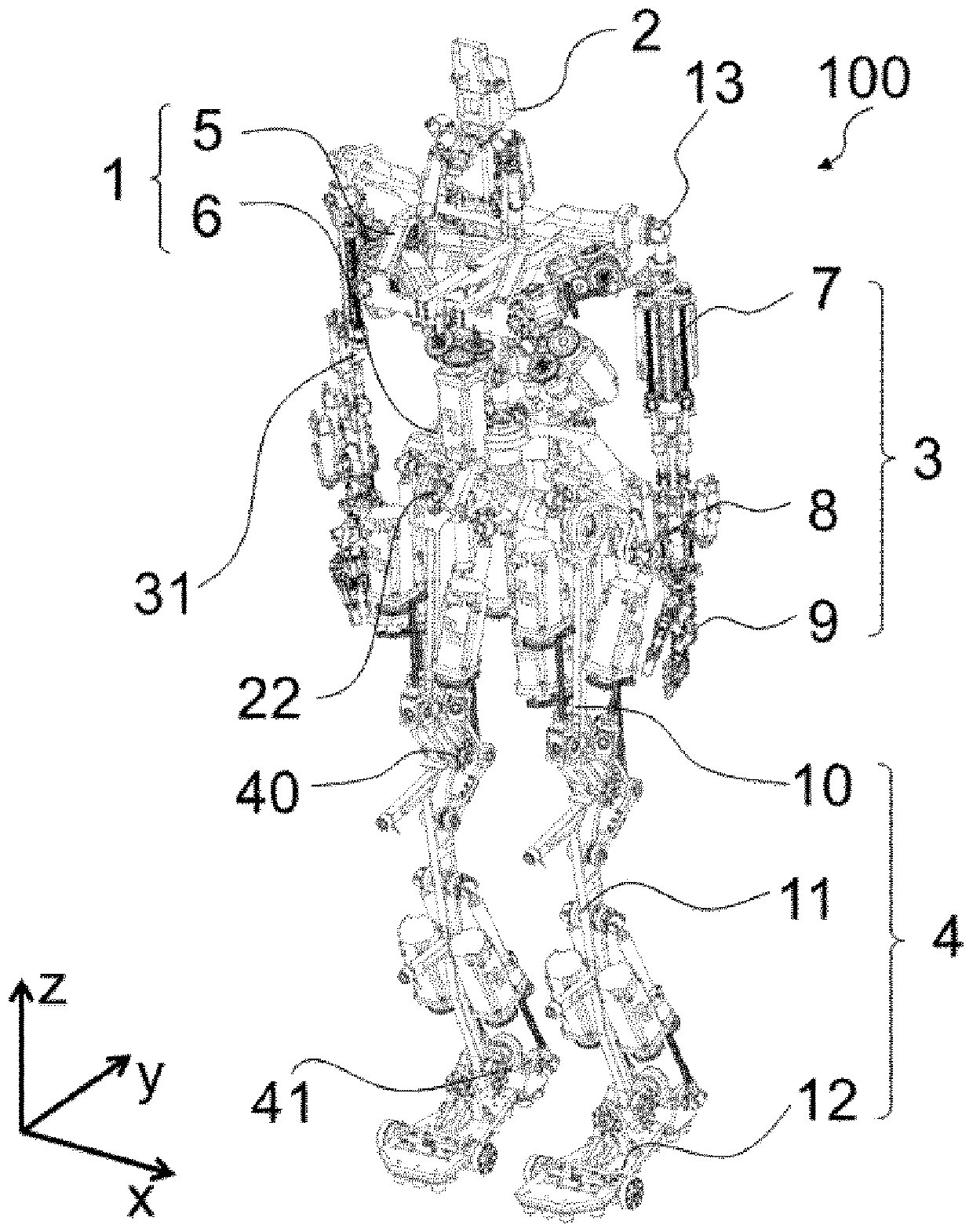
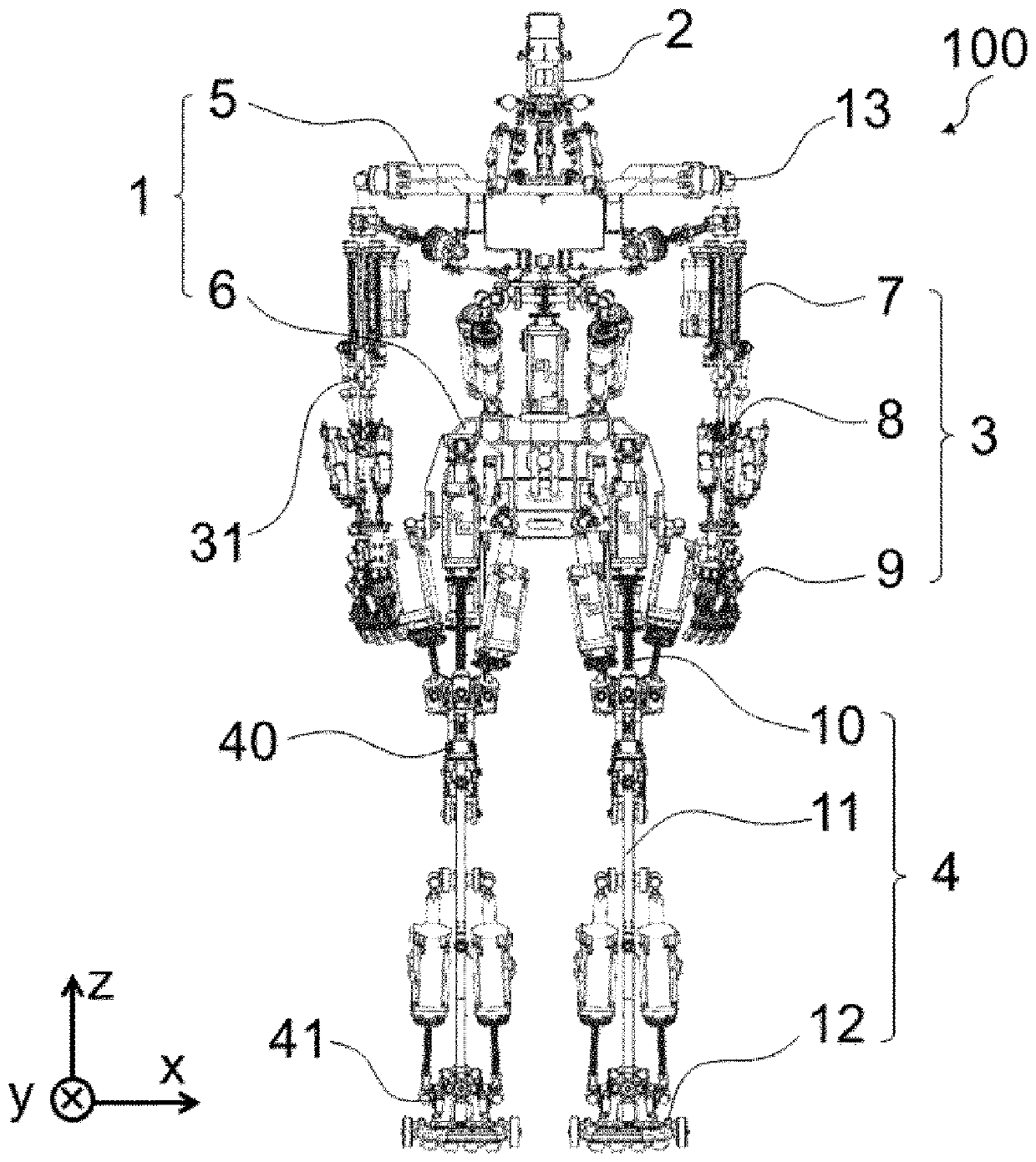
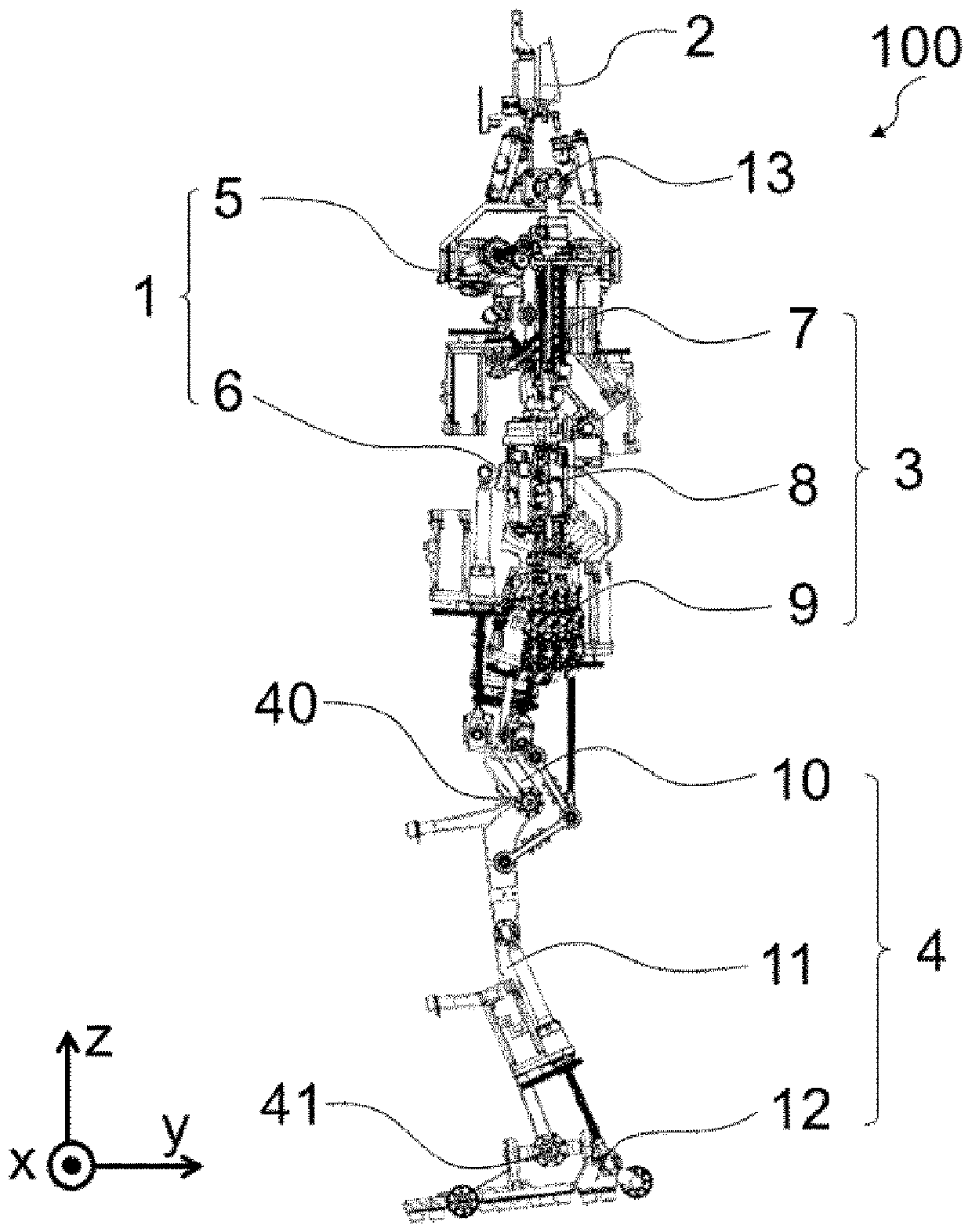
[0136] figure 1 It is a perspective view of the humanoid robot 100 according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. exist figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 and Figure 5 A front view, a left side view, a rear view and a plan view of the humanoid robot 100 are shown in . exist Figure 6 A perspective view illustrating the skeleton structure of the humanoid robot 100 is shown in . exist Figure 7 , Figure 8 , Figure 9 and Figure 10 , respectively show a front view, a left view, a rear view, and a plan view in the case where the humanoid robot 100 is represented only by skeletons. Let the axis in the left-right direction of the humanoid robot 100 be an X-axis, the axis in the front-back direction be a Y-axis, and the axis in the height direction be a Z-axis. Let the direction from right to left be the positive direction of the X-axis, the direction from front to back be the positive direction of the Y-axis, and the direction from top to bottom be the positive dire...
Embodiment approach 2
[0746] Embodiment 2 is a case where the knee drive link 42 for driving the knee joint 40 is connected only to the lower leg 11 side. Figure 86 It is a perspective view of a humanoid robot 100X according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. The front view, left view, rear view and plan view of the humanoid robot 100X are shown in Figure 87 , Figure 88 and Figure 89 middle.
[0747]In the humanoid robot 100X, one end of the knee drive link 42L is not attached to the thigh 10X. One end of the knee drive link 42L is attached only to the lower leg 11X. In the humanoid robot 100X, when the knee joint 40X is largely bent until the thigh 10X is substantially parallel to the lower leg 11X, the force for extending the knee joint 40X may not be sufficiently output. The humanoid robot 100X can be used in the same manner as the humanoid robot 100 according to Embodiment 1 when it is not necessary to take a posture in which the knee joint portion 40X is greatly bent. In the h...
Embodiment approach 3
[0749] Embodiment 3 is a case where an actuator for changing the angle formed by the toe portion and the foot body portion is provided. exist Figure 90 , Figure 91 , Figure 92 and Figure 93 A plan view, a left side view, a front view, and a perspective view of the left foot of the humanoid robot 100Y according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention are shown in .
[0750] The foot 12Y of the humanoid robot 100Y has a toe driving actuator 47 that changes the angle formed by the foot main body 12A and the toe 12B. The toe drive actuator 47 is aligned with the ankle joint 41 in the longitudinal direction and arranged on the toe 12B side. The foot body portion 12A is provided with a foot body portion side link mounting portion J43. One end of the toe drive link 47L is rotatably attached to the foot main body side link attachment portion J43. The toe portion 12B is provided with a toe portion side link attachment portion J44 to which the other end of the toe portion dri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com