Parallel decoupling identification method for induction motor stator resistance and speed
A technology of induction motor and stator resistance, which is applied in the fields of power electronics and electric drive, can solve the problems of inaccurate observation values, and achieve the effect of ensuring decoupling, reducing influence and realizing accurate compensation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
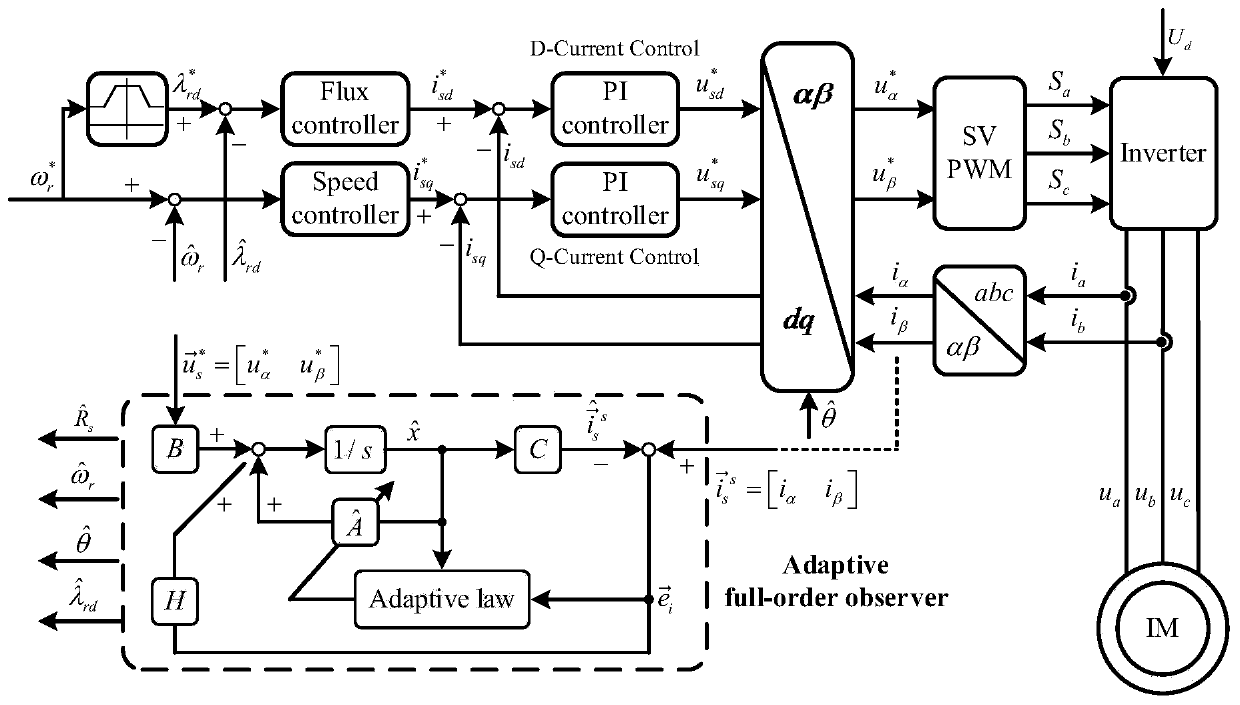
[0032] A parallel decoupling identification method for induction motor stator resistance and rotational speed according to this embodiment, the decoupling identification method is realized through the following steps:
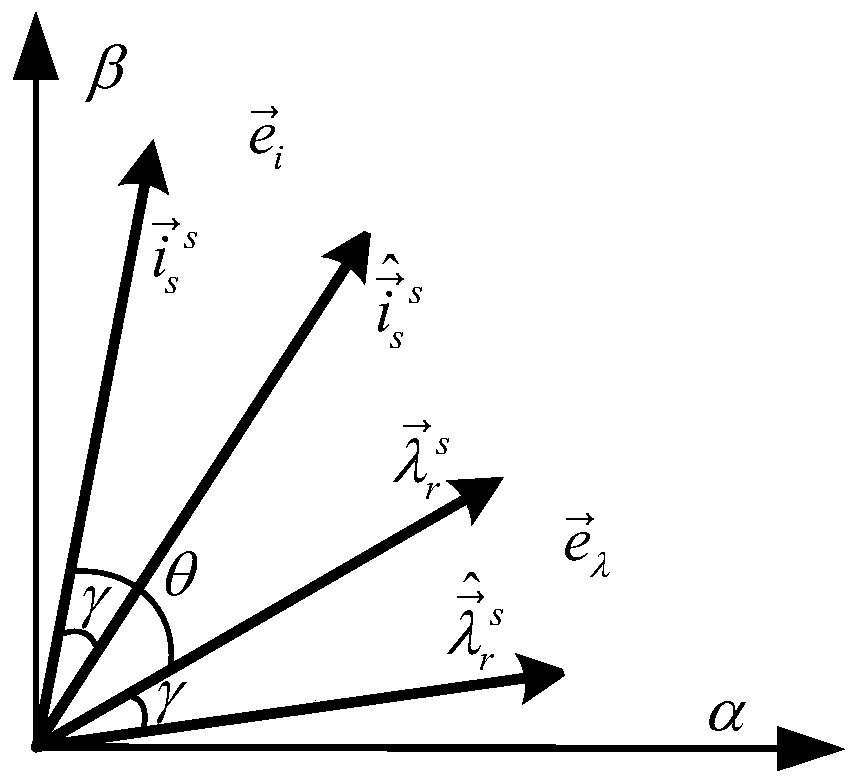
[0033] Step 1. Design the relationship between the rotor flux error and the stator current error:
[0034]
[0035] In the formula, Indicates the stator current error, Indicates the rotor flux linkage error; L m Represents the mutual inductance of the induction motor; θ represents the power angle of the induction motor, which is the angle between the electronic current and the rotor flux linkage;
[0036] Step 2. Using the relationship between the rotor flux error and the stator current error in step 1, decoupling the stator resistance error part of the stator current error, the obtained stator resistance error part is expressed as:
[0037]
[0038] In the formula, is the stator current error The rotational speed error part in is the stator ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0047] The difference from the specific embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, a parallel decoupling identification method between the stator resistance and the rotational speed of an induction motor, the process of designing the relationship between the rotor flux linkage error and the stator current error described in step 1 is as follows:
[0048] Step 1. Select stator current and rotor flux linkage as state variables, and determine the induction motor mathematical model as:
[0049]
[0050] is the stator current, is the rotor flux linkage, is the motor input voltage,
[0051]
[0052]
[0053] R s Indicates the induction motor stator resistance, R r Indicates the induction motor rotor resistance, L s Indicates the induction motor stator inductance, L r Indicates the induction motor rotor inductance, L m Indicates the induction motor mutual inductance, T r Indicates the induction motor rotor time constant, δ is the leakage inductance coefficient, ω e...
specific Embodiment approach 3
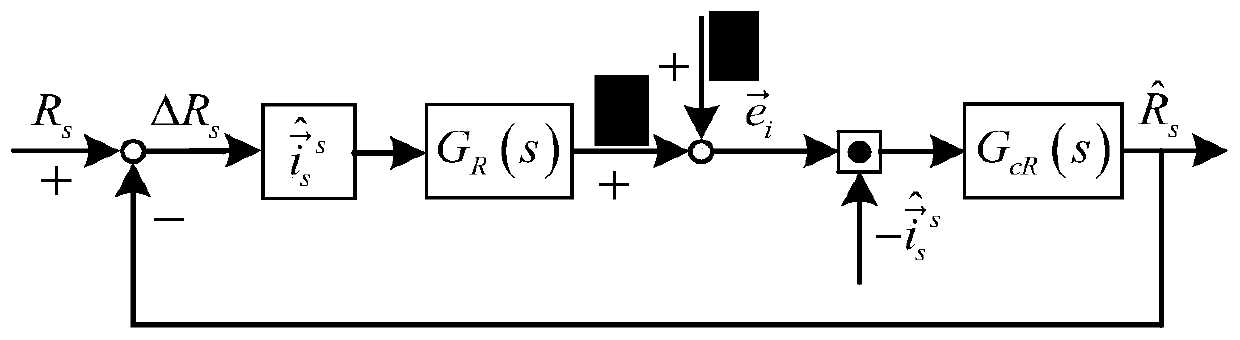
[0085] The difference from the second specific embodiment is that in this embodiment, a parallel decoupling identification method between the stator resistance and the rotational speed of an induction motor uses the relationship between the rotor flux error and the stator current error described in step two to decouple the stator current error The process of the stator resistance error part is:
[0086] Step 2 1. Current error by the rotational speed error part and the stator resistance error part Composition, the current error is expressed as:
[0087]
[0088] in,
[0089]
[0090]
[0091] Indicates the stator current error of the induction motor, Indicates the part of the speed error in the stator current error of the induction motor, Indicates the stator resistance error part of the induction motor stator current error;
[0092] Step two 2, combining formula (7), (8), (9) and (11), obtain the relation of speed error part and stator resistance error p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com