Improved no-tillage reseeding machine ditching cutter suitable for high and cold natural grassland
A trenching knife, an improved technology, applied in the directions of excavation/covering trenches, application, planting methods, etc., can solve the problems of large scale and dense distribution of gravel, and achieve uniform trenching depth and width, and the trenching process is continuous. , the effect of high durability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
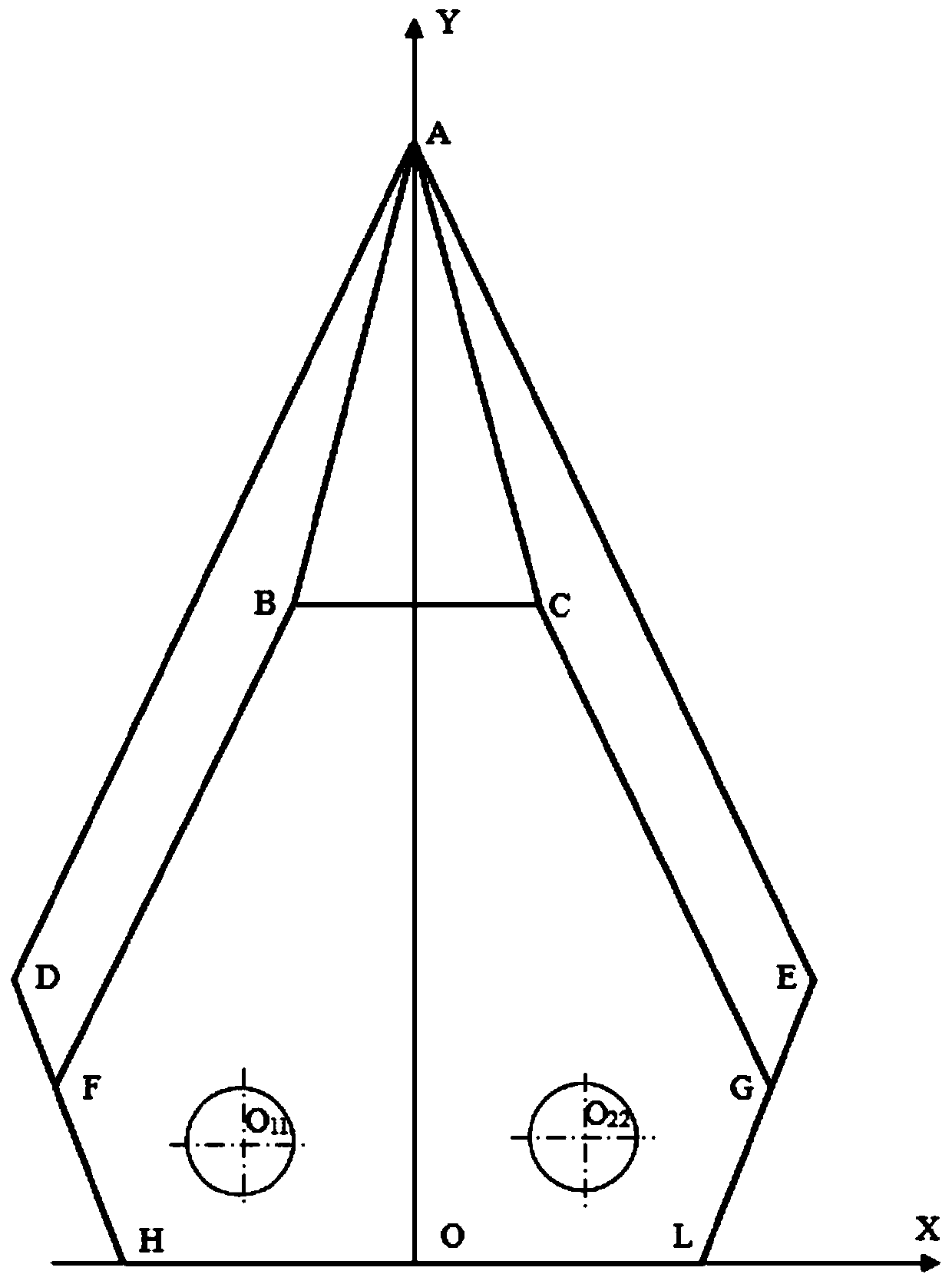
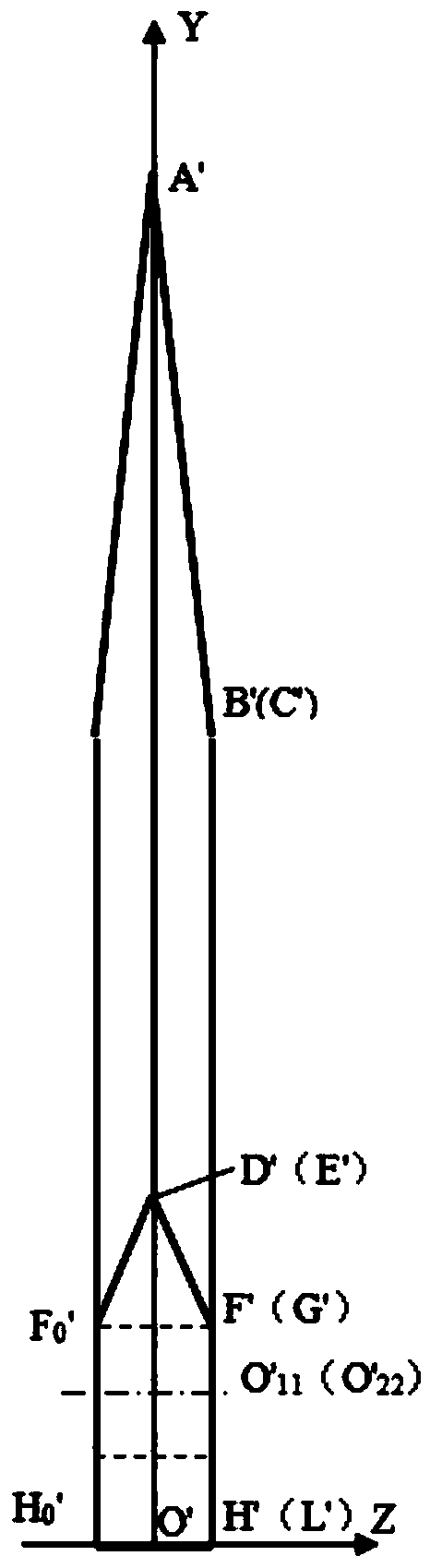
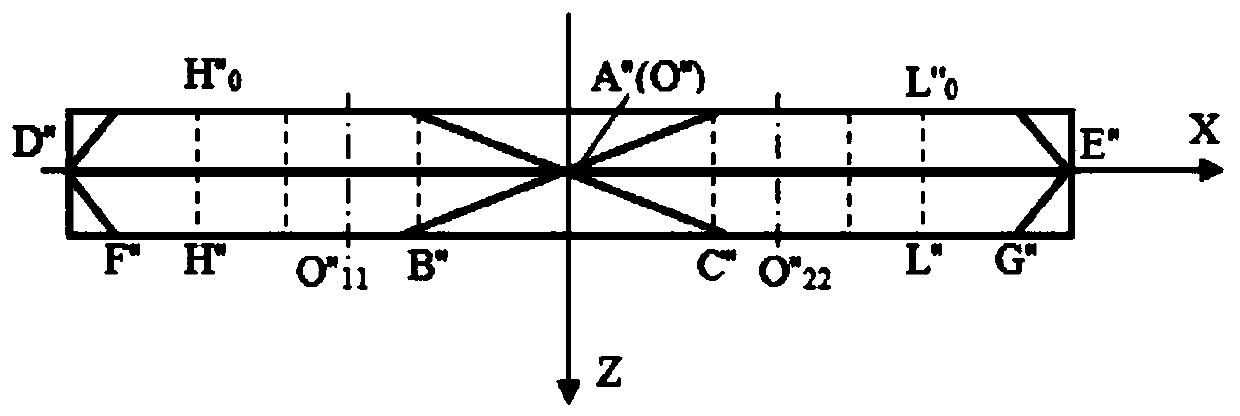
[0050] In this embodiment, 60 ordinary ditching knives are evenly installed on six flanges through 120 bolts, and the flanges are welded on the rotating shaft of a no-tillage supplementary seeding machine. When installing, as Figure 1-Figure 3 , Ordinary ditching knife rotates counterclockwise after installation, and the movement direction of the no-tillage supplementary seeding machine is to the right. The forward speed of the no-tillage supplementary seeding machine is set to 10 km / h, and the rotational speed of the rotating shaft is set to 600 rpm. In the surface layer of alpine natural grassland with dense distribution of pebbles (within 10 cm below the ground, the distribution density of large pebbles with an average diameter of more than 30 cm exceeds 2.5 pieces / m3, and the distribution of small and medium-sized pebbles with an average diameter of 3 to 30 cm Density over 3000 pieces / cubic meter), the ditching test was carried out with a ditching distance of 500 meters. ...
Embodiment 2
[0065] In this example, the test scheme is the same as that in Example 1, the difference is that the trenching knife used in this example is an improved trenching knife. When installing, such as Figure 4-Figure 6, After the improved ditching knife is installed, turn it counterclockwise, and the movement direction of the no-tillage supplementary seeding machine is to the right. The test results are shown in Table 6-Table 9:
[0066] Table 6 Statistical table of trenching depth values randomly selected from 30 points (unit: mm)
[0067]
[0068] Table 7 Statistical table of ditch width values randomly selected from 30 points (unit: mm)
[0069]
[0070] Table 8 Cobblestone Quantity Statistics
[0071]
[0072] Table 9 Statistical table of damage to components of the ditching system
[0073]
[0074] The test data of the improved ditching knife shows that the ditching test is carried out on the natural grassland surface with dense distribution of cobblestones...
Embodiment 3
[0078] In this embodiment, the impact durability test is carried out on the improved ditching knife.
[0079] Such as Figure 7-Figure 10 As shown, the ditch knife-cobblestone impact test device is mainly composed of five parts: container system I, left forward system II, right forward system III, protection system IV, and ditching system V.
[0080] The storage container system I includes a box body I-1, a vibrating plate I-2, and pebbles I-3. The vibrating plate I-2 is placed on the inner bottom of the box I-1, and the pebbles I-3 are placed on the vibrating plate I-2 and surrounded by the inner wall of the box I-1. The box Ⅰ-1 is fixed to the ground and will not move in the horizontal direction; the vibration plate Ⅰ-2 vibrates up and down when it is working, and the vibration frequency ranges from 9000 to 15000 times per minute; the role of pebbles Ⅰ-3 on the vibration plate Ⅰ-2 Rearrange the positions below; the left forward system II is located on the left side of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com