Apparatus and method for fault classification of three-phase distribution power cables
A technology for power distribution cables and fault classification, applied in fault locations, circuit devices, emergency protection circuit devices, etc., can solve problems such as failure, high cost, wrong fault classification results, etc., and achieve cost reduction, reliability improvement, and financial savings. effect of investment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
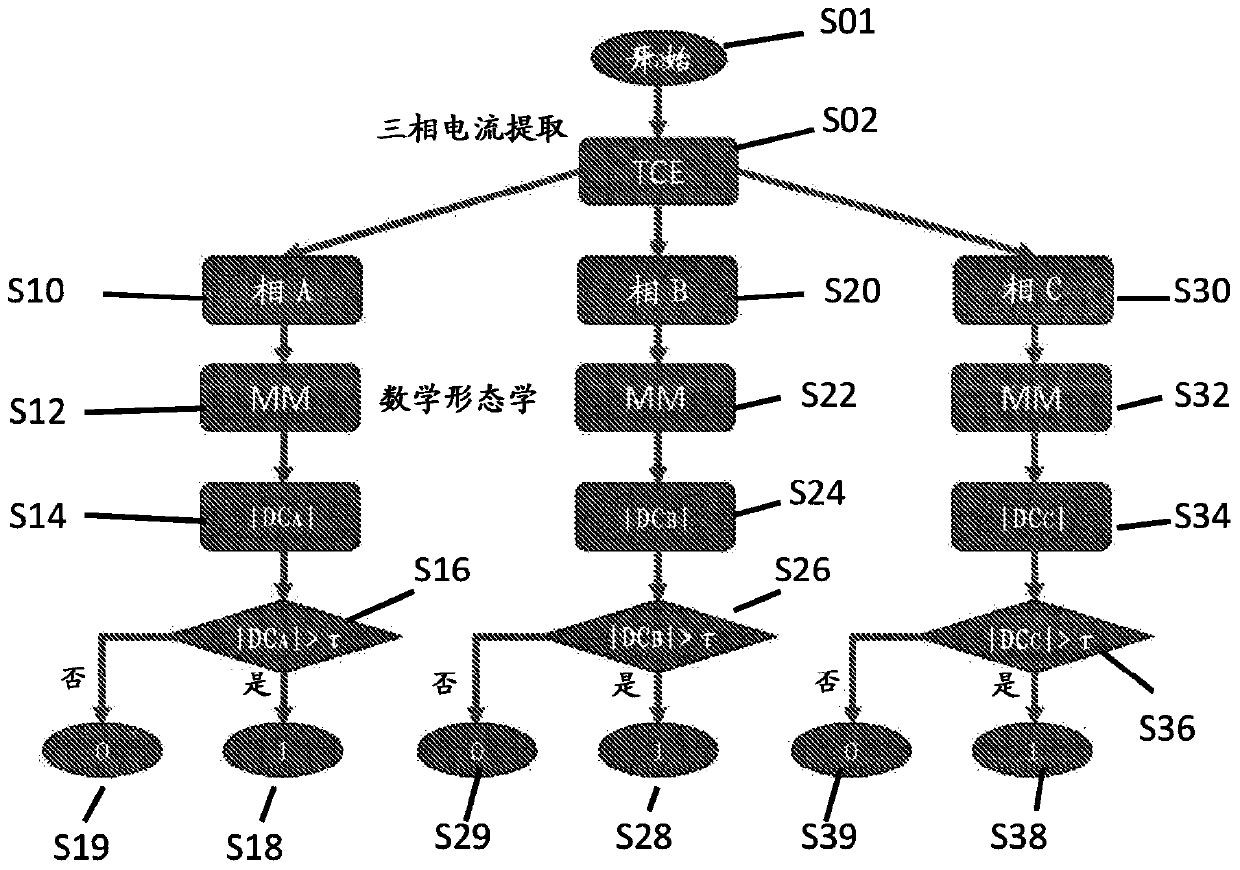
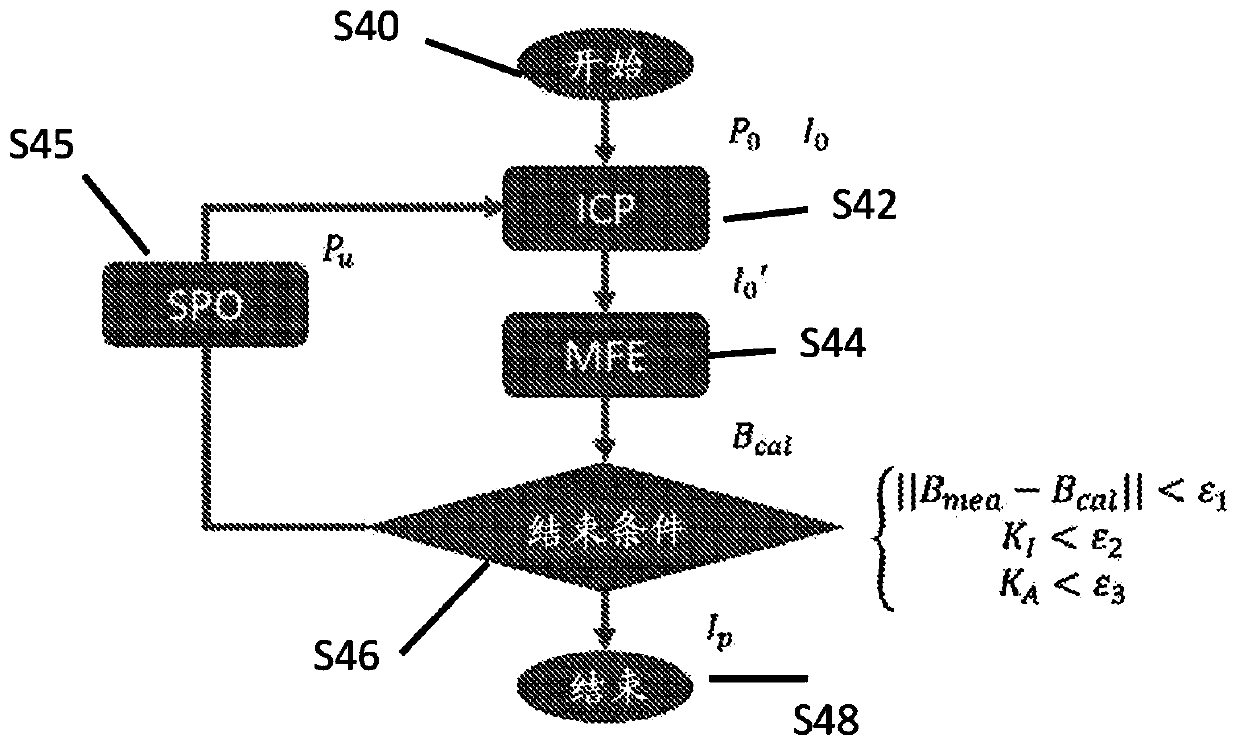
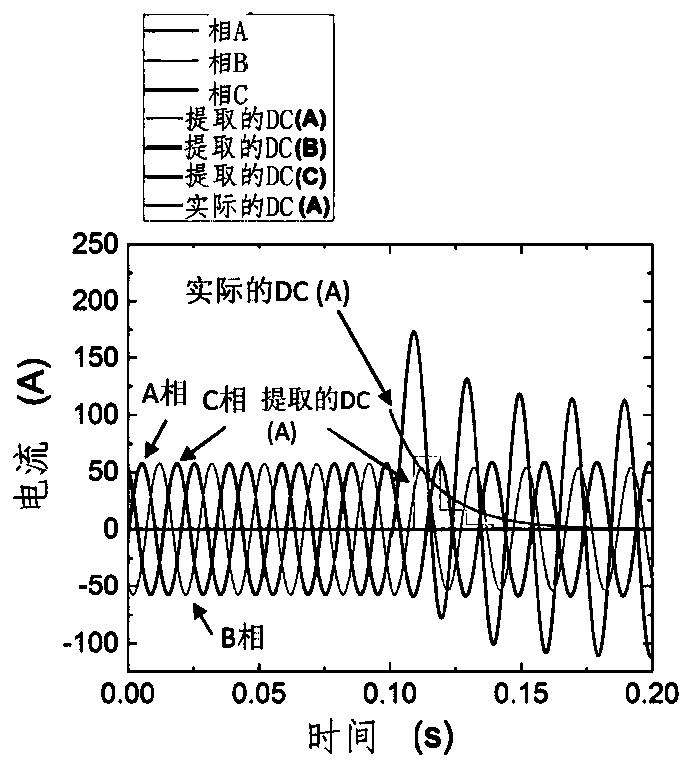
[0028] The invention relates to a device and method for fault classification of three-phase power distribution cables. It relies on magnetic field measurements to reconstruct the three-phase currents and to identify the DC components present in each phase of the current during post-fault transients to differentiate fault classes. This method avoids the waveform distortion problem that may be caused by the DC bias when using the existing transformer (the most common current transformer) to detect the DC component in the power system. Current transformers cannot be used because the DC bias distorts the secondary output current waveform. While it is possible to use optical current transformers (OCS) based on the magneto-optical effect (Faraday effect) for DC measurements, they are very expensive.
[0029] A device 10 for measuring a magnetic field around a three-phase distribution cable 20 is shown in FIG. 1 divided into upper and lower parts 11 , 11 ′. The device comprises a m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com