Multi-robot collaborative scheduling method and device, equipment and medium
A collaborative scheduling and multi-robot technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, instruments, control/regulation systems, etc., to achieve the effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
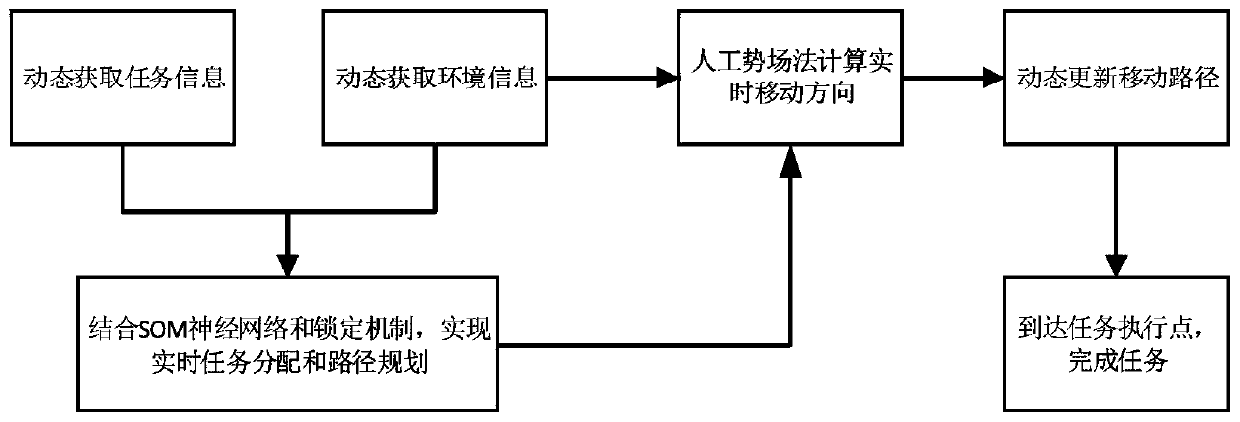
[0062] This embodiment provides a collaborative scheduling method for multi-robots, aiming to complete the real-time task assignment and path planning of multi-robots through the fusion of SOM neural network and locking mechanism, so that the total cost spent by multi-robots on the basis of completing tasks The cost is the least, and the tasks are executed in an orderly and independent manner in the process of traveling without interfering with each other. Combined with the artificial potential field method, the real-time path is dynamically planned, and the obstacle avoidance process is realized, so that the robot performing the task can safely and without collision. Follow the planned path to reach the task execution point, and execute the task content.
[0063] According to the above principles, the collaborative scheduling method for multi-robots is introduced, such as figure 1 As shown, the collaborative scheduling method for multi-robots specifically includes the followi...
Embodiment 2
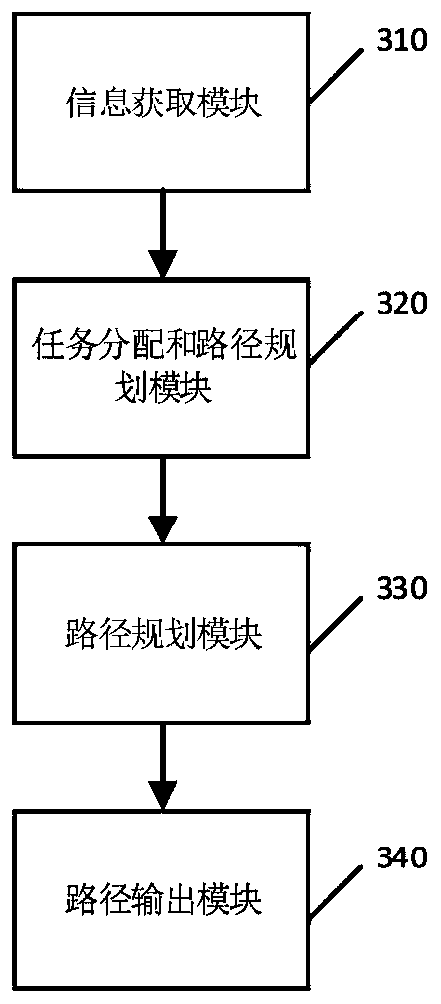
[0135] This embodiment corresponds to the multi-robot collaborative scheduling method in Embodiment 1, and discloses a multi-robot collaborative scheduling device, which is the virtual device structure of the above-mentioned embodiment 1, please refer to image 3 shown, including:
[0136] An information acquisition module 310, configured to acquire task information and environment information of the robot, the task information includes task execution points and task content, and the environment information includes the robot's own positioning and obstacle information;
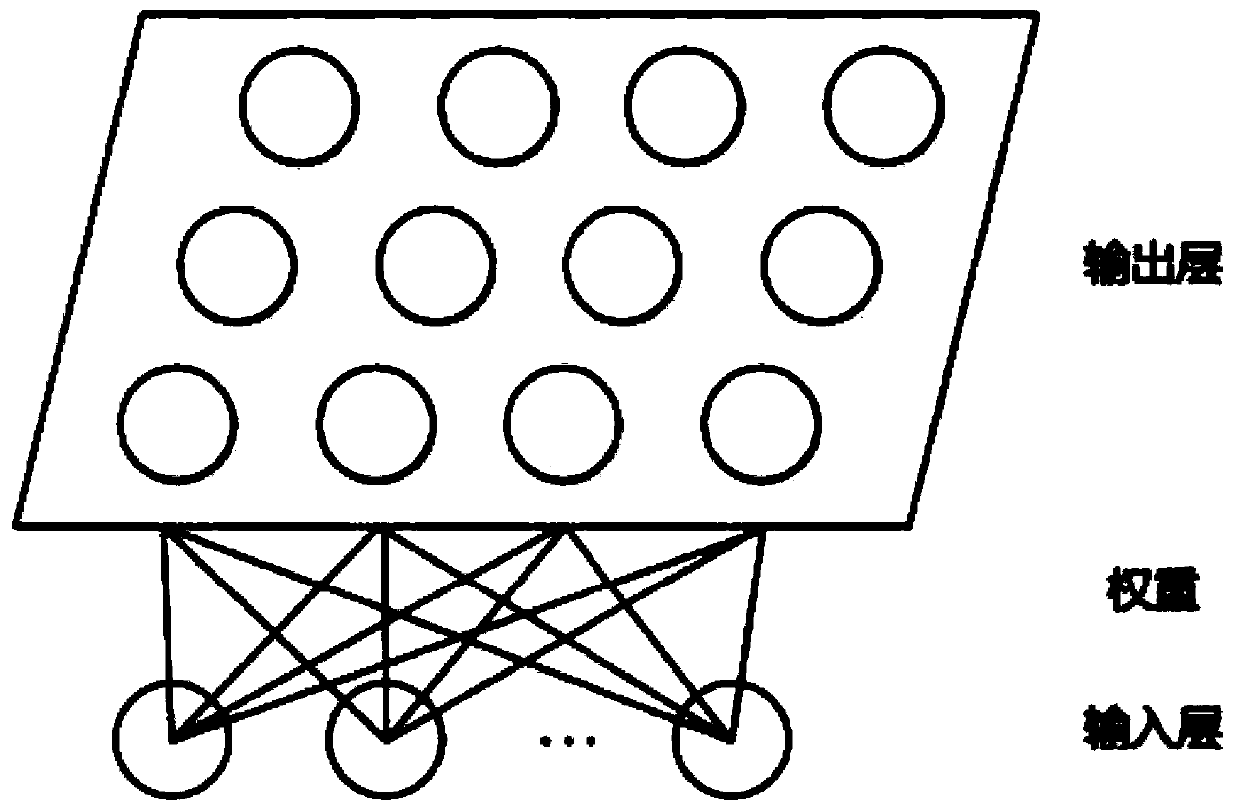
[0137] The task assignment and path planning module 320 uses the SOM neural network and the locking mechanism to assign tasks to the robot and simultaneously plan the initial movement path;
[0138] The path update module 330, according to the environmental information, uses the artificial potential field method to dynamically calculate the real-time moving direction of the robot performing the task, and dynam...
Embodiment 3
[0143] In this embodiment, based on the collaborative scheduling method and device for multi-robots in Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, simulation experiments are carried out for static working environments and different dynamic working environments.
[0144] In this embodiment, a computer with 4G memory and a 3.07GHz Pentium processor is used for simulation in the Windows7 system. The size of the two-dimensional workspace is set to 30*30. In order to ensure that the experiment is more representative and convincing, the initial position of the mobile robot, the position of the task and the position of the obstacle are set randomly in each experiment.
[0145] In the simulation experiment of this embodiment, the completion of the task by the robot is defined as the arrival of the task execution point by the robot, wherein, in Figure 4 to Figure 8 In , the robot is denoted as R, and the task execution point is denoted as T. The specific experimental results are as follows:
[01...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com