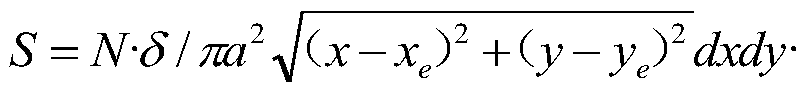Shortest path routing calculation method for underwater wireless sensor network
A technology of wireless sensor and shortest path, which is applied in the field of shortest path routing calculation of underwater wireless sensor network, which can solve the problems of unusable routing algorithm and inability to obtain the global position information of underwater wireless sensor network, so as to reduce the data packet loss rate, Improve the protection mechanism and reduce the effect of energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
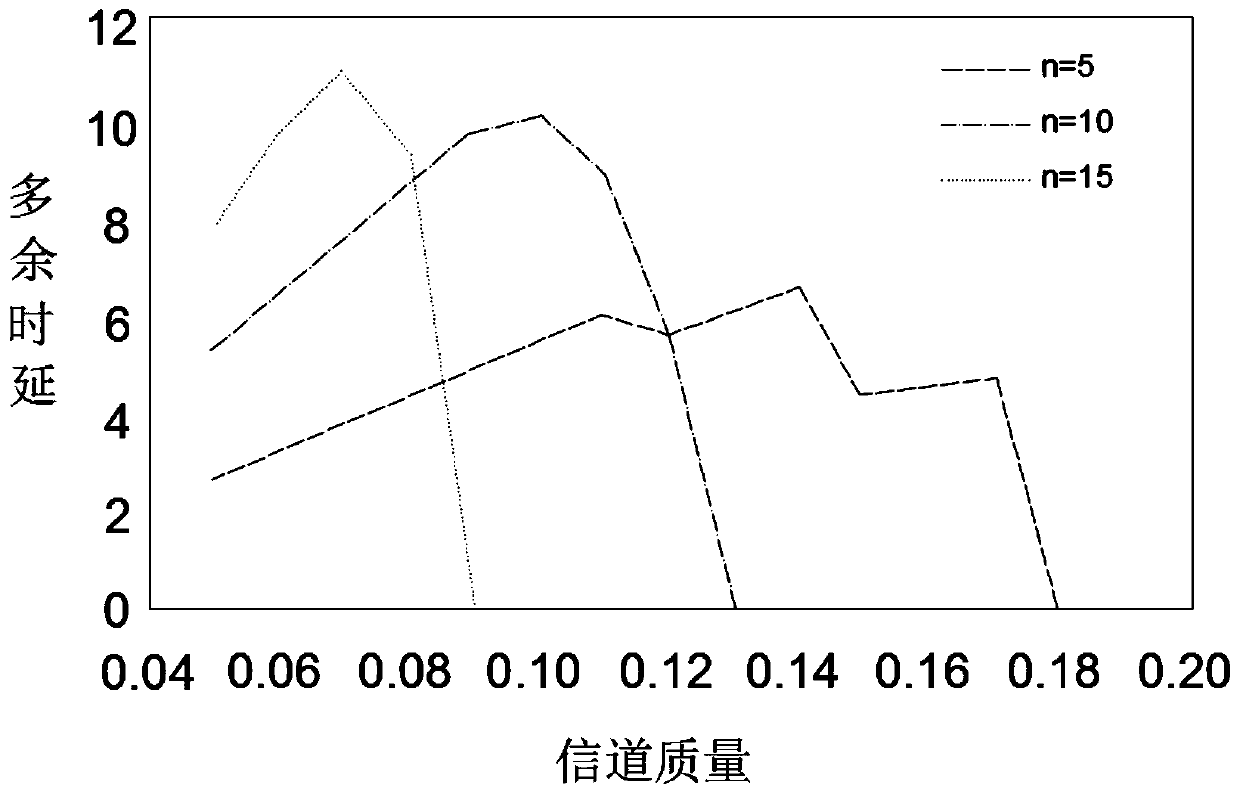
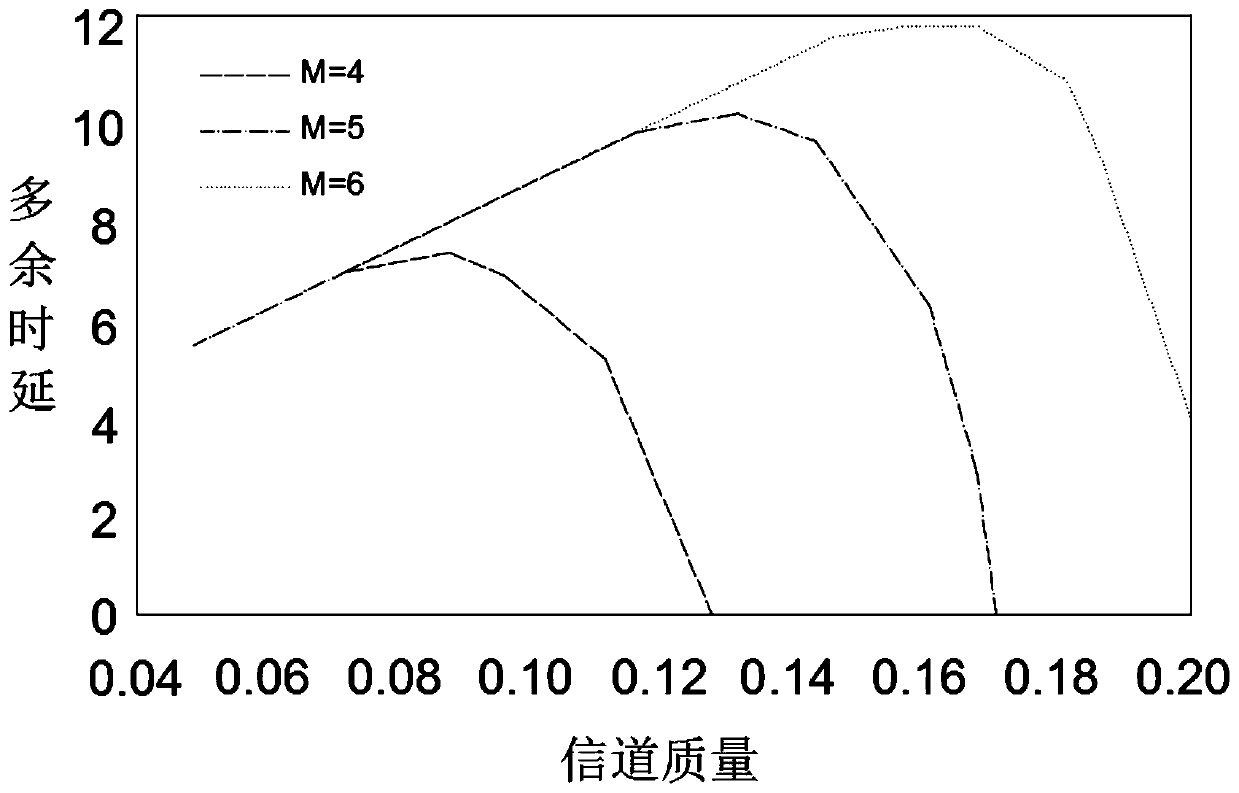
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A method for calculating the shortest path route of an underwater wireless sensor network, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0036] Step 1. Select the node closest to the node as the cache node, divide the monitoring environment into a Voronoi diagram, and the cache node is the center of each Voronoi unit. After the data passes through multiple nodes in the Voronoi unit, it is forwarded to the sink node through the cache node. Among them, when the Voronoi unit is A, the center coordinates are (x e ,y e ), the path length limit formula for data to be transmitted from nodes in A to cache nodes is:
[0037]
[0038] Among them, N is the total number of nodes, a is the radius of the monitoring area, and the distribution density of nodes is N / πa 2 ;
[0039] Each Voronoi space is equal in size, and the radius of each space is
[0040] Step 2, set the number of cache nodes as i, and obtain the path for data in a single unit to be transmitted to the cache...
Embodiment 2
[0059] On the basis of the above embodiments, further, the simulation arranges 5000 nodes in a circular monitoring area with a radius of 1000m, and each node transmits data to the cache nodes in the respective Voronoi units, and finally the cache nodes compress the data and transmit to the Sink node;
[0060] Select the node closest to the node as the cache node, divide the monitoring environment into a Voronoi diagram, and the cache node is the center of each Voronoi unit. After passing through multiple nodes in the Voronoi unit, the data is forwarded to the sink node through the cache node. Among them, the Voronoi When the unit is A, the center coordinate is (x e ,y e ), the path length limit formula for data to be transmitted from nodes in A to cache nodes is:
[0061]
[0062] Among them, N is the total number of nodes, a is the radius of the monitoring area, and the distribution density of nodes is N / πa 2 ;
[0063] Each Voronoi space is equal in size, and the radi...
Embodiment 3
[0079] On the basis of the above embodiments, further, the number of retransmissions in the single-path routing mechanism is equal to the total number of data transmissions in all paths in the multi-path routing;
[0080] Through the transmission path length of the data in the Voronoi unit, the energy consumption model of the underwater sensor node is established, and the underwater energy loss is calculated;
[0081] Transfer the data of i cache nodes to the sink node, and calculate the energy consumption value of lbit transmission in the entire monitoring area, obtain the minimum unit of energy consumption value, mark the number of cache nodes corresponding to the minimum energy consumption value separately, and set it as the center of the Voronoi unit;
[0082] Establish a multi-path routing mechanism model. In a multi-path network structure, data completes n hops in the cache node and reaches the sink node, and the data packet is transmitted in a multi-path route;
[0083...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com