High maneuvering target tracking method and system based on LS and NEU-ECEF space-time registration
A high-mobility target and space tracking technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as complex calculations, large registration errors, and huge computing overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
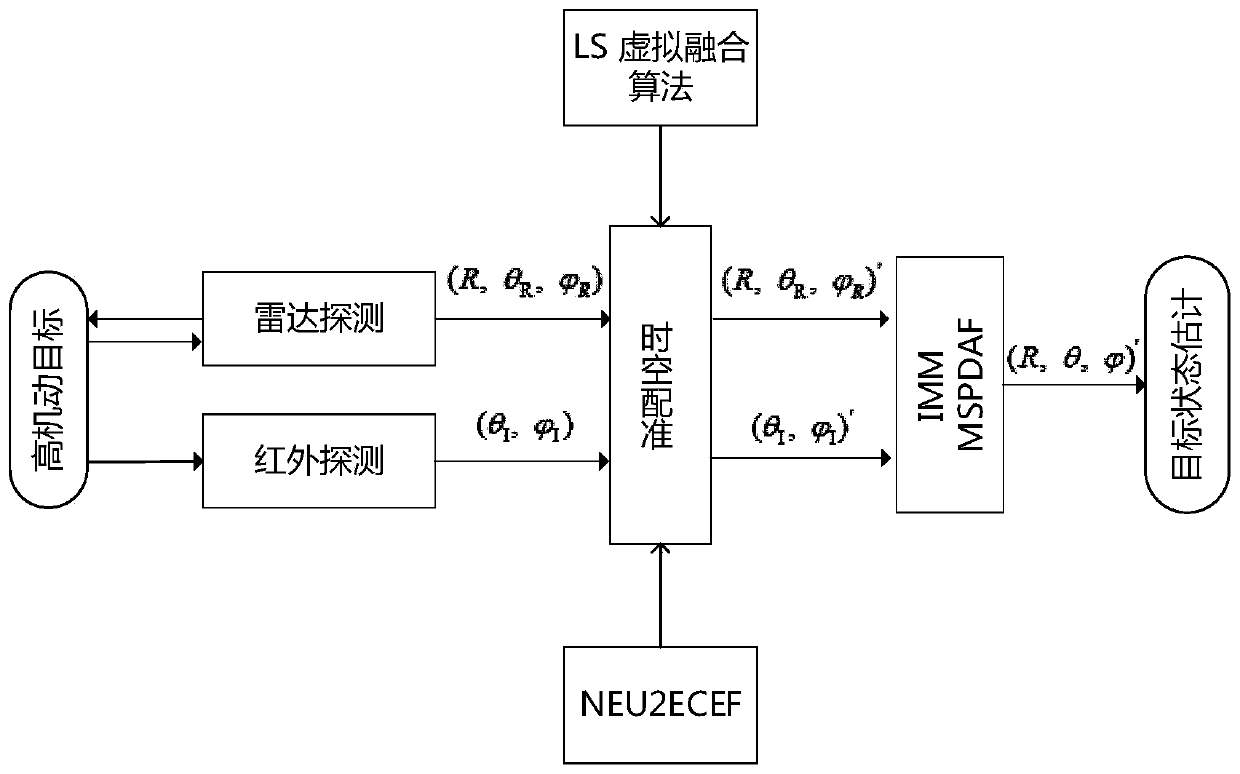
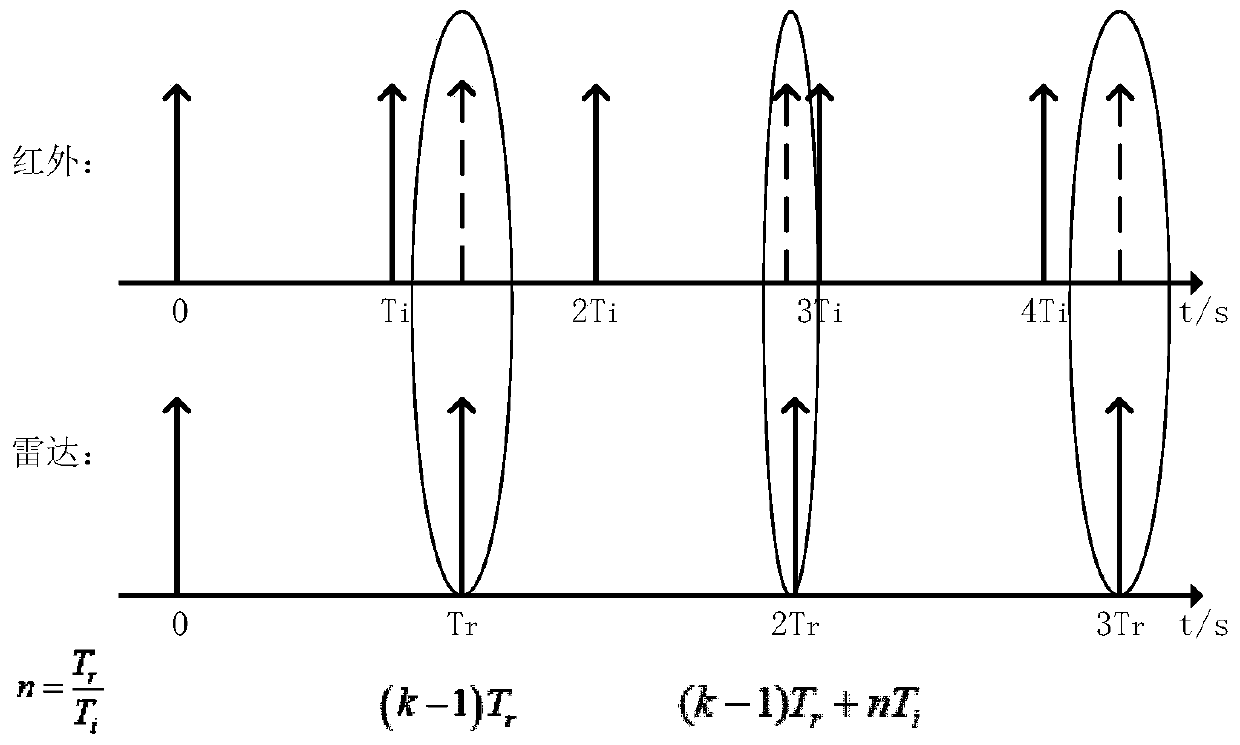
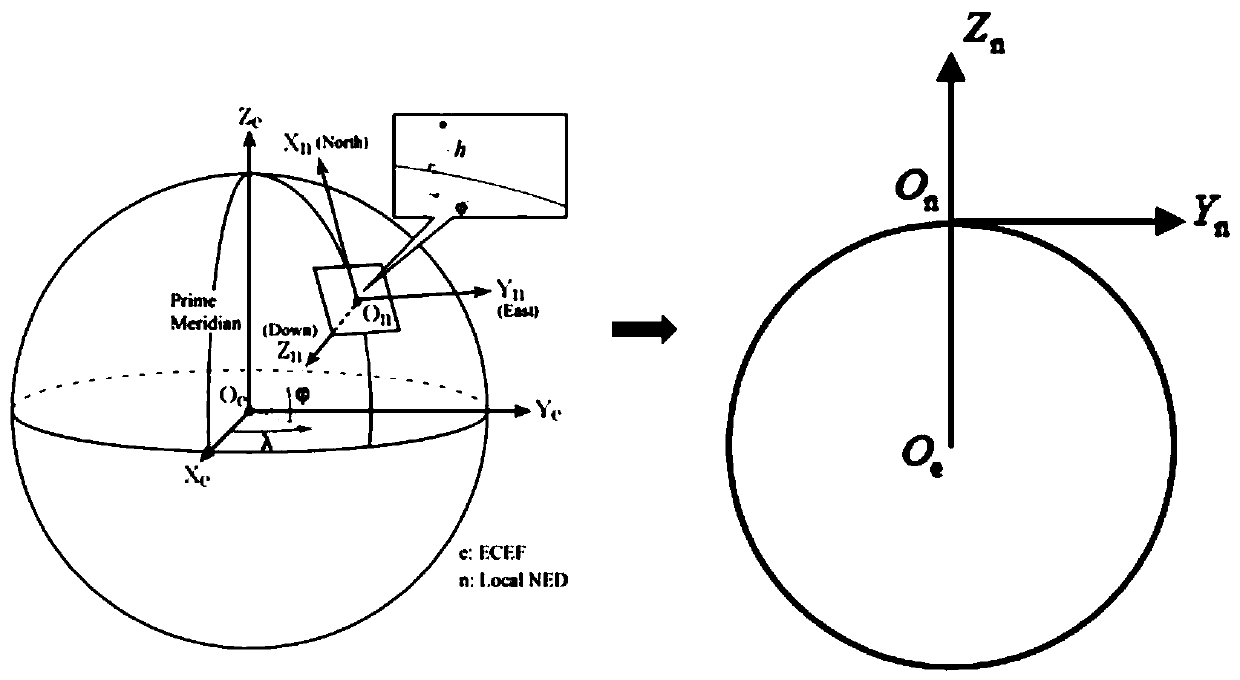
[0091]In this specific embodiment, an infrared sensor and an active radar are used as examples for illustration. For the detection and tracking of highly maneuverable targets, active radar provides complete position and state information of the target as an active sensor, and infrared passive detection of target angle information. Active radar and infrared are used together to build a multi-source tracking and detection method that is independent and complementary to each other. Different multi-sensor cooperative working modes reflect that the target mostly runs in a highly maneuverable attitude, and it is difficult to describe the actual target motion state from different dimensions with any single target motion model. A target motion model is used, and the state estimation of each model is weighted by a certain probability for fusion. Different from the traditional multi-sensor probabilistic data interconnection (MSPDAF) algorithm, which is only aimed at the fusion of radar ...
Embodiment 2
[0154] The application of the present invention is extended to three-dimensional space.
[0155] In the case that 3-D radar only provides distance and azimuth angle information and the accuracy of angle measurement is limited, infrared can be used to provide accurate azimuth and elevation data to supplement the lack of radar detection angle information. The data set of this embodiment is measured data, which is obtained by using three-dimensional radar and infrared sensors. For a constant velocity motion model, the X, Y, and Z axis velocity power spectral densities S w =1m 2 / s, sampling interval T=1. For the constant speed model, speed Ω=(π / 18)rad / s, X, Y and Z axis acceleration power spectral density S w =1m 2 / s 3 , the sampling interval T=1s. Figure 8 Actual and fused trajectories of the target are shown. Note that in both cases of motion (constant speed and constant speed) the trajectory is perfectly tracked. Models 1 and 2 are the uniform motion model and the co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com