A method for detecting developmental toxicity of chemicals
A technology of toxicity detection and detection method, applied in the direction of measuring devices, scientific instruments, biological testing, etc., can solve the problems of research, many influencing factors, and long experiment cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0100] The cultivation of embodiment 1 human embryonic stem cells
[0101] hES will be provided in a state of normal growth after recovery. When the cell density reaches more than 70%, the cells are inoculated into Matrigel pre-coated (self-prepared, 1:20 dilution) culture dishes in the form of clumps.
[0102] (1) Passage of hES: Cells were passaged using cell separation medium A.
[0103] On the 4th to 5th day after hES inoculation, the proliferation of stem cells reached a certain level, and colonies with larger diameters and higher densities (about 70%) could be observed in the culture dish, at which time they could be subcultured.
[0104] Aspirate the hES medium to be passaged and wash it twice with D-PBS.
[0105] Add 2ml of cell separation solution A to the culture dish, incubate in a 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator, take it out for about 20-25 minutes, it can be observed that the clone structure is obviously loose, and when the outer edge of the clone appears curled, add 6ml ...
Embodiment 2
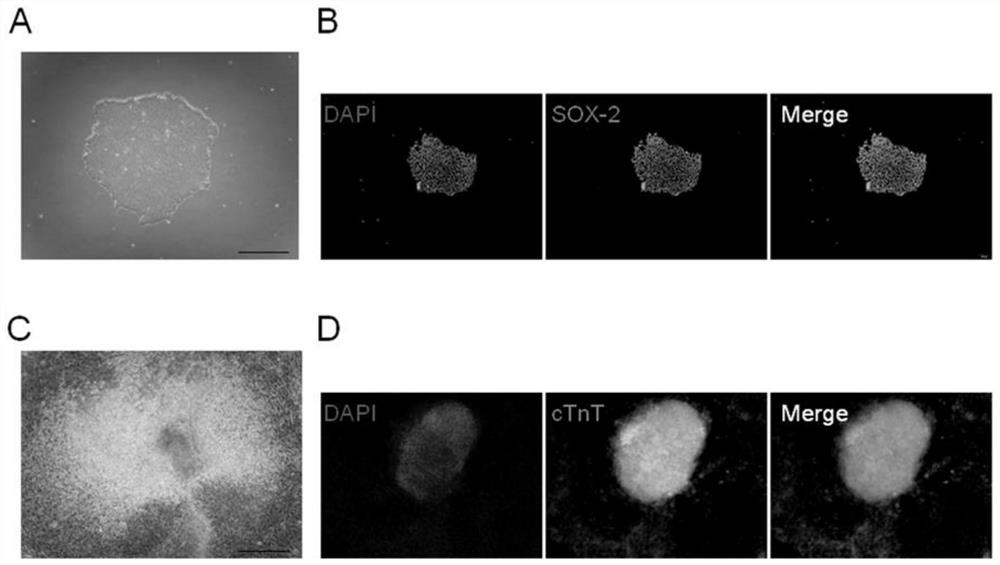
[0107] Example 2 Identification of Pluripotency of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
[0108] In this example, the identification of pluripotency of human embryonic stem cells was achieved by rapid alkaline phosphatase (AKP) staining (the kit needs to be purchased separately).
[0109] (1) Configure 5ml of 100mmol / L Tris HCl, adjust the pH to 8.2, add the dyeing reagent to it according to the kit instructions, and mix well for later use; absorb the culture medium in the ES cell culture dish, and use a high-temperature and high-pressure sterilized Wash with PBS, 5 minutes / time, 3 times in total, to remove the influence of the culture medium on the staining effect;
[0110] (3) Add an appropriate amount of staining reagent to the culture dish, and incubate in a 37°C incubator for 20 minutes in the dark;
[0111] (4) After washing with PBS, add 4% paraformaldehyde, wash with TBST after 2 minutes, and observe on the microscope.
Embodiment 3
[0112] Example 3 Induced differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into cardiomyocytes
[0113] When the cells passaged by cell separation medium A grow to 70%, use 10ml of culture medium #2 per 10cm dish, place at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cells continued to grow in the incubator.
[0114] The day 1 of differentiation was recorded when the culture medium #2 was changed.
[0115] On day 3 of differentiation, continue to culture cells using 10 ml of medium #3 per 10 cm dish.
[0116] On the 6th day of differentiation, use 10ml of culture medium #4 for each 10cm dish to continue culturing the cells, and replace the culture medium once on the 9th day, 11th day, and 15th day of differentiation respectively.
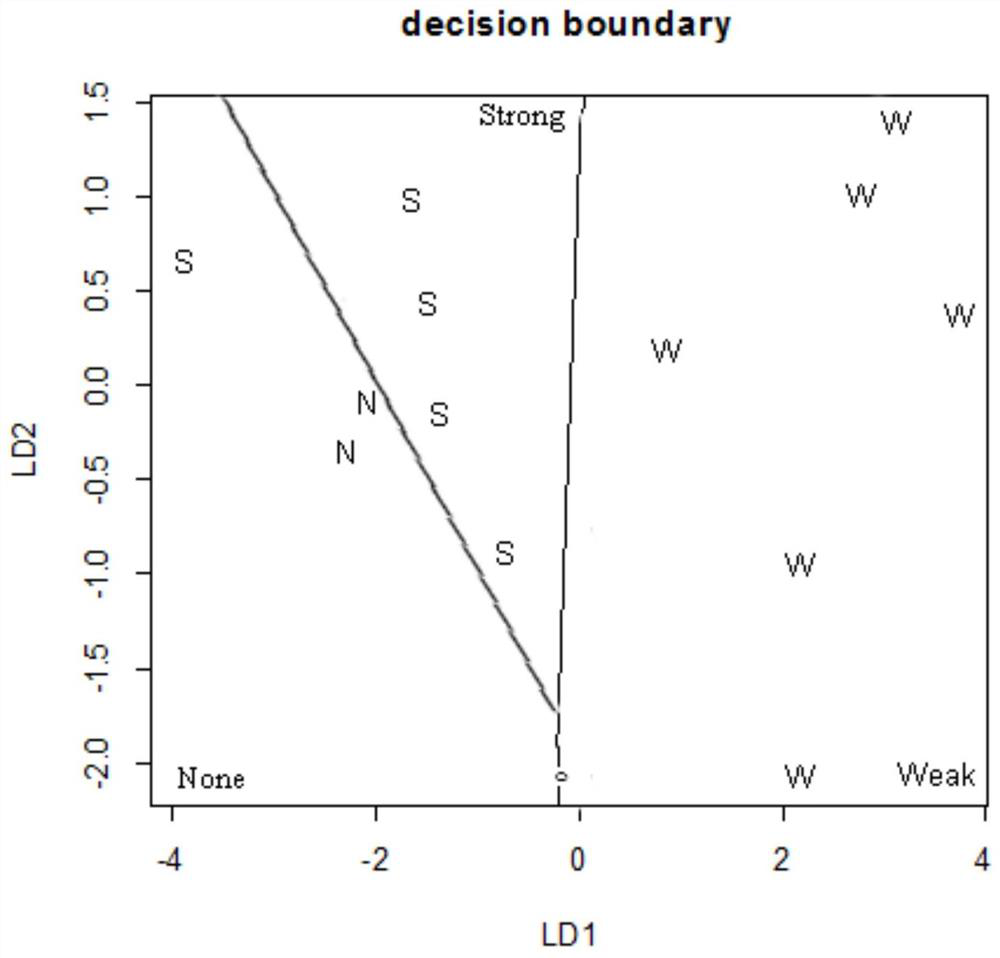
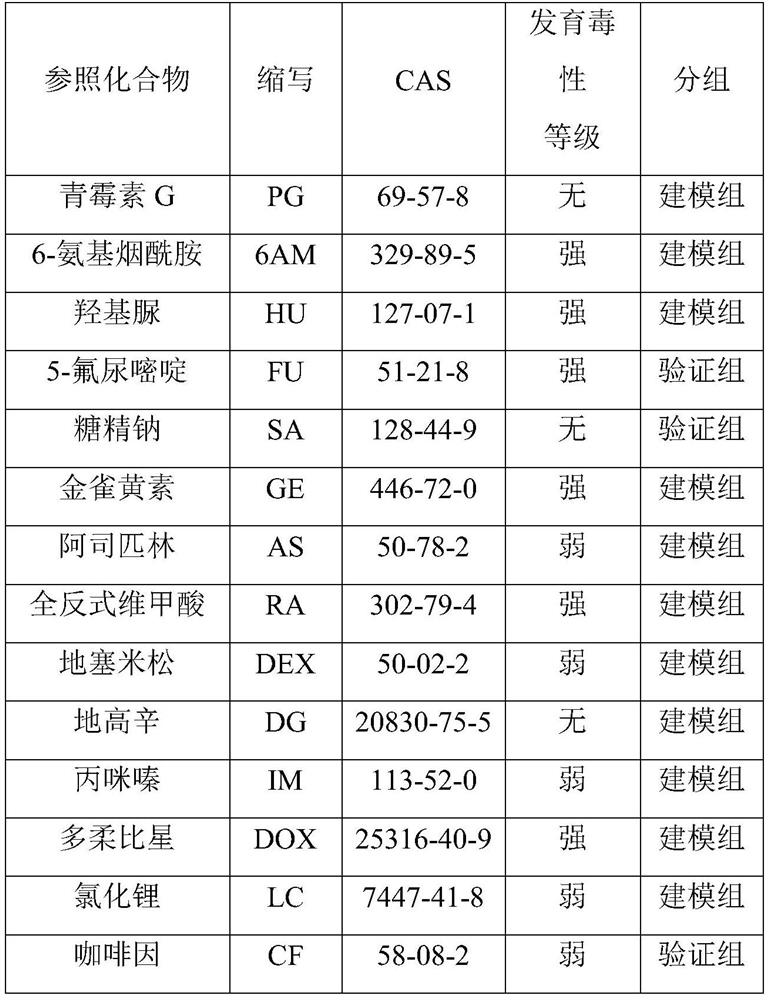
[0117] Cells differentiated from day 15 to day 20 were used to test the developmental toxicity of compounds.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com